Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nursing Care Plan Neonatal Sepsis
Uploaded by
deric100%(20)100% found this document useful (20 votes)
27K views2 pagesA free sample nursing care plan (ncp) for Neonatal Sepsis.
Original Title
NursingCrib.com Nursing Care Plan Neonatal Sepsis
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentA free sample nursing care plan (ncp) for Neonatal Sepsis.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(20)100% found this document useful (20 votes)
27K views2 pagesNursing Care Plan Neonatal Sepsis
Uploaded by
dericA free sample nursing care plan (ncp) for Neonatal Sepsis.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
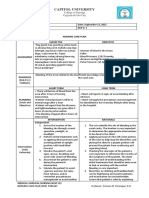
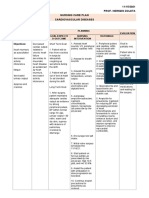
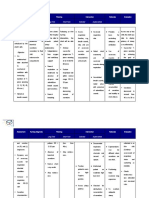
NURSING CARE PLAN
ASSESSMENT DIAGNOSIS INFERENCE PLANNING INTERVENTION RATIONALE EVALUATION
INDEPENDENT:
SUBJECTIVE: Risk for Sepsis is a clinical After 8 hours of • Provide isolation • Body substance After 8 hours of
infection related term used to nursing and monitor visitors isolation (BSI) nursing
“Walng gana to compromised describe interventions, as indicated. should be used interventions,
dumede ang immune symptomatic the patient will for all infectious the patient was
anak ko, parang system. bacteremia, with or achieve timely patients. Reverse able to achieve
mainit sya at without organ healing and free isolation/restricti timely healing
matamlay” (it’s dysfunction. from further on of visitors and free from
difficult to feed my Sustained infection. may be needed further
baby, she feels to protect the infection.
warm to touch and bacteremia, in
contrast to immunosuppress
not very active) as
transient ed patient.
verbalized by the
mother. bacteremia, may
result in a • Wash hands before • Reduces risk of
sustained febrile or after each care cross
OBJECTIVE:
response that may activity, even gloves contamination
be associated with are used. because gloves
• Increased
organ dysfunction. may have
body
Septicemia refers to noticeable
temperature.
the active defects, get torn
• Flushed skin.
multiplication of or damaged
• Increased
bacteria in the during use.
respiratory
rate. bloodstream that
results in an • Limit use of invasive • Prevents spread
• V/S taken as
overwhelming devices or of infection via
follows:
infection. procedure as airborne
possible. droplets.
T: 37.7
P: 130
• Inspect wounds or • May provide clue
R: 45
site of invasive to portal entry,
devices, paying type of primary
particular attention infecting
to parenteral lines. organisms, as
well as early
identification
secondary
infection.
• Maintain sterile • Prevents
technique when introduction of
changing dressings, bacteria,
suctioning or reducing risk of
providing site care. nosocomial
infection.
• Provide tepid • Used to reduce
sponge bath and fever.
avoid use of alcohol.
• Observe for chills • Chills often
and profuse precede
diaphoresis. temperature
spikes in
presence of
generalized
infection.
♦ Monitor for signs of • May reflect
deterioration of inappropriate
condition or failure antibiotic therapy
to improve in or overgrowth of
therapy. secondary
infections.
COLLABORATIVE:
• Obtain specimens of • Identification of
urine, blood, portal entry and
sputum, wound as organism causing
indicated for gram the septicemia is
stain, and crucial in
sensitivity. effective
treatment.
• Administer anti- • To prevent
biotics as further spread of
prescribed. infection.
