Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Drug Interactions
Uploaded by
sweetlifeulivOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Drug Interactions
Uploaded by
sweetlifeulivCopyright:
Available Formats
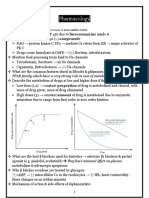
DRUG INTERACTIONS
REDUCED RATE OF ABSORPTION
-Area under curve is independent of absorption rate same total whether rate is rapid (IV) or slow (PO) Area under the curve is same
B Normal absorption C Reduced absorption
FRACTION & ABSORPTION RATE REDUCTION
-Drug 2 (Antacids) quantity & absorption rate of Drug 1 -Area under curve is reduced due to reduction of the fraction of the dose that is absorbed
B Normal absorption C Reduced rate and fraction absorbed
80 70 60
Concentration
Concentration
0 0 10 20 30 40 50 60
50 40 30 20 10 0 0 2 4 6
Time ( hr)
Time
10
12
14
16
REDUCED RATE OF ELIMINATION
-Concentration above normal b/c elimination is impaired -Drug 2 interferes w/ kidneys excretion of Drug 1
Abs. Normal Elim Reduced
ENZYME INDUCTION
-Drug 2 enhances levels of p450 action/loss of Drug 1 1. Barbituates action of Coumadin & Digitoxin 2. Phenytoin action of Cortisol, Digitoxin, & Theophylline
ENZYME INHIBITION
-Drug 2 inhibits p450 metabolism of Drug 1 1. Cimetidine (gastric acid inhibitor) metabolism of Diazepam, Quinidine, etc 2. EtOH metabolism of Diazepam, etc.
0 0 10 20 30 40 50 60
Concentration
Time
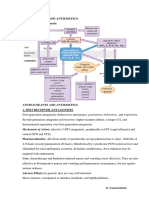
DRUG-DRUG INTERACTION
May have opposing or synergistic effect Antagonistic Effects: Cholinergic & Adrenergics Addictive Effects: Much greater effect w/ 2 drugs Commonly, pt take unknowingly several different products containing the same NSAID (OTC Ibuprofen & Rx) risk of Adverse Effects Ex. Chloropromazine (antipsychotic) & Amitryptyline (antidepressant) results in excessive anticholinergic effects: a. Dry mouth, associated dental complications, blurref vision, Hyperpyrexia in pt exposed to temp & humidity Thiazide Diuretics ( BP) TGs, Blood Sugar; avoid if diabetic
PROTEIN BINDING
-If a drug is normally bound to plasma proteins (Albumin) drug interaction w/ receptor & drug transfer out of the vascular compartment -Drug 2 competitively binds to protein Drug 2 = 1 drug 1. Drug 1 (Tolbutamine) binds to protein (Albumin) 2. Drug 2 (Sulfonamide) competes for receptor 3. Transient [Drug 1]
1.
2.
ADDITIVE & SYNERGISTIC INTERACTIONS
Additives have same 1 action (Tylenol, Advil) Dose remains same whether w/ or w/o additive Synergy effect goes beyond predicted effect based on individual potency take dose good & bad Ex. EtOH + Barbituates = too much sedation
You might also like
- 1 Drug Interaction Spring 2024Document68 pages1 Drug Interaction Spring 2024192315No ratings yet
- Drugs in The Neonatal Unit: 1 Julia PettyDocument5 pagesDrugs in The Neonatal Unit: 1 Julia PettyMarjoNo ratings yet
- OBAT ANTIHIPERTENSI YANG EFEKTIFDocument38 pagesOBAT ANTIHIPERTENSI YANG EFEKTIFNi Made Dwiki AndriyaniNo ratings yet
- UG Graphs-1Document74 pagesUG Graphs-1Rakshith S AradhyaNo ratings yet
- Antihypertensive AgentsDocument33 pagesAntihypertensive AgentsJuwairia tariqNo ratings yet
- Drug Interactions ExplainedDocument30 pagesDrug Interactions ExplainedArk Olfato Parojinog100% (1)
- COPD Medications Reduce Inflammation Improve BreathingDocument3 pagesCOPD Medications Reduce Inflammation Improve BreathingKdamnzNo ratings yet
- Irsan-Drug Interaction 2020Document65 pagesIrsan-Drug Interaction 2020Bayu WisnuNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Review: Characteristics of DrugsDocument11 pagesPharmacology Review: Characteristics of DrugsPaige Heath ButlerNo ratings yet
- Pharmacological-Management-of-HypertensionDocument35 pagesPharmacological-Management-of-Hypertensiontf.almutairi88No ratings yet
- Drugs in PediatricsDocument18 pagesDrugs in PediatricsKarla Sanchez100% (5)
- Combizar Drug StudyDocument6 pagesCombizar Drug StudymrnmrsllNo ratings yet
- Losartan Drug StudyDocument2 pagesLosartan Drug StudyXerxes DejitoNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Bioavailability and Drug InteractionsDocument12 pagesPharmacology Bioavailability and Drug InteractionsDarshi BNo ratings yet
- Course Task 2Document2 pagesCourse Task 2John Elton TangpuzNo ratings yet
- 8 Drug StudyDocument19 pages8 Drug StudyLoyloy D ManNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology - Use of Beta-Blockers & Arbs in Cardiovascular Disease Treating HypertensionDocument5 pagesPharmacology - Use of Beta-Blockers & Arbs in Cardiovascular Disease Treating HypertensionDana20SNo ratings yet
- HYPERTENSION For Internal WrkshopDocument27 pagesHYPERTENSION For Internal Wrkshopwalter agyemanNo ratings yet
- Reference ID: 4052798Document9 pagesReference ID: 4052798Hasnaa ShomanNo ratings yet
