Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bio Terms Def
Uploaded by
api-31355470Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bio Terms Def
Uploaded by
api-31355470Copyright:
Available Formats
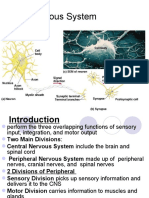
The foundations of neuroscience key terms: CH 2
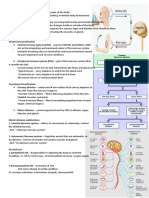
Neuron- an individual nerve cell Sensory Neuron- a nerve cell that carries information from the outer parts of the body, caused by external stimuli, to the central nervous system Motor Neuron- a nerve cell that carries motor commands from the CNS to muscles and glands Interneuron- connect various neurons to the brain and spinal cord Dendrite- neuron fiber that receives incoming messages Soma- the main body of a neuron or other cell Axon- fiber that carries information away from the cell body of a neuron Resting Potential- the electrical charge of a neuron at rest Action Potential- the nerve impulse All-or-none principal- a nerve impulse occurs completely or not at all Synapse- the microscopic space between two neurons over which messages pass Terminal buttons- receive the messages transferred down the axon, store them in their synaptic vesicles, and secrete these transmitter substances. Synaptic transmission- when a neural impulse moves from one neuron to another Synaptic Vesicle- tiny oval sacs on the axon terminal filled with a chemical transmitter substance Neurotransmitters- any chemical released by a neuron that alters activity in other neurons Plasticity- the brains capacity to change its structure and functions Glial Cells- part of the nervous system, aid neurons by providing nutrition and insulation, structural support, make up myelin sheath, may play an important role in intelligence and affect learning Nervous system- made up of voluntary and involuntary nerves, composed of the brain, spinal cord, and sensory nerves, carries messages to the brain from the body and motor nerves CNS Central Nervous System- the brain and spinal cord Reflex- the simplest behavior in which a stimulus provokes an automatic response Peripheral nervous system- all parts of the nervous system outside the brain and spinal cord Somatic Nervous System- the system of nerves linking the spinal cord with the body and sense organs Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)- the system of nerves carrying information to and from the internal organs and glands Sympathetic division- the part of the ANS that alerts or excites the body Parasympathetic division- the part of the ANS that quiets the body Endocrine system- glands whose secretions pass directly into the bloodstream or lymph system Hormone- a glandular secretion that affects bodily functions or behavior Pituitary gland- the master gland whose hormones influence other endocrine glands; regulates growth Agonist Antagonist Neural pathway- a series of synapses that form a network in the brain, connect relatively distant areas of the brain or nervous system. EEG Electroencephalograph- a device that detects, amplifies, and records electrical activity in the brain CT computerized tomography- a computer enhanced x-ray image of the brain or body PET position emission tomography- a computer generated image of brain
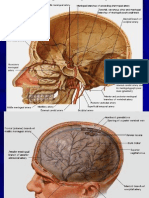
activity based on glucose consumption in the brain MRI Magnetic resonance imaging- a computer enhanced three-dimensional representation of the brain or body based on the bodys response to a magnetic field. fMRI functional MRI- magnetic resonance imaging that records and makes visible brain activity Brain Stem- the lowest portions of the brain, including the cerebellum, medulla, pons, and reticular formation; connects to the spinal cord Medulla- The structure that connects the brain with the spinal cord and controls vital life functions (heart rate, breathing, swallowing etc.) Pons- an area on the brainstem that acts as a bridge between the medulla and other structures