You might also like
- Basics of Duct DesignDocument2 pagesBasics of Duct DesignRiza BahrullohNo ratings yet
- Newton Raphson Method MCQDocument15 pagesNewton Raphson Method MCQmd junaidNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Overflow Urinary Incontinence NCPDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Overflow Urinary Incontinence NCPderic71% (7)
- Nursing Diagnosis HyperthermiaDocument2 pagesNursing Diagnosis HyperthermiaErl Driz100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan Pedia TB MeningitisDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Pedia TB Meningitisderic100% (10)
- Nursing Care Plan For Pneumonia NCPDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For Pneumonia NCPderic79% (133)
- SMChap 018Document32 pagesSMChap 018testbank100% (8)
- NURSING CARE PLAN Chicken PoxDocument2 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN Chicken Poxderic87% (62)
- Nursing Care Plan For Disturbed Sleep Pattern NCPDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For Disturbed Sleep Pattern NCPderic67% (3)
- Case Study, g6Document62 pagesCase Study, g6julie pearl peliyoNo ratings yet
- NCP SviDocument4 pagesNCP SviEjie Boy IsagaNo ratings yet
- NCP - Hyperbilirubinemia - Staff NursingDocument3 pagesNCP - Hyperbilirubinemia - Staff NursingnurseM67% (3)
- Capitol University: College of Nursing Cagayan de Oro CityDocument2 pagesCapitol University: College of Nursing Cagayan de Oro CityChaine Agolito100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For Rabies NCPDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For Rabies NCPderic100% (9)
- Nursing Care Plan For HemodialysisDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Hemodialysisderic80% (20)
- NCP InfectionDocument2 pagesNCP InfectionAngie Dino100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan For Multiple Sclerosis NCPDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Multiple Sclerosis NCPderic88% (17)
- Special Proceedings Case DigestDocument14 pagesSpecial Proceedings Case DigestDyan Corpuz-Suresca100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For Liver Cirrhosis NCPDocument14 pagesNursing Care Plan For Liver Cirrhosis NCPderic92% (12)
- Nursing Care Plan For Myocardial Infarction NCPDocument8 pagesNursing Care Plan For Myocardial Infarction NCPderic87% (15)
- Nursing Care Plan LeukemiaDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Leukemiaderic87% (30)
- NCP Priority 1 Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument5 pagesNCP Priority 1 Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDenice100% (1)
- Assessing Seizure Risk and InterventionsDocument2 pagesAssessing Seizure Risk and Interventionshanyaklein100% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan For Smoke Poisoning NCPDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Smoke Poisoning NCPderic100% (3)
- 021SAACK Burner Operating Instructions PDFDocument136 pages021SAACK Burner Operating Instructions PDFmekidmu tadesse100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For Risk For Aspiration NCPDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan For Risk For Aspiration NCPderic100% (8)
- Nursing Care Plan Diarrhea Assessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument8 pagesNursing Care Plan Diarrhea Assessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationKrah100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For Readiness For Enhanced Sleep NCPDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan For Readiness For Enhanced Sleep NCPderic100% (2)
- NEONATAL SEPSIS ASSESSMENT AND MANAGEMENTDocument12 pagesNEONATAL SEPSIS ASSESSMENT AND MANAGEMENTPamela laquindanumNo ratings yet
- Cues/Needs Nursing Rationale Goals and Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesCues/Needs Nursing Rationale Goals and Intervention Rationale Evaluationnj_pink08179460% (5)
- Nursing Care Plan For Insomnia NCPDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Insomnia NCPderic83% (23)
- Nursing Care Plan For Seizure NCPDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Seizure NCPderic88% (40)
- Nursing Care Plan For Risk For Compromised Human Dignity NCPDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For Risk For Compromised Human Dignity NCPderic100% (2)
- 14 - Hydraulic Design of Urban Drainage Systems PDFDocument45 pages14 - Hydraulic Design of Urban Drainage Systems PDFDeprizon SyamsunurNo ratings yet
- NCP NicuDocument3 pagesNCP NicuNoel Telosa100% (1)
- Cardiovascular Disease NCPDocument5 pagesCardiovascular Disease NCPShyla ManguiatNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Insufficient Breastmilk NCPDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Insufficient Breastmilk NCPderic100% (17)
- Nursing Care Plan For Neonatal Sepsis NCPDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For Neonatal Sepsis NCPderic67% (9)
- NURSING CARE PLAN Risk For InfectionDocument3 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN Risk For InfectionEvelyn Lampios100% (1)
- Neonatal Sepsis NCPDocument9 pagesNeonatal Sepsis NCPHollan Galicia100% (1)
- Buyers FancyFoodDocument6 pagesBuyers FancyFoodvanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Post Trauma NCPDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan For Post Trauma NCPderic82% (11)
- NCPs For InfantDocument6 pagesNCPs For InfantRay Carlo Ybiosa Antonio33% (3)
