Professional Documents
Culture Documents
INFECTIOUS DISEASE NOTES: 1. What's The Difference Between Pathology
Uploaded by
api-259652410 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views1 pageMalaria is the ______________ most deadly disease in the world. As many as _____________________ people are infected every year, and _________________ will die. CHANGE THIS BY CORNER BY: kill the pathogen or vector (pesticides, antibiotics)
Original Description:
Original Title
INFECTIOUS DISEASE NOTES: 1. What’s the Difference Between Pathology
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentMalaria is the ______________ most deadly disease in the world. As many as _____________________ people are infected every year, and _________________ will die. CHANGE THIS BY CORNER BY: kill the pathogen or vector (pesticides, antibiotics)
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views1 pageINFECTIOUS DISEASE NOTES: 1. What's The Difference Between Pathology
Uploaded by
api-25965241Malaria is the ______________ most deadly disease in the world. As many as _____________________ people are infected every year, and _________________ will die. CHANGE THIS BY CORNER BY: kill the pathogen or vector (pesticides, antibiotics)
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
INFECTIOUS DISEASE NOTES:
1. What’s the difference between pathology and epidemiology?
Pathology: how a disease affects an individual (symptoms, treatment, cure, etc.)
Epidemiology: how a disease affects a whole population (how it spreads, prevention, etc.)
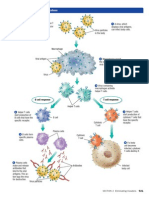
2. Scientists analyze and stop infectious diseases using the “epidemiologic triangle”:
**“germs”—pathogens that cause **people who might get infected
disease, like bacteria, viruses,
parasites HOST CHANGE THIS BY CORNER BY:
--bug spray
** “vectors” carry and transmit --wash hands, hygiene
pathogens (mosquitoes) -- vaccines
-- education
CHANGE THIS BY CORNER -- behavior change
BY: -- general health and immune system
** kill the pathogen or vector
(pesticides, antibiotics)
ENVIRONMENT
AGENT
** place where agent lives (wet, warm)
CHANGE THIS BY:
--clean environment, water
-- proper cooking & freezing food
UNDERSTANDING MALARIA (p. 509):
1. Malaria is the ______________ most deadly disease in the world. As many as
_____________________ people are infected every year, and __________________ will die.
2. Malaria is caused by sporozoans of the genus __________________. These are spread
between hosts by _______________________. Here’s how it develops:
STAGE 1: A __________________ mosquito bites a host and injects _________________
containing the Plasmodium parasite. ____________________ first invade _______________
cells, and produce _______________ of new parasites, destroying cells in the process.
STAGE 2: _____________________ infect __________________ cells, where more
merozoites are created, that _____________ out and infect more cells. When the cells die,
malaria causes these medical problems:
3. Malaria is transferred to another person when…… a mosquito bites and infected host, and
then carries the Plasmodium parasite to someone who is not yet infected.
You might also like
- Ecology Unit Test NAMEDocument5 pagesEcology Unit Test NAMEapi-25965241No ratings yet
- Animal Behavior Intro, Nervous System Intro To Animal BehaviorDocument19 pagesAnimal Behavior Intro, Nervous System Intro To Animal Behaviorapi-25965241No ratings yet
- NullDocument7 pagesNullapi-25965241No ratings yet
- NullDocument3 pagesNullapi-25965241No ratings yet
- INFECTIOUS DISEASE NOTES: 1. What's The Difference Between PathologyDocument1 pageINFECTIOUS DISEASE NOTES: 1. What's The Difference Between Pathologyapi-25965241No ratings yet