- Hypertension: Increase in Blood PressureDocument29 pagesHypertension: Increase in Blood PressureKeesha Mae AnteNo ratings yet
- Antinauseants and AntiemeticsDocument8 pagesAntinauseants and AntiemeticsHamad AlshabiNo ratings yet
- HIV Drug Interactions GuideDocument36 pagesHIV Drug Interactions GuideditabokNo ratings yet
- Drug InterractionsDocument15 pagesDrug InterractionsYIKI ISAACNo ratings yet
- IsoniazidDocument2 pagesIsoniazidMichael Kuzbyt100% (1)
- Adrenergic AntagonistDocument29 pagesAdrenergic AntagonistAreesha ArifNo ratings yet
- Pharmacokinetic Drug Interaction: Bagian Farmakologi Dan Terapeutik, Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Sumatera UtaraDocument49 pagesPharmacokinetic Drug Interaction: Bagian Farmakologi Dan Terapeutik, Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Sumatera UtaraSamuel TanNo ratings yet
- Faktor Yang Mempengaruhi Respon ObatDocument23 pagesFaktor Yang Mempengaruhi Respon ObatYelli SidabutarNo ratings yet
- AcetazolamideDocument1 pageAcetazolamideKyuSheenNo ratings yet
- Kuliah-Geriatri FarmakoDocument60 pagesKuliah-Geriatri FarmakoTenta Hartian HendyatamaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyJaylean Abrigo AguinaldoNo ratings yet
- Interaksi ObatDocument37 pagesInteraksi ObatYustia SariNo ratings yet
- Drug InteractionDocument77 pagesDrug InteractionAthirah Muhammad NoerNo ratings yet
- Lec9 د ذو الفقارDocument4 pagesLec9 د ذو الفقارMohammed JaberNo ratings yet
- Atropine SulfateDocument2 pagesAtropine SulfateKureaa OhNo ratings yet
- Sunitha - Drug InteractionsDocument49 pagesSunitha - Drug InteractionsSunitha Katta100% (1)
- Fludrocortisone For Orthostatic HypotensionDocument5 pagesFludrocortisone For Orthostatic Hypotension4everythingwedoNo ratings yet
- Dobutamine Injection Usp: Product MonographDocument13 pagesDobutamine Injection Usp: Product MonographAmeliaNo ratings yet
- Coreg (Carvedilol) 6.25mgDocument3 pagesCoreg (Carvedilol) 6.25mgE100% (2)
- Final Interactions 2019 PDFDocument55 pagesFinal Interactions 2019 PDFHadeer DaifAllahNo ratings yet
- Side Effects:: AtropineDocument7 pagesSide Effects:: AtropinekletadaNo ratings yet
- Coxib 2Document4 pagesCoxib 2ras emil sazuraNo ratings yet
- Drug LosartanDocument2 pagesDrug LosartanNezuko KamadoNo ratings yet
- Group 4 - Cardioactive Drugs and Antibiotics CC3Document15 pagesGroup 4 - Cardioactive Drugs and Antibiotics CC3mayabangkurtipotNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology - 4 Inflamatory and RelatedDocument25 pagesPharmacology - 4 Inflamatory and RelatedLaura Lopez RocaNo ratings yet
- Ultimate Pre-Reg BNF NotesDocument29 pagesUltimate Pre-Reg BNF NotesBob100% (7)
- Drug Study: Mechanis M OF ActionDocument9 pagesDrug Study: Mechanis M OF ActionLovely San SebastianNo ratings yet
- Psychopharmacology in PsychiatryDocument94 pagesPsychopharmacology in PsychiatryOslo SaputraNo ratings yet
- Pharma Drug Tables - 1st ShiftingDocument29 pagesPharma Drug Tables - 1st ShiftingHei LeeNo ratings yet
- L5 Drug Action and ToxicityDocument26 pagesL5 Drug Action and Toxicitymurphy 1087No ratings yet
- Antipsicoticos 2da Gen 3Document21 pagesAntipsicoticos 2da Gen 3drarodriramosNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Therapeutic Action Indication & Dosage Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing ConsiderationDocument5 pagesDrug Name Therapeutic Action Indication & Dosage Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing ConsiderationArvan SebastianNo ratings yet
- Drugs Coronary Ward IIDocument7 pagesDrugs Coronary Ward IITimothy Joy VercelesNo ratings yet
- PharmacologyDocument116 pagesPharmacologyvargheseNo ratings yet
- Understanding Drug InteractionsDocument40 pagesUnderstanding Drug Interactionsdevaky paramasivanNo ratings yet
- 1 Drugs For HypertensionDocument62 pages1 Drugs For HypertensionSaniNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Drug Interaction and the Mechanism of InteractionFrom EverandHandbook of Drug Interaction and the Mechanism of InteractionRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesFrom EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Drug InteractionsDocument1 pageDrug InteractionssweetlifeulivNo ratings yet
- OSHA CommunityHealthDocument6 pagesOSHA CommunityHealthsweetlifeulivNo ratings yet
- Gi DisordersDocument1 pageGi Disorderssweetlifeuliv100% (1)
- ADRENERGICSDocument5 pagesADRENERGICSsweetlifeulivNo ratings yet
- Drugs of AbuseDocument3 pagesDrugs of AbusesweetlifeulivNo ratings yet
- ANS Organ Inner Vat IonsDocument1 pageANS Organ Inner Vat IonssweetlifeulivNo ratings yet
- MUSCLE Study GuideDocument7 pagesMUSCLE Study GuidesweetlifeulivNo ratings yet