Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ACS NSTEMI Clinical Pathway
Uploaded by
XtiaROriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ACS NSTEMI Clinical Pathway
Uploaded by
XtiaRCopyright:
Available Formats
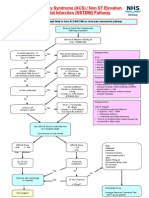
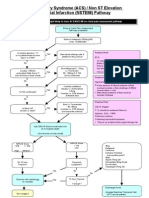
Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS) / Non ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction (NSTEMI) Pathway
Eligibility: Patients thought likely to have ACS/NSTEMI on chest pain assessment pathway
Ensure Chest Pain Assessment Pathway completed
Start s/c Dalteparin 120U/kg BID (max. 10,000units)2
Is random glucose > 11 or is patient known to have type I or II DM? No
Yes
Start insulin sliding scale in addition to this protocol
Practice Point ECG On admission Within 24 hours Prior to discharge Any time symptomatic Clinical changes Practice Point Hypotension (Systolic BP < 90)
Is pulse > 65/min and patient Killip Score I? (Use formula on back sheet) No
Yes
Give Metoprolol 5 - 15mg i.v. PLUS start 50 - 100mg P.O TID (to be continued)
Is Pain continuing? No
Yes
Consider additional dose(s) i.v. Diamorphine 2.5mg Consider i.v. GTN infusion at titrated dose
In the absence of clinical evidence of fluid
overload consider a fluid challenge of 250ml normal saline i.v. stat With clinical evidence of fluid overload consider inotropes Practice Point
Is there LVF (known or new)?
Yes
Give i.v. Furosemide 40 - 80mg Consider i.v. GTN infusion (see separate protocol)
Use of Oxygen
should be continued if there is:
Hypoxia - SaO2 < 90% Pulmonary oedema Continuing myocardial ischaemia There is no evidence that oxygen therapy has any benefit in other cases
Use GRACE Score to estimate risk of in hospital death (Use formula on back sheet)
GRACE Score > 9% 1 - 9% High Medium
GRACE Score < 1% Low
Do 12 hour Troponin I Yes
Recurrent symptoms? No No
Stop Dalteparin Continue -blocker if started (see practice point1) Start Aspirin 75mg OD Simvastatin 40mg Nocte Do not start Clopidogrel 75mg OD
Discuss with cardiology re: transfer
Yes
12 hour Troponin I > 0.5g/l ? Discharge home
Go to page 2
Arrange Exercise Tolerance Test (ETT) as out-patient
Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS) / NSTEMI Pathway
Patient discussed with cardiologists at ARI
Patient awaiting transfer
Declined or not suitable for transfer
Start Aspirin 75mg OD Clopidogrel 75mg OD Simvastatin 40mg Nocte Continue s/c Dalteparin 120U/kg BID (max. 10,000 U) -blocker (see practice point1)
Start Aspirin 75mg OD Clopidogrel 75mg OD Simvastatin 40mg Nocte Continue s/c Dalteparin 120U/kg BID (max. 10,000 U) for duration of admission -blocker (see practice point1)
Consider starting Tirofiban infusion (only after discussion with cardiologists) See separate protocol Yes Is pain ongoing No Consider additional dose(s) i.v. Diamorphine 2.5mg Consider i.v. GTN infusion at titrated dose
Within 36 hours add p.o. Ramipril 1.25mg - 2.5mg od (dose to be titrated up)
Optimise anti-anginal therapy
Within 36 hours add p.o. Ramipril 1.25 - 2.5mg OD (dose to be titrated up)
Within 48 hours change Metoprolol to Atenolol (Metoprolol 50mg TID = Atenolol 50mg OD)
Aim to discharge when symptom free after one week Transfer patient to ARI CCU with letter and any relevant investigation results (blood results, ECGs etc)
Refer to cardiac nurses for cardiac rehab programme GP should aim to titrate Ramipril to 10mg OD or max. tolerated dose Clopidogrel should be continued for 3 months
Practice Point
-Blockers
-blockers not without problems. Check no contraindications No strong evidence for any particular one - appears to be class effect. Atenolol, having od dosage, will aid compliance Start with Metoprolol but if no problems change to Atenolol within 48 hours -blockers should be withheld in patients with LV failure/pulmonary oedema. Subsequent cautious addition of highly selective -blocker (e.g.