Reticular Formation- a network within the medulla and brainstem; associated with attention, alertness, and some reflexes Thalamus- a brain structure that relays sensory information to the cerebral cortex Cerebellum- a brain structure that controls posture and coordination Limbic System- A system in the forebrain that is closely linked with the emotional response Hippocampus- a part of the limbic system associated with storing memories Amygdala- A part of the limbic system associated with fear responses Hypothalamus- a small area of the brain that regulates emotional behaviors and motives Cerebral cortex- the outer layer of the cerebrum (the two large hemispheres that cover the upper part of the brain) Frontal lobes- a brain area associated with movement, the sense of smell, and higher mental functions
Motor cortex- a brain area associated with control of movement Parietal lobes- area of the brain where bodily sensations (touch, temperature, pressure etc.) register Somatosensory cortex- a receiving area for bodily sensations Occipital lobes- portion of the cerebral cortex where vision registers in the brain Visual cortex Temporal lobes- areas that include the sites where hearing registers in the brain Association cortex- all areas of the cerebral cortex that are not primarily sensory or motor in function Cerebral dominance- ability of one cerebral hemisphere (right or left side of the brain) to control specific tasks; related to handedness Corpus callosum- the bundle of fibers connecting the cerebral hemispheres (the right and left halves of the cerebrum) Cerebrum- enables reasoning, planning, creating, and problem solving; topmost layer of the brain. Aphasia- the loss of speech caused by brain damage Left Hemisphere- spontaneous speaking and writing, responses to complex commands, word recognition, memory for words and numbers, sequences of movements, feelings of anxiety, positive emotions Right Hemisphere- repetitive but not spontaneous speaking, responses to simple commands, facial recognition, memory for shapes and music, spatial interpretation, emotional responses, negative Dopamine- produces sensations of pleasure and reward; used by CNS neurons in voluntary movement: problems w/imbalance include schizophrenia and Parkinsons: affected by: cocaine, amphetamines, Ritalin, alcohol
Serotonin- regulates sleep and dreaming, mood, pain, aggression, appetite, sexual behavior. Problems- depression, certain anxiety disorders, OCD. Drugs- Prozac, hallucinogenics (LSD) Norepinephrine- controls heart rate, sleep, sexual responsiveness, stress, vigilance, appetite. Problems- high blood pressure, depression. Drugs- tricyclic antidepressants, beta blockers. Acetylcholine- primary transmitter used by neurons carrying messages from CNS, involved in some kinds of learning and memory. Problems- certain muscular disorders, Alzheimers. Drugs- nicotine, butolism toxin, curare, atropine. GABA- most prevalent inhibitory neurotransmitter in neurons of CNS. Problems- anxiety, epilepsy. Drugsbarbiturates, tranquilizers (ex. Valium, Librium), alcohol. Glutamin- primary excitatory neurotransmitter in CNS, involved in learning and memory. Problems- brain damage after stroke. Drugs- PCP (angel dust) Endorphins- pleasurable sensations, control of pain. Problems- lowered levels resulting from opiate addiction. Drugsopiates: opium, heroin, morphine, methadone.
THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM WORKS SLOWER THAN THE NERVOUS SYSTEM DOES.
You might also like
- Nervous System: A Tutorial Study GuideFrom EverandNervous System: A Tutorial Study GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Nervous System and Brain Structures OverviewDocument43 pagesNervous System and Brain Structures OverviewDweep BajajNo ratings yet
- AP Psychology Chapter 2 NotesDocument8 pagesAP Psychology Chapter 2 NoteshannabbiiNo ratings yet
- Nervous System: Science 6 - Second QuarterDocument25 pagesNervous System: Science 6 - Second QuarterRegin BaguioNo ratings yet
