Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Engineering Mathematics II Formulas Studyhaunters PDF
Uploaded by
Sriram JOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Engineering Mathematics II Formulas Studyhaunters PDF
Uploaded by
Sriram JCopyright:
Available Formats
Unit I (Ordinary Differential Equation)
1.ODE with constant coefficients: Solution C.F + P.I y = == =
Complementary functions:
Sl.No. NatureofRoots C.F
1.
1 2
m m = == =
( )
mx
Ax B e + ++ +
2.
1 2 3
m m m = = = = = = = =
( (( ( ) )) )
2 mx
Ax Bx c e + + + + + + + +
3.
1 2
m m
1 2
m x m x
Ae Be + ++ +
4.
1 2 3
m m m
3 1 2
m x m x m x
Ae Be Ce + + + + + + + +
5.
1 2 3
, m m m = == =
3
( )
m x mx
Ax B e Ce + + + + + + + +
6. m i = = = =
( cos sin )
x
e A x B x
+ ++ +
7. m i = = = = cos sin A x B x + ++ +
Particular Integral:
Type-I
If ( ) 0 f x = == =
then . 0 P I = == =
Type-II
If ( )
ax
f x e = == =
1
.
( )
ax
P I e
D
= == =
www.studyhaunters.blogspot.in
www.studyhaunters.blogspot.in
Replace Dby a .If ( ) 0 D ,thenitisP.I.If ( ) 0 D = == = ,thendiff.denominator
w.r.t Dandmultiply x innumerator.Againreplace Dby a .Ifyougetdenominator
againzerothendothesameprocedure.
Type-III
Case: i If ( ) sin ( ) cos f x ax or ax = == =
1
. sin (or) cos
( )
P I ax ax
D
= == =
Hereyouhavetoreplaceonlyfor
2
D notfor D.
2
D isreplacedby
2
a .Ifthe
denominatorisequaltozero,thenapplysameprocedureasinTypeI.
Case: iiIf
2 2 3 3
( ) (or) cos (or) sin (or) cos f x Sin x x x x = == =
Usethefollowingformulas
2
1 cos 2
2
x
Sin x
= == = ,
2
1 cos 2
cos
2
x
x
+ ++ +
= == = ,
x x x = = = =
3
3 1
sin sin sin3
4 4
, x x x = + = + = + = +
3
3 1
cos cos cos 3
4 4
andseparate
1 2
. & . P I P I
Case: iiiIf ( ) sin cos ( ) cos sin ( ) cos cos ( ) sin sin f x A B or A B or A B or A B = == =
Usethefollowingformulas:
( (( ( ) )) )
( (( ( ) )) )
( (( ( ) )) )
( (( ( ) )) )
1
( ) in cos ( ) sin( )
2
1
(ii) cos sin ( ) sin( )
2
1
( ) cos cos cos( ) cos( )
2
1
( ) sin sin cos( ) cos( )
2
i s A B sin A B A B
A B Sin A B A B
iii A B A B A B
iv A B A B A B
= + + = + + = + + = + +
= + = + = + = +
= + + = + + = + + = + +
= + = + = + = +
Type-IV
If ( )
m
f x x =
1
.
( )
m
P I x
D
=
1
1 ( )
m
x
g D
=
+
www.studyhaunters.blogspot.in
www.studyhaunters.blogspot.in
( )
1
1 ( )
m
g D x
= +
HerewecanuseBinomialformulaasfollows:
i) ( )
1
2 3
1 1 ... x x x x
+ = + +
ii) ( )
1
2 3
1 1 ... x x x x
= + + + +
iii) ( )
2
2 3
1 1 2 3 4 ... x x x x
+ = + +
iv) ( )
2
2 3
1 1 2 3 4 ... x x x x
= + + + +
v)
3 2 3
(1 ) 1 3 6 10 ... x x x x
+ = + +
vi)
3 2 3
(1 ) 1 3 6 10 ... x x x x
= + + + +
Type-V
If ( )
ax
f x e V = where sin , cos ,
m
V ax ax x =
1
.
( )
ax
P I e V
D
=
Firstoperate
ax
e byreplacingDbyD+a.
1
( )
ax
e V
D a
=
+
Type-VI
If ( )
n
f x x V = where sin , cos V ax ax =
sin I.P of
cos R.P of
iax
iax
ax e
ax e
=
=
Type-VII(SpecialTypeProblems)
If ( ) sec (or) cosec (or) tan f x ax ax ax =
1
. ( ) ( )
ax ax
P I f x e e f x dx
D a
= =
1. ODEwithvariableco-efficient:(EulersMethod)
Theequationisoftheform
2
2
2
( )
d y dy
x x y f x
dx dx
+ + =
www.studyhaunters.blogspot.in
www.studyhaunters.blogspot.in
Impliesthat
2 2
( 1) ( ) x D xD y f x + + =
Toconvertthevariablecoefficientsintotheconstantcoefficients
Put log z x = implies
z
x e =
2 2
3 3
( 1)
( 1)( 2)
xD D
x D D D
x D D D D
=
=
=
where
d
D
dx
= and
d
D
dz
=
Theaboveequationimpliesthat ( ) ( 1) 1 ( ) D D D y f x + + = whichisO.D.E
withconstantcoefficients.
