Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Leak Off Test, Formation Integrity Test, Equivalent Mud Weight, Equivalent Circulating Density
Uploaded by
Mufti GhazaliCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Leak Off Test, Formation Integrity Test, Equivalent Mud Weight, Equivalent Circulating Density
Uploaded by
Mufti GhazaliCopyright:
Available Formats
Formation Integrity Test, Leak Off Test, Equivalent Circulating Density
Some of the question that seems to be asking frequently in drilling operation is: what differences between Formation Integrity Test (FIT), and Leak Off Test (LOT), and it application, I hope this sharing can give little information for you all In the drilling, Formation Integrity Test (FIT) and Leak Off Test (LOT), are two methods to determine: 1. Strength of cement around the casing shoe after setting. 2. Approximate the fracture gradient, later will be use to create mud programs. 3. To determine the current Maximum Allowable Annular Surface Pressure (MAASP) well control event. LOT and FIT in principle the same, by pumping mud without circulation to the surface. (BOP closed, the choke closed). LOT is usually done on exploration wells, and FIT is usually done on the well development (because the value of fracture pressure be expected from well data neighbors who've done a LOT). But for several person which need more time to read I write down the lecturer definition for it, as shown below. Leak Off Test Leak Off Test is conducted in order to find the fracture gradient of certain formation. The results of the leak off test also dictate the maximum equivalent mud weight that should be applied to the well during drilling operations. Leak Off Test (LOT) guide line procedures are as follows (note: this is just only guide line. You may need to follow your standard procedure in order to perform leak off test): 1. 2. 3. Drill out new formation few feet, circulate bottom up and collect sample to confirm that new formation is drilled to and then pull string into the casing. Close annular preventer or pipe rams, line up a pump, normally a cement pump, and circulate through an open choke line to ensure that surface line is fully filled with drilling fluid. Gradually pump small amount of drilling fluid into well with constant pump stroke. Record total pump strokes, drill pipe pressure and casing pressure. Drill pipe pressure and casing pressure will increase continually while pumping mud in hole. When plot a graph between strokes pumped and pressure, if formation is not broken, a graph will demonstrate straight line relationship. When pressure exceeds formation strength, formation will be broken and let drilling fluid permeate into formation, therefore a trend of drill pipe/casing pressure will deviate from straight line that mean formation is broken and is injected by drilling fluid. We may call pressure when deviated from straight line as leak off test pressure. Note: the way people call leak off test pressure depends on each company standard practices. Leak off test pressure can be calculated into equivalent mud weight in ppg as formula below:
Page | 1
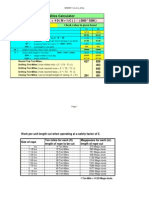
Leak off test in equivalent mud weight (ppg) = (Leak off test pressure in psi) 0.052 (Casing Shoe TVD in ft) + (current mud weight in ppg) Pressure gradient in psi/ft = (Leak off test pressure in psi) (Casing Shoe TVD in ft) Example: Leak off test pressure= 1600 psi Casing shoe TVD = 4000 ft Mud weight = 9.2 ppg Leak off test in equivalent mud weight (ppg) = 1600 psi 0.052 4000 ft + 9.2ppg ppg = 16.9 ppg Pressure gradient = 1600 4000 = 0.4 psi/ft 4. Bleed off pressure and open up the well. Then proceed drilling operation.
Formation Integrity Test
Formation Integrity Test is the method to test strength of formation and shoe by increasing Bottom Hole Pressure (BHP) to designed pressure. FIT is normally conducted to ensure that formation below show will not be broken while drilling the next section with higher BHP. Normally, engineers in town will design how much formation integrity test pressure required mostly in ppg. Before forming formation integrity test, you should know pressure required for Formation Integrity Test. The formula showed below demonstrates you how to calculate required FIT pressure. Pressure required for FIT (psi) = (Required FIT in ppg Current Mud Weight in ppg) x 0.052 x True Vertical Depth of shoe in ft Example: Required FIT (ppg) = 14.5 Current mud weight (ppg) = 9.2 Shoe depth TVD (ft) = 4000 TVD Pressure required for FIT= (14.5-9.2) x 0.052 x 4000 = 1102 psi Formation Integrity Test (FIT) as guide line as follows: (note: this is just only guide line. You may need to follow your standard procedure in order to perform formation integrity test):
Page | 2
1. 2. 3.