2
Practice Point
Dalteparin in Renal Impairment Dalteparin (and other LMW heparins) are excreted mainly by the kidneys . LMW heparins, having smaller molecular size, bind less to plasma proteins, platelets and endothelium and so have greater bioavailablity Unfractionated heparins ( e.g. heparin sodium) are excreted mainly by the liver
In patients with a creatinine of > 200mmol/L heparin sodium should be used. o Prophylactic dose is 5000units sc twice daily (but use Dalteparin 2500units once daily if heparin sodium is unavailable) o Treatment doses are administered as a continuous infusion of heparin sodium with 6-8 hourly APTT monitoring (target ratio usually 2 2.5)
In patients with a creatinine of 130 - 200mmol/L consult BNF to calculate Dalteparin dose reductions both for treatment and prophylactic
Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS) / NSTEMI Pathway
Killip Score
Used to assess degree of acute cardiac failure Excluded if pre-hospital cardiac arrest Killip Score
I II III IV No clinical signs of heart failure Crackles, S3 gallop and elevated jugular venous pressure Frank pulmonary oedema Cardiogenic shock - hypotension (systolic < 90mmHg) and evidence of peripheral vasoconstriction (oliguria, cyanosis, sweating)
GRACE Score (Global Registry of Acute Coronary Events)
Used to assess risk of in-hospital death in ACS 1. Find Points for Each Predictive Factor:
Killip Score I II III IV Points 0 20 39 59 SBP mm Hg 80 80 - 99 100 - 119 120 - 139 140 - 159 160 - 199 200 Points 58 53 43 34 24 10 0 Heart Rate Beats/min 50 50 - 69 70 - 89 90 - 109 110 - 149 150 - 199 200 Points 0 3 9 15 24 38 46 Age years 30 30 - 39 40 - 49 50 - 59 60 - 69 70 - 79 80 - 89 Points 0 8 25 41 58 75 91 Serum Creatinine mol/l 0 - 34 35 - 70 71 - 105 106 - 140 141 - 176 177 - 353 353 Points 1 4 7 10 13 21 28
90100
Other Risk Factors Cardiac Arrest at Admission ST-Segment Deviation Elevated Cardiac Enzyme Levels
Points 39 28 14
2. Sum Points for All Predictive Factors:
Killip Class 59 + Systolic BP 53 + Heart Rate 9 +
Age 25
Creatinine Level 1
Cardiac Arrest at Admissio n 39
ST Segment Deviation 0
Elevated Cardiac Enzymes 0
TOTAL POINTS
186
3. Look Up Risk Corresponding to Total Points:
Total Points 60 Probability of InHospital Death, % 0.2 70 0.3 80 0.4 90 0.6 100 0.8 110 1.1 120 1.6 130 2.1 140 2.9 150 3.9 160 5.4 170 7.3 180 9.8 190 13 200 18 210 23 220 29 230 36 240 44 250 52
For example, a patient has Killip class II, SBP of 100mm Hg, heart rate of 100 beats/min, is 65 years of age, has serum creatinine level of 1mg/dL, did not have a cardiac arrest at admission but did have ST-segment deviation and elevated enzyme levels. His score would be: 20+53+15+58+7+0+28+14=196 This person would have about a 16% risk of having an in-hospital death. Similarly, a patient with Killip class I, SBP of 80mm Hg, heart rate of 60 beats/min, is 55 years of age, has serum creatinine level of 0.4, and no risk factors would have the following score: 0+58+3+41+1=103, which gives approximately a 0.9% risk of having an in-hospital death.
