Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ac Year 4 Maths
Uploaded by
api-230679736Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ac Year 4 Maths
Uploaded by
api-230679736Copyright:
Available Formats
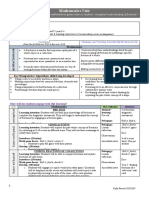
Identify curriculum
Measurement and Geometry, and Statistics and Probability. The proficiencies reinforce the significance of working mathematically with developed. They provide the language to build in the developmental aspects of the learning of mathematics. At this year level: Understanding includes making connections between representations of numbers, partitioning and combining numbers flexibly, extend communicate times and describing properties of symmetrical shapes Fluency includes recalling multiplication tables, communicating sequences of simple fractions, using instruments to measure accuratel and collecting and recording data Problem Solving includes formulating, modelling and recording authentic situations involving operations, comparing large numbers wit of numbers to continue patterns Reasoning includes using generalising from number properties and results of calculations, deriving strategies for unfamiliar multiplicat information using graphical displays and evaluating the appropriateness of different displays. Achievement standard
By the end of Year 4, students choose appropriate strategies for calculations involving multiplication and division. They recognise com connections between fraction and decimal notations up to two decimal places. Students solve simple purchasing problems. They iden number patterns resulting from multiplication. Students compare areas of regular and irregular shapes using informal units. They solve contained in maps. Students identify dependent and independent events. They describe different methods for data collection and repr Students use the properties of odd and even numbers. They recall multiplication facts to 10 x 10 and related division facts. Students lo number sequences involving multiples of single digit numbers. Students use scaled instruments to measure temperatures, lengths, sh Students create symmetrical shapes and patterns. They classify angles in relation to a right angle. Students list the probabilities of eve collected data. Term 1 During this term students will: recognise, represent, order and apply place value of numbers up to tens of thousands apply multiplication facts (2, 3, 4, 5, 10) investigate fractions (count by halves, quarters and thirds) investigate multiplication number patterns investigate time and length revise and consolidate Year 3 concepts as required. Term 2 Exemplar unit: Shapes, area, angles and symmetry in the environment During this term students will: revise and consolidate Term 1 concepts as required recognise, represent and order numbers up to tens of thousands apply multiplication and related division facts (2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 9, 10) investigate properties of odd and even numbers investigate number sequences involving multiples (3, 4 ,6, 7, 8, 9) split and combine two-dimensional shapes investigate the area of regular and irregular shapes compare and classify angles investigate symmetry. Term 3
Source: Australian Curriculum, Assessment and Reporting Authority (ACARA), Australian Curriculum v3.0: Mathematics for Foundation10, <www.australiancurriculum
Term overview
During this term students will: revise and consolidate Terms 1 concepts as required apply place value to partition, re and regroup numbers to at least thousands apply multiplication and related facts (2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10) use efficient written and mental for multiplication and division apply place value of numbers to hundredths make connections between frac decimals (equivalence) locate and represent fractions o line use addition and subtraction to f unknown quantities investigate mass, capacity and t investigate location (scale, legen direction) explore chance collect data, and create and eva displays.