Drill out new formation few feet, circulate bottom up and collect sample to confirm that new formation is drilled to and then pull string into the casing. Close annular preventer or pipe rams, line up a pump, normally a cement pump, and circulate through an open choke line to ensure that surface line is fully filled with drilling fluid. Gradually pump small amount of drilling fluid into well with constant pump stroke. Record total pump strokes, drill pipe pressure and casing pressure. Pump until casing pressure reaches the pressure required for formation integrity test. Hold pressure for few minutes to confirm pressure.
4.
Bleed off pressure and open up the well. Then proceed drilling operation.
Creating mud program Basic principles in making mud program are as follows: 1. Determine the pore pressure and fracture pressure along the depth that we will drill. Some also stressed the need for a data field minimum stress and overburden. Such data can be obtained from measurements at the nearest drill wells that we will drill. The data can be obtained directly from measurements (PWDpressure while drilling) or of the processed D-exponent correction (a function of ROP, RPM, WOB, bit diameter). If the well is the first well to be drilled / exploration (no data from nearby wells), the data can be estimated by converting sonic travel time of the seismic survey. 2. Once we have a pore pressure vs. depth plot and frac pressure, we can determine casing setting depth and mud weight (density). In normal drilling (overbalance), we design the best possible mud weight greater than the pore pressure (so as not to kick) but smaller than the fracture pressure (so that no formation fracturing). 3. Determine what type of mud that will be based on lithologic formations penetrated. There are three general categories of types of mud, the water-based mud (for wells with simple trajectories, no reactive shale), oil-based mud (for wells with more complex trajectorie, many reactive shale zone), synthetic based mud (OBM has similar properties but more environmental friendly). 4. Designing Rheology (viscosity, yield point, gel strength) and mud additive required under circumstances that will be penetrated lithologic, avoid formation damage while drilling the reservoir zone, reducing the thickness of the mud cake, or other specific purposes. It can be consulted with mud representative company. 5. After step 2, 3, and 4 then need to count how much pressure loss when the mud that we design circulated during drilling. Then we calculate the ECD as mud hydrostatic pressure + pressure loss. ECD (equivalent circulating density), we compare it to the plot in step 2. ECD must live between pore pressure and fracture pressure. Often added to the calculation / density margin to avoid differential pipe sticking, surge effects, swab effect, etc. 6. 7. Optimization of hydraulic mud. Using data from a mud drilling program to determine other parameters (pump rate, pump pressure, bit nozzle area, etc.) to get that optimum drilling performance. Iterations of the above steps until all criteria is reached with the optimum.
From my own experiences sharing the formula to obtain equivalent mud weight which is write down as:
Page | 3
EMW (ppg) = (Pressure in psi) 0.052 (Casing Shoe TVD in ft) + (current mud weight in ppg)
Taking too long to calculate in fields itself and so I modify the formula as below: EMW (ppg) = ((Pressure in psi) 19.25 (Casing Shoe TVD in ft)) + (current mud weight in ppg)
Dont worry EMW will result the same answer, some say that formula I use is thumbs rules for EMW but I dont know whether its true or not.
Equivalent Circulating Density Equivalent Circulating Density (ECD) is the effective density that combines current mud density and annular pressure drop. ECD is critical for drilling operations because it can caused losses due to high pressure loss in annulus. Moreover, ECD is very critical in both well control and losses aspects in the areas where have narrow room between pore pressure and fracture gradient. For Equivalent Circulating Density formula itself: Equivalent Circulating Density (ECD) in ppg = (annular pressure loss in psi) 0.052 true vertical depth (TVD) in ft + (current mud weight in ppg) Or it can be writing like this: Equivalent Circulating Density (ECD) in ppg = ((annular pressure loss in psi) 19.25 true vertical depth (TVD) in ft) + (current mud weight in ppg) Dont be confused why all the formula seems to use single formula for Pressure Hydrostatic one, cause in drilling operation itself we only maintenance formation pressure to the hydrostatic one, not to exceed formation pressure so the formation is not leak, or below formation pressure which can make kick to well itself. compiling from several pages, you can simply open it using link below. This article is