Definitions Acute MI: symptoms ? consistent with cardiac ischaemia within 24 hours of presentation with a rise in Troponin I Unstable Angina: symptoms consistent with cardiac ischaemia within 24 hours of hospital admission with no rise in Troponin I AND at least one of: 1 Hx MI cardiac arrest, angina or ischaemic CCF 2 Hx of positive ETT 3 Documented cardiac catheterisation of 50% stenosis and 1 coronary artery 4 Hx of angioplasty with CABG 5 ECG transient ST elevation 1mm in 3 continuous chest leads, St depression 1mm, new T wave inversion 1mm, pseudonormaligatin of previously inverted T
You might also like
- Acs Nstemi PathwayDocument3 pagesAcs Nstemi PathwayAliey's SKeplek NgeNersNo ratings yet
- Unstable AnginaDocument5 pagesUnstable AnginaAria AlysisNo ratings yet
- Bagi Percakapan EnglishDocument4 pagesBagi Percakapan EnglishFatimatuz ZahroNo ratings yet
- Topic / Organ-System:: 1. General Data/InformationDocument5 pagesTopic / Organ-System:: 1. General Data/InformationDan Angelo MatiasNo ratings yet
- Acute Gastroenteritis (AGE)Document37 pagesAcute Gastroenteritis (AGE)Sari HariyaniNo ratings yet
- Esophageal Varices Week 4 T2T3Document37 pagesEsophageal Varices Week 4 T2T3liewhuilianNo ratings yet
- Retention of Ca in kidneys causes kidney stonesDocument2 pagesRetention of Ca in kidneys causes kidney stonesQueenie Rose ArsenalNo ratings yet
- Eisenmenger SyndromeDocument41 pagesEisenmenger SyndromeJennifer DixonNo ratings yet
- Pathway - Urethral StrictureDocument1 pagePathway - Urethral StrictureCiptaningrum Marisa PNo ratings yet
- Cardiology Case 1Document2 pagesCardiology Case 1vil62650% (2)
- CABGDocument9 pagesCABGBilal Ali KhanNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Arterial Occlusive DiseaseDocument4 pagesPeripheral Arterial Occlusive Diseasekrisfred14100% (1)
- Generic Name T Rade Name Classification Diltiazem Cardizem Antianginals, AntiarrhythmicsDocument1 pageGeneric Name T Rade Name Classification Diltiazem Cardizem Antianginals, AntiarrhythmicsChristopher LeeNo ratings yet
- Dr. Sunatrio - Management Hypovolemic ShockDocument59 pagesDr. Sunatrio - Management Hypovolemic ShockArga Putra SaboeNo ratings yet
- Medical Management of Postpartum HemorrhageDocument17 pagesMedical Management of Postpartum HemorrhageCatherine PingNo ratings yet
- Dyslipidemia Update by DR SarmaDocument96 pagesDyslipidemia Update by DR SarmaDewi NofiantiNo ratings yet
- Cardiogenic Shock: BY Dr. M L Patel MD Associate Professor Deptt. of MedicineDocument19 pagesCardiogenic Shock: BY Dr. M L Patel MD Associate Professor Deptt. of MedicineDurgesh PushkarNo ratings yet
- Schistosomiasis (From Anatomy To Pathophysiology)Document10 pagesSchistosomiasis (From Anatomy To Pathophysiology)Tiger Knee100% (1)
- TriageDocument40 pagesTriageI'made SinchanNo ratings yet
- DKA Study GroupDocument24 pagesDKA Study GroupAqila MumtazNo ratings yet
- PYOMYOSITISDocument6 pagesPYOMYOSITISChristine CoridoNo ratings yet
- Acute Coronary Syndrome: Dr. H.M. Saifullah Napu, SPJP, FihaDocument47 pagesAcute Coronary Syndrome: Dr. H.M. Saifullah Napu, SPJP, FihaJual Beli Promosi100% (1)
- Nephrolithiasis AnatomyDocument3 pagesNephrolithiasis AnatomyKevin Ker Campaner MerillesNo ratings yet
- HANDOUT - Vomiting in AdultsDocument3 pagesHANDOUT - Vomiting in Adults2012No ratings yet
- Cardiogenic ShockDocument18 pagesCardiogenic ShockBagus Andi PramonoNo ratings yet
- Congestive Heart Failure !1 Running Head: Congestive Heart FailureDocument11 pagesCongestive Heart Failure !1 Running Head: Congestive Heart Failureapi-543558169No ratings yet
- MIDocument22 pagesMIGagauz SiliviaNo ratings yet
- 22 Ventricular Septal DefectDocument26 pages22 Ventricular Septal Defectdhiraj parmarNo ratings yet
- Perforated Peptic Ulcer Symptoms and DiagnosisDocument68 pagesPerforated Peptic Ulcer Symptoms and DiagnosisSaibo BoldsaikhanNo ratings yet
- Acute Tubular Necrosis 2Document19 pagesAcute Tubular Necrosis 2Sangeeta BSRNo ratings yet