2. LegendresLineardifferentialequation:
Theequationifoftheform
2
2
2
( ) ( ) ( )
d y dy
ax b ax b y f x
dx dx
+ + + + =
Put log( ) z ax b = + implies ( )
z
ax b e + =
2 2 2
3 3 3
( )
( ) ( 1)
( ) ( 1)( 2)
ax b D aD
ax b D a D D
ax b D a D D D
+ =
+ =
+ =
where
d
D
dx
= and
d
D
dz
=
3. MethodofVariationofParameters:
Theequationisoftheform
d y dy
a b cy f x
dx dx
+ + = + + = + + = + + =
2
2
( )
1 2
. C F Ay By = + and
1 2
. P I Py Qy = +
where
2
1 2 1 2
( ) y f x
P dx
y y y y
=
and
1
1 2 1 2
( ) y f x
Q dx
y y y y
=
www.studyhaunters.blogspot.in
www.studyhaunters.blogspot.in
4.
Curlof F
1 2 3
/ / /
i j k
XF x y z
F F F
= =
5.
If F
isSolenoidalvectorthen 0 F =
i
6.
7.
If F
isIrrotationalvectorthe 0 XF =
8.
MaximumDirectionalderivative =
9.
Directionalderivativeof inthedirectionof a
a
a
=
10.
Anglebetweentwonormalstothesurface
1 2
1 2
cos
n n
n n
=
i
Where ( )
1 1 1
1 1
( , , ) at x y z
n =
& ( )
2 2 2
2 2
( , , ) at x y z
n =
11.
UnitNormalvector, n
12.
Equationoftangentplane
1 1 1
( ) ( ) ( ) 0 l x x m y y n z z + + =
Wherel,m,narecoefficientof , , i j k
in .
13.
Equationofnormalline
1 1 1
x x y y z z
l m n
= =
14.
WorkDone=
C
F dr
i ,where dr dxi dyj dzk = + +
15.
If .
C
F dr
beindependentofthepathisthat curl 0 F =
16.
Inthesurfaceintegral
.
dxdy
dS
n k
=
,
.
dydz
dS
n i
=
,
.
dzdx
dS
n j
= & dS ndS =
Unit II (Vector Calculus)
1. Vectordifferentialoperatoris / / / i x j y k z = + +
2. Gradientof / / / i x j y k z = = + +
3. Divergenceof F
F =
www.studyhaunters.blogspot.in
www.studyhaunters.blogspot.in
17. Greens Theorem:
If , , ,
u v
u v
y x
arecontinuousandone-valuedfunctionsintheregionRenclosed
bythecurveC,then
C R
v u
udx vdy dxdy
x y
| |
+ =
|
\
.
18. Stokes Theorem:
Let F
bethevectorpointfunction,aroundasimpleclosedcurveCandoverthe
opensurfaceShavingasitsboundary,then
( )
x
C S
F dr F nds =
i i
19. Gauss Divergence Theorem:
Let F
beavectorpointfunctioninaregionRboundedbyaclosedsurfaceS,
then
S V
F nds Fdv =
i i
www.studyhaunters.blogspot.in
www.studyhaunters.blogspot.in
Unit III (Analytic Function)
1. Necessaryconditionforf(z)isanalyticfunction
CauchyRiemannEquations: &
u v v u
x y x y
= =
(C-Requations)
2. PolarformofCauchy-RiemannEquations:
1 1
&
u v v u
r r r r
= =
3. ConditionforHarmonicfunction:
2 2
2 2
0
u u
x y
+ =
4. Ifthefunctionisharmonicthenitshouldbeeitherrealorimaginarypartofa
analyticfunction.
5. Milne Thomson method:(Tofindtheanalyticfunctionf(z))
i) Ifuisgiven ( ) ( , 0) ( , 0)
x y
f z u z iu z dz =
ii) Ifvisgiven ( ) ( , 0) ( , 0)
y x
f z v z iv z dz = +
6. Tofindtheanalyticfunction
i) ( ) ; ( ) f z u iv if z iu v = + = addingthesetwo
Wehave ( ) ( ) (1 ) ( ) u v i u v i f z + + = +
then ( ) F z U iV = + where , & ( ) (1 ) ( ) U u v V u v F z i f z = = + = +
HerewecanapplyMilneThomsonmethodforF(z).