Teaching and learning
Teaching and learning
Social, historical and cultural contexts associated with different uses of mathematical concepts in Australian Indigenous societies Aboriginal peoples and Torres Strait Islander peoples contributions to Australian society and cultures. Mathematics provides opportunities to explore aspects of Australian Indigenous knowing in connection to, and with guidance from, the approach, students have the opportunity to explore mathematical concepts in Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander lifestyles including Through these experiences, students have opportunities to learn that Aboriginal peoples and Torres Strait Islander peoples have soph be applied in other peoples ways of knowing. General capabilities and cross-curriculum priorities Opportunities to engage with: Opportunities to engage with: Opportunities to engage with:
Key to general capabilities and cross-curriculum priorities
Literacy
Numeracy
ICT capability
Critical and creative thinking
Ethical behaviour
Personal and social capability Sustainability
Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander histories and cultures
Asia and Australias engagement with Asia
Assessment For advice and guidelines on assessment, see www.qsa.qld.edu.au
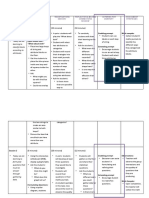
A folio is a targeted selection of evidence of student learning and includes a range of responses to a variety of assessment techniques about student achievement and progress at appropriate points and informs the reporting process. Term 1 Week 1 Assessment instrument Initial assessment Identify Year 4 consolidation needs and learning goals (e.g. KWL, teacher/student conference). Modelling and problem-solving task (Spoken/signed) Explore number patterns and properties. Term 2 Week 4 Assessment instrument Modelling and problem-solving task (Written) Explore symmetrical patterns in art work. Mathematical investigation: Journal (Written) Investigate shapes, area, angles and symmetry in the environment. The assessment package Angles and symmetry in the built environment in the QSA Assessment Bank could be used in this unit. Supervised assessment: Short response (Written) Solve multiplication and division problems. Term 3 Week 38
Assessment instrument
Develop assessment
Modelling and problem-so Using a map (Written) Show compass points aro school on a map (treasure
68
Supervised assessment: response (Written) Solve problems related to
67
Supervised assessment: Short response (Written) Apply place value. Modelling and problem-solving task: Demonstration (Spoken/signed) Explore time.
89
QCATs: Identify the curriculum targ appropriate to the sequence of lear Teachers develop tasks and plan units. Teachers identify AE samples before marking tasks, and moderate to ensure consistency of judgments. Curriculum leaders randomly sample folios to check for consistency of judgments.
Make judgments nd use feedback
Moderation
Teachers develop tasks and plan units. Teachers co-mark tasks to ensure consistency of judgments.
Teachers develop tasks and plan u Teachers identify AE samples bef the treasure hunt task, and modera ensure consistency of judgments. Teachers moderate the QCATs to i samples to take to cluster moderati Term 4.
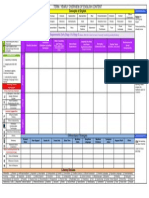
(ACMNA071) using the four operations with pairs of odd or X X even numbers or one odd and one even number, then using the relationships established to check the accuracy of calculations Resources: IXL A7, New Zealand Maths, Thats odd, Scootle Envision, Study Ladder Recognise, represent and order numbers to at least tens of thousands (ACMNA072) reproducing five-digit numbers in words X using their numerical representations, and vice versa Resources: IXL A Number sense, Scootle, Envision topic 1, Study Ladder Apply place value to partition, rearrange and regroup numbers to at least tens of thousands to assist calculations and solve problems (ACMNA073) recognising and demonstrating that the X place-value pattern is built on the operations of multiplication or division of tens Resources: IXL A