Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ecg Recording and Interpretation
Uploaded by
jh_ajjOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ecg Recording and Interpretation
Uploaded by
jh_ajjCopyright:
Available Formats
ECG RECORDING AND INTERPRETATION INTRODUCTION Electrocardiography (ECG) records the information regarding electrical activity of the heart
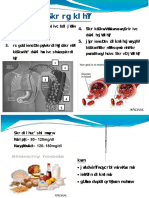
during cardiac cycle over a time period as detected by electrodes attached over the surface of the skin and connected to Electrocardiography or ECG machine. It is a noninvasive procedure used to measure electrical changes including rate, rhythm and conduction of impulse of heart. ECG is used to clarify or confirm any change in cardiac conduction perceived during cardiac monitoring. IT helps in making diagnosis associated with ischemia whether new or old, hypertrophic cardiovascular changes or presence of electrolyte or drug effect. BASIC ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF HEART Heart chambers and normal blood flow The heart has four chambers: the right and left atriums and right and left ventricles. The right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from the body through the superior and inferior vena cava. The right ventricle receives deoxygenated blood through tricuspid valves and pushes deoxygenated blood forward into pulmonary arteries through pulmonary valves. The blood is oxygenated in the lungs and enters into the left atrium through pulmonary veins and further into left ventricle through mitral valve. The left ventricle pushes oxygenated blood directly into aorta which further supply oxygenated blood to the other body parts. The left ventricle is three time thicker than right ventricle and is a high pressure chamber.
You might also like
- PneumothoraxDocument7 pagesPneumothoraxjh_ajjNo ratings yet
- Job Desc. of ANSDocument2 pagesJob Desc. of ANSjh_ajjNo ratings yet
- Icu Psychosis DeliriumDocument32 pagesIcu Psychosis Deliriumjh_ajjNo ratings yet
- Critical Care NursingDocument17 pagesCritical Care Nursingsanish4u100% (1)
- Get Started With Dropbox PDFDocument10 pagesGet Started With Dropbox PDFantonetteNo ratings yet
- Response StationDocument5 pagesResponse Stationjh_ajjNo ratings yet
- Get Started With Dropbox PDFDocument10 pagesGet Started With Dropbox PDFantonetteNo ratings yet
- Interpret ECG Rhythms & Manage ArrhythmiasDocument6 pagesInterpret ECG Rhythms & Manage Arrhythmiasjh_ajjNo ratings yet
- Checklist Home AssessmentDocument5 pagesChecklist Home Assessmentjh_ajjNo ratings yet
- Progressive Patient CareDocument2 pagesProgressive Patient Carejh_ajj100% (2)
- Central line bundle components & calculating dopamine drip rateDocument4 pagesCentral line bundle components & calculating dopamine drip ratejh_ajjNo ratings yet
- Nursing MCQsDocument2 pagesNursing MCQsjh_ajj0% (1)
- Pre/Post Test Questions for Preventing Hospital InfectionsDocument1 pagePre/Post Test Questions for Preventing Hospital Infectionsjh_ajjNo ratings yet
- Diabetic TeachingDocument21 pagesDiabetic Teachingjh_ajjNo ratings yet
- ELTS Writing Intro: Short & SimpleDocument1 pageELTS Writing Intro: Short & Simplejh_ajjNo ratings yet
- Advance Cardiac Life SupportDocument75 pagesAdvance Cardiac Life Supportjh_ajjNo ratings yet
- Punjabi ModuleDocument9 pagesPunjabi Modulejh_ajjNo ratings yet
- CELBANDocument2 pagesCELBANjh_ajj82% (17)
- Stress & Burnout SyndromeDocument16 pagesStress & Burnout Syndromejh_ajjNo ratings yet
- 12 Lead ECG Mod 1Document31 pages12 Lead ECG Mod 1johnmmenahNo ratings yet
- IELTS Writing Task 1 - Band 9Document2 pagesIELTS Writing Task 1 - Band 9jh_ajjNo ratings yet
- Registered Nurse Job DutiesDocument1 pageRegistered Nurse Job Dutiesjh_ajjNo ratings yet
- Structural Cardiac DisorersDocument24 pagesStructural Cardiac Disorersjh_ajjNo ratings yet
- Dna Gyrase InhibitorsDocument4 pagesDna Gyrase Inhibitorsjh_ajjNo ratings yet
- Hepatic EncephalopathyDocument16 pagesHepatic Encephalopathyjh_ajjNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5782)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)