Source:
http://drillingclub.proboards.com/index.cgi?board=wellcontrol&action=display&thread=4913 http://www.migas-indonesia.com/2012/06/mud-program.html
Page | 4
You might also like
- Note For Directional Drilling CalculationDocument22 pagesNote For Directional Drilling CalculationMufti Ghazali96% (25)
- Torque & DragDocument66 pagesTorque & Dragjoonak konwar91% (11)
- Drilling Formulas Calculation Sheet Version 1.5Document208 pagesDrilling Formulas Calculation Sheet Version 1.5Pham Tin100% (5)
- Directional Drilling EquationDocument4 pagesDirectional Drilling EquationMufti Ghazali67% (3)
- Clay ChemistryDocument44 pagesClay ChemistryMufti GhazaliNo ratings yet
- CementingDocument4 pagesCementing07103091100% (2)
- ANZ-37MH Final Drilling ProgramDocument37 pagesANZ-37MH Final Drilling ProgramWilson OdiaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Drilling Engineering: MCQs and Workout Examples for Beginners and EngineersFrom EverandFundamentals of Drilling Engineering: MCQs and Workout Examples for Beginners and EngineersNo ratings yet
- IWCF Drilling Levels 3 and 4 SyllabusDocument37 pagesIWCF Drilling Levels 3 and 4 SyllabusNacer Lagraa100% (1)
- Drilling Engineering Assignment FactorsDocument14 pagesDrilling Engineering Assignment FactorsApostolos AvraamidesNo ratings yet
- WellPlan Exercie Book PDFDocument115 pagesWellPlan Exercie Book PDFMJ arab100% (1)
- Coiled Tubing Operations at a Glance: What Do You Know About Coiled Tubing Operations!From EverandCoiled Tubing Operations at a Glance: What Do You Know About Coiled Tubing Operations!Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Drilling Optimization PDFDocument22 pagesDrilling Optimization PDFRoyNo ratings yet
- 5 4 Primary Cementing Calculations PDFDocument38 pages5 4 Primary Cementing Calculations PDFAbrarhassan100% (1)
- Formation Integrity Test (FIT) and Leak Off Test (LOT)Document1 pageFormation Integrity Test (FIT) and Leak Off Test (LOT)mmohsinaliawanNo ratings yet
- Manual, Type 80 Koomey UnitDocument52 pagesManual, Type 80 Koomey Unitstevo3009100% (9)
- 37 Drill Stem Tools 1 PDFDocument2 pages37 Drill Stem Tools 1 PDFRizwan FaridNo ratings yet
- Formulas and Calculations for Drilling, Production, and Workover: All the Formulas You Need to Solve Drilling and Production ProblemsFrom EverandFormulas and Calculations for Drilling, Production, and Workover: All the Formulas You Need to Solve Drilling and Production ProblemsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (9)
- Well Control OpenDocument311 pagesWell Control OpenRobert Verret100% (1)
- Distance Learning Drilling Calculations Part 1Document211 pagesDistance Learning Drilling Calculations Part 1Eddy Rochmadi100% (2)
- Torque and Drag CalculationsDocument67 pagesTorque and Drag CalculationsStalin ChugchilánNo ratings yet
- Week 4 - ReadingDocument2 pagesWeek 4 - Readingapi-254428474100% (1)
- Drilling Formulae - 9th Edition PDFDocument87 pagesDrilling Formulae - 9th Edition PDFEng Mohamed SaberNo ratings yet
- Formulas and Calculations For Drilling Operations by Robello Samuel - Discount FlyerDocument1 pageFormulas and Calculations For Drilling Operations by Robello Samuel - Discount Flyerarzafar0% (1)
- Formation and Stabilization of Rock Cavern Roof ArchesDocument6 pagesFormation and Stabilization of Rock Cavern Roof Archesdafo407No ratings yet
- National Drilling Company Exam Factors Affecting Penetration RatesDocument9 pagesNational Drilling Company Exam Factors Affecting Penetration RatesShakeel Ahmed100% (2)
- Production of Biofuels and Chemicals With Ultrasound: Zhen Fang Richard L. Smith, Jr. Xinhua Qi EditorsDocument363 pagesProduction of Biofuels and Chemicals With Ultrasound: Zhen Fang Richard L. Smith, Jr. Xinhua Qi EditorsHa Nhut Khang100% (1)