- Understanding the Nervous System: An Overview of its Structure and FunctionsDocument27 pagesUnderstanding the Nervous System: An Overview of its Structure and FunctionsNARESH JANDIALNo ratings yet
- Physiology ReviewDocument65 pagesPhysiology ReviewNandita KNo ratings yet
- Nervous System 2Document23 pagesNervous System 2TinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Biological Foundations of BehaviorDocument50 pagesChapter 3 - Biological Foundations of BehaviorShermel Joy SolisNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Part 1Document6 pagesNervous System Part 1rb YangzonNo ratings yet
- The human nervous system and its major componentsDocument2 pagesThe human nervous system and its major componentsPoppy MargoNo ratings yet
- CHP 3 PSYCHDocument8 pagesCHP 3 PSYCHEmma Mahoney100% (1)
- Pertemuan 8 - Sistem Saraf MinDocument43 pagesPertemuan 8 - Sistem Saraf MinErsha PutriNo ratings yet
- SSYA1013 Chapter 3 BiologicalDocument27 pagesSSYA1013 Chapter 3 BiologicalPing Ping TanNo ratings yet
- Overview of The Nervous SystemDocument32 pagesOverview of The Nervous Systemanita adamsNo ratings yet
- 3A Neurology FlashcardsDocument14 pages3A Neurology FlashcardsJustin ChangNo ratings yet
- Psychology Week 3 NotesDocument9 pagesPsychology Week 3 Notes01234No ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument10 pagesNervous SystemPogi BearNo ratings yet
- Interface Between Pituitary and BrainDocument4 pagesInterface Between Pituitary and BrainHuck KimNo ratings yet
- Biology of MindOK1Document120 pagesBiology of MindOK16130019037 FATCHUR RIZQI HAMZAHNo ratings yet
- Brain and BehaviourDocument9 pagesBrain and BehaviourKenya BaileyNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System: Components, Functions, and DivisionsDocument21 pagesThe Nervous System: Components, Functions, and Divisionshenrylangam100% (1)
- Nervous SystemDocument26 pagesNervous SystemAe-jay CacalNo ratings yet
- The Central Nervous SystemDocument59 pagesThe Central Nervous SystemJuliville Hora Salinas100% (1)
- Human Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument8 pagesHuman Anatomy and Physiologyzairis21No ratings yet
- Biological Basis of BehaviorDocument57 pagesBiological Basis of BehaviorJAMES ALDRIN CALVEZ PAMPOSANo ratings yet
- Psyc Biology & BehaviorDocument3 pagesPsyc Biology & BehaviorJudeMartinOptionalMaglanaNo ratings yet
- Nervous System: 1. CerebrumDocument5 pagesNervous System: 1. CerebrumNgọc BảoNo ratings yet
- .Document71 pages.nathanielstanaj.mNo ratings yet
- Report in Physiological Psy. (Nervous System)Document27 pagesReport in Physiological Psy. (Nervous System)Francia VenancioNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3Document4 pagesLesson 3JessieNo ratings yet
- Intro To Psych PrelimDocument113 pagesIntro To Psych PrelimAlexandra San PedroNo ratings yet
- Functions of the Nervous SystemDocument25 pagesFunctions of the Nervous SystemRocky MrRockyNo ratings yet
- Science 3RD QuarterDocument3 pagesScience 3RD QuarterG03 Bonavente, Mickaela Vhey M.No ratings yet
- Medical SurgicalDocument119 pagesMedical SurgicalTammy TamNo ratings yet
- ISAP Lecture 1 Module 1 - Studocu NotesDocument6 pagesISAP Lecture 1 Module 1 - Studocu NotesLyndonNo ratings yet
- Nervous System OverviewDocument5 pagesNervous System Overviewapi-306398192No ratings yet
- The Human Nervous System - 71911Document49 pagesThe Human Nervous System - 71911Rome Voltaire GomezNo ratings yet
- Recap: Nervous System Biological Basis of Behavior Peripheral Nervous SystemDocument27 pagesRecap: Nervous System Biological Basis of Behavior Peripheral Nervous Systemfatima shahNo ratings yet
- Myer's AP Psychology 8th Edition Chapter 2 VocabDocument4 pagesMyer's AP Psychology 8th Edition Chapter 2 Vocabcardenass100% (3)
- What Is The Nervous SystemDocument3 pagesWhat Is The Nervous SystemSittie Asleah SandiganNo ratings yet