- Contributing Factors and Treatment of Benign Prostatic HyperplasiaDocument1 pageContributing Factors and Treatment of Benign Prostatic HyperplasiaSarah RonquilloNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of HydrocephalusDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of HydrocephalusJan Rae Barnatia AtienzaNo ratings yet
- Heart FailureDocument4 pagesHeart FailureDane WrightNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal History and ExaminationDocument4 pagesGastrointestinal History and ExaminationAtif Rasool MaharNo ratings yet
- Concept Map 3 MM (Abdominal Pain)Document2 pagesConcept Map 3 MM (Abdominal Pain)Matt McKinleyNo ratings yet
- 2 Acute Myocardial InfarctionDocument15 pages2 Acute Myocardial InfarctionpauchanmnlNo ratings yet
- Uremic Encephalopathy-ReviewDocument30 pagesUremic Encephalopathy-ReviewFeddyFebriyantoManurung100% (1)
- Careplan Medication ListDocument17 pagesCareplan Medication ListGiorgia ScorsoneNo ratings yet
- PATHOPHYDocument3 pagesPATHOPHYArlly Faena AbadNo ratings yet
- Fever of Unknown OriginDocument26 pagesFever of Unknown OriginFiona Yona Sitali100% (1)
- Concept MapDocument1 pageConcept Mapapi-252910411No ratings yet
- Acute Limb Ischemia SiteDocument23 pagesAcute Limb Ischemia Sitedokteraan100% (2)
- CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES: SIGNS, SYMPTOMS AND TREATMENT OF HEART FAILUREDocument27 pagesCARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES: SIGNS, SYMPTOMS AND TREATMENT OF HEART FAILURESanthoshi Sadhanaa SankarNo ratings yet
- 49-Year-Old Man With Chest PainDocument35 pages49-Year-Old Man With Chest PainFitriya Syaifuddin100% (1)
- Periampullary TumorsDocument30 pagesPeriampullary TumorsAsif.N.IqbalNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology-Kni Ns PLZZZDocument8 pagesPathophysiology-Kni Ns PLZZZAnna Lira Manluyang MungcalNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Prostate Cancer Risk FactorsDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Prostate Cancer Risk FactorsmkhoNo ratings yet
- Cirrhosis in Adults: Overview of Complications, General Management, and Prognosis - UpToDateDocument21 pagesCirrhosis in Adults: Overview of Complications, General Management, and Prognosis - UpToDateDan ChicinasNo ratings yet
- Acute Renal Failure: Dr. Bobi Ahmad S, S.KPDocument62 pagesAcute Renal Failure: Dr. Bobi Ahmad S, S.KPdr.Bobi Ahmad Sahid, S.KepNo ratings yet
- Congestive Heart FailureDocument25 pagesCongestive Heart FailuredevianiamalinaNo ratings yet
- PERITONITIS EDUCATIONAL GUIDEDocument8 pagesPERITONITIS EDUCATIONAL GUIDEmuhammad ridwanNo ratings yet
- Mitral Valve Replacement Procedure OverviewDocument3 pagesMitral Valve Replacement Procedure OverviewSony TonNo ratings yet
- Chapter Q 045Document1 pageChapter Q 045sammm996No ratings yet
- Acute Pancreatitis NOTESDocument17 pagesAcute Pancreatitis NOTESsameeha semiNo ratings yet
- EdemaDocument27 pagesEdemarapadilNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Pressure UlcersDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Pressure UlcersSTORAGE FILENo ratings yet
- CHC-PC-0033: Procedure Number Version NosDocument7 pagesCHC-PC-0033: Procedure Number Version NosQari Ramadhan AminNo ratings yet
- CCU HandoverDocument9 pagesCCU Handoverapi-192342497No ratings yet
- Chest Pain Protocol in EDDocument3 pagesChest Pain Protocol in EDshahidchaudharyNo ratings yet
- 6 - Fahad Class 6 Cardiac AnesthesiaDocument18 pages6 - Fahad Class 6 Cardiac AnesthesiaOne ClickNo ratings yet
- Elective Termination: Client Assessment Data Base CirculationDocument8 pagesElective Termination: Client Assessment Data Base CirculationLei OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Revised NBI Clearance Application Form V1.7 (Fill-In PDFDocument1 pageRevised NBI Clearance Application Form V1.7 (Fill-In PDFDavid RobertNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Rheumatic Heart DiseaseDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Rheumatic Heart DiseaseXtiaR85% (13)
- FNCP - HPNDocument7 pagesFNCP - HPNXtiaRNo ratings yet
- ACS NSTEMI Clinical PathwayDocument3 pagesACS NSTEMI Clinical PathwayXtiaRNo ratings yet
