Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SPM Additional Mathematics Paper 2 + Ans
Uploaded by
Sim Kwang YawCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
SPM Additional Mathematics Paper 2 + Ans
Uploaded by
Sim Kwang YawCopyright:
Available Formats
SPM 2012 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS PAPER 2 1.
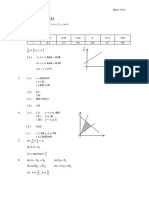
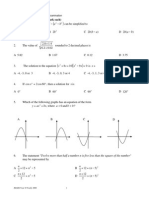
Solve the following simultaneous equations: [(a) (i) 4 i 3 j 3x + y = 1, 5x2 + y2 + 4xy 5 = 0 [x = 1, y = 4; x = 2, y = 5] (b) 20] A quadratic equation x2 + 4(3x + k) = 0, where k is a constant has roots p and 2p, p 0. (a) Find the value of p and of k. (b) Hence, form the quadratic equation which has roots p 1 and p + 6. [(a) p = 4, k = 8 (b) x2 + 3x 10 = 0] 2. 3. A curve has a gradient function kx 6, where k is a constant. Given that the minimum point of the curve is (3, 5), find (a) the value of k, (b) the y-intercept of the curve. [(a) 2 (b) 4] 4. Table 4 shows the sum and the sum of squares of x, where x is the monthly income, in RM, of Mr. Ahmad for the first 6 months of the year 2012. 6. (a) Prove that (b) (i)
(ii)
4 i 3 j 5
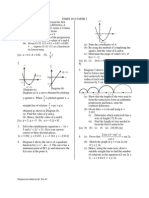
2 = sec2 x. cos 2 x 1
Sketch the graph of y = cos 2x + 1 for 0 x 2. (ii) Hence, use the same axes, sketch a suitable straight line to find the number of solutions for the equation
2 x 1 for 0 2 sec x 4
x 2. State the number of solutions. [(b) (i)/(ii)
4 solutions
x x
12 240
2
7.
24 975 000
(a) Find the standard deviation of the monthly income. (b) If Mr. Ahmads son gives him RM500 every month during the period, find the new mean and new standard deviation of his monthly income. [(a) RM30 (b) new mean = RM2540, new standard deviation = RM30]
SECTION B Table 7 shows the values of two variables, x and y, obtained from an experiment. The values of x and y are related by the equation y
h 1 2 , where h and k are kx kx
3
0.194
x y
constants. 1 2
2.601 0.551
4
0.089
5
0.040
6
0.017
5. It is given that AB 3i 2 j and
AC 7 i 5 j . (a) Find (i) BC
BC . (b) Given AD = pi 15 j , where p is a constant and AD is parallel to BC ,
find the value of p.
(ii) the unit vector in the direction of
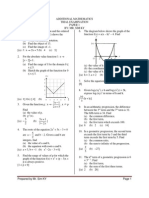
(a) Based on Table 7, construct a table for the values of x2y. (b) Plot x2y against x, using a scale of 2 cm to 1 unit on the x-axis and 2 cm to 0.5 unit on the x2y axis. Hence, draw the line of best fit. (c) Use the graph in 7(b) to find the value of (i) y, when x = 2.5, (ii) k, (iii) h. [(c) (i) 0.32 (ii) 0.33 (b) 0.13] 8. The curve y = x3 6x2 + 9x + 1 passes through the point A(2, 3) and has two turning points P(3, 1) and Q. Page 1
Retyped by Mr. Sim Kwang Yaw
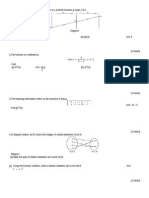
Find (a) the gradient of the curve at A, (b) the equation of the normal to the curve at A, (c) the coordinates of Q and determine where Q is a maximum or a minimum point. [(a) 3 (b) 3y = x + 7 (c) Q(1, 5), max] 9. Diagram 9 shows a sector POQ of a circle, centre O with radius 16 cm. Point R lies on OP.
(d) the coordinates of R if the area of quadrilateral PQRS is 30 unit2. [(a) y + 2x = 8 (b) (5, 2) (c) (2, 4) (d) (7, 5) 11. (a) In a survey carried out in a particular district, it is found that three out of five families own a national car. If 10 families are chosen at random from the district, calculate the probability that at least 8 families own a national car. (b) In a school, 300 students sat for a test. The marks obtained follow a normal distribution with a mean of 56 and a standard deviation of 8. (i) Find the number of students who pass the test if the passing mark is 40. (ii) If 12% of the students pass the test with grade A, find the minimum mark to obtain grade A. [(a) 0.1209 (b) (i) 293 (ii) 60.7 ] SECTION C 12. Diagram 12 shows a straight line KOL.