7. Bilineartransformation:
( )( )
( )( )
( )( )
( )( )
1 2 3 1 2 3
1 2 3 1 2 3
w w w w z z z z
w w w w z z z z
=
www.studyhaunters.blogspot.in
www.studyhaunters.blogspot.in
www.studyhaunters.blogspot.in
www.studyhaunters.blogspot.in
Unit IV (Complex Integration)
1.
Cauchys Integral Theorem:
Iff(z)isanalyticand ( ) f z iscontinuousinsideandonasimpleclosedcurveC,
then ( ) 0
c
f z dz =
.
2.
Cauchys Integral Formula:
Iff(z)isanalyticwithinandonasimpleclosedcurveCand
0
z isanypointinside
C,then
( )
2 ( )
C
f z
dz if a
z a
=
3.
Cauchys Integral Formula for derivatives:
Ifafunctionf(z)isanalyticwithinandonasimpleclosedcurveCandaisany
pointlyinginit,then
( )
2
1 ( )
( )
2
C
f z
f a dz
i
z a
Similarly
( )
3
2! ( )
( )
2
C
f z
f a dz
i
z a
, Ingeneral
( )
( )
1
! ( )
( )
2
n
n
C
n f z
f a dz
i
z a
+
=
4.
Cauchys Residue theorem:
Iff(z)beanalyticatallpointsinsideandonasimpleclosedcuvec,exceptfora
finitenumberofisolatedsingularities
1 2 3
, , ,...
n
z z z z insidec,then
( ) 2 (sum of the residues of ( ))
C
f z dz i f z =
.
5. Critical point:
Thepoint,atwhichthemappingw=f(z)isnotconformal,(i.e) ( ) 0 f z = iscalled
acriticalpointofthemapping.
6. Fixed points (or) Invariant points:
Thefixedpointsofthetransformation
az b
w
cz d
+
=
+
isobtainedbyputtingw=zin
theabovetransformation,thepointz=aiscalledfixedpoint.
7. Re { ( )} ( ) ( )
z a
s f z Lt z a f z
= (Simplepole)
8. ( )
( )
1
1
1
Re { ( )} ( )
( 1)!
m
m
m
z a
d
s f z Lt z a f z
m dz
(MultiPole(or)Poleoforderm)
www.studyhaunters.blogspot.in
www.studyhaunters.blogspot.in
9.
( )
Re { ( )}
( )
z a
P z
s f z Lt
Q z
10.
Taylor Series:
Afunction ( ) f z ,analyticinsideacircleCwithcentreata,canbeexpandedin
theseries
2 3
( )
( ) ( ) ( ) ( )
( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ... ( ) ...
1! 2! 3! !
n
n
z a z a z a z a
f z f a f a f a f a f a
n
= + + + + + +
Maclaurins Series:
Takinga=0,Taylorsseriesreduceto
2 3
( ) (0) (0) (0) (0) ...
1! 2! 3!
z z z
f z f f f f = + + + +
11.
Laurents Series:
0 1
( ) ( )
( )
n n
n n
n n
b
f z a z a
z a
= =
= +
where
1
1
1 ( )
2 ( )
n n
C
f z
a dz
i z a
+
=
&
2
1
1 ( )
2 ( )
n n
C
f z
b dz
i z a
=
,theintegralsbeing
takenanticlockwise.
12.
Isolated Singularity:
Apoint
0
z z = issaidtobeisolatedsingularityof ( ) f z if ( ) f z isnotanalyticat
0
z z = andthereexistsaneighborhoodof
0
z z = containingnoothersingularity.
Example:
1
( ) f z
z
= .Thisfunctionisanalyticeverywhereexceptat 0 z = .
0 z = isanisolatedsingularity.
13. Removable Singularity:
Asingularpoint
0
z z = iscalledaremovablesingularityof ( ) f z if
0
lim ( ) f z
z z
existsfinitely.
Example:
sin
lim ( ) lim 1
0 0
z
f z
z
z z
= =
(finite) 0 z = isaremovable
singularity.
www.studyhaunters.blogspot.in
www.studyhaunters.blogspot.in
CONTOUR INTEGRATION:
15.
Type: I
Theintegralsoftheform
2
0
(cos , sin ) f d
Hereweshallchoosethecontour
astheunitcircle : 1 or , 0 2
i
C z z e
= = .Onthistype
2
1
cos
2
z
z
+
= ,
2
1
sin
2
z
iz
= and
1
d dz
iz
= .
16.
