Professional Documents
Culture Documents
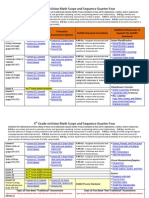
Alg 2 Scope and Sequence 4th Quarter 2012-2013
Uploaded by
api-70433300Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Alg 2 Scope and Sequence 4th Quarter 2012-2013
Uploaded by
api-70433300Copyright:
Available Formats
Larson Algebra 2 Scope and Sequence (SY 2012-2013)
Standards NOT addressed by Larson Algebra 2: A2.1.5: Determine and interpret maximum and minimum values for quadratic equations A2.3.1: Use the definition of logarithms to translate between logarithms in any base; A2.5.4a Solve equations and inequalities involving absolute values of linear expressions; A2.5.7: Determine the type of function that best fits the context of a basic application (e.g., linear to solve distance/time problems; quadratic to explain the motion of a falling object, exponential; to model bacteria growth, piece-wise to model postage rates, or absolute value functions to represent distance from the mean);
4th Quarter
Chapter 9: Quadratic Relations & Conic Sections
Lesson 9.1: Apply the Distance and Midpoint Formulas (Pgs 614 619) Prerequisite for: Lesson 9.2: Graph and Write Equations of Parabolas (Pgs 620-625) Lesson 9.3: Graph and Write Equations of Circles (Pgs 626 633) Lesson 9.4: Graph and Write Equations of Ellipses (Pgs 634 640) Lesson 9.1-9.4 : Mixed Review of Problem Solving (Pg 641)
DoDEA Standard Correlation
A2.4.1 Describe connections between the geometric definition and the algebraic equations of the conic sections (parabola, circle, ellipse, hyperbola); A2.4.1 Describe connections between the geometric definition and the algebraic equations of the conic sections (parabola, circle, ellipse, hyperbola); A2.4.1 Describe connections between the geometric definition and the algebraic equations of the conic sections (parabola, circle, ellipse, hyperbola); A2.4.1 Describe connections between the geometric definition and the algebraic equations of the conic sections (parabola, circle, ellipse, hyperbola); DoDEA Process Standards
Additional Resources to Support the DoDEA Standards
Smart Exchange: Parabolas (Question Set) [question set] Algebra 2 - Graphing Conic Sections - Parabolas Graph Conic Sections Conic Sections (Question Set) [question set] Circles (Question Set) [question set] Graphing Circles Ellipses (Question Set) [question set] Hyperbolas (Question Set) [question set] Discovery Education: Math Factor: Quadratic Relations Review (29:15) Defining General Characteristics of Conic Sections (04:40) Math Factor: General Quadratic Relation: Parabolas and Hyperbolas (29:15) Manipulating General Term Coefficients to Produce Parabolas (08:26) Creating Conic Degenerates from Parabolic Equations (05:06) Math Factor: General Quadratic Relation: An Introduction Lesson Plans: Equations of Circles
Larson Algebra 2 Scope and Sequence (SY 2012-2013)
Standards NOT addressed by Larson Algebra 2: A2.1.5: Determine and interpret maximum and minimum values for quadratic equations A2.3.1: Use the definition of logarithms to translate between logarithms in any base; A2.5.4a Solve equations and inequalities involving absolute values of linear expressions; A2.5.7: Determine the type of function that best fits the context of a basic application (e.g., linear to solve distance/time problems; quadratic to explain the motion of a falling object, exponential; to model bacteria growth, piece-wise to model postage rates, or absolute value functions to represent distance from the mean);
Lesson 9.5: Graph and Write Equations of Hyperbolas (Pgs 642 648) Lesson 9.6: Translate and Classify Conic Sections (Pgs 650 657) Incorporate w/ Lessons 9.2 9.5 Lesson 9.7: Solve Quadratic Systems (Pgs 658 666) Lesson 9.5-9.7 : Mixed Review of Problem Solving (Pg 667) Chapter 9: Summary, Review, Test Practice (Pgs 668 679)
A2.4.1 Describe connections between the geometric definition and the algebraic equations of the conic sections (parabola, circle, ellipse, hyperbola); A2.4.2 Identify specific characteristics (center, vertex, foci, directrix, asymptotes etc.) of conic sections from their equation or graph; A2.4.3 Use the techniques of translations and rotation of axis in the coordinate plane to graph conic sections No DODEA Algebra 2 Standards