- Ecology Unit Test NAMEDocument5 pagesEcology Unit Test NAMEapi-25965241No ratings yet
- Interactions in Communities: Section 2Document16 pagesInteractions in Communities: Section 2api-25965241No ratings yet
- INFECTIOUS DISEASE NOTES: 1. What's The Difference Between PathologyDocument1 pageINFECTIOUS DISEASE NOTES: 1. What's The Difference Between Pathologyapi-25965241No ratings yet
- NullDocument7 pagesNullapi-25965241No ratings yet
- NullDocument3 pagesNullapi-25965241No ratings yet
- NullDocument2 pagesNullapi-25965241No ratings yet
- The Immune Response System: Figure 7 Antigens (Small GreenDocument1 pageThe Immune Response System: Figure 7 Antigens (Small Greenapi-25965241No ratings yet
- A. Big Idea of Ecology-Interdependence: - Everything Is ConnectedDocument11 pagesA. Big Idea of Ecology-Interdependence: - Everything Is Connectedapi-25965241No ratings yet
- Ritchie Player School RD 1 RD 2RD 3RD 4RD 5RD 6 Total Points Martacho Player School RD 1RD 2RD 3RD 4RD 5RD 6total PointsDocument4 pagesRitchie Player School RD 1 RD 2RD 3RD 4RD 5RD 6 Total Points Martacho Player School RD 1RD 2RD 3RD 4RD 5RD 6total Pointsapi-25965241No ratings yet
- Name Class DateDocument2 pagesName Class Dateapi-25965241No ratings yet
- 12.4.3: Evolution Fill in The Blank WithDocument3 pages12.4.3: Evolution Fill in The Blank Withapi-25965241No ratings yet
- Name Class DateDocument2 pagesName Class Dateapi-25965241No ratings yet
- Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Section 3 Bellringer AlternatelyDocument10 pagesSkeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Section 3 Bellringer Alternatelyapi-25965241No ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Test: Patterns of InheritanceDocument3 pagesChapter 12 Test: Patterns of Inheritanceapi-25965241100% (1)
- QuickTime and A TIFF (Uncompressed) Decompressor Are Needed To SeeDocument2 pagesQuickTime and A TIFF (Uncompressed) Decompressor Are Needed To Seeapi-25965241No ratings yet
- NameDocument3 pagesNameapi-25965241No ratings yet
- Chapter Test: Cell ReproductionDocument3 pagesChapter Test: Cell Reproductionapi-25965241No ratings yet
- Tissue Identification QuizDocument1 pageTissue Identification Quizapi-25965241No ratings yet
- A&P Tissue Quiz 2008Document2 pagesA&P Tissue Quiz 2008api-25965241No ratings yet
- QUESTIONS 1) Connects With Myosin During Muscle Contraction 2)Document2 pagesQUESTIONS 1) Connects With Myosin During Muscle Contraction 2)api-25965241No ratings yet
- Animal Anatomy and Physiology A. Organisms Are "Organized" CellsDocument3 pagesAnimal Anatomy and Physiology A. Organisms Are "Organized" Cellsapi-25965241No ratings yet
- A&P TISSUE TEST: 1,2. Tissues Are Made of Cells andDocument3 pagesA&P TISSUE TEST: 1,2. Tissues Are Made of Cells andapi-25965241No ratings yet
- Overview of Major Organ Systems (P. 841) SystemDocument2 pagesOverview of Major Organ Systems (P. 841) Systemapi-25965241No ratings yet
- Overview of Major Organ Systems (P. 841) SystemDocument2 pagesOverview of Major Organ Systems (P. 841) Systemapi-25965241No ratings yet
- Overview of Major Organ Systems (P. 841) SystemDocument2 pagesOverview of Major Organ Systems (P. 841) Systemapi-25965241No ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Sample Outline For Monroes Motivated SequenceDocument1 pageSample Outline For Monroes Motivated SequenceAtiqah Nadirah100% (1)
- Var TMP TMP Generated AABBTechnicalManual18thEd2014 AABB Technical Manual 18th Ed 2014Document824 pagesVar TMP TMP Generated AABBTechnicalManual18thEd2014 AABB Technical Manual 18th Ed 2014Hoàng Nguyễn VănNo ratings yet
- Common Hospital Diseases Requiring Isolation PrecautionsDocument1 pageCommon Hospital Diseases Requiring Isolation Precautionsjerimiah_manzonNo ratings yet