Number sense, Scootle, Envision topic 1, Study Ladder Investigate number sequences involving multiples of 3, 4, 6, 7, 8, and 9 (ACMNA074) recognising that number sequences can be X X X extended indefinitely, and determining any patterns in the sequences Resources: IXL D, Scootle, Envision topic 4, Study Ladder Recall multiplication facts up to 10 10 and related division facts (ACMNA075) using known multiplication facts to calculate X X X X related division facts Resources: IXL D, E, Scootle, Envision topic 4,7, Study Ladder Develop efficient mental and written strategies and use appropriate digital technologies for multiplication and for division where there is no remainder (ACMNA076) using known facts and strategies, such as X X X X commutativity, doubling and halving for
of fractions (halves, quarters and eighths or thirds and sixths) by folding a series of paper strips to construct a fraction wall Resources: IXL M,N,O, Scootle, Envision topic 9, Study Ladder Count by quarters halves and thirds, including with mixed numerals. Locate and represent these fractions on a number line (ACMNA078) converting mixed numbers to improper X X fractions and vice versa investigating the use of fractions and sharing X X as a way of managing Country: for example taking no more than half the eggs from a nest to protect future bird populations Resources: IXL M,N,O, Scootle, Envision topic 9, Study Ladder Recognise that the place value system can be extended to tenths and hundredths. Make connections between fractions and decimal notation (ACMNA079) using division by 10 to extend the place-value X X system using knowledge of fractions to establish X X equivalences between fractions and decimal notation Resources: IXL M,N,O, Scootle, Envision topic 9, Study Ladder National grid for learning (Top Marks) tenths and hundredths Money and financial mathematics Solve problems involving purchases and the calculation of change to the nearest five cents with and without digital technologies (ACMNA080) recognising that not all countries use dollars X X X and cents, eg India uses rupees. carrying out calculations in another currency X X X as well as in dollars and cents, and identifying both as decimal systems Resources: IXL I, Scootle, Envision topic 3.10, Study Ladder Patterns and algebra Explore and describe number patterns resulting from performing multiplication (ACMNA081) identifying examples of number patterns in X X X everyday life Resources: IXL D,G Scootle, Envision topic 4,7.7, 8.1, 8.3 Study Ladder Top Marks Number Patterns
sentence Resources: Envision to Use equiva to find unk writing num answer que added to 2 minus 19. W using partit in number Resources:
occurring (ACMSP092) using lists of events familiar to students and ordering them from least likely to most likely to occur
Resources: IXL H,Q Scootle, Envision topic 12.7 Study L
Marks
Identify everyday events where one cannot happen if happens (ACMSP093) using examples such as weather, which cannot be dry and wet at the same time
Resources: IXL H,Q Scootle, Envision topic 12.8 Study L
Identify events where the chance of one will not be a occurrence of the other (ACMSP094) explaining why the probability of a new baby being either a boy or a girl does not depend on the sex of the previous baby
Resources: IXL H, Q Scootle, Envision topic 12.9 Study Data representation and interpretation
Select and trial methods for data collection, includin questions and recording sheets (ACMSP095) comparing the effectiveness of different methods of collecting data choosing the most effective way to collect data for a given investigation
X X
Resources: IXL H, Q Scootle, Envision topic 12.1 Study
Construct suitable data displays, with and without th technologies, from given or collected data. Include ta graphs and picture graphs where one picture can re many data values (ACMSP096) exploring ways of presenting data and showing the results of investigations investigating data displays using many-to-one correspondence
Resources: IXL H, Q Scootle, Envision topic 12 Study La
Data analysis explorer