The Standard and General Form of the Parabola Given Its Graph Thar She Blows! Chapter 9 Opener Formative: Flashcards: Al2-Quadratic Relations & Conic Sections Functions 2 - Cubics & Quadratics Quadratics Quadratics and Axis of Symmetry (Lula-ipod) Conic Sections (chapter 9 review) Conic Sections formulas Circles - Intro Ellipses - Intro Parabolas - Intro Hyperbolas - Intro Circles - The Formula & Graphing Ellipses - The Formula & Graphing Hyperbolas - The Formula & Graphing Tutorials: Introduction to Conic Sections (Khan) Identifying Conics 1 (Khan) Algebra ||: Conic Sections (Khan) Identifying Conics 2 (Khan) Conic Identification 3 (Khan) Parabola Focus and Directrix 1 (Khan) Focus and Directrix of a Parabola 2 (Khan) Non-Linear Systems of Equations 1 (Khan) Non-Linear Systems of Equations 2 (Khan) Non-Linear Systems of Equations 3 (Khan) Conic Sections: Intro to Circles (Khan)
DoDEA Process Standards
Last Edit: 4 Apr 2013
Algebra 2: 4th Quarter Planning Guide (SY 2012-2013)
Larson Algebra 2 Scope and Sequence (SY 2012-2013)
Standards NOT addressed by Larson Algebra 2: A2.1.5: Determine and interpret maximum and minimum values for quadratic equations A2.3.1: Use the definition of logarithms to translate between logarithms in any base; A2.5.4a Solve equations and inequalities involving absolute values of linear expressions; A2.5.7: Determine the type of function that best fits the context of a basic application (e.g., linear to solve distance/time problems; quadratic to explain the motion of a falling object, exponential; to model bacteria growth, piece-wise to model postage rates, or absolute value functions to represent distance from the mean);
Web-Based Activities: Graphing the Circle Graphing the Ellipse and Hyperbola Graphing the Hyperbola Technology Connection: Quadratic Relations vs. Quadratic Functions (ti-84+) Circle (ti-84+) Ellipse (ti-84+) Parabola (ti-84+) Hyperbola (ti-84+) Circle Equations (ti-84+) Circles - Exploring the Equation (ti-84+) Conic Sections (ti-84+) Parabola Construction (ti-84+) Properties of Parabolas (ti-84+) Last Edit: 4 Apr 2013
Algebra 2: 4th Quarter Planning Guide (SY 2012-2013)
Algebra II: Circles and Logarithms (Khan) Three Points Defining a Circle (Khan) Conic Sections: Intro to Ellipses (Khan) Foci of an Ellipse (Khan) Conic Sections: Intro to Hyperbolas (Khan) Conic Sections: Hyperbolas 2 (Khan) Conic Sections: Hyperbolas 3 (Khan) Foci of a Hyperbola (Khan) Proof: Hyperbola Foci (Khan) Introduction to Conic Sections (Brightstorm) The Circle (Brightstorm) The Ellipse (Brightstorm) The Hyperbola (Brightstorm) Transformations of a Hyperbola (Brightstorm) Conic Section Formulas (Brightstorm)
Larson Algebra 2 Scope and Sequence (SY 2012-2013)
Standards NOT addressed by Larson Algebra 2: A2.1.5: Determine and interpret maximum and minimum values for quadratic equations A2.3.1: Use the definition of logarithms to translate between logarithms in any base; A2.5.4a Solve equations and inequalities involving absolute values of linear expressions; A2.5.7: Determine the type of function that best fits the context of a basic application (e.g., linear to solve distance/time problems; quadratic to explain the motion of a falling object, exponential; to model bacteria growth, piece-wise to model postage rates, or absolute value functions to represent distance from the mean);
Chapter 10: Counting Methods & Probability Chapter 11: Data Analysis & Statistics
No DODEA Algebra 2 Standards No DODEA Algebra 2 Standards
Chapter 12: Sequences & Series
Lesson 12.1: Define & Use Sequences & Series (Pgs 794 801)
DoDEA Standard Correlation