Type: II
Improperintegralsoftheform
( )
( )
P x
dx
Q x
,whereP(x)andQ(x)arepolynomials
inxsuchthatthedegreeofQexceedsthatofPatleastbytwoandQ(x)doesnot
vanishforanyx.Here ( ) ( ) ( )
R
C R
f z dz f x dx f z dz
= +
as ( ) 0 R f z dz
.
14. Essential Singularity:
Iftheprincipalpartcontainsaninfinitenumberofnonzeroterms,then
0
z z = is
knownasaessentialsingularity.
Example:
( )
2
1
1/
1/
( ) 1 ...
1! 2!
z
z
z
f z e = = + + + has 0 z = asanessential
singularity.
17. Type: III
Theintegralsoftheform ( ) cos (or) ( ) sin f x mxdx f x mxdx
where
( ) 0 as f x x .
www.studyhaunters.blogspot.in
www.studyhaunters.blogspot.in
Unit V (Laplace Transform)
1.
Definition: [ ]
0
( ) ( )
st
L f t e f t dt
2.
Sl.No
1. [ ] 1 L
1
s
2.
n
L t (
1 1
! ( 1)
n n
n n
s s
+ +
+
=
3.
at
L e (
1
s a
4.
at
L e
1
s a +
5. [ ] sin L at
2 2
a
s a +
6. [ ] cos L at
2 2
s
s a +
7. [ ] sinh L at
2 2
a
s a
8. [ ] cosh L at
2 2
s
s a
3.
LinearProperty: [ ] [ ] [ ] ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) L af t bg t aL f t bL g t =
4.
FirstShiftingproperty:
If [ ] ( ) ( ) L f t F s = ,then
i)
[ ] ( ) ( )
at
s s a
L e f t F s
( =
ii)
[ ] ( ) ( )
at
s s a
L e f t F s
+
( =
www.studyhaunters.blogspot.in
www.studyhaunters.blogspot.in
5. SecondShiftingproperty:
If [ ] ( ) ( ) L f t F s = ,
( ),
( )
0,
f t a t a
g t
t a
>
=
<
then [ ] ( ) ( )
as
L g t e F s
=
6. Changeofscale:
If [ ] ( ) ( ) L f t F s = ,then
[ ]
1
( )
s
L f at F
a a
| |
=
|
\
7. Transformofderivative:
If [ ] ( ) ( ) L f t F s = ,then
[ ] ( ) ( )
d
L tf t F s
ds
= ,
2
2
2
( ) ( )
d
L t f t F s
ds
( =
,
Ingeneral ( ) ( 1) ( )
n
n n
n
d
L t f t F s
ds
( =
8. TransformofIntegral;
If [ ] ( ) ( ) L f t F s = ,then
1
( ) ( )
s
L f t F s ds
t
(
=
(
9. Initial value Theorem:
If [ ] ( ) ( ) L f t F s = ,then
( ) ( )
0 s
Lt f t Lt sF s
t
=
10. Final value Theorem:
If [ ] ( ) ( ) L f t F s = ,then
( ) ( )
s 0
Lt f t Lt sF s
t
=
11.
Sl.No
1.
1
1
L
s
(
(
1
2.
1
1
L
s a
(
(
at
e
3.
1
1
L
s a
(
(
+
at
e
4.
1
2 2
s
L
s a
(
(
+
cos at
5.
1
2 2
1
L
s a
(
(
+
1
sin at
a
www.studyhaunters.blogspot.in
www.studyhaunters.blogspot.in
6.
1
2 2
s
L
s a
(
(
cosh at
7.
1
2 2
1
L
s a
(
(
1
sinh at
a
8.
1
1
n
L
s
(
(
1
( 1)!
n
t
n
12. DeriativeofinverseLaplaceTransform:
[ ] [ ]
1 1
1
( ) ( ) L F s L F s
t
=
13. Colvolutionoftwofunctions:
0
( ) ( ) ( ) ( )
t
f t g t f u g t u du =
14. Covolution theorem:
Iff(t)&g(t)arefunctionsdefinedfor 0 t then [ ] [ ] [ ] ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) L f t g t L f t L g t =
15. ConvolutiontheoremofinverseLaplaceTransform:
[ ] [ ] [ ]
1 1 1
( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) L F s G s L F s L G s
=
16. SolvingODEforsecondorderdifferentialequationsusingLaplaceTransform
i) [ ] [ ] ( ) ( ) (0) L y t sL y t y =
ii) [ ] [ ]
2
( ) ( ) (0) (0) L y t s L y t sy y =
iii) [ ] [ ]
3 2
( ) ( ) (0) (0) (0) L y t s L y t s y sy y = take [ ] ( ) y L y t =
17. Solvingintegralequation:
[ ]
0
1
( ) ( )
t
L y t dt L y t
s
(
=
(
18. InverseLaplaceTransformbyContourIntegralmethod
[ ]
1
1
( ) ( )
2
st
c
L F s F s e ds
i
19. PeriodicfunctioninLaplaceTransform:
Iff(x+T)=f(x),thenf(x)isperiodicfunctionwithperiodT.
