Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Antonio - Indirect Lesson Plan
Uploaded by
api-211234915Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Antonio - Indirect Lesson Plan
Uploaded by
api-211234915Copyright:
Available Formats
Jessica Antonio ELED 3221 3/18/13
INDIRECT INSTRUCTION LESSON PLAN Elementary Science Big Idea: Structures and Functions of Living Organisms- The Human Body: Muscular System Grade Level: 3rd Rationale: It is important for students to learn this because the muscular system is critical to our survival and is part of the human body. Our muscular systems helps us move, digest, breathe, blink, and other important tasks. We could not live without it. NC Science Essential Standards: 3.L.1 Understand human body systems and how they are essential for life: protection, movement and support. 3.L.1.1 Compare the different functions of the skeletal and muscular system. National Science Education Content Standards Reference: Life Science Life Science Content Standard C: As a result of activities in grades K - 4, all students should develop understanding of The characteristics of organisms
The characteristics of organisms Each plant or animal has different structures that serve different functions in growth, survival, and reproduction. For example, humans have distinct body structures for walking, holding, seeing, and talking
Instructional Objective: Students will complete an index card stating the muscles they learned such as pectorals, biceps, triceps, quadriceps, calves, back, hamstrings, forearms or abdominals, their functions, and why we need them for survival, and they will list any questions they have. By doing hands-on experience with a partner, groups and individually, the students will learn about muscles and their functions. Through this learning process, they will learn why we need muscles to survive. Prerequisite knowledge and skills: Students Knowledge: The body contains muscles that have different functions, muscles are essential to our survival Students Skills: Observe different structures of the body Teacher: There are over 600 muscles in the body. There are three different types of muscles: Smooth, Cardiac and Skeletal. Smooth muscles are also called involuntary muscles because we
do not control them such as muscles in our digestive system. Cardiac muscles are the muscles that make up our heart, and they pump blood through our body. These are the hardest working muscles. Skeletal muscles are our voluntary muscles because we can control them. These are the muscles such as quadriceps, biceps, hamstrings, the face muscles (mouth, eyebrows, cheeks, eyes) and even the tongue. Tendons connect skeletal muscles to the bones. The gluteus maximus located in the buttocks is the largest muscle in the body. Muscles our important to our survival because they allow us to move, breathe, pump blood, swallow, blink, and more. Materials/Resources: Body Outline Worksheet for each student Five copies of Name that Muscle worksheet Name that Muscle Answer Sheet for teacher Computers for the students Promethean Board to play video http://anatomyarcade.com http://kidshealth.org
Estimated Time: Appoximately 45 minutes to an hour Accommodation for Special Needs: Struggling students will be paired up with an advanced student in the Explore section. Visually impaired students should explore their muscles by feeling. ESL, hearing impaired and autistic students may play the muscle games on http://anatomyarcade.com if they are struggling during the lesson. The teacher will give assistance as needed. _____________________________________________________________________________ Content and Strategies (Procedure) Engage: Have the class start running in place, doing jumping jacks, swinging their legs and arms, and any other kind of movement. Ask the class what they are doing and how. Assuming the children say they are moving using their body, ask the students: o What parts of my body am I using? o Am using parts of my body that you cant see? Try to elicit a response of muscles from the students o Where are muscles in your body? o How can you tell where a muscle is? o Can you see muscles? o Are there muscles in your face? o Are there muscles in your arms and legs? o Are there muscles in your fingers? o Are there muscles you cant see?
Explore: With a partner, the students will explore the muscles in their body and what they do. They will try to feel their muscles as they flex them and relax them. The students will use the body outline to mark where they found a muscle in their body, and they will also list the name of that muscle if they know it. The students will have to find all the muscles they can and mark them on the body outline worksheet. If the students are trying to determine if something is a muscle, they may consult with other pairs. Students can also use kidshealth.org to research the muscles and find the functions. Have students determine the function of the muscles they listed and write them down on their paper. If students are struggling, the teacher will ask them questions such as: o What muscles do you already know? o Try flexing different parts of your body. Where do you see muscles? o What parts of your body are moving when you flex these muscles?