A2.2.1 Use recursion to describe a sequence; A2.2.2 Determine the terms and partial sums of arithmetic and geometric series and the infinite sum for geometric series; A2.2.3 Explain and use summation notation to model an arithmetic series and of both finite and infinite geometric series; A2.2.6 Solve word problems involving applications of sequences and series; A2.2.2 Determine the terms and partial sums of arithmetic and geometric series and the infinite sum for geometric series; A2.2.4 Prove and use the sum formulas for arithmetic series and for finite and infinite geometric series; A2.2.6 Solve word problems involving applications of sequences and series;
Additional Resources to Support the DoDEA Standards
Smart Exchange: Arithmetic Sequences Sequence and Series Foldable Geometric Sequences (Question set) Arithmetic and Geometric Series (Question set) Discovery Education: Math Factor: Sequences and Series Review (29:15) Using Formulae and Patterns to Define Sequences (07:33) Defining Arithmetic Sequences (03:56) Defining Geometric Sequences (05:08) Math Factor: Geometric Series (29:15) Defining Geometric Series (09:22) Using Formulae to Solve for Variables in Geometric Series (09:52) Using Alternative Methods to Solve Geometric Series (06:14) Math Factor: Arithmetic Series (29:15)
Lesson 12.2: Analyze Arithmetic Sequences & Series (Pgs 802 809)
Last Edit: 4 Apr 2013
Algebra 2: 4th Quarter Planning Guide (SY 2012-2013)
Larson Algebra 2 Scope and Sequence (SY 2012-2013)
Standards NOT addressed by Larson Algebra 2: A2.1.5: Determine and interpret maximum and minimum values for quadratic equations A2.3.1: Use the definition of logarithms to translate between logarithms in any base; A2.5.4a Solve equations and inequalities involving absolute values of linear expressions; A2.5.7: Determine the type of function that best fits the context of a basic application (e.g., linear to solve distance/time problems; quadratic to explain the motion of a falling object, exponential; to model bacteria growth, piece-wise to model postage rates, or absolute value functions to represent distance from the mean);
Lesson 12.3: Analyze Geometric Sequences & Series (Pgs 810 817)
A2.2.2 Determine the terms and partial sums of arithmetic and geometric series and the infinite sum for geometric series; A2.2.3 Explain and use summation notation to model an arithmetic series and of both finite and infinite geometric series; A2.2.4 Prove and use the sum formulas for arithmetic series and for finite and infinite geometric series; A2.2.6 Solve word problems involving applications of sequences and series;
Finding the Sum of Terms in Arithmetic Series (10:15) Graphing and Solving Arithmetic Series (08:11) Using Alternative Methods to Solve Arithmetic Series (08:28) Lesson Plans: SparkNotes: Sequences and Series General Sequences and Series Arithmetic Sequences Geometric Sequences Sequence and Series Geometric Sequences and Series Recursive Sequences Cartoon Sequencing - a Warm-Up to Sequences Arithmetic Sequences and Series Geometric Sequences and Series Introduction to Sequences and Series Chapter12 Opener Formative: Practice with Recursive Sequences Practice with Sequences Practice with Arithmetic Sequences and Series Practice with Application Problems Alg 2: Series and Sequences Sequences & Series: What's a Sequence? Sequences & Series: Sequences With Formulas Sequences & Series: Series and Sigma Notation Sequences & Series: Some Sigma Properties Sequences & Series: Arithmetic Sequences Sequences & Series: Gauss's Problem and Sums of
Lesson 12.1 12.3: Mixed Review of Problem Solving (Pg 818) Lesson 12.4: Find Sums of Infinite Geometric Series (Pgs 819 825)
DoDEA Process Standards A2.2.5 Explain and use the concept of limit of a sequence or function as the independent variable approaches infinity or a number; A2.2.6 Solve word problems involving applications of sequences and series; A2.2.1 Use recursion to describe a sequence; A2.2.6 Solve word problems involving applications of sequences and series;
Lesson 12.5: Use Recursive Rules with Sequences & Functions (Pgs 826 832)
Last Edit: 4 Apr 2013
Algebra 2: 4th Quarter Planning Guide (SY 2012-2013)
Larson Algebra 2 Scope and Sequence (SY 2012-2013)