Evaluate the effectiveness of different displays in illustrating data features including variability (ACMS
on a range of measuring instruments to the nearest graduation
Resources: IXL J Scootle, Envision topic 10.6, 11 Study Ladder
Compare objects using familiar metric units of area and volume (ACMMG290) comparing areas using grid paper comparing volume using centicubes recognising that metric units are not the only units used throughout the world, for example measuring the area of floor space using tatami mats (Japan), using squares for room and house area (Australia)
X X X X
Resources: IXL L12,13,14 Scootle, Envision topic 11 Study Ladder
Top Marks area and perimeter
Convert between units of time (ACMMG085) identifying and using the correct operation for converting units of time
Resources: IXL K Scootle, Envision topic 10.2, 10.3, Study Ladder Use am and pm notation and solve simple time problems (ACMMG086) calculating the time spent at school during a normal school day calculating the time required to travel between two locations determining arrival time given departure time
X X X
X X X
X X X
X X X
Resources: IXL K Scootle, Envision topic 10, Study Ladder Top Marks
telling
time
Shape Compare the areas of regular and irregular shapes by informal means (ACMMG087) comparing areas using metric units, such as counting the number of square centimetres required to cover two areas by overlaying the areas with a grid of centimetre squares
Resources: IXL L Scootle, Envision topic 5,11 Study Ladder Top Marks
perimeter and area using irregular shapes
Compare and describe two dimensional shapes that result from
Location and transformation Use simple scales, legends and directions to interpret information contained in basic maps (ACMMG090) identifying the scale used on maps of cities and rural areas in Australia and a city in Indonesia and describing the difference using directions to find features on a map
X X
Resources: IXL J6, J7 Scootle, Envision topic 6, Study Ladder Create symmetrical patterns, pictures and shapes with and without digital technologies (ACMMG091) using stimulus materials such as the motifs in Central Asian textiles, Tibetan artefacts, Indian lotus designs and symmetry in Yolngu or Central and Western Desert art
Resources: IXL L15, 16 Scootle, Envision topic 6 Study Ladder Top Marks Geometric reasoning Compare angles and classify them as equal to, greater than or less than a right angle (ACMMG089) creating angles and comparing them to a right X X angle using digital technologies Resources: CTJ 2012 IXL L 10, L11 Scootle, Envision topic 5.1 Study
Ladder Google sketch up Top Marks angles
You might also like
- Year 7 Maths Course Outline 2018Document15 pagesYear 7 Maths Course Outline 2018Avtar SinghNo ratings yet
- Persuasive Text Unit PlannerDocument10 pagesPersuasive Text Unit Plannerapi-318610627No ratings yet
- Year 5 6 Fractions Unit PlanDocument9 pagesYear 5 6 Fractions Unit Planapi-525404544No ratings yet
- Assess Reporting A3 Marked NaplanDocument22 pagesAssess Reporting A3 Marked Naplanapi-3541683400% (1)
- Small Signal AnalysisDocument4 pagesSmall Signal Analysissamaiyasamp3No ratings yet
- LabVIEW Sound and Vibration Analysis User Manual (2007)Document199 pagesLabVIEW Sound and Vibration Analysis User Manual (2007)Jefferson MartinezNo ratings yet
- Literacy OverviewDocument20 pagesLiteracy Overviewapi-459118418100% (1)
- AUS LessonPlans Year ALL Mathletics PDFDocument52 pagesAUS LessonPlans Year ALL Mathletics PDFguptamaths8676No ratings yet
- Mathematics Term 1Document16 pagesMathematics Term 1api-313701922No ratings yet
- Unit Planning Maths EditedDocument13 pagesUnit Planning Maths Editedapi-480320763No ratings yet
- On Oxygen-Induced Corrosion of An Oil Refinery Condensate Fraction at Ion UnitDocument17 pagesOn Oxygen-Induced Corrosion of An Oil Refinery Condensate Fraction at Ion UnitAzmi Mohammed NorNo ratings yet
- Year 3 Maths Conceptual Overview Term 2Document20 pagesYear 3 Maths Conceptual Overview Term 2api-236594353No ratings yet
- Prefixes and SuffixesDocument15 pagesPrefixes and SuffixesRita Otero100% (1)