- Family Code CodalDocument44 pagesFamily Code CodalLita Indz Nuevo BudomoNo ratings yet
- Revenue Budget: Description Detail AmountDocument1 pageRevenue Budget: Description Detail AmountXtiaRNo ratings yet
- CMO 09 s2007Document55 pagesCMO 09 s2007XtiaRNo ratings yet
- Table Appa 1Document1 pageTable Appa 1Ary DoeNo ratings yet
- Informatics ThingyDocument22 pagesInformatics ThingyXtiaRNo ratings yet
- MGMT 2 Week 15Document3 pagesMGMT 2 Week 15DarkxeiDNo ratings yet
- ABC Healthcare Industry IMPDocument42 pagesABC Healthcare Industry IMPanishokm2992No ratings yet
- Bab Vii Daftar PustakaDocument5 pagesBab Vii Daftar Pustaka19 110 Setya Maharani KadirNo ratings yet
- Bias and Confounding: Nayana FernandoDocument31 pagesBias and Confounding: Nayana FernandoanojNo ratings yet
- ISMP Preventing Medication Errors HospitalsDocument23 pagesISMP Preventing Medication Errors HospitalsRayNo ratings yet
- Florian1995, Mental HealthDocument9 pagesFlorian1995, Mental Healthade ubaidahNo ratings yet
- Indian Herbs For Healthy Body - Healing Properties of Adalodakam, Arogya Pacha, Ashokam, IrattimadhuDocument4 pagesIndian Herbs For Healthy Body - Healing Properties of Adalodakam, Arogya Pacha, Ashokam, IrattimadhuNEELNo ratings yet
- REPORT ON YOGA RESEARCH STUDIES AT ACYTER, JIPMER: 2008 To 2012.Document126 pagesREPORT ON YOGA RESEARCH STUDIES AT ACYTER, JIPMER: 2008 To 2012.Yogacharya Dr Ananda Balayogi BhavananiNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology: A Career inDocument2 pagesPharmacology: A Career insnikt7863443No ratings yet
- Basic Tools in NutritionDocument23 pagesBasic Tools in NutritionSeanmarie Cabrales0% (1)
- Progestin Only ContraceptionDocument4 pagesProgestin Only ContraceptionTareq SawanNo ratings yet
- TreadsDocument4 pagesTreadsKimberly FajardoNo ratings yet
- Quiz2 1 Issue2Document2 pagesQuiz2 1 Issue2Jazur AhamedNo ratings yet
- BIOEN 345: Failure Analysis of Physiology: Lecture 4 May 4, 2020: Vessel PathologiesDocument45 pagesBIOEN 345: Failure Analysis of Physiology: Lecture 4 May 4, 2020: Vessel PathologiesasdfghjklNo ratings yet
- STROKE AND TRANSIENT ISCHEMIC ATTACK-dikonversi-dikonversiDocument5 pagesSTROKE AND TRANSIENT ISCHEMIC ATTACK-dikonversi-dikonversiOcing TanNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions 1 - YoungDocument12 pagesPractice Questions 1 - Youngejyoung928100% (1)
- NOSA-National Price List 2013Document2 pagesNOSA-National Price List 2013Kevin Raman100% (1)
- 4 Coercion in Mental Healthcare The Principle of Least Coercive CareDocument8 pages4 Coercion in Mental Healthcare The Principle of Least Coercive CarePedro Y. LuyoNo ratings yet
- Efudix Leaflet With PicturesDocument2 pagesEfudix Leaflet With PicturesyehyaNo ratings yet
- Pathology MBBSDocument12 pagesPathology MBBSDinah Penserga100% (1)
- Database Clerk Vacancy in MawlamyineDocument3 pagesDatabase Clerk Vacancy in MawlamyineHein Min NaingNo ratings yet
- Cook 2009 Oropharyngeal DysphagiaDocument21 pagesCook 2009 Oropharyngeal DysphagiaDesiré MagalhãesNo ratings yet
- Food Contact Materials FDA NSF and Other StandardsDocument3 pagesFood Contact Materials FDA NSF and Other StandardsMuhammad Brilian Syifa HabibiNo ratings yet
- Viva XT Brochure - 201203539IEp3Document6 pagesViva XT Brochure - 201203539IEp3Lubna LuaiNo ratings yet
- Lab Activity #8Document3 pagesLab Activity #8Kristelito Grace MarinoNo ratings yet
- Ielts Speaking 3Document34 pagesIelts Speaking 3Asad GondalNo ratings yet
- Handwashing NarrativeDocument9 pagesHandwashing NarrativeMaria Angelica BermilloNo ratings yet
- The New Jose L. Amante Emergency HospitalDocument29 pagesThe New Jose L. Amante Emergency HospitalRiah Ramirez FojasNo ratings yet
- Full Name Nationality Status SEX Place of Birth Date of Birth Passport Number Languages Educational QualificationsDocument3 pagesFull Name Nationality Status SEX Place of Birth Date of Birth Passport Number Languages Educational QualificationsHoseinNo ratings yet
- Case Study Report (Peptic Ulcer) Group 1Document9 pagesCase Study Report (Peptic Ulcer) Group 1Khrizlynne SoberanoNo ratings yet