Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nursing Care Plan Hyperbilirubinemia Jaundice)
Uploaded by
deric81%(47)81% found this document useful (47 votes)
127K views2 pagesA free sample nursing care plan (ncp) for Hyperbilirubinemia (Jaundice).
Original Title
NursingCrib.com Nursing Care Plan Hyperbilirubinemia Jaundice)
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentA free sample nursing care plan (ncp) for Hyperbilirubinemia (Jaundice).
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
81%(47)81% found this document useful (47 votes)
127K views2 pagesNursing Care Plan Hyperbilirubinemia Jaundice)
Uploaded by
dericA free sample nursing care plan (ncp) for Hyperbilirubinemia (Jaundice).
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
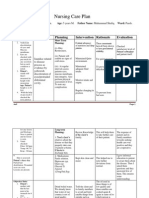
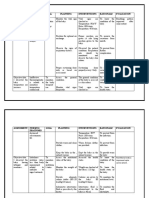
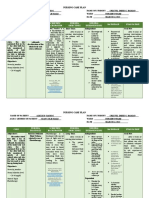
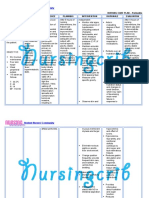
NURSING CARE PLAN
ASSESSMENT DIAGNOSIS INFERENCE PLANNING INTERVENTION RATIONALE EVALUATION
Independent:
Subjective: • Risk for • Hyperbilirubinemia • After 7 • Note the • May aids in • After 7 days
injury days of infant’s age. diagnosing of nursing
“Naninilaw ang (jaundice) in the
related to nursing underlying intervention
mata at balat ng prematurity neonate is an interventio cause in s, the
baby ko” as . accumulation of ns, the connection with patient skin
verbalized by the serum bilirubin patient the appearance color was
mother. above normal skin color of jaundice. normal.
levels. Onset of
will be • Assist with • To allow for
Objective: normal. phototherapy utilization of
clinical jaundice is treatment. alternate
• Skin seen when serum pathways for
appearing light bilirubin levels are bilirubin
to bright 5 to 7 mg/100 dL. excretion
yellow. Physiologic • Have the infant • To expose the
completely entire skin in
jaundice occurs 3
• Sclerae undressed. phototherapy.
appearing to 5 days after birth • Keep the eyes • To protect them
yellow. and is an increase and gonads from the
in unconjugated covered. constant
• Dark amber bilirubin levels that exposure to
urine. do not exceed 5 high intensity
light.
mg/100 dL/ day.
• V/S taken as • Develop a • Ideally every 2
follows: systematic hours so that all
schedule of the surfaces are
T: 36.3 turning the exposed.
P: 110 infant.
R: 30 .
Collaborative: • To have a
• Obtain bilirubin baseline data if
level as the therapeutic
directed. regimen is
effective.
• To ensure
adequate
• Administer hydration.
fluids as
directed.
You might also like
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care PlanGino Carlo BrionesNo ratings yet
- SDL1 NCP Case2Document3 pagesSDL1 NCP Case2Alec AnonNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan JaundiceDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Jaundicepapadaad86% (35)
- NCP - Hyperbilirubinemia - Staff NursingDocument3 pagesNCP - Hyperbilirubinemia - Staff NursingnurseM67% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan for Newborn with JaundiceDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan for Newborn with Jaundicebluewipes67% (3)
- NCP JaundiceDocument3 pagesNCP Jaundiceanilobaid84% (25)
- NCP For RDSDocument3 pagesNCP For RDSKevin P. Feliciano74% (23)
- NCP Altered Skin ColorDocument2 pagesNCP Altered Skin ColorJessa Lyn100% (1)
- Prioritize NCPDocument19 pagesPrioritize NCPzey young94% (34)
- NCP For FT, SGADocument7 pagesNCP For FT, SGAJule Santoya80% (5)
- Hyperbilirubinemia Case PresentationDocument25 pagesHyperbilirubinemia Case PresentationEricka B. Banaszczuk100% (3)
- Neonatal Jaundice and Ineffective Breundiceeding Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesNeonatal Jaundice and Ineffective Breundiceeding Nursing Care Planpapadaad100% (1)
- Care Plan Redo For NeonateDocument2 pagesCare Plan Redo For NeonateIris Lopez100% (6)
- NCP NewbornDocument2 pagesNCP Newbornsonylynne94% (17)
- NCP Preterm NeonateDocument3 pagesNCP Preterm NeonateLilia Priscilla Tuibuen Aureus100% (2)
- Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Goals/ Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument20 pagesNursing Diagnosis Rationale Goals/ Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationElaine Grace Timbol-Babasa100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For A Premature InfantDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For A Premature InfantVillablanca Michelle84% (102)
- Newborn Nursing CareplanDocument7 pagesNewborn Nursing CareplanSamantha MillerNo ratings yet