[ ]
0
1
( ) ( )
1
T
st
sT
L f t e f t dt
e
www.studyhaunters.blogspot.in
www.studyhaunters.blogspot.in
www.studyhaunters.blogspot.in
www.studyhaunters.blogspot.in
You might also like
- Mathematics Formula SheetDocument35 pagesMathematics Formula SheetChandra Kishore Paul67% (3)
- © Ncert Not To Be Republished: Design of The Question PaperDocument14 pages© Ncert Not To Be Republished: Design of The Question PaperArjit TyagiNo ratings yet
- 1.2important TheoremDocument11 pages1.2important TheoremShubhamNo ratings yet
- m4 PDFDocument23 pagesm4 PDFSantosh SanthuNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula Booklet Jeemain - GuruDocument60 pagesPhysics Formula Booklet Jeemain - GuruArshNo ratings yet
- Calculus of Residue and Contour IntegrationDocument78 pagesCalculus of Residue and Contour IntegrationPrateekKumarJaysinghaniNo ratings yet
- Numerical Methods I PDFDocument44 pagesNumerical Methods I PDFRahul PinnamaneniNo ratings yet
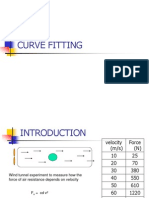
- Curve FittingDocument28 pagesCurve FittingCillalois Marie FameroNo ratings yet
- Notes LagrangeDocument8 pagesNotes LagrangeLennard PangNo ratings yet
- 4 9Document1 page4 9Eric Kial0% (1)
- Multiple IntegralsDocument133 pagesMultiple Integralsmanasa raajheshNo ratings yet
- Meter Bridge Experiment Using Wheatstone Bridge Principle PDFDocument12 pagesMeter Bridge Experiment Using Wheatstone Bridge Principle PDFOm Kumar100% (1)
- 6 MaxwelleqDocument7 pages6 MaxwelleqChristopher Jordan EvoniukNo ratings yet
- Esic Lab Technician 2016Document65 pagesEsic Lab Technician 2016Narasimhulu Pidem100% (1)
- Laplace Transform of The Dirac Delta Function PDFDocument6 pagesLaplace Transform of The Dirac Delta Function PDFmuchapeNo ratings yet
- Pair of Straight Lines 13 14 PDFDocument34 pagesPair of Straight Lines 13 14 PDFSoniyaKanwalG83% (23)
- GATE Two by RK MathsDocument24 pagesGATE Two by RK Mathskasarviv100% (3)
- Differential Equations-1st Order, 1st DegreeDocument9 pagesDifferential Equations-1st Order, 1st DegreeVince Rabin CandidatoNo ratings yet
- Math Formulas Book For JEE MAIN - Advanced - D.T PDFDocument41 pagesMath Formulas Book For JEE MAIN - Advanced - D.T PDFyogeshNo ratings yet
- MA2211 Transforms and Partial Differential Equations Lectrue Notes PDFDocument145 pagesMA2211 Transforms and Partial Differential Equations Lectrue Notes PDFDhiviya100% (1)
- Unit 3Document30 pagesUnit 3bala904260No ratings yet
- Shreyash Bhimanwar 111907050 Entc Experiment No. 1 Characterization of RTDDocument49 pagesShreyash Bhimanwar 111907050 Entc Experiment No. 1 Characterization of RTDshreyash100% (1)
- JatinDocument8 pagesJatinJatin Bhardwaz0% (1)
- 50 TOP FET Questions and Answers PDFDocument10 pages50 TOP FET Questions and Answers PDFAasheeshSingh100% (2)
- MA8353 Transforms and Partial Differential Equations 02 - by LearnEngineering - in PDFDocument282 pagesMA8353 Transforms and Partial Differential Equations 02 - by LearnEngineering - in PDFPayangaati PradeepNo ratings yet
- Fourier Series Two Marks QuestionsDocument3 pagesFourier Series Two Marks Questionsvignanaraj100% (1)
- Math I HandwrittenDocument31 pagesMath I HandwrittenTanishq Gosavi100% (3)
- Ordinary Differential EquationsDocument9 pagesOrdinary Differential EquationsAnonymous gViEc4100% (1)
- Engineering Mathematics Formula SheetDocument2 pagesEngineering Mathematics Formula Sheetsimpsonequal100% (1)
- Clairaut's Equation:: Standard Form IIDocument12 pagesClairaut's Equation:: Standard Form IISaad Ahmed SazanNo ratings yet
- Mfcs-Recurrence RelationsDocument35 pagesMfcs-Recurrence RelationsRama Krishna P100% (1)
- Relation and FunctionsDocument14 pagesRelation and FunctionsArpit KumarNo ratings yet
- Quantum Mechanics IIDocument10 pagesQuantum Mechanics IIAyush SinghNo ratings yet
