Professional Documents
Culture Documents
IC 555 Projects
Uploaded by
Parth LadOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
IC 555 Projects
Uploaded by
Parth LadCopyright:
Available Formats
Metal Detector Circuit Diagram Using IC555
Description Figure shows the circuit of the Metal Detector . Here I have used a coil and some transistor switching and a 555 mono stable multi vibrator for making this circuit . Use a 22 nH toroid coil at the L1 .Part list and applications are showing below . Part List Component No: Value Usage R1 R2 R3 R4 R5 C1 C2 C3 C4 Q1 Q2 L1 B1 U1 1.5k 10k 10K 1K Oscillation Base Biasing Base Biasing Current Limiting
100K Emitter Load
103PF Discharging 103PF Noise Grounding 100PF Oscillation 1MF Coupling BC548 Switching BC548 Switching 22nH Oscillation 6V Sound NE555 Mono Stable
Applications: Metal Detector
Seven Segment Counter Display Circuit
Here is the circuit diagram of a seven segment counter based on the counter IC CD 4033.This circuit can be used in conjunction with various circuits where a counter to display the progress adds some more attraction. IC NE 555 is wired as an astable multivibrator for triggering the CD 4033.For each pulse the out put of CD 4033 advances by one count.The output of CD 4033 is displayed by the seven segment LED display LT543.Switch S1 is used to initiate the counting.Diode D1 prevents the risk of accidental polarity reversal.
Voltage doubler circuit using NE555
Description. The circuit diagram of a very simple voltage doubler using NE555 timer is shown here. Here IC NE555 is wired as an astable mutivibrator operating at around 9KHz. The base of the two transistors (Q1 and Q2) is shorted and output of the astable multivibrator (pin 3) is connected to it. When the output of astable multivibrator is low, Q1 will be OFF and Q2 will be ON. The negative terminal of the capacitor C3 will be shorted to ground through T2 and it will be charged to the input supply voltage. When the output of the astable multi vibrator is high, transistor Q1 will be ON and transistor Q2 will be OFF. The capacitor C4 will be charged to the voltage across capacitor C3 plus the input supply voltage (that is double the input voltage). This is how the circuit works. This voltage doubler circuit can deliver only up to 50mA output current and above that current limit the output voltage will be dramatically reduced. The actual output voltage will be around 19V for a 12V DC input and also the output voltage will be a bit unstable. Anyway, for low current applications this circuit is well enough. Circuit diagram.
Notes. The circuit can be assembled on a vero board. The output current should not be allowed to exceed 70mA. IC1 must be mounted on a holder.
Remote controlled switch for Appliance
Description.
Here is a versatile remote controlled switch that can ON or OFF any appliance connected to it using a TV remote. IR remote sensor IC TSOP 1738 is used for receiving the signal. Normally when no signal is falling on IC3 the output of it will be high. This makes Q1 OFF.When a signal of 38 KHz from the TV remote falls on the IC3 its output goes low.This makes Q1 conduct and a negative pulse is obtained at pin 2 of IC 1 NE 555. Due to this IC1 wired as a monostable multivibrator produces a 4 Sec long high signal at its out put.This high out put is the clock for IC 2 which is wired as a Flipflop and of , its two outputs pin 3 goes low and pin 2 goes high. The high output at pin 2 is amplified to drive the relay. For the next signal the outputs of IC2 toggles state. Result, we get a relay toggling on each press on the remote. Any appliance connected to this circuit can be switched ON or OFF.
Remote Controlled Switch Circuit Diagram with Parts List
Notes:
* Before wiring the circuit make sure that the carrier frequency of the TV remote you have is 38 kHz.For that wire the sensor part only ,point your remote to the TSOP1738 and press any switch.If out put of TSOP1738 goes low then OK, your remote is of 38Khz type.Nothing to worry almost all TV remote are of this type. * You can use any switch of the remote because for any switch the code only changes, the carrier frequency remains same.We need this carrier frequency only. * Assemble the circuit on a good quality PCB or common board.
* The appliance can be connected through NO or NC and C contacts of the relay . * Use a regulated 6V power supply for the circuit.