- Com +Nursing+Care+Plan+Chicken+PoxDocument2 pagesCom +Nursing+Care+Plan+Chicken+PoxDahl Obañana Erojo100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For Interrupted Breastfeeding NCPDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For Interrupted Breastfeeding NCPderic88% (8)
- NCP TbiDocument4 pagesNCP TbiWyen CabatbatNo ratings yet
- Nursing Assessment, Diagnosis, Intervention, and EvaluationDocument5 pagesNursing Assessment, Diagnosis, Intervention, and EvaluationNikael Patun-ogNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Carbon Monoxide PoisoningDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For Carbon Monoxide Poisoningderic73% (11)
- 4th Summative Test Science 6Document5 pages4th Summative Test Science 6ANNALIZA FIECASNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For AIDS/HIVDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For AIDS/HIVderic81% (16)
- Nursing Care Plan - SepsisDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan - SepsisJoe Mark Salamero86% (21)
- Nursing Care Plan For GlaucomaDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For Glaucomaderic79% (28)
- Nursing Care Plan For Readiness For Enhanced Spiritual Well Being NCPDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan For Readiness For Enhanced Spiritual Well Being NCPderic83% (6)
- Nursing Care Plan For Readiness For Enhanced Hope NCPDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan For Readiness For Enhanced Hope NCPderic100% (6)
- Nursing Care Plan For Peptic Ulcer NCPDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Peptic Ulcer NCPderic85% (46)
- Nursing Care Plan For AmputationDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For Amputationderic80% (25)
- Nursing Care Plan For Rape Trauma Syndrome NCPDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan For Rape Trauma Syndrome NCPderic100% (4)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument6 pagesNursing Care PlanAnthea ValinoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis Background Study Inference Goals and Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument5 pagesNursing Diagnosis Background Study Inference Goals and Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationAubrey SungaNo ratings yet
- VISCOSITY CLASSIFICATION GUIDE FOR INDUSTRIAL LUBRICANTSDocument8 pagesVISCOSITY CLASSIFICATION GUIDE FOR INDUSTRIAL LUBRICANTSFrancisco TipanNo ratings yet
- NCP HivDocument3 pagesNCP HivARISNo ratings yet
- NCP Preterm NeonateDocument3 pagesNCP Preterm NeonateLilia Priscilla Tuibuen Aureus100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan for 1-Year-Old Male Admitted for Dehydration and SeizuresDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan for 1-Year-Old Male Admitted for Dehydration and SeizuresKwini Jeyn50% (2)
- NCP For CHDDocument2 pagesNCP For CHDMonica Rivera100% (1)
- NCP SepsisDocument6 pagesNCP SepsisgopscharanNo ratings yet
- FEver NCPDocument1 pageFEver NCPSam AlipioNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Peritonitis NCPDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Peritonitis NCPderic83% (6)
- Nursing Care Plan For Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding NCPDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding NCPderic79% (14)
- NCP CoughDocument4 pagesNCP CoughKingJayson Pacman06No ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance ChildDocument3 pagesNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance ChildMarion Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Ineffective Infant Feeding Pattern NCPDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For Ineffective Infant Feeding Pattern NCPderic71% (14)
- Assessment Diagnisis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnisis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDanica Kate GalleonNo ratings yet
- Dwarf Boas of The Caribbean PDFDocument5 pagesDwarf Boas of The Caribbean PDFJohn GamesbyNo ratings yet
- Student Nurses' Community: NURSING CARE PLAN Neonatal SepsisDocument2 pagesStudent Nurses' Community: NURSING CARE PLAN Neonatal SepsisPanJan BalNo ratings yet
- Student Nurses' Community: NURSING CARE PLAN Neonatal SepsisDocument2 pagesStudent Nurses' Community: NURSING CARE PLAN Neonatal SepsisChristian Remetio100% (1)
- NURSING CARE PLAN ON FOUL-SMELLING LOCHIADocument3 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN ON FOUL-SMELLING LOCHIANE Tdr100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan for Billy Admitted with Ear and Throat InfectionsDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan for Billy Admitted with Ear and Throat InfectionsNatukunda Dianah100% (1)
- Hypothyroidism Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesHypothyroidism Nursing Care PlanRizza Mae MaglacionNo ratings yet
- After 8 hours of nursing interventions, the patient was able to demonstrate behaviors and lifestyle changes to reduce risk factors and protect self from injuryDocument2 pagesAfter 8 hours of nursing interventions, the patient was able to demonstrate behaviors and lifestyle changes to reduce risk factors and protect self from injuryTeresa JunioNo ratings yet
- Chicken Pox N C P BY BHERU LALDocument2 pagesChicken Pox N C P BY BHERU LALBheru Lal100% (1)
- Delayed Growth NCPDocument3 pagesDelayed Growth NCPPau-pau BasiNo ratings yet
- Cutaneous Anthrax Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesCutaneous Anthrax Nursing Care PlanYayin Pestaño100% (1)
- Novilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii: Assessment Diagnosi S Pathophysiolog Y Planning Interevention Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageNovilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii: Assessment Diagnosi S Pathophysiolog Y Planning Interevention Rationale EvaluationCharina AubreyNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan For Ineffective Airway ClearanceCaroline ChaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Risk For InfectionDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan: Risk For Infectiongeorgeborja414726100% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan PrenatalDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan PrenatalKim Galamgam100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan For Client With Parent-Infant AttachmentDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Client With Parent-Infant AttachmentThe Right WayNo ratings yet
- NCP DobDocument3 pagesNCP DobLester BuhayNo ratings yet
- Delayed Growth and Development Assessment N.Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesDelayed Growth and Development Assessment N.Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluationkreny10No ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Goals/ Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument20 pagesNursing Diagnosis Rationale Goals/ Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationElaine Grace Timbol-Babasa100% (1)
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Evaluation No Subjective Cues ObjectiveDocument3 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Evaluation No Subjective Cues ObjectiveMaverick LimNo ratings yet
- Nursing Intervention for Hyperthermia: Objectives, Interventions, Rationale and EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Intervention for Hyperthermia: Objectives, Interventions, Rationale and EvaluationMary Joyce LimoicoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for ChickenpoxDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan for ChickenpoxAkeroNo ratings yet
- NCPSLHDocument2 pagesNCPSLHjoanaferrerNo ratings yet
- Far East Ern University: Nursing Care PlanDocument6 pagesFar East Ern University: Nursing Care PlanmharieeeNo ratings yet
- Potential Nursing Diagnosis: Risk for InfectionDocument2 pagesPotential Nursing Diagnosis: Risk for InfectionKarl KiwisNo ratings yet
- Risk For Infection: Nursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDocument3 pagesRisk For Infection: Nursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveAngelica Charisse BuliganNo ratings yet
- Integumentary Disoder: Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesIntegumentary Disoder: Nursing Care PlanFrancise Elyn OcubilloNo ratings yet
- NOVIDA, ALEYA CRYSTINE G. BSN 3BDocument4 pagesNOVIDA, ALEYA CRYSTINE G. BSN 3BMelvin D. RamosNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Pedia TB Meningitis NCPDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Pedia TB Meningitis NCPderic100% (1)
- tsb16 0008 PDFDocument1 pagetsb16 0008 PDFCandy QuailNo ratings yet
- Trabajo de Investigación FormativaDocument75 pagesTrabajo de Investigación Formativalucio RNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Communication & Change MGT - HS Planning & Policy Making ToolkitDocument62 pagesModule 5 Communication & Change MGT - HS Planning & Policy Making ToolkitKristine De Luna TomananNo ratings yet
- Efficient Power Supply for Inductive LoadsDocument7 pagesEfficient Power Supply for Inductive LoadsMary AndersonNo ratings yet
- EE114-1 Homework 2: Building Electrical SystemsDocument2 pagesEE114-1 Homework 2: Building Electrical SystemsGuiaSanchezNo ratings yet
- Operation Manual TempoLink 551986 enDocument12 pagesOperation Manual TempoLink 551986 enBryan AndradeNo ratings yet
- A Development of The Test For Mathematical Creative Problem Solving AbilityDocument27 pagesA Development of The Test For Mathematical Creative Problem Solving AbilityanwarNo ratings yet
- Unitary Small Air-Conditioners and Air-Source Heat Pumps (Includes Mixed-Match Coils) (RATED BELOW 65,000 BTU/H) Certification ProgramDocument65 pagesUnitary Small Air-Conditioners and Air-Source Heat Pumps (Includes Mixed-Match Coils) (RATED BELOW 65,000 BTU/H) Certification ProgramAmer GaladNo ratings yet
- What Is Inventory Management?Document31 pagesWhat Is Inventory Management?Naina SobtiNo ratings yet
- Influence of Social Media on Youth Brand Choice in IndiaDocument7 pagesInfluence of Social Media on Youth Brand Choice in IndiaSukashiny Sandran LeeNo ratings yet
- Expected OutcomesDocument4 pagesExpected OutcomesPankaj MahantaNo ratings yet
- Imp RssDocument8 pagesImp RssPriya SharmaNo ratings yet
- Priming An Airplane EngineDocument6 pagesPriming An Airplane Enginejmoore4678No ratings yet
- Beyond B2 English CourseDocument1 pageBeyond B2 English Coursecarlitos_coolNo ratings yet
- Citation GuideDocument21 pagesCitation Guideapi-229102420No ratings yet
- Technical CommunicationDocument35 pagesTechnical CommunicationPrecious Tinashe NyakabauNo ratings yet
- Batool2019 Article ANanocompositePreparedFromMagn PDFDocument10 pagesBatool2019 Article ANanocompositePreparedFromMagn PDFmazharNo ratings yet
- Module-1 STSDocument35 pagesModule-1 STSMARYLIZA SAEZNo ratings yet
- Working With Session ParametersDocument10 pagesWorking With Session ParametersyprajuNo ratings yet