- Second Order Linear Differential Equation With Constant CoefficientsDocument7 pagesSecond Order Linear Differential Equation With Constant CoefficientsMarwan ElsayedNo ratings yet
- Definite INTEGRATION ASSIGNMENT FOR IIT-JEEDocument36 pagesDefinite INTEGRATION ASSIGNMENT FOR IIT-JEEApex Institute100% (1)
- II Puc Physics Hand BookDocument58 pagesII Puc Physics Hand BookBeeresha R SNo ratings yet
- Question Bank Centroid&MIDocument13 pagesQuestion Bank Centroid&MIrubyNo ratings yet
- MeasurementsDocument8 pagesMeasurementsSethu Naidu0% (1)
- Relation and Function MCQSDocument5 pagesRelation and Function MCQSNoo EntryNo ratings yet
- Engineering MathematicsDocument74 pagesEngineering MathematicsSurendra Babu Koganti100% (1)
- Objective Questions: Level - IDocument23 pagesObjective Questions: Level - IHarsh TyagiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6-Clairaut EquationDocument17 pagesLecture 6-Clairaut EquationTech LuckyNo ratings yet
- Actr PPT MatlabDocument20 pagesActr PPT MatlabmaulikNo ratings yet
- Beta and Gamma FunctionsDocument9 pagesBeta and Gamma Functionsadithi udupaNo ratings yet
- Cosine SeriesDocument5 pagesCosine SeriesBarasat HelpDeskNo ratings yet
- Shooting MethodDocument7 pagesShooting MethodKrish Pavan100% (2)
- Thermal Properties of Matter Handwritten Notes Class 11 JeeDocument22 pagesThermal Properties of Matter Handwritten Notes Class 11 Jeesmeet mehta100% (1)
- N (N + 1) (N + 5) Is Not A Multiple of 3 Where N Is A Positive IntegerDocument2 pagesN (N + 1) (N + 5) Is Not A Multiple of 3 Where N Is A Positive IntegerMadhavan SowrirajanNo ratings yet
- QP02D 1Document2 pagesQP02D 1पंकज काळे50% (2)
- Exp 11 Forward InterpolationDocument3 pagesExp 11 Forward InterpolationHasibur100% (1)
- 9 GuguuDocument5 pages9 GuguuShreyaSharmaNo ratings yet
- Scilab CodesDocument18 pagesScilab CodesPrateek_1450% (2)
- Notice For Project Submission-190Document2 pagesNotice For Project Submission-190Umesh MewaraNo ratings yet
- Maths II FormulasDocument13 pagesMaths II Formulaskr_padmavathiNo ratings yet
- 3 Unit FormulasDocument4 pages3 Unit FormulasDhanalakshmi VadivelanNo ratings yet
- Calculus Cheat Sheet IntegralsDocument5 pagesCalculus Cheat Sheet Integralsapi-322359712No ratings yet
- Calculus Cheat Sheet Integrals ReducedDocument3 pagesCalculus Cheat Sheet Integrals ReducedShahnaz GazalNo ratings yet
- Integral Calculus by Arihant B016Document27 pagesIntegral Calculus by Arihant B016Luis Anderson60% (5)
- Arihant PhysicsDocument22 pagesArihant PhysicsManishKumar0% (1)
- De Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandDe Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuit Lab ManualDocument38 pagesElectrical Circuit Lab Manualecessec67% (3)
- Microprocessor and Microcontroller April May 2010 QPDocument2 pagesMicroprocessor and Microcontroller April May 2010 QPSriram JNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Theory Question Bank Semester-III StudyhauntersDocument8 pagesElectromagnetic Theory Question Bank Semester-III StudyhauntersSriram JNo ratings yet
- I Sem - Curr & Syllabus-Regulation 2013-StudyhauntersDocument13 pagesI Sem - Curr & Syllabus-Regulation 2013-StudyhauntersSriram JNo ratings yet
- Instruction To TNPSC Group IV Exam CandidatesDocument32 pagesInstruction To TNPSC Group IV Exam CandidatesSriram JNo ratings yet
- Environmental Science & Engineering Third Semester Lecture NotesDocument73 pagesEnvironmental Science & Engineering Third Semester Lecture NotesSriram JNo ratings yet
- Basic Civil and Mechanical-Unit-4-Ic Engines-Support Notes-Studyhaunters PDFDocument13 pagesBasic Civil and Mechanical-Unit-4-Ic Engines-Support Notes-Studyhaunters PDFSriram JNo ratings yet
- Basic Civil and Mechanical Nov-Dec-2010 Question Paper StudyhauntersDocument2 pagesBasic Civil and Mechanical Nov-Dec-2010 Question Paper StudyhauntersSriram JNo ratings yet