It is given that OR = RQ = 10 cm. [Use = 3.142] Calculate (a) the value of , in radians, correct to three decimal places. (b) the perimeter, in cm, of the shaded region, (c) the area, in cm2, of the shaded region. [(a) 0.644 rad (b) 26.30 cm (c) 34.37 cm2] 10. Diagram 10 shows a quadrilateral PQRS. The straight line PQ is perpendicular to the straight line PS. Point T lies on the straight line PS.
A particle moves along the straight line and passes through the fixed point O. Its velocity, v m s-1, is given by v = 8 4t, where t is the time, in seconds, after leaving the point O. The particle stops instantaneously at point L. [Assume motion to the right as positive] Find (a) the acceleration, in m s-2, of the particle, (b) the time, in second, when the particle is at L, (c) the velocity, in m s-1, of the particle when it passes through K, (d) the total distance, in m, travelled by the particle from O to K passing through L. [(a) 4 m s-2 (b) 2 s (c) 16 m s-1 (d) 32 m]
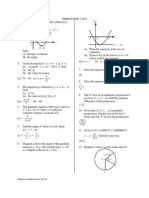
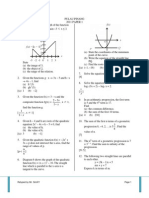
Find (a) the equation of the straight line PS, (b) the coordinates of S, (c) the coordinates of T if PT : TS = 1 : 3,
Retyped by Mr. Sim Kwang Yaw
Page 2
13. Table 13 shows the price indices of three types of fuel for the year 2008 based on the year 2006. Diagram 13 shows a pie chart which represents the proportion of the fuel used in a factory. Fuel Price index for 2008 based on 2006 Diesel 150 Petrol 120 Gas 110
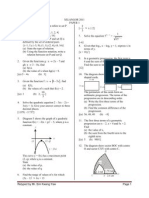
It is given that the area of triangle ABC is 28 cm2. (a) Calculate (i) the length, in cm, of BC, (ii) the length, in cm, of AC, (iii) ACB. (b) Point C lies on BC such that AC = AC. (i) Sketch the triangle ABC. (ii) Calculate the area, in cm2, of triangle ABC. [(a) (i) 11.13 cm (ii) 6.228 cm (iii) 53o 55 (b) (i) (ii) 9.547 cm2]
(a) If the factory spends RM9 000 per week for diesel in the year 2008, find the corresponding expenditure for diesel for the year 2006. (b) Calculate the composite index for the fuel expenditure of the factory in the year 2008 based on the year 2006. (c) The fuel expenditure used by the factory is RM30 000 per week in the year 2006. Calculate the corresponding fuel expenditure in the year 2008. (d) The price of diesel increases by 30%, the price of petrol increases by 20% while the price of gas remains unchanged from the year 2008 to the year 2010. Calculate the composite index for the fuel expenditure of the factory in the year 2010 based on the year 2006. [(a) RM6000 (b) 133 (c) RM39900 (d) 162.7] 14. Diagram 14 shows triangle ABC such that ABC = 34o and AB = 9 cm.
15. A carpenter makes two types of furniture, table and chair. In a week, he makes x tables and y chairs. He has a capital of RM6 000. The production of furniture is based on the following constraints: I: The cost of making a table is RM80 and a chair is RM60. II: The minimum total number of tables and chairs must be 50. III: The number of chairs must be at least 80% of the number of tables. (a) Write three inequalities, other than x 0 and y 0, which satisfy all the above constraints. (b) Using a scale of 2 cm to 10 furnitures on both axes, construct and shaded the region R which satisfies all the above constraints. (c) Using the graph construct in 15(b), find (i) the minimum number of chairs made if 24 tables are made, (ii) the maximum profit obtained if the profit for a table is RM40 and the profit for a chair is RM20. [(a) 4x + 3y 300, x + y 50, y
4 x 5
(c) (i) 26 (ii) RM2600 when x = 46, y = 38]