Rain alarm circuit
Description. Here is a simple rain alarm circuit that produces an audible alarm when ever rain falls. The rain detector circuit is based on two transistors (Q1 & Q2) and a NE555IC (IC1). The two transistors are wired as a switch which goes on when the base of Q1 is shorted to the positive of the supply by the rainwater falling on the sensor. When the transistors are ON power supply is available to the IC1 which is wired as an astable multivibrator. The output of IC1 drives the speaker to produce an alarm.
Notes.
Assemble the circuit on a good quality PCB or common board. For assembling the sensor cut a 22 inch mica or plastic sheet. Arrange two single stranded wires (running parallel 2mm close to each other) on the sheet as shown in figure below. Remember the wires have to be non-insulated. Sensor ready. Now you can connect the points A&B on the sensor to corresponding points A&B on the circuit. POT R2 can be used to adjust the sensitivity. To test the circuit, make all connections and power up.Place a drop of water on the sensor so that two wires become shorted through water. Now the alarm starts sounding. If not adjust R2 to get the alarm sounding. Use a 9v battery or a 9V regulated DC supply for powering the circuit.
Do not connect speakers less than8 Ohm impedance as load. It will damage the IC. A piezo buzzer can be also used instead of the speaker.
Sensor schematic.
Water level controller circuit
Description. A simple but very reliable and effective water level controller circuit diagram is shown here. The circuit uses 6 transistors, 1 NE555 timer IC, a relay and few passive components. The circuit is completely automatic which starts the pump motor when the water level in the over head tank goes below a preset level and switches OFF the pump when the water level in the over head tank goes above the full level. Probe D is positioned at the bottom level of the tank while probes A, B and C are placed at full, half and medium levels of the tank respectively. The level sensing part of the circuit is built around transistors Q1, Q2 and Q3. When water level is below the quarter level probes A, B and C are open and the transistor Q1, Q2 and Q3 remains OFF. When the water level rises and touches the probes the corresponding transistors gets biased and switches ON. Resistors R1, R2, R3 limit the bases current of corresponding transistors while resistors R4, R5, R6 limit their collector current. LEDs D1, D2 and D3 provide a visible indication of the current water level. When the water level goes below medium, transistor Q2 gets switches OFF and its collector goes positive. Collector of Q2 is connected to the base of transistor Q6 and as result transistor Q6 gets switched ON. Transistor Q5 will be also ON because its base in connected to the collector of Q4 which is presently OFF. As a result when the water level goes below medium relay K1 gets energized and the pump is driven. The relay is wired in the latching mode so that even if the water level goes above medium level the pump remains ON so that the tank gets completely filled. For wiring the relay in latching mode one set of N/O contacts is used. When relay is activated these contacts close which forms a short across collector and emitter of Q6. This makes the state of Q6 irrelevant to the operation of the relay and the relay remains ON as long as the transistor Q5 is ON. The only way to make the relay OFF is by switching OFF Q5 and it is done automatically when the water level reaches the full level. Collector of transistor Q1 is connected to the trigger pin (pin2) of IC1. When the water level reaches full level the transistor Q1 gets switched ON. As a result its collector goes to ground level which triggers the IC1 which is wired as a monostable. The output of IC1 goes high for about 1S. This makes the transistor Q4 ON for the same time and transistor Q5 whose base is connected to the collector of Q4 is switched OFF cutting the supply to the relay. This makes the motor OFF and it remains OFF until the water level again goes below the medium level. Resistor R8 is a pull up resistor for the trigger pin of the NE555. Capacitor C3 couples the collector of Q1 to the trigger pin of NE555 and facilitates edge triggering whenever the transistor Q1 goes ON. A monostable circuit can be made edge triggered by connecting the trigger signal to the trigger input pin through a capacitor. The capacitor blocks DC and passes sudden changes. The circuit used here is termed as negative edge triggered because the monostable is triggered when ever the trigger input signal falls. R10 and R12 limits the collector current of Q4 and Q5 respectively while R9 and R11 limits their base current. R13 limits the base current of Q6 while D4 is a freewheeling diode which protects the switching transistors from voltage transients.