- NCP RHDocument3 pagesNCP RHKirstie Durano Goc-ong0% (1)
- Client Care Plan: Assessment/Nursing Dx. Outcome Identification/Planning Implementation EvaluationDocument2 pagesClient Care Plan: Assessment/Nursing Dx. Outcome Identification/Planning Implementation EvaluationTiese Lopez79% (14)
- NCP Hyperbilirubinemia Staff NursingDocument3 pagesNCP Hyperbilirubinemia Staff NursingVerajoy DaanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan of The NewbornDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan of The Newbornappleliciouz0860% (10)
- Newborn Nursing Care Plan With ReferncesDocument6 pagesNewborn Nursing Care Plan With Referncesneuronurse92% (63)
- NCP Risk For Impaired Skin Integrity Related To Ongoing Phototherapy Secondary To Increased Bilirubin LevelsDocument2 pagesNCP Risk For Impaired Skin Integrity Related To Ongoing Phototherapy Secondary To Increased Bilirubin LevelsIrish Bantolo100% (1)
- Bronchopneumonia Care PlanDocument6 pagesBronchopneumonia Care PlanAbhijit Soundade0% (1)
- Plan of Care Week Diaper RashDocument1 pagePlan of Care Week Diaper RashKatie_Poindext_515450% (4)
- Child - Bronchiolitis NCPDocument2 pagesChild - Bronchiolitis NCPjoeti80% (5)
- NCP JaundiceDocument9 pagesNCP JaundiceMeena Koushal100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan Ineffective ThermoregulationDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Ineffective Thermoregulationrjalavazo198979% (71)
- Novilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii: Assessment Diagnosi S Pathophysiolog Y Planning Interevention Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageNovilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii: Assessment Diagnosi S Pathophysiolog Y Planning Interevention Rationale EvaluationCharina AubreyNo ratings yet
- NCP Imbalanced Nutrition IUGR PatientDocument2 pagesNCP Imbalanced Nutrition IUGR Patientanreilegarde100% (10)
- NCP NewbornDocument8 pagesNCP Newbornsupacalifragirlistic67% (9)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument7 pagesNursing Care PlanDaniel Marcos80% (10)
- Nursing Care Plan for Newborn HypothermiaDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan for Newborn Hypothermiaxchardx73% (11)
- Case Presentation on Hyperbilirubinemia in InfantsDocument54 pagesCase Presentation on Hyperbilirubinemia in InfantsRam-Ram Martiniano88% (8)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument6 pagesNursing Care PlanAnthea ValinoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan JaundiceDocument24 pagesNursing Care Plan Jaundicegandhialpit76% (29)
- Lisa Elibox Nursing Care Plan for HyperthermiaDocument1 pageLisa Elibox Nursing Care Plan for Hyperthermiasamanthabox50% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan NephritisDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Nephritisderic82% (17)
- Preterm Infant Nursing Care PlanDocument19 pagesPreterm Infant Nursing Care Planysamariano100% (1)
- Preterm infant care planDocument21 pagesPreterm infant care planGil Aswigui81% (27)
- Nursing Care Plan PrenatalDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan PrenatalKim Galamgam100% (2)
- NCP Risk For Fluid Volume DeficitDocument3 pagesNCP Risk For Fluid Volume DeficitAtheena Diaz50% (4)
- Nursing Care of HyperbilirubinemiaDocument12 pagesNursing Care of HyperbilirubinemiaFri-fri Manila67% (3)
- Understanding Malaria and Treatment PlanDocument2 pagesUnderstanding Malaria and Treatment Planchristian quiaoit33% (3)
- Newborn Careplan 9-15-2011Document17 pagesNewborn Careplan 9-15-2011Brittany Wood100% (1)
- NCP NicuDocument3 pagesNCP NicuNoel Telosa100% (1)
- Risk for Infection Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesRisk for Infection Nursing Care PlanMariquita Buenafe57% (7)
- Case Study Hyperbilirubinemia FinalDocument21 pagesCase Study Hyperbilirubinemia FinalPrecious Ophelia Nana Adjoa100% (2)
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance ChildDocument3 pagesNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance ChildMarion Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for a Baby with Respiratory DistressDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan for a Baby with Respiratory DistressKavi rajput76% (17)
- Nursing care for newborn with jaundiceDocument2 pagesNursing care for newborn with jaundiceLance CornistaNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Jaundice Treatment GuidelinesDocument12 pagesNeonatal Jaundice Treatment GuidelinesJustine NyangaresiNo ratings yet
- PG JaundiceDocument2 pagesPG Jaundicesudha2040No ratings yet