Retyped by Mr. Sim Kwang Yaw
Page 3
You might also like
- SPM Additional Mathematics 2012 P1Document3 pagesSPM Additional Mathematics 2012 P1kysim100% (1)
- Trial MRSM SPM 2014 Physics Skema K1 K2 K3Document14 pagesTrial MRSM SPM 2014 Physics Skema K1 K2 K3NgauHWNo ratings yet
- SPM 2007 Mathematics P2Document24 pagesSPM 2007 Mathematics P2pss smk selandar33% (3)
- Solaf Add Maths AnswerDocument38 pagesSolaf Add Maths AnswerJoe Keen100% (6)
- SPM Am X-Project Lesson 1-4Document107 pagesSPM Am X-Project Lesson 1-4Tutor TayNo ratings yet
- Jawapan Modul 21Document11 pagesJawapan Modul 21mdmema100% (2)
- Module 11 (B) Add Math - Index NumberDocument10 pagesModule 11 (B) Add Math - Index NumberHayati Aini AhmadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Matrices Form 5Document22 pagesChapter 4 Matrices Form 5CHONG GEOK CHUAN100% (2)
- SPM 2010 Paper 2Document78 pagesSPM 2010 Paper 2Suriyati YusoffNo ratings yet
- Paper 2 Bah ADocument13 pagesPaper 2 Bah AHamidah MA50% (2)
- Modul Menggilap Mutiara Jawapan Kertas 2 Set 1Document1 pageModul Menggilap Mutiara Jawapan Kertas 2 Set 1mohamed zikri bin mahmoodNo ratings yet
- Paper 2 Form 4 2020Document28 pagesPaper 2 Form 4 2020Yusfalina Mohd YusoffNo ratings yet
- Matematik Kertas 2 With Answer SchemeDocument48 pagesMatematik Kertas 2 With Answer SchemeelvivNo ratings yet
- Question Maths Exam Form 4 Paper2Document10 pagesQuestion Maths Exam Form 4 Paper2Linda ZaharNo ratings yet
- C07 Add Maths Answers Form 4 PDFDocument36 pagesC07 Add Maths Answers Form 4 PDFLee Sun TaiNo ratings yet
- Skema Fizik Kertas 2 Trial PerlisDocument9 pagesSkema Fizik Kertas 2 Trial Perlisenasizuka100% (1)
- C04 Add Maths Answers Form 4 PDFDocument33 pagesC04 Add Maths Answers Form 4 PDFLee Sun Tai25% (4)
- Understanding relations and functions in mathematicsDocument35 pagesUnderstanding relations and functions in mathematicsAegil Wiell50% (4)
- Skema Pppa Kimia k2 SPM 2011 Selangor Kertas 2Document14 pagesSkema Pppa Kimia k2 SPM 2011 Selangor Kertas 2Siraf IldaNo ratings yet
- Set Soalan Additional MathematicsDocument11 pagesSet Soalan Additional Mathematicssszma100% (10)
- Additional Maths SPM 2019 Paper 2 SolutionsDocument9 pagesAdditional Maths SPM 2019 Paper 2 SolutionsFadhli Faudzi0% (1)
- Function Past Year SPM QuestionsDocument6 pagesFunction Past Year SPM Questionsjesunathan44@yahoo.comNo ratings yet
- SPM Percubaan 2008 SBP Chemistry AnswersDocument19 pagesSPM Percubaan 2008 SBP Chemistry AnswersChinWynn.com94% (16)
- Marking Scheme Paper 1 2 3 SBP Trial SPM 2009Document21 pagesMarking Scheme Paper 1 2 3 SBP Trial SPM 2009Mohd Khairul AnuarNo ratings yet
- Additional Mathematics SPM P1 2006Document17 pagesAdditional Mathematics SPM P1 2006CheanSiangLong19970% (2)
- Skema Fizik Tingkatan 5 Kertas 2 Pep Percubaan SPM SBP 2011Document8 pagesSkema Fizik Tingkatan 5 Kertas 2 Pep Percubaan SPM SBP 2011Chin Shee YanNo ratings yet
- SPM 2011 Add Maths Paper 2 Suggested SolutionsDocument17 pagesSPM 2011 Add Maths Paper 2 Suggested SolutionsHazri Mohd HamzahNo ratings yet
- (Addmath) Skema K2 MRSM Trial 2022Document22 pages(Addmath) Skema K2 MRSM Trial 2022Christian Qing GeorgyNo ratings yet
- Soalan Kertas 2 BiologiDocument15 pagesSoalan Kertas 2 BiologiHaslinda SheikhNo ratings yet
- Whole Book Answers PDFDocument174 pagesWhole Book Answers PDFVKZ cuberNo ratings yet
- Log Truck Speed and Force CalculationsDocument3 pagesLog Truck Speed and Force CalculationsChel SonNo ratings yet