Explanation: The teacher will draw an outline of the human body on the paper board and ask the students: o Where did you find muscles in your body? o How did you find the muscles? o Do you know the names of the muscles you found? o Do you know what the function of the muscles could be? The teacher will mark down the areas they found muscles and the possible names and functions. If the students are stating functions that are incorrect ask the students: o What part of your body are you moving when you feel that muscle contract? Have the students do the movement with you. If the students do not know the names of all the muscles play this video: http://kidshealth.org/kid/htbw/MSmovie.html#cat20580
Elaborate: Students will play Name that Muscle. They will be divided into groups of four or five, and each group will be given the Name that Muscle worksheet. The teacher will go around each group to check for accuracy and assist as needed. The students may use the list they made in Explore as well as the board for guidance. After they have successfully completed the game, the students should answer the following questions on a piece of paper: o What are two muscles you learned?
o What are the functions of these muscles? o What are two reasons that we need muscles to survive? o What are two questions do you have about muscles?
Evaluate: An informal formative assessment will be used to evaluate students understandings. Written responses by the students will be evaluated on the following: Muscles they learned Functions of the muscles Why we need muscles to survive Questions they have
Rubric for Evaluation Muscles they learned 0 points: Students did not list any muscles the learned 1 point: Students listed 1 muscle they learned 2 points: Student listed 2 or more muscles the learned Functions of muscles 0 points: Students did not list any functions of muscles 1 point: Student listed 1 function of a muscle 2 points: Student listed 2 or more functions of a muscle Why we need muscles to survive 0 points: Student did not state why we need muscles to survive 1 point: Student stated 1 reason why we need muscles to survive 2 points: Student stated 2 or more reasons why we need muscles to survive Questions 0 points: Students did not list a question they have 1 points: Student listed 1 question they have 2 points: Student listed 2 or more questions they have
Mastery: 8 out of 8 points Partial Mastery: 4 or more out of 8 points No Mastery: 3 or fewer points out of 8 (re-teaching necessary)
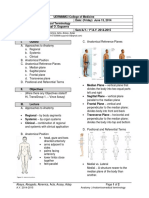
Body Outline Worksheet Directions: Mark the areas on the outline where you find muscles. List the names and functions of these muscles if you know them. Front Back
Name that Muscle Names________________________________________________________________________ 1) Using the word bank write the correct name of each muscle in the boxes. 2) Figure out which muscle goes with which functions.
1. Allows us to straighten our knee and move our upper leg: ___________________________ 2. Allows us to bend our knee: ________________________________ 3. Allows us to straighten our foot:__________________________ 4. Allows us to push our arms forward and bring our shoulder blades down:_________________ 5. Allows movement of the spine, neck, and shoulders:_______________________ 6. Allows us to raise our arms:_____________________________ 7. Allows us to straighten our arms:_____________________________ 8. Allows us to bend our arms:______________________________
9. Allows movement of the hands:_______________________ 10. Allows movement and support of our trunk while holding in organs:___________________ 11. Protects our bones when we sit: ____________________________
Word Bank Abdominals Pectorals Quadriceps Calves Gluteus Maximus Back Forearms Biceps Triceps Hamstrings Shoulders
Name that Muscle: Answer Sheet for Teacher
1. Quadriceps: Allows us to straighten our knee and move our upper leg 2. Hamstrings: Allows us to bend our knee 3. Calves: Allows us to straighten our foot 4. Pectorals: Allows us to push our arms forward and bring our shoulder blades down. 5. Back: Allows movement of the spine, neck, and shoulders. 6. Shoulders: Allows us to raise our arms 7. Triceps: Allows us to straighten our arms 8. Biceps: Allows us to bend our arms 9. Forearms: Allows movement of the hands 10. Abdominals: Allows movement and support of our trunk while holding in organs. 11. Gluteus Maximus: Protects our bones when we sit
You might also like