- Presented by G3Document23 pagesPresented by G3Bernadette GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7a: Functional NeuroanatomyDocument5 pagesLecture 7a: Functional NeuroanatomyBetty MaiNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument36 pagesThe Nervous SystemespirituronnierickNo ratings yet
- PY1101 Lecture 3 NotesDocument9 pagesPY1101 Lecture 3 NotesSeah Fu MeiNo ratings yet
- General Psychology - Biological FoundationDocument55 pagesGeneral Psychology - Biological FoundationKomala PodapatiNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System-13 Dr. Hazim AL-RawiDocument16 pagesThe Nervous System-13 Dr. Hazim AL-RawiDrAli Al-FendiNo ratings yet
- Science NotesDocument1 pageScience NotesAshley Babe ServianoNo ratings yet
- Unit-Two Biological Bases of BehaviorDocument27 pagesUnit-Two Biological Bases of Behaviorरोशन सिग्देलNo ratings yet
- Unit-Two Biological Bases of BehaviorDocument27 pagesUnit-Two Biological Bases of Behaviorरोशन सिग्देलNo ratings yet
- Nervous System - Overview: FunctionDocument11 pagesNervous System - Overview: FunctionAadil JuttNo ratings yet
- Introduction To NeuroanatomyDocument49 pagesIntroduction To NeuroanatomyPratik Dhakal100% (1)
- Biological Basis of BehaviorDocument6 pagesBiological Basis of BehaviorLyanna MormontNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 - An Introduction To The Nervous System: Peripheral Nerves)Document7 pagesChapter 12 - An Introduction To The Nervous System: Peripheral Nerves)tomorrow.today.yesterday .yesterdayNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System: Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument85 pagesThe Nervous System: Anatomy & PhysiologyJamie Bagundol100% (3)
- The Structure and Major Divisions of the Nervous SystemDocument2 pagesThe Structure and Major Divisions of the Nervous SystemCharlotte Celocia NiniNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument16 pagesUntitled Documentpierre TritzNo ratings yet
- Physiological Basis of Psychology: Neurons Serve To Receive and Transmit Impulses FromDocument4 pagesPhysiological Basis of Psychology: Neurons Serve To Receive and Transmit Impulses FromPatrick RilleraNo ratings yet
- Wonders of Nervous SystemDocument2 pagesWonders of Nervous SystemMa Victoria Shainee GaliciaNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Anatomy and FunctionsDocument4 pagesNervous System Anatomy and FunctionsIrish Buaya Gementiza100% (1)
- Human Physiology: The Nervous System ExplainedDocument29 pagesHuman Physiology: The Nervous System Explainedzandrex delunaNo ratings yet
- CH 3 ActivitiesDocument11 pagesCH 3 Activitiesapi-31355470No ratings yet
- Legislative Branch ActivitiesDocument21 pagesLegislative Branch Activitiesapi-31355470No ratings yet
- Supreme Court Case AnalysisDocument1 pageSupreme Court Case Analysisapi-31355470No ratings yet
- Supreme Court Case AnalysisDocument1 pageSupreme Court Case Analysisapi-31355470No ratings yet
- This Is A Journey/marathon - Work Hard, Be Positive, and Ask ?s. You Can ALL Earn AsDocument9 pagesThis Is A Journey/marathon - Work Hard, Be Positive, and Ask ?s. You Can ALL Earn Asapi-31355470No ratings yet
- Unit 3 ObjectivesDocument2 pagesUnit 3 Objectivesapi-31355470No ratings yet
- CH 2 Objectives Application - Version 2Document4 pagesCH 2 Objectives Application - Version 2api-31355470No ratings yet
- Creating Political Parties 2012Document2 pagesCreating Political Parties 2012api-31355470No ratings yet
- Bio Terms DefDocument3 pagesBio Terms Defapi-31355470No ratings yet
- CH 10 Objectives ApplicationDocument2 pagesCH 10 Objectives Applicationapi-31355470No ratings yet
- BrainmnemonicsDocument32 pagesBrainmnemonicsapi-31355470No ratings yet
- Classical ConditioningDocument12 pagesClassical Conditioningapi-31355470No ratings yet
- CH 2 ActivitiesDocument22 pagesCH 2 Activitiesapi-31355470No ratings yet
- Unit 3 Executive BranchDocument14 pagesUnit 3 Executive Branchapi-31355470No ratings yet