Standards NOT addressed by Larson Algebra 2: A2.1.5: Determine and interpret maximum and minimum values for quadratic equations A2.3.1: Use the definition of logarithms to translate between logarithms in any base; A2.5.4a Solve equations and inequalities involving absolute values of linear expressions; A2.5.7: Determine the type of function that best fits the context of a basic application (e.g., linear to solve distance/time problems; quadratic to explain the motion of a falling object, exponential; to model bacteria growth, piece-wise to model postage rates, or absolute value functions to represent distance from the mean);
Lesson 12.4 12.5 : Mixed Review of Problem Solving (Pg 838) Chapter 12: Summary, Review, Test Practice (Pgs 839 849)
DoDEA Process Standards
Arithmetic Sequences (Series) Sequences & Series: Geometric Sequences Sequences & Series: Sums of Geometric Sequences (Series) Sequences & Series: The Binomial Theorem Tutorials: Sequences and Series (part 1) (Khan) Sequences and series (part 2) (Khan) Geometric Sequences (Introduction) Sequences (Khan) Series (Khan) Arithmetic Sequences (Khan) Geometric Sequences (Khan) Binomial Expansion (Khan) Introduction to Sequences (Brightstorm) Series and Summation Notation (Brightstorm) Arithmetic Sequences (Brightstorm) Arithmetic Series (Brightstorm) Geometric Sequences (Brightstorm) Geometric Series (Brightstorm) Recursion Sequences (Brightstorm) Mathematical Induction (Brightstorm) Web-Based Activities: Towers of Hanoi The Sequencer Activity (Shodor) Pattern Generator (Shodor) Technology Connection: Arithmetic Sequences & Series (ti-84+) Geometric Sequences & Series (ti-84+) Recursive Sequences (ti-84+)
Last Edit: 4 Apr 2013
Algebra 2: 4th Quarter Planning Guide (SY 2012-2013)
Larson Algebra 2 Scope and Sequence (SY 2012-2013)
Standards NOT addressed by Larson Algebra 2: A2.1.5: Determine and interpret maximum and minimum values for quadratic equations A2.3.1: Use the definition of logarithms to translate between logarithms in any base; A2.5.4a Solve equations and inequalities involving absolute values of linear expressions; A2.5.7: Determine the type of function that best fits the context of a basic application (e.g., linear to solve distance/time problems; quadratic to explain the motion of a falling object, exponential; to model bacteria growth, piece-wise to model postage rates, or absolute value functions to represent distance from the mean);
Sequence Investigation (ti-84+) Sums of Sequences (ti-84+)
Chapter 13: Trigonometric Ratios & Functions Chapter 14: Trigonometric Graphs, Identities, and Equations
No DODEA Algebra 2 Standards No DODEA Algebra 2 Standards
Last Edit: 4 Apr 2013
Algebra 2: 4th Quarter Planning Guide (SY 2012-2013)
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- 2019 Staar Algebra I Test TaggedDocument44 pages2019 Staar Algebra I Test TaggedBUBBLEGUMDUM sicklesNo ratings yet
- Omer G G10 Summative Assessment - Criterion B Linear EquationDocument6 pagesOmer G G10 Summative Assessment - Criterion B Linear EquationOmerG100% (1)
- Dam Safety PDFDocument51 pagesDam Safety PDFAndyara DuarteNo ratings yet
- Learning Module: AlgebraDocument166 pagesLearning Module: AlgebraJunel Icamen EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Transport Phenomena - Monash University Final - Exam - 2010 - SolutionDocument15 pagesTransport Phenomena - Monash University Final - Exam - 2010 - SolutionKunal BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Absolute ValueDocument19 pagesAbsolute Valueapi-70433300No ratings yet
- Thom. Structural Stability, Catastrophe Theory, and Applied Mathematics. The John Von NeumannDocument14 pagesThom. Structural Stability, Catastrophe Theory, and Applied Mathematics. The John Von NeumannMikhail IampolskiNo ratings yet
- BDA (Before, During After) Lesson Plan TemplateDocument3 pagesBDA (Before, During After) Lesson Plan Templateapi-404225281No ratings yet
- 8th Grade Quarter Four Planning Guide 2012-2013Document6 pages8th Grade Quarter Four Planning Guide 2012-2013api-70433300No ratings yet
- 6th Grade Quarter Four Planning Guide 2012-2013Document8 pages6th Grade Quarter Four Planning Guide 2012-2013api-70433300No ratings yet