- (Form 5 Maths) Chapter 3 Advance ExerciseDocument6 pages(Form 5 Maths) Chapter 3 Advance ExerciseYap Mei En100% (1)
- PHYSICS Revision For FINAL Sem F4 2020Document9 pagesPHYSICS Revision For FINAL Sem F4 2020Nicole ChuaNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Mathematics Chapter 4Document2 pagesForm 4 Mathematics Chapter 4Chong Jie Mee67% (3)
- Index NumberDocument11 pagesIndex NumbertheuniquecollectionNo ratings yet
- Additional Mathematics K1Document6 pagesAdditional Mathematics K1Fadhli FaudziNo ratings yet
- (Spmsoalan) Skema SPM 2014 MathematicsDocument10 pages(Spmsoalan) Skema SPM 2014 Mathematicsyievia25% (4)
- SPM 1449 2006 Mathematics p2 BerjawapanDocument18 pagesSPM 1449 2006 Mathematics p2 Berjawapanpss smk selandar71% (7)
- Physics Paper 2.SPMDocument19 pagesPhysics Paper 2.SPMRamliRem100% (1)
- Review 1-10Document13 pagesReview 1-10angNo ratings yet
- SPM 4551 2007 Biology k2 BerjawapanDocument22 pagesSPM 4551 2007 Biology k2 Berjawapanpss smk selandarNo ratings yet
- Stationery and Toy Price Index CalculationsDocument2 pagesStationery and Toy Price Index CalculationsMJ Chow0% (1)
- SPM 2008 Additional Mathematics Paper 1Document22 pagesSPM 2008 Additional Mathematics Paper 1pss smk selandar80% (10)
- Linear ProgrammingDocument11 pagesLinear ProgrammingAnna LeeNo ratings yet
- MRSM-ANSWER PHYSICS-Trial SPM 2008Document20 pagesMRSM-ANSWER PHYSICS-Trial SPM 2008kamalharmoza100% (3)
- Selangor 2011 P2Document4 pagesSelangor 2011 P2Sim Kwang YawNo ratings yet
- MRSM 2011paper 2Document4 pagesMRSM 2011paper 2Sim Kwang YawNo ratings yet
- SPM 2011 Paper 2Document4 pagesSPM 2011 Paper 2Sim Kwang YawNo ratings yet
- ANALYSIS OF PAST YEAR QUESTIONS FORM 4 MATHEMATICSDocument8 pagesANALYSIS OF PAST YEAR QUESTIONS FORM 4 MATHEMATICSJarnice Ling Yee ChingNo ratings yet
- Times 2012 Paper 2Document5 pagesTimes 2012 Paper 2kysimNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument4 pagesUntitled DocumentAnany SinghNo ratings yet
- Maths Paper 2 November 2005Document10 pagesMaths Paper 2 November 2005sandieletasNo ratings yet
- Add Maths Form 5 2013Document2 pagesAdd Maths Form 5 2013Rohana YahyaNo ratings yet
- Times Paper 1 2012Document3 pagesTimes Paper 1 2012kysimNo ratings yet
- 10icse Prelim PaperDocument7 pages10icse Prelim PapertraderprabhakarNo ratings yet
- James Ruse 2008 Year 10 Maths Yearly & SolutionsDocument16 pagesJames Ruse 2008 Year 10 Maths Yearly & SolutionsRicha Ng50% (2)
- Add Math p2 Trial SPM SBP 2007Document11 pagesAdd Math p2 Trial SPM SBP 2007Carolyn Chang Boon ChuiNo ratings yet
- RevisionDocument1 pageRevisionhpchen9407No ratings yet
- FX X X FX Axp Q: Program 2 Paper 2 (A) CB BDDocument4 pagesFX X X FX Axp Q: Program 2 Paper 2 (A) CB BDLoh AlexNo ratings yet
- Sky Trial Examination p2Document4 pagesSky Trial Examination p2kysimNo ratings yet
- SPM 2011 Paper 1Document3 pagesSPM 2011 Paper 1Sim Kwang YawNo ratings yet
- Sky Trial Exam p1Document3 pagesSky Trial Exam p1kysimNo ratings yet
- Sky Trial Examination p2Document4 pagesSky Trial Examination p2kysimNo ratings yet
- MRSM 2011paper 2Document4 pagesMRSM 2011paper 2Sim Kwang YawNo ratings yet
- SPM 2011 Paper 2Document4 pagesSPM 2011 Paper 2Sim Kwang YawNo ratings yet
- Pulau Pinang 2011 p2Document4 pagesPulau Pinang 2011 p2Sim Kwang YawNo ratings yet
- Pulau Pinang 2011 p1Document3 pagesPulau Pinang 2011 p1Sim Kwang YawNo ratings yet
- MRSM 2011P1Document3 pagesMRSM 2011P1Sim Kwang YawNo ratings yet
- Selangor 2011 P1Document3 pagesSelangor 2011 P1Sim Kwang YawNo ratings yet