- CH 10 Language NotebookDocument14 pagesCH 10 Language Notebookapi-31355470No ratings yet
- Legislative Branch Objectives - 3-1-11Document3 pagesLegislative Branch Objectives - 3-1-11api-31355470No ratings yet
- Brainpref Vaksurvey Middle HighDocument9 pagesBrainpref Vaksurvey Middle Highapi-31355470No ratings yet
- Unit 1 Gov NotebookDocument20 pagesUnit 1 Gov Notebookapi-31355470No ratings yet
- Student Self2Document2 pagesStudent Self2api-31355470No ratings yet
- Ap Psychology Syllabus - Filled inDocument6 pagesAp Psychology Syllabus - Filled inapi-31355470No ratings yet
- Syllabus Preamble Analysis 4 5 Ch2.2 Analysis 10 Heritage Analysis 16 Federalism Review GuideDocument16 pagesSyllabus Preamble Analysis 4 5 Ch2.2 Analysis 10 Heritage Analysis 16 Federalism Review Guideapi-31355470No ratings yet
- Prologue ActivitiesDocument10 pagesPrologue Activitiesapi-31355470No ratings yet
- Five Types of SchizophreniaDocument9 pagesFive Types of Schizophreniaapi-31355470No ratings yet
- Very Much Alike Yet Completely Different AP Psych Final Exam Review WorksheetDocument7 pagesVery Much Alike Yet Completely Different AP Psych Final Exam Review Worksheetapi-31355470No ratings yet
- AP Psychology Review Types of Psychologists and PerspectivesDocument4 pagesAP Psychology Review Types of Psychologists and Perspectivesapi-31355470No ratings yet
- Ap Psych Exam Review SheetDocument4 pagesAp Psych Exam Review Sheetapi-31355470No ratings yet
- 445 Terms ListDocument4 pages445 Terms Listapi-31355470No ratings yet
- Taking Notes in PsychDocument1 pageTaking Notes in Psychapi-31355470No ratings yet
- Study SkillsDocument1 pageStudy Skillsapi-31355470No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 The Biological PerspectiveDocument39 pagesChapter 2 The Biological PerspectiveSULDAANUL CAASHIQIINNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Powerpoint SlidesDocument47 pagesNervous System Powerpoint SlidesTay Kai xin (Ahs)No ratings yet
- Psych 1101 FinalDocument25 pagesPsych 1101 FinalSimon HagosNo ratings yet
- Alpha Motor NeuronsDocument12 pagesAlpha Motor NeuronsRafu DestajoNo ratings yet
- Christopher D. Moyes, Patricia M. Schulte - Principles of Animal Physiology-Pearson (2016)Document775 pagesChristopher D. Moyes, Patricia M. Schulte - Principles of Animal Physiology-Pearson (2016)salvatore.sara323No ratings yet
- Psychology Review SheetDocument7 pagesPsychology Review Sheetfalbokhiti_827121084No ratings yet
- Collège de La Salle (Frères) Amman - Jordan: Biology / Cells: Cell SpecialisationDocument3 pagesCollège de La Salle (Frères) Amman - Jordan: Biology / Cells: Cell Specialisationwafa eliasNo ratings yet
- Structural Organization of The Nervous SystemDocument14 pagesStructural Organization of The Nervous SystemGhaidaa SadeqNo ratings yet
- Cognition 6th Edition Ashcraft Test BankDocument35 pagesCognition 6th Edition Ashcraft Test Bankmaygluish5leo38100% (20)
- Introduction to Cells and Signaling in the Nervous SystemDocument23 pagesIntroduction to Cells and Signaling in the Nervous SystemadfhNo ratings yet
- Neural Control and CoordinationDocument4 pagesNeural Control and CoordinationSipranjali SubudhiNo ratings yet
- 185 Nervous System MCQs by Monsef - KarkorDocument60 pages185 Nervous System MCQs by Monsef - KarkorMostafa Montaser100% (5)
- Questions Examens PhysioDocument32 pagesQuestions Examens PhysioZeineb KammounNo ratings yet
- Biology and Behavior PDFDocument62 pagesBiology and Behavior PDFsalvadorNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument39 pagesThe Nervous SystemReizel Mae Noel Laurente100% (1)
- Introduction to Physiological PsychologyDocument28 pagesIntroduction to Physiological PsychologyRM April AlonNo ratings yet
- Emg, NCVDocument38 pagesEmg, NCVMaria Isabel Nabor100% (1)
- 1184bns 1Document14 pages1184bns 1Daniela GanchasNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Lateralization and Theory of MindDocument23 pagesCerebral Lateralization and Theory of MindEdgardo100% (3)