Circuit diagram.
The probes can be arranged as shown in the diagram above. Insulated Aluminium wires can be used as the probes. The probes can be binded on a plastic rod and should be erected vertically inside the tank. The length of the probes wires and the supporting plastic rod must be chosen according to the depth of the tank. Since DC is used in the level sensing section electrolysis will occur in the probes and so the probes require small maintenances in 1 or 2 month intervals. Using AC in the sensing section will completely eliminates the chance of electrolysis and I am presently working on such a circuit. You can expect it soon. Notes.
Use 12V DC for powering the water level controller circuit.
The relay I used was a 5V/220 ohm relay and thats why the current limits resistor R12 was added in the circuit. If you use a 12V relay then the R12 can be shorted. Do not use a relay that consumes 500mA. Maximum collector current PN2222 can handle is 600mA. Use insulated single strand aluminium wires for probe and they can be arranged in the tank as per the probe arrangement diagram. Use a holder for mounting NE555. The circuit can be assembled on a Perf board. K1 must be a double pole relay. The load current, voltage ratings of the relay must be selected according to the ratings of the pump motor. The type number of the transistors used here are not very critical and you can do suitable replacements if any type number is not available. Most of the components required for this project can be found inside your scrap box.
Power supply for this circuit.
A classic 12V regulated DC supply based on 7812 is shown above. A power ON indicator LED is also added in the circuit.Resistor R13 limits the LED current. A small aluminium heatsink can be fitted to the 7812 for better saftey.Small Al heatsinks for TO-220 package are readily available in the market.
Mobile incoming call indicator
Description. This circuit can be used to escape from the nuisance of mobile phone rings when you are at home. This circuit will give a visual indication if placed near a mobile phone even if the ringer is deactivated. When a call is coming to the mobile phone, the transmitter inside it becomes activated. The frequency of the transmitter is around 900MHz.The coil L1 picks up these oscillations by induction and feds it to the base of Q1. This makes the transistor Q1 activated.Since the Collector of Q1 is connected to the pin 2 of IC1 (NE555) , the IC1 is triggered to make the LED connected at its output pin (pin 3) to blink. The blinking of the LED is the indication of incoming call. Circuit diagram with Parts list.
Notes.
The coil L1 can be made by making 150 turns of 36 SWG enameled copper wire on a 5mm dia plastic former.Or you can purchase a 10 uH coil from shop if available. The circuit can be powered from a 6V battery. Assemble the circuit on a good quality PCB. C1 & C3 are to be polyester capacitors. The electrolytic capacitor C2 must be rated 10V.
Missing pulse detector circuit using NE555
Description. An NE555 timer IC connected as shown here can detect a missing pulse or abnormally long period between two consecutive pulses in a train of pulses. Such circuits can be used to detect the intermittent firing of the spark plug of an automobile or to monitor the heart beat of a sick patient. The signal from the pick up transducer is shaped to form a negative going pulse and is applied to pin 2 of the IC which is connected as a mono stable. As long as the spacing between the pulse is less than the timing interval,the timing cycle is continuously reset by the input pulses and the capacitor is discharged via T1. A decrease in pulse frequency or a missing pulse permits completion of time interval which causes a change in the output level. Circuit diagram with Parts list.
Notes.
Assemble the circuit on a good quality PCB or common board. The circuit can be powered from a 9V battery or 9V DC power supply. The IC1 NE555 could be mounted on a holder.
10 Minute timer circuit.
Description. When ever you need to get an alarm or intimation after ten minutes ,the circuit shown below can be used.The circuit is nothing but a monostable multivibrator based on IC NE 555.When ever you press the reset push button the green LED D1 glows after 10 minutes. Circuit diagram with Parts list.
Notes.
Assemble the circuit on a good quality PCB or common board. The time duration can be set by varying the POT R5. The switch S1 can be a push button switch. The IC1 must be mounted on an IC base.