- Casing Setting Depth DesignDocument26 pagesCasing Setting Depth Designehsan100% (1)
- Drilling Engineering Problems and Solutions: A Field Guide for Engineers and StudentsFrom EverandDrilling Engineering Problems and Solutions: A Field Guide for Engineers and StudentsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- COMPREHENSIVE GUIDE TO STUCK PIPE PREVENTIONDocument83 pagesCOMPREHENSIVE GUIDE TO STUCK PIPE PREVENTIONمحمد سعيد100% (2)
- Casing Design1.9 Burst, Collapse, TensionDocument19 pagesCasing Design1.9 Burst, Collapse, Tensionjuanca_eduNo ratings yet
- 5) Plug CementingDocument35 pages5) Plug Cementingeng20072007No ratings yet
- Drilling Questions and SolutionsDocument10 pagesDrilling Questions and SolutionsJohn Joseph100% (3)
- Ton-Miles Calculator Excel SheetDocument4 pagesTon-Miles Calculator Excel Sheetice_PLNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To Drilling Engineering Latest PDFDocument118 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To Drilling Engineering Latest PDFIkhmal Firdaus100% (5)
- Curtin University Drilling Engineering GuideDocument282 pagesCurtin University Drilling Engineering Guidejultur4oNo ratings yet
- Compressibility Factor On Displacement Oil Base MudDocument2 pagesCompressibility Factor On Displacement Oil Base MudMufti Ghazali100% (7)
- IWCF Drilling Well Control Syllabus - Level 3 and 4Document97 pagesIWCF Drilling Well Control Syllabus - Level 3 and 4Sohaib Tahir100% (1)
- Drilling NotebookDocument96 pagesDrilling NotebookOmar Rosado Roldan0% (1)
- Casing Design ExampleDocument42 pagesCasing Design ExampleSudish Bhat100% (1)
- Well Engineering Level 1Document4 pagesWell Engineering Level 1SHOBHIT KUMARNo ratings yet
- 03 Shut-In ProcedureDocument15 pages03 Shut-In Proceduresitemaster60No ratings yet
- David W. Richerson, William E. Lee - Modern Ceramic PDFDocument837 pagesDavid W. Richerson, William E. Lee - Modern Ceramic PDFUzair Anwar100% (5)
- Master of Petroleum Engineering Drilling Bit SelectionDocument10 pagesMaster of Petroleum Engineering Drilling Bit SelectionKaveh Bahiraee100% (1)
- Bit Hydraulics Optimization for Maximum Drilling PerformanceDocument23 pagesBit Hydraulics Optimization for Maximum Drilling PerformanceShakerMahmood100% (1)
- Introduction To Drilling OperationsDocument36 pagesIntroduction To Drilling Operationsomer dafallahNo ratings yet
- Proposals For New One-Way Shear Equations For The 318 Building CodeDocument4 pagesProposals For New One-Way Shear Equations For The 318 Building CodepicottNo ratings yet
- WEll ControlDocument60 pagesWEll Controlbennimitz100% (1)
- Lost Circulation: Mechanisms and SolutionsFrom EverandLost Circulation: Mechanisms and SolutionsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Drilling an Extended Reach Well: Key ConsiderationsDocument33 pagesDrilling an Extended Reach Well: Key ConsiderationsKutz100% (2)
- Several Tests For Drilling Fluid in FieldDocument9 pagesSeveral Tests For Drilling Fluid in FieldMufti Ghazali100% (1)
- Determine Flow Back Volume To SurfaceDocument4 pagesDetermine Flow Back Volume To SurfaceMufti Ghazali100% (4)
- Measurement While Drilling: Signal Analysis, Optimization and DesignFrom EverandMeasurement While Drilling: Signal Analysis, Optimization and DesignNo ratings yet
- Polymers in Drilling FluidsDocument60 pagesPolymers in Drilling FluidsMufti GhazaliNo ratings yet
- Wellsite Geologist Training Report 3Document7 pagesWellsite Geologist Training Report 3tonyxcrime100% (3)
- Cementing Example ProblemDocument10 pagesCementing Example ProblemChilledambienceNo ratings yet
- Applied Gaseous Fluid Drilling Engineering: Design and Field Case StudiesFrom EverandApplied Gaseous Fluid Drilling Engineering: Design and Field Case StudiesNo ratings yet
- Well PlanningDocument55 pagesWell Planningmts1234100% (1)
- TestsDocument10 pagesTestsShakeel AhmedNo ratings yet
- 14 IWCF Formula Sheet - Well Intervention - English APIDocument2 pages14 IWCF Formula Sheet - Well Intervention - English APIryaneschultzhotmail.com100% (1)
- Shale Shaker and Drilling Fluids Systems:: Techniques and Technology for Improving Solids Control ManagementFrom EverandShale Shaker and Drilling Fluids Systems:: Techniques and Technology for Improving Solids Control ManagementRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Drilling Program MSSM01 280808 SPUD Rev00Document64 pagesDrilling Program MSSM01 280808 SPUD Rev00Andrian Arif100% (1)