- 7th Grade Math Connects Planning Guide Quarter Four 2012-2013Document4 pages7th Grade Math Connects Planning Guide Quarter Four 2012-2013api-70433300No ratings yet
- 4th Quarter 4 Planning Guide 2012-2013Document9 pages4th Quarter 4 Planning Guide 2012-2013api-70433300No ratings yet
- 3rd Quarter 4 Planning Guide 2012-2013Document10 pages3rd Quarter 4 Planning Guide 2012-2013api-70433300No ratings yet
- 5th Quarter 4 Planning Guide 2012-2013Document8 pages5th Quarter 4 Planning Guide 2012-2013api-70433300No ratings yet
- Alg I Scope and Sequence 4th Quarter 2012-2013Document7 pagesAlg I Scope and Sequence 4th Quarter 2012-2013api-70433300No ratings yet
- Analysis Scope and Sequence 4th Quarter 2012-2013Document5 pagesAnalysis Scope and Sequence 4th Quarter 2012-2013api-70433300No ratings yet
- Discrete Math Scope and Sequence 4th Quarter 2012-2013Document3 pagesDiscrete Math Scope and Sequence 4th Quarter 2012-2013api-70433300No ratings yet
- Geometry Scope and Sequence 4th Quarter 2012-2013Document6 pagesGeometry Scope and Sequence 4th Quarter 2012-2013api-70433300No ratings yet
- Ap Job-Alike Agenda 2012Document1 pageAp Job-Alike Agenda 2012api-70433300No ratings yet
- Algebric Modeling Scope and Sequence 4th Quarter 2012-2013Document3 pagesAlgebric Modeling Scope and Sequence 4th Quarter 2012-2013api-70433300No ratings yet
- Grad Credit Course Guidelines-Nspire TechnologyDocument3 pagesGrad Credit Course Guidelines-Nspire Technologyapi-70433300No ratings yet
- Ap Job-Alike Facilitator Summary 2012Document1 pageAp Job-Alike Facilitator Summary 2012api-70433300No ratings yet
- TI-Nspire CX ManualDocument118 pagesTI-Nspire CX Manualjsmith96No ratings yet
- OR QuizDocument5 pagesOR QuizMr NerdNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ProjectDocument51 pagesChemistry ProjectSiddhanth AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Day 6 - Remedial - Radical ExpressionsDocument3 pagesDay 6 - Remedial - Radical ExpressionsDaryll Andre Keith AsuncionNo ratings yet
- FmseDocument5 pagesFmseJacky Boy Endencio AtienzaNo ratings yet
- Development of A Correlation For The Estimation of Condensate To Gas Ratio and Other Key Gas Properties From Density Molecular WeightDocument18 pagesDevelopment of A Correlation For The Estimation of Condensate To Gas Ratio and Other Key Gas Properties From Density Molecular WeightDorothyNRNo ratings yet
- Analisis Bertopik Form 3 Chap 6 10 RDocument23 pagesAnalisis Bertopik Form 3 Chap 6 10 RSean GomezNo ratings yet
- FVM PresentationDocument33 pagesFVM PresentationManas Manoj RedijNo ratings yet
- Scientific Work PlaceDocument551 pagesScientific Work Placepeloton10No ratings yet
- Solution of A Partial Differential Equations Using The Method of LinesDocument16 pagesSolution of A Partial Differential Equations Using The Method of LinesSandip KadoliNo ratings yet
- Maths X Assertion Reasoning Chapter 03Document14 pagesMaths X Assertion Reasoning Chapter 03Katyayini ShettyNo ratings yet
- Add Maths Practice Set 12Document6 pagesAdd Maths Practice Set 12Athanaseus ShazamNo ratings yet
- ECON 1003 - Maths For Social Sciences IDocument4 pagesECON 1003 - Maths For Social Sciences IKalsia RobertNo ratings yet
- EeDocument33 pagesEeAhtide OtiuqNo ratings yet
- M.S.thesis Zhong - Inverse Algorithm For Determination of Heat FluxDocument123 pagesM.S.thesis Zhong - Inverse Algorithm For Determination of Heat FluxJinsoo KimNo ratings yet
- Syllabus BTech Civil 2019 1Document72 pagesSyllabus BTech Civil 2019 1ravi maskeNo ratings yet
- A Formula For Resistance Substation Grounding Grid in Two-Layer SoilDocument8 pagesA Formula For Resistance Substation Grounding Grid in Two-Layer SoilGabriel A. Gabriel MarmolejosNo ratings yet
- Daa2 Te CH4 PDFDocument70 pagesDaa2 Te CH4 PDFjordybeltNo ratings yet
- Class 8 Math Worksheet 05-CDocument5 pagesClass 8 Math Worksheet 05-CAdam shakilNo ratings yet
- Algebra 02 07 16 SolutionsDocument7 pagesAlgebra 02 07 16 SolutionsCheah Chee YoongNo ratings yet
- Math 7 Episode 1 Q3 SLMDocument5 pagesMath 7 Episode 1 Q3 SLMCaryll BaylonNo ratings yet
- Lec 17Document13 pagesLec 17vishnu anilNo ratings yet