Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Stirling Engine Mini Project-Abstract
Uploaded by
Vishnu PullanikkatOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Stirling Engine Mini Project-Abstract
Uploaded by
Vishnu PullanikkatCopyright:
Available Formats
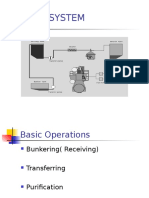
ABSTRACT Stirling Engine
A Stirling engine is a heat engine operating by cyclic compression and expansion of air or other gas, the working fluid, at different temperature levels such that there is a net conversion of heatenergy to mechanical work. Or more specifically, a closed-cycle regenerative heat engine with a permanently gaseous working fluid, where closed-cycle is defined as a thermodynamic system in which the working fluid is permanently contained within the system, and regenerative describes the use of a specific type of internal heat exchanger and thermal store, known as the regenerator. It is the inclusion of a regenerator that differentiates the Stirling engine from other closed cycle hot air engines. Originally conceived in 1816 as an industrial prime mover to rival the steam engine, its practical use was largely confined to low-power domestic applications for over a century. The Stirling engine is noted for its high efficiency compared to steam engines, quiet operation, and the ease with which it can use almost any heat source. This compatibility with alternative and renewable energy sources has become increasingly significant as the price of conventional fuels rises, and also in light of concerns such as peak oil and climate change. This engine is currently exciting interest as the core component of micro combined heat and power (CHP) units, in which it is more efficient and safer than a comparable steam engine. As a part of our mini-project , we are visualizing the use of Stirling engine in various fields where waste energy is of large concern . Simply(say for eg;) , we can utilize the exhaust gas temperature from restaurant chimnnis itself for running the exhaust fan/turbine.
Group members: Vishnu P , Vipin P V , Vincent G Thomas , Vineeth C
You might also like
- CARTEX Operating Manual Incl - Sctional DRWG Rev 4Document11 pagesCARTEX Operating Manual Incl - Sctional DRWG Rev 4keyur1109No ratings yet
- Cylinder Head AssignmentDocument17 pagesCylinder Head Assignmentabhishek_m_moreNo ratings yet
- Engine Overhauling AssignmentDocument11 pagesEngine Overhauling AssignmentSabeeh Safdar100% (1)
- How Do I Write The First Email To A Professor For PHD ApplicationDocument10 pagesHow Do I Write The First Email To A Professor For PHD ApplicationVishnu PullanikkatNo ratings yet
- Stirling Engine - WikipediaDocument33 pagesStirling Engine - WikipediaH.J.PrabhuNo ratings yet
- High Performance Free-Piston Stirling EnginesDocument6 pagesHigh Performance Free-Piston Stirling EnginesSergiu GritarovschiNo ratings yet
- Information Service: Cylinder Reconditioning On Aluminium Cylinder BlocksDocument0 pagesInformation Service: Cylinder Reconditioning On Aluminium Cylinder BlocksMoaed KanbarNo ratings yet
- TATA Minibus 407 MaintainanceDocument13 pagesTATA Minibus 407 MaintainancePraveen Kumar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Vidya Vardhaka College of Engineering Mysuru: "Diesel Particulate Filter"Document15 pagesVidya Vardhaka College of Engineering Mysuru: "Diesel Particulate Filter"dhanalakshmi k sNo ratings yet
- Bio Ethanol DBGDocument30 pagesBio Ethanol DBGGhulam RabbaniNo ratings yet
- Diesel EnginesDocument23 pagesDiesel EnginesSanket BalapurkarNo ratings yet
- MotoHawk Software PSDocument6 pagesMotoHawk Software PSCABean1No ratings yet
- Gasoline Particulate FiltersDocument23 pagesGasoline Particulate FiltersvigneshwaranNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four.1Document160 pagesChapter Four.1Marew GetieNo ratings yet
- Engine Performance Optimization - GT PowerDocument2 pagesEngine Performance Optimization - GT Powermanoj262400/2No ratings yet
- MAN发动机Document1 pageMAN发动机blueseatxNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Automobile EngineeringDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Automobile EngineeringSaurabh AwacharNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 - Ignition SystemDocument12 pagesChapter 16 - Ignition SystemsezarNo ratings yet
- Technical Presentation On Engine ValvesDocument32 pagesTechnical Presentation On Engine ValvesRockey RahulNo ratings yet
- Fuel System-4Document23 pagesFuel System-4Gian Carlo RamirezNo ratings yet
- Top Ten Basic Diesel Engine Maintenance SecretsDocument20 pagesTop Ten Basic Diesel Engine Maintenance SecretsdonlynNo ratings yet
- Air Charge-Air Cooling: Diesel Generator SetDocument4 pagesAir Charge-Air Cooling: Diesel Generator Settctctc123No ratings yet