- Basic Civil and Mechanical Nov-Dec-2011 Question Paper StudyhauntersDocument3 pagesBasic Civil and Mechanical Nov-Dec-2011 Question Paper StudyhauntersSriram JNo ratings yet
- Basic Civil and Mechanical Nov-Dec-2009 Question Paper StudyhauntersDocument2 pagesBasic Civil and Mechanical Nov-Dec-2009 Question Paper StudyhauntersSriram JNo ratings yet
- Basic Civil and Mechanical May-June-2010 Question Paper StudyhauntersDocument2 pagesBasic Civil and Mechanical May-June-2010 Question Paper StudyhauntersSriram JNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mathematics 2-Nov-Dec-2011 Question Paper Studyhaunters PDFDocument3 pagesEngineering Mathematics 2-Nov-Dec-2011 Question Paper Studyhaunters PDFSriram JNo ratings yet
- Basic Civil and Mechanical May-June-2011 Question Paper StudyhauntersDocument3 pagesBasic Civil and Mechanical May-June-2011 Question Paper StudyhauntersSriram JNo ratings yet
- Basic Civil and Mechanical May-June-2009 Question PaperDocument2 pagesBasic Civil and Mechanical May-June-2009 Question PaperSriram JNo ratings yet
- Engineering Chemistry-II - May-June 2009 Question Paper Studyhaunters PDFDocument3 pagesEngineering Chemistry-II - May-June 2009 Question Paper Studyhaunters PDFSriram JNo ratings yet
- Basic Civil and Mechanical-unit-3-Pumps and Turbines-Support Notes-StudyhauntersDocument10 pagesBasic Civil and Mechanical-unit-3-Pumps and Turbines-Support Notes-StudyhauntersSriram JNo ratings yet
- Basic Civil and Mechanical-Unit-4-Boilers-Support Notes-Studyhaunters PDFDocument11 pagesBasic Civil and Mechanical-Unit-4-Boilers-Support Notes-Studyhaunters PDFSriram J100% (1)
- WWW - Studyhaunters.blogspot - In: Question Paper Code: 22115Document5 pagesWWW - Studyhaunters.blogspot - In: Question Paper Code: 22115Sriram JNo ratings yet
- CIRCUIT THEORY-June2009 PDFDocument3 pagesCIRCUIT THEORY-June2009 PDFSriram JNo ratings yet
- Basic Civil and Mechanical Unit 1 Support Notes StudyhauntersDocument9 pagesBasic Civil and Mechanical Unit 1 Support Notes StudyhauntersSriram JNo ratings yet
- Engineering Chemistry-II - Nov - Dec 2009 Question Paper Studyhaunters PDFDocument2 pagesEngineering Chemistry-II - Nov - Dec 2009 Question Paper Studyhaunters PDFSriram JNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mathematics April May 2011 Question Paper Studyhaunters PDFDocument3 pagesEngineering Mathematics April May 2011 Question Paper Studyhaunters PDFSriram JNo ratings yet
- Engineering Chemistry-II - May-June 2010 Question Paper Studyhaunters PDFDocument2 pagesEngineering Chemistry-II - May-June 2010 Question Paper Studyhaunters PDFSriram JNo ratings yet
- Basic Civil and Mechanical Unit 2 Power Plants Support Notes StudyhauntersDocument19 pagesBasic Civil and Mechanical Unit 2 Power Plants Support Notes StudyhauntersSriram JNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mathematics II Model Question Paper StudyhauntersDocument3 pagesEngineering Mathematics II Model Question Paper StudyhauntersSriram JNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mathematics II May June 2010 Question Paper Studyhaunters PDFDocument3 pagesEngineering Mathematics II May June 2010 Question Paper Studyhaunters PDFSriram JNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mathematics II Nov Dec 2009 Question Paper Studyhaunters PDFDocument3 pagesEngineering Mathematics II Nov Dec 2009 Question Paper Studyhaunters PDFSriram JNo ratings yet
- Technical English-II Nov Dec 2009 Question Paper StudyhauntersDocument5 pagesTechnical English-II Nov Dec 2009 Question Paper StudyhauntersSriram JNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mathematics II May June 2009 Question Paper StudyhauntersDocument3 pagesEngineering Mathematics II May June 2009 Question Paper StudyhauntersSriram JNo ratings yet