Brightness controller for low power lamps
Description. The circuit given here can be used to control the brightness of low power incandescent lamps. The circuit is based on IC NE555 which is wired as an astable multivibrator with variable duty cycle. The output of IC is connected to the base of transistor Q1.The Q1 drives the lamp. The duty cycle of the multivibrator can be varied by varying the POT R4.As a result, the brightness of the lamp varies according to the position of the POT R4.The same circuit can be also used for speed control of small DC motors. Circuit diagram with Parts list.
Notes.
The lamp L1 can be a 6V / 200 mA lamp. The switch S1 can be SPST ON/OFF switch. The IC1 must be mounted on a holder. The circuit can be wired on a good quality PCB or common board.
You might also like
- Wi-Fi Home AutomationDocument23 pagesWi-Fi Home Automationchandru_8No ratings yet
- Water level controller circuit guideDocument7 pagesWater level controller circuit guideYudi Mahato0% (1)
- Power Supply Projects: A Collection of Innovative and Practical Design ProjectsFrom EverandPower Supply Projects: A Collection of Innovative and Practical Design ProjectsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Variable Power Supply With Digital ControlDocument15 pagesVariable Power Supply With Digital ControlSubhash Bajaj100% (1)
- Power Electronics ProjectsDocument5 pagesPower Electronics ProjectsEngr FN ANo ratings yet
- Rangkaian RangkaianDocument30 pagesRangkaian RangkaianAhmad JuheriNo ratings yet
- Passive and Discrete Circuits: Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 2From EverandPassive and Discrete Circuits: Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 2No ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- 3W LED Driver Circuits UC3842 UC3845Document2 pages3W LED Driver Circuits UC3842 UC3845Gleison PrateadoNo ratings yet
- Infrared Object CounterDocument9 pagesInfrared Object CounterMohideen NazimNo ratings yet
- Burglar Alarm ProjectDocument4 pagesBurglar Alarm ProjectAvik PathakNo ratings yet
- External Current Limiting CircuitDocument3 pagesExternal Current Limiting CircuitmikcomiNo ratings yet
- LM317 Adjustable Power Supply CircuitDocument4 pagesLM317 Adjustable Power Supply Circuitsud100% (1)
- RF Controlled ApplianceDocument14 pagesRF Controlled ApplianceNEX456No ratings yet
- Video AmplifierDocument13 pagesVideo AmplifierPradyumna YambarNo ratings yet
- Automatic Night Lamp With Morning AlarmDocument47 pagesAutomatic Night Lamp With Morning Alarmbalajig47375% (8)
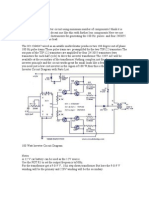
- 12V DC To 220V AC Converter DesignDocument7 pages12V DC To 220V AC Converter DesigntintuvrNo ratings yet
- IR Based Security AlarmDocument4 pagesIR Based Security AlarmManjeet SinghNo ratings yet
- Dual Adjustable Power Supply Circuit LM317 LM387Document4 pagesDual Adjustable Power Supply Circuit LM317 LM387andree w100% (1)
- 60MHz LCD Frequency CounterDocument3 pages60MHz LCD Frequency CounterHector Ledesma IIINo ratings yet
- Minor Project FileDocument29 pagesMinor Project FilePoorva ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Temperature controlled DC fan circuit using NTC thermistorDocument2 pagesTemperature controlled DC fan circuit using NTC thermistorNealWhite100% (1)
- Exp 9 Boost ConverterDocument8 pagesExp 9 Boost ConverterusmpowerlabNo ratings yet