- Neonatal Jaundice: Miriti M.D Master of Clinical Medicine:Accidents and Emerrgency MAY 2018Document25 pagesNeonatal Jaundice: Miriti M.D Master of Clinical Medicine:Accidents and Emerrgency MAY 2018Dennis MiritiNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Jaundice Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesNeonatal Jaundice Nursing Care PlanCristyl Shine BariaoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Assessment and Plan for an Infant with JaundiceDocument2 pagesNursing Assessment and Plan for an Infant with JaundiceValledor Ian MosesNo ratings yet
- 2 NURSING CARE PLAN (NURSERY WARD - Masingal District Hospital)Document2 pages2 NURSING CARE PLAN (NURSERY WARD - Masingal District Hospital)kimtalaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument6 pagesNursing Care PlanAngeline MacarioNo ratings yet
- Nursing Assessment and Intervention for Jaundiced InfantDocument2 pagesNursing Assessment and Intervention for Jaundiced InfantValledor Ian MosesNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For HemodialysisDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Hemodialysisderic80% (20)
- Nursing Care Plan For AIDS/HIVDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For AIDS/HIVderic81% (16)
- Nursing Care Plan For Carbon Monoxide PoisoningDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For Carbon Monoxide Poisoningderic73% (11)
- Nursing Care Plan For Smoke Poisoning NCPDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Smoke Poisoning NCPderic100% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan For Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding NCPDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding NCPderic79% (14)
- Nursing Care Plan For AmputationDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For Amputationderic80% (25)
- Nursing Care Plan For GlaucomaDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For Glaucomaderic79% (28)
- Nursing Care Plan For Risk For Compromised Human Dignity NCPDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For Risk For Compromised Human Dignity NCPderic100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan For Post Trauma NCPDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan For Post Trauma NCPderic82% (11)
- Nursing Care Plan For Readiness For Enhanced Spiritual Well Being NCPDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan For Readiness For Enhanced Spiritual Well Being NCPderic83% (6)
- Nursing Care Plan For Seizure NCPDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Seizure NCPderic88% (40)
- Nursing Care Plan For Rabies NCPDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For Rabies NCPderic100% (9)
- Nursing Care Plan For Readiness For Enhanced Sleep NCPDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan For Readiness For Enhanced Sleep NCPderic100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan For Risk For Aspiration NCPDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan For Risk For Aspiration NCPderic100% (8)
- Nursing Care Plan For Readiness For Enhanced Hope NCPDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan For Readiness For Enhanced Hope NCPderic100% (6)
- Nursing Care Plan For Overflow Urinary Incontinence NCPDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Overflow Urinary Incontinence NCPderic83% (6)
- Nursing Care Plan For Rape Trauma Syndrome NCPDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan For Rape Trauma Syndrome NCPderic100% (4)
- Nursing Care Plan For Pneumonia NCPDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For Pneumonia NCPderic79% (133)
- Nursing Care Plan For Liver Cirrhosis NCPDocument14 pagesNursing Care Plan For Liver Cirrhosis NCPderic92% (12)
- Nursing Care Plan For Peritonitis NCPDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Peritonitis NCPderic83% (6)
- Nursing Care Plan For Peptic Ulcer NCPDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Peptic Ulcer NCPderic85% (46)
- Nursing Care Plan For Insufficient Breastmilk NCPDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Insufficient Breastmilk NCPderic100% (17)
- Nursing Care Plan For Multiple Sclerosis NCPDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Multiple Sclerosis NCPderic88% (17)
- Nursing Care Plan For Pedia TB Meningitis NCPDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Pedia TB Meningitis NCPderic100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For Neonatal Sepsis NCPDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For Neonatal Sepsis NCPderic67% (9)