- In Practice Blood Transfusion in Dogs and Cats1Document7 pagesIn Practice Blood Transfusion in Dogs and Cats1何元No ratings yet
- 1 Introduction To AnemiaDocument60 pages1 Introduction To AnemiaKhisha RangasNo ratings yet
- Hematology: H. NO. 1-9-645, Vidyanagar, Adikmet Road, Near SBH, Hyderabad-500 044Document3 pagesHematology: H. NO. 1-9-645, Vidyanagar, Adikmet Road, Near SBH, Hyderabad-500 044Yours PharmacyNo ratings yet
- Bacterial and Viral InfectionsDocument4 pagesBacterial and Viral InfectionsFrancisco CastroNo ratings yet
- Pandemic - On The Brink (Manual)Document8 pagesPandemic - On The Brink (Manual)Friedslick6No ratings yet
- Blood Grouping ReagentsDocument7 pagesBlood Grouping ReagentsDominic EmerencianaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 24 VirusesDocument3 pagesChapter 24 VirusesBlairNo ratings yet
- Table of Blood Group Systems v. 9.0 03-FEB-2021Document3 pagesTable of Blood Group Systems v. 9.0 03-FEB-2021AnthonyNo ratings yet
- Aloa Chromogenic Media For Listeria Sales Flyer Du407a PDFDocument2 pagesAloa Chromogenic Media For Listeria Sales Flyer Du407a PDFazalea freyaNo ratings yet
- Vaccination Certificate: Pet's Name Specie Breed Date of Birth Color/Marking Owner Address Contact NoDocument8 pagesVaccination Certificate: Pet's Name Specie Breed Date of Birth Color/Marking Owner Address Contact NoMaria GraciaNo ratings yet
- Renal MicrobiologyDocument36 pagesRenal MicrobiologyHayelom MichaelNo ratings yet
- Bacteraemia Caused by Kytococcus Schroeteri in A Pneumonia Patient PDFDocument3 pagesBacteraemia Caused by Kytococcus Schroeteri in A Pneumonia Patient PDFeko subiantoNo ratings yet
- CBC ResultsDocument2 pagesCBC ResultsNamithaNo ratings yet
- Examination of Bacterial Contamination in Blood ComponentsDocument21 pagesExamination of Bacterial Contamination in Blood ComponentsCik KahadiNo ratings yet
- Gram Staining:: Gram-Negative Bacteria Such As The Salmonella Typhi That Is Associated With Typhoid Fever. PurposeDocument2 pagesGram Staining:: Gram-Negative Bacteria Such As The Salmonella Typhi That Is Associated With Typhoid Fever. PurposeIravati RayNo ratings yet
- ID Prevalensi Dan Serovar Penyebab LeptospiDocument5 pagesID Prevalensi Dan Serovar Penyebab LeptospiEmeliana JoviantyNo ratings yet
- Bacteria: Small Living Things That Can Be Found Almost EverywhereDocument4 pagesBacteria: Small Living Things That Can Be Found Almost EverywhereIsmilNo ratings yet
- Emerging & Reemerging InfectionsDocument18 pagesEmerging & Reemerging InfectionsBiManda Rizki NurhidayatNo ratings yet
- Hemolytic Disease of the Fetus and Newborn (HDFNDocument46 pagesHemolytic Disease of the Fetus and Newborn (HDFNK.M.S. ChathunikaNo ratings yet
- Gram Negative BacilliDocument15 pagesGram Negative BacilliFabasyira JamalNo ratings yet
- Build Your Own VirusDocument3 pagesBuild Your Own ViruschobynetNo ratings yet
- Ocular Microbiology PDFDocument2 pagesOcular Microbiology PDFKarissaNo ratings yet
- Compatibility Testing: Dr. Mohammed H Saiem Aldahr Blood Bank 3 Medical TechnologyDocument44 pagesCompatibility Testing: Dr. Mohammed H Saiem Aldahr Blood Bank 3 Medical TechnologyAnne Lorraine Margarette DulayNo ratings yet
- Baby UZMA's Complete Haemogram ReportDocument2 pagesBaby UZMA's Complete Haemogram ReportmonsterindiaNo ratings yet
- Brosur AcrossDocument8 pagesBrosur Acrossnurul fadhilahNo ratings yet
- Overview of Hemolytic Disease of Fetus and Newborn Erythroblastosis FetalisDocument3 pagesOverview of Hemolytic Disease of Fetus and Newborn Erythroblastosis FetalisEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- EMQ Samples MicrobiologyDocument5 pagesEMQ Samples MicrobiologyHugh JacobsNo ratings yet