- Antonio - Math Mini-LessonDocument2 pagesAntonio - Math Mini-Lessonapi-211234915No ratings yet
- Antonio - Clinical Lesson ReflectionDocument2 pagesAntonio - Clinical Lesson Reflectionapi-211234915No ratings yet
- Antonio - Reading Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesAntonio - Reading Lesson Planapi-211234915No ratings yet
- Antonio - Social Studies LessonDocument5 pagesAntonio - Social Studies Lessonapi-211234915No ratings yet
- Antonio - Student Interview On Fractions MaedDocument1 pageAntonio - Student Interview On Fractions Maedapi-211234915No ratings yet
- Antonio - Math Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesAntonio - Math Lesson Planapi-211234915No ratings yet
- Antonio-Teacher Interview MaedDocument2 pagesAntonio-Teacher Interview Maedapi-211234915No ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Practical No. 3 - Comparative Study of Mammalian Skeleton ProceduresDocument9 pagesPractical No. 3 - Comparative Study of Mammalian Skeleton ProceduresSana cheema100% (1)
- AnaPhysio of The LarynxDocument6 pagesAnaPhysio of The LarynxAce Ashley BaronNo ratings yet
- Horgoláshoz Kéz BemelegítésDocument1 pageHorgoláshoz Kéz BemelegítésKrisztaNo ratings yet
- An Assessment of The Relationship Between The Maxillary Sinus Floor and The Maxillary Posterior Teeth Root Tips Using Dental Cone-Beam Computerized TomographyDocument6 pagesAn Assessment of The Relationship Between The Maxillary Sinus Floor and The Maxillary Posterior Teeth Root Tips Using Dental Cone-Beam Computerized TomographyLuciana EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Exercise On Strength: Joshua Lester J. ArellanoDocument17 pagesExercise On Strength: Joshua Lester J. ArellanoBryantNo ratings yet
- NMS Tests RevisedDocument12 pagesNMS Tests Revisednoname4No ratings yet
- Charting Examples For Physical AssessmentDocument16 pagesCharting Examples For Physical Assessmentim3in1No ratings yet
- Stroke HandoutDocument5 pagesStroke HandoutAdebayo Tob AdeyinkaNo ratings yet
- Science Long Test Grade 1Document4 pagesScience Long Test Grade 1Mitch-ChedyLanoriaNo ratings yet
- Sinelnikov Vol IIIDocument395 pagesSinelnikov Vol IIIOana Musteaţǎ100% (12)
- Anatomy StudyDocument124 pagesAnatomy StudyPragya ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Shoulder Exam - Shoulder & Elbow - OrthobulletsDocument8 pagesShoulder Exam - Shoulder & Elbow - Orthobulletsbrokenlimit5No ratings yet
- InomyalgiaDocument30 pagesInomyalgiaNtz LinaNo ratings yet
- Oral Anatomy Lesson 2Document2 pagesOral Anatomy Lesson 2Rosette GoNo ratings yet
- Modified Weber-Fergusson Incision With Borle's Extension: Technical NoteDocument2 pagesModified Weber-Fergusson Incision With Borle's Extension: Technical NoteUmer HussainNo ratings yet
- T6hehehev Hejeh Y2vbles1-5lDocument623 pagesT6hehehev Hejeh Y2vbles1-5lVincenzo PassarielloNo ratings yet
- Unit-8-Ear, Nose, Mouth, Sinus and Pharynx ExaminationDocument104 pagesUnit-8-Ear, Nose, Mouth, Sinus and Pharynx ExaminationMinlik-alew Dejenie100% (5)
- Chiropractic Green Books - V09 - 1923Document582 pagesChiropractic Green Books - V09 - 1923Fernando BernardesNo ratings yet
- Baseline Risk Identification of Ergonomics Factor (BRIEF Survey)Document20 pagesBaseline Risk Identification of Ergonomics Factor (BRIEF Survey)Sumeet GhodkeNo ratings yet
- Kai Biceps CompressedDocument17 pagesKai Biceps CompressedSascha BrahmannNo ratings yet
- Hand-Tai Yin) Lung MeridianDocument4 pagesHand-Tai Yin) Lung MeridianimanuelNo ratings yet
- Functional Anatomy of Temporomandibular JointDocument44 pagesFunctional Anatomy of Temporomandibular JointRomzi Hanif0% (1)
- Anatomski Atlas PDFDocument68 pagesAnatomski Atlas PDFIVANANo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The DogDocument226 pagesAnatomy of The DogAlina Ioana100% (24)
- Anatomy 1.1 - Anatomicomedical TerminologyDocument2 pagesAnatomy 1.1 - Anatomicomedical Terminologylovelots1234No ratings yet
- Fingerprint Analysis Summary and DuplicatesDocument8 pagesFingerprint Analysis Summary and DuplicatesCincinnatiEnquirerNo ratings yet
- Kriya - Kantha Padma Kriya: (Level One Teacher Training Manual (Old Version), Pp. 409-410)Document6 pagesKriya - Kantha Padma Kriya: (Level One Teacher Training Manual (Old Version), Pp. 409-410)Moisés Jonathan Saldaña Salazar100% (1)
- Shoulder ExcerciseDocument7 pagesShoulder Excerciseapi-26140473No ratings yet
- Chi Kung Five Animals FrolicDocument99 pagesChi Kung Five Animals Frolicslsbs1100% (1)
- Appendicular MusclesDocument6 pagesAppendicular MusclesJayson Diez CastilloNo ratings yet