- Brain Thesis StatementDocument5 pagesBrain Thesis Statementzyxnlmikd100% (2)
- 7a. Cellular Aberration With PAIN ConceptDocument25 pages7a. Cellular Aberration With PAIN ConceptRENEROSE TORRESNo ratings yet
- Group 10: Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)Document24 pagesGroup 10: Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)Tara DolotaNo ratings yet
- NeurophysiologyDocument200 pagesNeurophysiologyashley nicholeNo ratings yet
- 02 - Control and CoordinationDocument20 pages02 - Control and CoordinationSamveg ClassesNo ratings yet
- The Divided Brain: Insights from Split-Brain Patient W.JDocument40 pagesThe Divided Brain: Insights from Split-Brain Patient W.Jbananita_2006533975% (4)
- Marjo S. Van Der Knaap MD, PHD, Jacob Valk MD, PHD Auth. Magnetic Resonance of Myelin, Myelination, and Myelin DisordersDocument570 pagesMarjo S. Van Der Knaap MD, PHD, Jacob Valk MD, PHD Auth. Magnetic Resonance of Myelin, Myelination, and Myelin Disordersali tidaNo ratings yet
- DEVPSY Module 4 InfancyDocument22 pagesDEVPSY Module 4 InfancyARCHIE MEDES BARTENo ratings yet
- Ion ChannelsDocument6 pagesIon ChannelsNicolas IsformermynameNo ratings yet
- Biomechanics and Neural Control of Posture and Movement by Jack M. Winters (Auth.), Jack M. Winters, Patrick E. Crago (Eds.)Document689 pagesBiomechanics and Neural Control of Posture and Movement by Jack M. Winters (Auth.), Jack M. Winters, Patrick E. Crago (Eds.)JulianoEscudeiro100% (1)
- Important McQs For Clinical and BNSDocument3 pagesImportant McQs For Clinical and BNSAbrar AhmadNo ratings yet
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionFrom EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (402)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityFrom EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (13)
- The Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingFrom EverandThe Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeFrom EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeNo ratings yet
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsFrom EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossFrom EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (78)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsFrom EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsNo ratings yet
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsFrom EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (169)
- The Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesFrom EverandThe Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (34)
- The Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsFrom EverandThe Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsNo ratings yet
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (31)
- Techniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementFrom EverandTechniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (40)
- Summary: It Didn't Start with You: How Inherited Family Trauma Shapes Who We Are and How to End the Cycle By Mark Wolynn: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: It Didn't Start with You: How Inherited Family Trauma Shapes Who We Are and How to End the Cycle By Mark Wolynn: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.From EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (110)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaFrom EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeFrom EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (253)
- Secure Love: Create a Relationship That Lasts a LifetimeFrom EverandSecure Love: Create a Relationship That Lasts a LifetimeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (16)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessFrom EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (327)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryFrom EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (44)