- Selangor 2011 P2Document4 pagesSelangor 2011 P2Sim Kwang YawNo ratings yet
- Selangor 2011 P1Document3 pagesSelangor 2011 P1Sim Kwang YawNo ratings yet
- An Improved Ant Colony Algorithm and Its ApplicatiDocument10 pagesAn Improved Ant Colony Algorithm and Its ApplicatiI n T e R e Y eNo ratings yet
- CONNECTIFYDocument3 pagesCONNECTIFYAbhishek KulshresthaNo ratings yet
- DJDocument907 pagesDJDeepak BhawsarNo ratings yet
- Rev F AvantaPure Logix 268 Owners Manual 3-31-09Document46 pagesRev F AvantaPure Logix 268 Owners Manual 3-31-09intermountainwaterNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument4 pagesUntitledMOHD JEFRI BIN TAJARINo ratings yet
- Product Data: T T 13 SEER Single - Packaged Heat Pump R (R - 410A) RefrigerantDocument36 pagesProduct Data: T T 13 SEER Single - Packaged Heat Pump R (R - 410A) RefrigerantJesus CantuNo ratings yet
- Teacher Commitment and Dedication to Student LearningDocument8 pagesTeacher Commitment and Dedication to Student LearningElma Grace Sales-DalidaNo ratings yet
- Publications FireSafetyDesign SDocument369 pagesPublications FireSafetyDesign SJayachandra Reddy AnnavaramNo ratings yet
- Networks Lab Assignment 1Document2 pagesNetworks Lab Assignment 1006honey006No ratings yet
- Newton Raphson Method MCQDocument15 pagesNewton Raphson Method MCQmd junaidNo ratings yet
- Modification Adjustment During Upgrade - Software Logistics - SCN WikiDocument4 pagesModification Adjustment During Upgrade - Software Logistics - SCN Wikipal singhNo ratings yet
- Excel Bill of Materials Bom TemplateDocument8 pagesExcel Bill of Materials Bom TemplateRavi ChhawdiNo ratings yet
- COP2251 Syllabus - Ellis 0525Document9 pagesCOP2251 Syllabus - Ellis 0525Satish PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- ASCP User GuideDocument1,566 pagesASCP User GuideThillai GaneshNo ratings yet
- Export - Import Cycle - PPSXDocument15 pagesExport - Import Cycle - PPSXMohammed IkramaliNo ratings yet
- Ace3 1122.03 GB PDFDocument16 pagesAce3 1122.03 GB PDFArpit VermaNo ratings yet
- The Collected Letters of Flann O'BrienDocument640 pagesThe Collected Letters of Flann O'BrienSean MorrisNo ratings yet
- John Williams - WikipediaDocument2 pagesJohn Williams - Wikipedia三木和代No ratings yet
- Ejemplo FFT Con ArduinoDocument2 pagesEjemplo FFT Con ArduinoAns Shel Cardenas YllanesNo ratings yet
- Special Proceedings Case DigestDocument14 pagesSpecial Proceedings Case DigestDyan Corpuz-Suresca100% (1)
- 2019 BioscienceJDocument14 pages2019 BioscienceJPatrícia Lima D'AbadiaNo ratings yet
- Hotels Cost ModelDocument6 pagesHotels Cost ModelThilini SumithrarachchiNo ratings yet
- Fuather, That Smid Govern-: Such Time As It May Deem Proper: TeDocument18 pagesFuather, That Smid Govern-: Such Time As It May Deem Proper: Tencwazzy100% (1)
- JTIL Purchase Requisition for Plasma Machine SparesDocument3 pagesJTIL Purchase Requisition for Plasma Machine Sparesshivam soniNo ratings yet
- Fi 7160Document2 pagesFi 7160maxis2022No ratings yet
- Clinical Indications, Treatment and Current PracticeDocument14 pagesClinical Indications, Treatment and Current PracticefadmayulianiNo ratings yet
- Rpo 1Document496 pagesRpo 1Sean PrescottNo ratings yet
- Nysc Editorial ManifestoDocument2 pagesNysc Editorial ManifestoSolomon Samuel AdetokunboNo ratings yet
- 3240-B0 Programmable Logic Controller (SIEMENS ET200S IM151-8)Document7 pages3240-B0 Programmable Logic Controller (SIEMENS ET200S IM151-8)alexandre jose dos santosNo ratings yet
- Buyers FancyFoodDocument6 pagesBuyers FancyFoodvanNo ratings yet