- Nursing Care Plan For Myocardial Infarction NCPDocument8 pagesNursing Care Plan For Myocardial Infarction NCPderic87% (15)
- Nursing Care Plan For Disturbed Sleep Pattern NCPDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For Disturbed Sleep Pattern NCPderic67% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan For Insomnia NCPDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Insomnia NCPderic83% (23)
- Nursing Care Plan For Interrupted Breastfeeding NCPDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For Interrupted Breastfeeding NCPderic88% (8)
- Nursing Care Plan For Ineffective Infant Feeding Pattern NCPDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For Ineffective Infant Feeding Pattern NCPderic71% (14)
- Reva ThyDocument182 pagesReva ThyJulia StantonNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Hyperbilirubinemia PATHOPHYSIOLOGYDocument11 pagesNeonatal Hyperbilirubinemia PATHOPHYSIOLOGYG Trinity DeepakNo ratings yet
- Sickle Cell Anemia: Hba Α Β Hba …….. Α Δ Hb F ……… Α, ΓDocument29 pagesSickle Cell Anemia: Hba Α Β Hba …….. Α Δ Hb F ……… Α, ΓYolanda UriolNo ratings yet
- Bsc. Nursing Examination: Revision QuestionsDocument79 pagesBsc. Nursing Examination: Revision QuestionsNixi MbuthiaNo ratings yet
- MD2120E Biochemistry III Version 1Document8 pagesMD2120E Biochemistry III Version 1Mah ShawdNo ratings yet
- Health Education On NEONATAL JAUNDICEDocument23 pagesHealth Education On NEONATAL JAUNDICEAsha jilu100% (2)
- Facts On PoopDocument32 pagesFacts On PoopchefchadsmithNo ratings yet
- Liver Function Tests GuideDocument38 pagesLiver Function Tests GuideshehnilaNo ratings yet
- Local AnesthesiaDocument22 pagesLocal Anesthesiamohamed elmahdyNo ratings yet
- An Open-Label, Phase 1 Study To Evaluate The Effects of Hepatic Impairment On Edoxaban Pharmacokinetics and PharmacodynamicsDocument11 pagesAn Open-Label, Phase 1 Study To Evaluate The Effects of Hepatic Impairment On Edoxaban Pharmacokinetics and PharmacodynamicsHendrawan RahmanNo ratings yet
- In Partial Fulfillment of Our Requirements IN Related Learning ExperienceDocument32 pagesIn Partial Fulfillment of Our Requirements IN Related Learning Experiencedolly joy100% (4)
- The Liver in Systemic Disease A Clinician's Guide To Abnormal LiverDocument285 pagesThe Liver in Systemic Disease A Clinician's Guide To Abnormal Liveroleksandra.bilotkachNo ratings yet
- Albumin Package InsertDocument2 pagesAlbumin Package InsertjairajNo ratings yet
- Timing of Umbilical Cord Clamping and Neonatal Jaundice in Singleton TermDocument5 pagesTiming of Umbilical Cord Clamping and Neonatal Jaundice in Singleton TerminesNo ratings yet
- Jaundice NeonatalDocument26 pagesJaundice Neonatalhunk2662No ratings yet
- Young InfantDocument69 pagesYoung InfantAurora Doris BatagaNo ratings yet
- Gentamicin Sulfate Drug StudyDocument7 pagesGentamicin Sulfate Drug StudyGabriel Rosales RM RNNo ratings yet
- Interference With Clinical Laboratory Analyses PDFDocument10 pagesInterference With Clinical Laboratory Analyses PDFBogdan TomaNo ratings yet
- Estimation of BilirubinDocument36 pagesEstimation of BilirubinNihalNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Labs-Full TableDocument6 pagesAbnormal Labs-Full TableGERIMAIA CRUZNo ratings yet
- Urine Reagent Strips Package InsertDocument3 pagesUrine Reagent Strips Package InsertgeraldineNo ratings yet
- Vitros 250, MicroSlide SummaryDocument16 pagesVitros 250, MicroSlide SummaryDiego Israel Gómez RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Hepatoprotective Activity of Ocimum Americanum L LDocument7 pagesHepatoprotective Activity of Ocimum Americanum L LNurul Rachman NasutionNo ratings yet
- BilichekDocument25 pagesBilichekPC Celular Samar PVHNo ratings yet
- Liver Function Tests: An OverviewDocument39 pagesLiver Function Tests: An OverviewchenlieNo ratings yet
- Thuatngu YkhoaDocument161 pagesThuatngu YkhoaTuyet-Lan BuiNo ratings yet
- Liver, Gallbladder, and Pancreatic Disorders Ch 40Document9 pagesLiver, Gallbladder, and Pancreatic Disorders Ch 40Stacey100% (2)
- Complete Urinalysis: A. Physical Characteristics of UrineDocument8 pagesComplete Urinalysis: A. Physical Characteristics of UrineKryza Dale Bunado BaticanNo ratings yet
- Liver Function Tests Explained in DetailDocument33 pagesLiver Function Tests Explained in DetailPriyanshu MandalNo ratings yet
- Spectrum Diagnostics Products List 2014-2015Document154 pagesSpectrum Diagnostics Products List 2014-2015smt athar100% (6)