- Optimize Drilling Hydraulics with Bit Nozzle Selection and Pressure Loss CalculationsDocument13 pagesOptimize Drilling Hydraulics with Bit Nozzle Selection and Pressure Loss CalculationsAgung Doank Yess100% (2)
- Rotating Equipment Interview QuestionsDocument5 pagesRotating Equipment Interview QuestionsSud100% (1)
- Stuck PipeDocument71 pagesStuck Pipemosli_No ratings yet
- Wind Tunnel DesignsDocument228 pagesWind Tunnel DesignsDinh LeNo ratings yet
- Mud LoggingDocument16 pagesMud LoggingShamia EssamNo ratings yet
- Blowouts: "Blowouts Continue To Occur at About A Constant Rate... "Document18 pagesBlowouts: "Blowouts Continue To Occur at About A Constant Rate... "Muhammad ShahrukhNo ratings yet
- Calculating Content of Horizontal Cylindrical TanksDocument2 pagesCalculating Content of Horizontal Cylindrical TanksMufti GhazaliNo ratings yet
- Forces and Direction Tubular Goods: Case 1Document1 pageForces and Direction Tubular Goods: Case 1Mufti GhazaliNo ratings yet
- Well ControlDocument2 pagesWell Controltimz_upNo ratings yet
- Nama: Mufti Ghazali M NIM: 060045 Tugas: Mekanika Fluida Dosen: Yanasari. SsiDocument20 pagesNama: Mufti Ghazali M NIM: 060045 Tugas: Mekanika Fluida Dosen: Yanasari. SsiMufti GhazaliNo ratings yet
- Radial Water Jetting Drilling: Selection Well CandidateDocument5 pagesRadial Water Jetting Drilling: Selection Well CandidateMufti GhazaliNo ratings yet
- Figure 1 Drilling Fluids SystemDocument4 pagesFigure 1 Drilling Fluids SystemMufti GhazaliNo ratings yet
- Strain PDFDocument14 pagesStrain PDFengineer bilalNo ratings yet
- Assignment 6 2023Document2 pagesAssignment 6 2023Linhan ChuNo ratings yet
- FractureDocument4 pagesFractureNitin YNo ratings yet
- Learning Unit 2 - AbsorptionDocument68 pagesLearning Unit 2 - AbsorptionTshwarelo MahlakoaneNo ratings yet
- Distillation, Ponchon Savarit, ShahzadDocument30 pagesDistillation, Ponchon Savarit, ShahzadMahad ZahidNo ratings yet
- Shear Behavior of Unbonded Post-TensionedDocument10 pagesShear Behavior of Unbonded Post-TensionedAnonymous eB2AZT3No ratings yet
- Fanno Flow PDFDocument20 pagesFanno Flow PDFZain EejazNo ratings yet
- CE6306 NotesDocument125 pagesCE6306 Noteskl42c4300No ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Ch4-Unsteady ConductionDocument11 pagesHeat Transfer Ch4-Unsteady ConductionDinesh Bala KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals Of Thermal Sciences Lab ManualDocument5 pagesFundamentals Of Thermal Sciences Lab ManualDavid JonesNo ratings yet
- White Paper ARI STD 550.590-98Document5 pagesWhite Paper ARI STD 550.590-98Julio Enrique Molina ChirinoNo ratings yet
- SINHA’s I. I.T. CHEMISTRY THERMODYNAMICS PROBLEMSDocument2 pagesSINHA’s I. I.T. CHEMISTRY THERMODYNAMICS PROBLEMSKathryn BellNo ratings yet
- p γ υ z H p γ υ z H: Problem 7Document4 pagesp γ υ z H p γ υ z H: Problem 7Ariel GamboaNo ratings yet
- Methods To Determine The Elastic Line: Description Learning Objectives/experimentsDocument3 pagesMethods To Determine The Elastic Line: Description Learning Objectives/experimentsDiego AvendañoNo ratings yet
- FRP STRUCTURAL GUIDELINES, ACI 440.1 r06Document1 pageFRP STRUCTURAL GUIDELINES, ACI 440.1 r06Gohar ZamanNo ratings yet
- IMPROVED MENEGOTTO-PINTO MODELDocument10 pagesIMPROVED MENEGOTTO-PINTO MODELSebastian Pozo OcampoNo ratings yet
- Turbulent Shear StressDocument5 pagesTurbulent Shear Stresssyedahmedali_276353No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Fluid StaticsDocument30 pagesChapter 2 - Fluid StaticsاشرفاللساميNo ratings yet
- Improvement of Aerodynamic Performance of An Aircraft Using Morphing WingDocument15 pagesImprovement of Aerodynamic Performance of An Aircraft Using Morphing Wingİhsan Alp OzdemirNo ratings yet
- Mass Transfer Presentation SlideDocument40 pagesMass Transfer Presentation SlidehibreNo ratings yet
- L&T Construction, Chennai G-O20002: Subarnarekha - Main Bridge SubstrcutureDocument7 pagesL&T Construction, Chennai G-O20002: Subarnarekha - Main Bridge SubstrcutureGopu RNo ratings yet
- Ribeiro 2019 PDFDocument16 pagesRibeiro 2019 PDFDavid Frias BastarNo ratings yet