- Efficiency Assessment of Condensing Steam Turbine-DL From Wseas - UsDocument6 pagesEfficiency Assessment of Condensing Steam Turbine-DL From Wseas - UsGirish OniyilNo ratings yet
- STF Industrial BoilersDocument20 pagesSTF Industrial BoilersDaniellzhangNo ratings yet
- Four Stroke Diesel EngineDocument9 pagesFour Stroke Diesel Engineteguh arif pratama adi putraNo ratings yet
- MWM 600Document4 pagesMWM 600Habib A. IslamNo ratings yet
- Audi A6 2.5TDiDocument25 pagesAudi A6 2.5TDiAudi A6 2.5TDi0% (1)
- Fuel Supply System System in S.I EngineDocument47 pagesFuel Supply System System in S.I EngineSanjay HedgeNo ratings yet
- Himanshu Singh Turbocharger-SeminarDocument20 pagesHimanshu Singh Turbocharger-SeminarHimanshu SinghNo ratings yet
- Guascor Biogas DepuradorasDocument8 pagesGuascor Biogas DepuradorasMartin KratkyNo ratings yet
- Multi-Fuel EnginesDocument23 pagesMulti-Fuel EnginesArpit Roy50% (2)
- Engine-Powered Laden Container Handler 36 000 KG and 40 000 KGDocument4 pagesEngine-Powered Laden Container Handler 36 000 KG and 40 000 KGNuñez JesusNo ratings yet
- VSI DI EnglishDocument4 pagesVSI DI EnglishZoli BorbelyNo ratings yet
- Wankel EngineDocument15 pagesWankel EngineMuhammad Bin RiazNo ratings yet
- Bow Thrusters: Speeds Your PerformanceDocument16 pagesBow Thrusters: Speeds Your PerformanceKelvin XuNo ratings yet
- Types of Scavenging: Loop or Cross Scavenge UniflowDocument22 pagesTypes of Scavenging: Loop or Cross Scavenge UniflowBharatiyulamNo ratings yet
- Stargas PDFDocument23 pagesStargas PDFcalinrettNo ratings yet
- Valvetronic Engine My ReportDocument29 pagesValvetronic Engine My ReportABINASH SAMANTARAYNo ratings yet
- Hubner Articulated Buses SystemsDocument4 pagesHubner Articulated Buses Systemspunk9891215No ratings yet
- How Diesel Engines WorkDocument23 pagesHow Diesel Engines WorkBabu Stunner100% (1)
- Category MotorsDocument4 pagesCategory MotorsKevin CondorNo ratings yet
- Variable Copression Ratio EnginesDocument18 pagesVariable Copression Ratio EnginesNicole LucasNo ratings yet
- 16 - E65 Automatic Trunk Lid LiftDocument9 pages16 - E65 Automatic Trunk Lid LiftKent Wai100% (1)
- HIMSEN Catalog 2010Document46 pagesHIMSEN Catalog 2010A87_navjNo ratings yet
- Installation Manual Esgi2 R115 EngDocument27 pagesInstallation Manual Esgi2 R115 EngKhateeb RehmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 - Cylinder Head With ValvesDocument18 pagesChapter 12 - Cylinder Head With Valvesshahin gholamiNo ratings yet
- M Combustion Chamber and Cold Starting of CDocument45 pagesM Combustion Chamber and Cold Starting of CAnonymous LFgO4WbIDNo ratings yet
- Ashok Leyland Inplant ReportDocument22 pagesAshok Leyland Inplant ReportafrithNo ratings yet
- Starter Motor: HistoryDocument4 pagesStarter Motor: HistoryKaiser CarloNo ratings yet
- Perkins 3.152 SpecsDocument12 pagesPerkins 3.152 SpecsMTU650No ratings yet
- 2011 Engine Tech Review MWMDocument2 pages2011 Engine Tech Review MWMGrietekeNo ratings yet
- Brake Assist Seminar ReportDocument19 pagesBrake Assist Seminar Reportyash1239No ratings yet
- Dual Fuel EngineDocument13 pagesDual Fuel EngineVIKASNo ratings yet
- Golf-March-2006 PDFDocument30 pagesGolf-March-2006 PDFCaroline PuckettNo ratings yet
- In-Pulse Universal NEWDocument4 pagesIn-Pulse Universal NEWFabio JuniorNo ratings yet
- L7044gsi 7045 0710Document2 pagesL7044gsi 7045 0710Martin Alejandro NievaNo ratings yet
- Air Mass Sensor For VW TDI Engines PDFDocument2 pagesAir Mass Sensor For VW TDI Engines PDFSrđan PavićNo ratings yet
- Working Fluid: Heat EngineDocument1 pageWorking Fluid: Heat EngineAbdul RaaufNo ratings yet
- Stirling Engine: Name and ClassificationDocument22 pagesStirling Engine: Name and ClassificationAbhishek NaikNo ratings yet
- Stirling MotorDocument14 pagesStirling MotorlinerNo ratings yet
- Stirling EngineDocument33 pagesStirling EnginepracheeNo ratings yet
- What Is The FEM?: FEM: Method For Numerical Solution of Field ProblemsDocument1 pageWhat Is The FEM?: FEM: Method For Numerical Solution of Field ProblemsVishnu PullanikkatNo ratings yet
- 13 PDFDocument1 page13 PDFVishnu PullanikkatNo ratings yet
- 4 PDFDocument1 page4 PDFVishnu PullanikkatNo ratings yet
- 3 PDFDocument1 page3 PDFVishnu PullanikkatNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Finite Element Analysis-5Document1 pageIntroduction To Finite Element Analysis-5Vishnu PullanikkatNo ratings yet
- 2 PDFDocument1 page2 PDFVishnu PullanikkatNo ratings yet
- Development of Radar Absorbing Nanocomposite Coatings Using Electroless TechnologyDocument2 pagesDevelopment of Radar Absorbing Nanocomposite Coatings Using Electroless TechnologyVishnu PullanikkatNo ratings yet