- DIAC and TRIAC Characteristics for AC ControlDocument16 pagesDIAC and TRIAC Characteristics for AC ControlUmashankar SubramaniamNo ratings yet
- Automatic Night Lamp With Morning AlarmDocument13 pagesAutomatic Night Lamp With Morning AlarmVamsy RSKNo ratings yet
- 0-50V 3A Variable Power SupplyDocument17 pages0-50V 3A Variable Power SupplyferdinandNo ratings yet
- 100 IC Circuits by Rev. Thomas Scarborough. PDFDocument60 pages100 IC Circuits by Rev. Thomas Scarborough. PDFArooge FK100% (1)
- 40A Power Supply UnitDocument6 pages40A Power Supply Unitrsira2001100% (3)
- 100 Watt Inverter Circuit DiagramDocument11 pages100 Watt Inverter Circuit DiagramscribdexpressNo ratings yet
- UC3842 Inside SchematicsDocument17 pagesUC3842 Inside Schematicsp.c100% (1)
- Simple 12V To 230VAC Inverter Circuit - MOSFETDocument10 pagesSimple 12V To 230VAC Inverter Circuit - MOSFETPramillaNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Alarm Project PDFDocument16 pagesEarthquake Alarm Project PDFAashish YadavNo ratings yet
- Younus College of Engineering & TechnologyDocument8 pagesYounus College of Engineering & TechnologySarath Mohan JNo ratings yet
- Musical Door BellDocument6 pagesMusical Door BellParikshit KadamNo ratings yet
- 12v Audio AmplifierDocument13 pages12v Audio AmplifierSusrita Barai100% (1)
- 5v DC SupplyDocument19 pages5v DC SupplyDev Agarwal100% (1)
- Arduino Solar Battery Charge ControllerDocument5 pagesArduino Solar Battery Charge Controllermuhaned190No ratings yet
- Analog Electronics ProjectDocument11 pagesAnalog Electronics ProjectASHUTOSH MOHAPATRA 18BLC1035No ratings yet
- Burglar AlarmDocument2 pagesBurglar AlarmErole Technologies Pvt ltd Homemade Engineer100% (1)
- Audio AmplifiersDocument11 pagesAudio AmplifiersWaqas AbroNo ratings yet
- Analog Circuits-II Answer KeyDocument30 pagesAnalog Circuits-II Answer KeyreneeshczNo ratings yet
- Automatic Night Lamp With Morning AlarmDocument4 pagesAutomatic Night Lamp With Morning AlarmijaertNo ratings yet
- TOUCHLESS DOOR BELL USING IR SENSORDocument3 pagesTOUCHLESS DOOR BELL USING IR SENSORVinay BharathaNo ratings yet
- EDN Design Ideas 1999Document201 pagesEDN Design Ideas 1999chag1956100% (5)
- Portable Usb Mobile Charger Using 9v BatterycsascaDocument3 pagesPortable Usb Mobile Charger Using 9v Batterycsascaeddddie100% (1)
- Sine Wave Generation and Implementation Using DsPIC33FJDocument27 pagesSine Wave Generation and Implementation Using DsPIC33FJpaaraib100% (1)
- Introduction To EMC: Electronic ComponentsDocument26 pagesIntroduction To EMC: Electronic ComponentsLakshitha Prabath WijesingheNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Operational AmplifiersDocument32 pagesIntroduction to Operational Amplifiersjaya1816100% (1)
- PIN Diode Based Fire SensorDocument9 pagesPIN Diode Based Fire SensorArravolu maheshNo ratings yet
- Quality Stereo Wireless Microphone or Audio Link Circuit DiagramDocument8 pagesQuality Stereo Wireless Microphone or Audio Link Circuit DiagramJose C. Lita Jr100% (1)
- Diode CharacteristicsDocument12 pagesDiode CharacteristicsAhmedElsiddiegA.AbdallaNo ratings yet
- 4 Watt Led Driver CircuitDocument17 pages4 Watt Led Driver CircuitNomade VoyageurNo ratings yet
- EC6401 Electronics Circuits II - Notes - AnnaunivupdatesDocument96 pagesEC6401 Electronics Circuits II - Notes - Annaunivupdatesmanimangai100% (2)
- VolsampDocument153 pagesVolsampSonny HutomoNo ratings yet