- Scheme of Work: Cambridge International AS & A Level Mathematics 9709 Pure Mathematics 3 (For Paper 3)Document41 pagesScheme of Work: Cambridge International AS & A Level Mathematics 9709 Pure Mathematics 3 (For Paper 3)Head of Mathematics DepartmentNo ratings yet
- Nucl - Phys.B v.688Document290 pagesNucl - Phys.B v.688Daniel Bogdan DincaNo ratings yet
- Gorg-2018-Euler Class and Intersection TDocument7 pagesGorg-2018-Euler Class and Intersection TGuido FranchettiNo ratings yet
- NCERT Exemplar Class 8 Maths Solutions Chapter 7 Algebraic Expressions Identities and FactorisationDocument11 pagesNCERT Exemplar Class 8 Maths Solutions Chapter 7 Algebraic Expressions Identities and FactorisationCheshta TolaniNo ratings yet
- Polynomial Characteristics HandoutDocument4 pagesPolynomial Characteristics HandoutAryan SinghNo ratings yet
- Lapierreeeee 2Document3 pagesLapierreeeee 2heather :]No ratings yet
- Mathematics 7: O.B. Montessori Center Professional High SchoolDocument36 pagesMathematics 7: O.B. Montessori Center Professional High SchoolSophia MagoNo ratings yet
- Module4 Complex Rational ExpressionsDocument6 pagesModule4 Complex Rational ExpressionsAlbert BalingitNo ratings yet
- TU TO RS: Ac Ad em yDocument5 pagesTU TO RS: Ac Ad em yGourav KumarNo ratings yet
- Pankaj Gandhi's Academy: Numbers 1Document2 pagesPankaj Gandhi's Academy: Numbers 1rajatNo ratings yet
- Further Mathematics/Mathematics (Elective) Aims of The SyllabusDocument18 pagesFurther Mathematics/Mathematics (Elective) Aims of The SyllabusHajara Abubakari SadiqNo ratings yet
- Ordered Pair:-An Ordered Pair Consist of Two Elements in A Fixed OrderDocument19 pagesOrdered Pair:-An Ordered Pair Consist of Two Elements in A Fixed OrderDipinNo ratings yet
- 2010 UPSR Practice Mathematcs Paper 2 - Fractons & DecimalsDocument4 pages2010 UPSR Practice Mathematcs Paper 2 - Fractons & DecimalsPuworkUtara OnScribdNo ratings yet
- JR Maths-Ia Saq SolutionsDocument69 pagesJR Maths-Ia Saq SolutionsKathakali Boys AssociationNo ratings yet
- 2 Mathematics 1Document3 pages2 Mathematics 1pathir KroNo ratings yet
- Ho07 ps3Document2 pagesHo07 ps3Wassim OweiniNo ratings yet
- Brian R. Greene, David R. Morrison and Andrew Strominger - Black Hole Condensation and The Unification of String VacuaDocument16 pagesBrian R. Greene, David R. Morrison and Andrew Strominger - Black Hole Condensation and The Unification of String VacuaVelveetNo ratings yet
- Lecture-4 Reduction of Quadratic FormDocument33 pagesLecture-4 Reduction of Quadratic FormRupesh100% (1)
- Homework 1-4 PDFDocument5 pagesHomework 1-4 PDFivan david alvarez herreraNo ratings yet
- Rational FunctionDocument34 pagesRational FunctionJames Marck BabieraNo ratings yet
- M402C8Document11 pagesM402C8VASUNo ratings yet
- 07 3DElasticity CompleteDocument45 pages07 3DElasticity CompleteSüleyman TüreNo ratings yet
- Introduction To DifferentiationDocument10 pagesIntroduction To DifferentiationaurennosNo ratings yet
- 10Document145 pages10keshavNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4: Partially Ordered Sets and LatticesDocument3 pagesLecture 4: Partially Ordered Sets and LatticesAnu EldoseNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Exponential FunctionsDocument29 pages1.3 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Exponential FunctionsHarmi HarlinaNo ratings yet
- SymPy CheatsheetDocument1 pageSymPy CheatsheetTaimoo Naseem0% (1)
- BSE Telangana 10th Maths Model Paper II by SakshiDocument3 pagesBSE Telangana 10th Maths Model Paper II by SakshiRamaKrishna ErrojuNo ratings yet
- Lunes Martes Miyerkules Huwebes Biyernes: Grade OneDocument3 pagesLunes Martes Miyerkules Huwebes Biyernes: Grade OneCharisse Pizarro DionisioNo ratings yet
- Mathematical DiagramDocument5 pagesMathematical Diagramwoodword99No ratings yet