- DC & AC Machines and Speed ControlDocument53 pagesDC & AC Machines and Speed ControlInsane Clown Prince60% (5)
- Axera 5-126 - 6232sd PDFDocument4 pagesAxera 5-126 - 6232sd PDFOscar Acevedo MirandaNo ratings yet
- Cladding & Hardfacing ProcessesDocument16 pagesCladding & Hardfacing ProcessesMuhammed SulfeekNo ratings yet
- CT Saturation and Its Influence On Protective Relays: Roberto Cimadevilla, Ainhoa FernándezDocument22 pagesCT Saturation and Its Influence On Protective Relays: Roberto Cimadevilla, Ainhoa FernándezANTONIO SOLISNo ratings yet
- Especificaciones de valvulasDIDocument4 pagesEspecificaciones de valvulasDIAlejandro ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Syllabus: Certificate in Subsea EngineeringDocument6 pagesSyllabus: Certificate in Subsea EngineeringJerome LIKIBINo ratings yet
- 08 Kobelco MARK 8 Mechatron Control SistemDocument45 pages08 Kobelco MARK 8 Mechatron Control SistemNadiel Aceto 46100% (1)
- ABB String Inverters: PVS-50/60-TLDocument4 pagesABB String Inverters: PVS-50/60-TLBianca OlaruNo ratings yet
- Power Generating Floor PDFDocument3 pagesPower Generating Floor PDFMeghjit MazumderNo ratings yet
- User Manual Mariner 50Document24 pagesUser Manual Mariner 50Cyrille PVNo ratings yet
- Electrical Plan SampleDocument1 pageElectrical Plan SampleKit67% (3)
- Wave Nature of The Motor Cable and Voltage Stress of The Motor in Inverter DriveDocument9 pagesWave Nature of The Motor Cable and Voltage Stress of The Motor in Inverter DrivealbertofgvNo ratings yet
- Competition Analysis On Iron and Steel IndustryDocument18 pagesCompetition Analysis On Iron and Steel Industryatre100% (1)
- BMU Titan Cradle: Standard Features Control BoxDocument2 pagesBMU Titan Cradle: Standard Features Control BoxKashyapNo ratings yet
- Bhagvender Singh XII-A Physics Project PDFDocument15 pagesBhagvender Singh XII-A Physics Project PDFvoid50% (4)
- Instructions for use and installation of a washing machineDocument16 pagesInstructions for use and installation of a washing machineVale MocanuNo ratings yet
- Nerc Sra 2022Document46 pagesNerc Sra 2022The Western Journal100% (1)
- LPG Parts Diagram BreakdownDocument43 pagesLPG Parts Diagram BreakdownناصرقوجيلNo ratings yet
- r2 Hy-Optima 720as-Gc Technical Data SheetDocument1 pager2 Hy-Optima 720as-Gc Technical Data SheetMohammed SaberNo ratings yet
- EPL 0006898 ArticleDocument28 pagesEPL 0006898 ArticleGuillermo IdarragaNo ratings yet
- Fermentor TypesDocument33 pagesFermentor TypesFahad MukhtarNo ratings yet
- BIOGAS 5000 Operating ManualDocument107 pagesBIOGAS 5000 Operating ManualmjsampaioNo ratings yet
- InternationalDocument11 pagesInternationalheeral patelNo ratings yet
- Concept of Microgrid AND Evolution of Smart Grid: Dileep GDocument45 pagesConcept of Microgrid AND Evolution of Smart Grid: Dileep GDileep GNo ratings yet
- Temperature Controlled DC Fan Using OpDocument24 pagesTemperature Controlled DC Fan Using OpAnwesha pradhan100% (4)
- Construction and Working Principle of BLDC MotorDocument5 pagesConstruction and Working Principle of BLDC Motormuralajaswini.21.cseNo ratings yet
- FP2 FP3 CRP 49691A Sanitary PumpDocument6 pagesFP2 FP3 CRP 49691A Sanitary PumpetmvmartNo ratings yet
- TP48200A-HD15A6 & HD15A7 & HD15A8 & HD15A9 & HT15A5 & HT15A6 & DX15A1 & HX15A1 V500R001 User Manual 01 PDFDocument116 pagesTP48200A-HD15A6 & HD15A7 & HD15A8 & HD15A9 & HT15A5 & HT15A6 & DX15A1 & HX15A1 V500R001 User Manual 01 PDFEla TorquataNo ratings yet