- Service Manual Kaeser SK 19Document75 pagesService Manual Kaeser SK 19Joe100% (8)
- Measurement Unit PlanDocument5 pagesMeasurement Unit Planapi-443252259No ratings yet
- Fractions Year 6Document12 pagesFractions Year 6api-221264431No ratings yet
- Unit of Work - Stage 3 Year 6Document11 pagesUnit of Work - Stage 3 Year 6api-465368143No ratings yet
- Year 6 t1 Unit 5 Mathematics TermDocument5 pagesYear 6 t1 Unit 5 Mathematics Termapi-267136654No ratings yet
- Complete AssDocument26 pagesComplete Assapi-435630130No ratings yet
- Year 5 t1 Unit 7Document4 pagesYear 5 t1 Unit 7api-267136654No ratings yet
- Maths Programming Bolwarra Ps - Year 5Document54 pagesMaths Programming Bolwarra Ps - Year 5api-267136654No ratings yet
- Maths Unit PlanDocument5 pagesMaths Unit Planapi-465432008No ratings yet
- Year 6 Geography PortfolioDocument0 pagesYear 6 Geography PortfolioS TANCREDNo ratings yet
- S2 English Scope and Sequence ChecklistDocument17 pagesS2 English Scope and Sequence ChecklistS TANCREDNo ratings yet
- Year 5 t1 Unit 9Document6 pagesYear 5 t1 Unit 9api-267136654No ratings yet
- Year 5 - Western Australian Curriculum v8.1: Mathematics - Eden Hill Primary SchoolDocument3 pagesYear 5 - Western Australian Curriculum v8.1: Mathematics - Eden Hill Primary SchoolSaniaMalikNo ratings yet
- Unit Plan - Area PerimeterDocument3 pagesUnit Plan - Area Perimeterapi-541531061No ratings yet
- Indian National Solar MissionDocument114 pagesIndian National Solar MissionH Janardan PrabhuNo ratings yet
- 216.1M-14 PreviewDocument4 pages216.1M-14 PreviewSantiago D. VelasquezNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Unit PlannerDocument5 pagesMathematics Unit Plannerapi-252779423No ratings yet
- Kla Maths Investigation PatternDocument6 pagesKla Maths Investigation PatternOliver Gabaon GalimbaNo ratings yet
- Kristinakarlsson 214168072 Emilychilds 213137003 Ecl310 AssignmenttwoDocument41 pagesKristinakarlsson 214168072 Emilychilds 213137003 Ecl310 Assignmenttwoapi-3525927380% (1)
- Maths Lesson 3d ShapesDocument6 pagesMaths Lesson 3d Shapesapi-462146812No ratings yet
- Unit Planner MathDocument6 pagesUnit Planner Mathapi-480118398No ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document39 pagesAssignment 1api-3686825950% (1)
- Good Teaching Differentiated Classroom Practice Learning For All PDFDocument36 pagesGood Teaching Differentiated Classroom Practice Learning For All PDFTing BieNo ratings yet
- Maths PlanDocument19 pagesMaths PlanmissedmondsNo ratings yet
- k6 Maths SylDocument201 pagesk6 Maths Syldrwho01No ratings yet
- English Planning Template-D Cherry-Cabramurrah PSDocument1 pageEnglish Planning Template-D Cherry-Cabramurrah PSS TANCRED100% (1)
- Assessment 2Document26 pagesAssessment 2api-297389221100% (1)
- Edst Lesson PlanDocument10 pagesEdst Lesson Planapi-317910994No ratings yet
- CTL Assignment 1Document52 pagesCTL Assignment 1api-485956198No ratings yet
- Cluster Writing Document Version 2Document34 pagesCluster Writing Document Version 2api-241525348No ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document34 pagesAssignment 2api-3686825950% (1)
- Year 6 7 Angles Unit PlanDocument2 pagesYear 6 7 Angles Unit Planapi-361274406No ratings yet
- Maths Kit PDFDocument184 pagesMaths Kit PDFSiti NurNo ratings yet
- English Writers Workshop Unit PlannerDocument9 pagesEnglish Writers Workshop Unit Plannerapi-494980198No ratings yet
- CBS BanshoDocument8 pagesCBS BanshoLiew2020No ratings yet
- Year 3 Unit Overview 4Document51 pagesYear 3 Unit Overview 4api-250249089No ratings yet
- Teaching Philosophy StatementDocument6 pagesTeaching Philosophy Statementkarensun21No ratings yet
- Unit Plan Informative TextsDocument5 pagesUnit Plan Informative Textsapi-361854774No ratings yet
- Different MathDocument8 pagesDifferent Mathapi-247482622No ratings yet
- Maths Unit PlanDocument7 pagesMaths Unit Planapi-469895619No ratings yet
- Big Ideas MathematicsDocument50 pagesBig Ideas Mathematicsapi-302139975100% (1)
- Lesson Plan Tyler Miller HistoryDocument7 pagesLesson Plan Tyler Miller Historyapi-534444991No ratings yet
- Edma360 - Assignment TwoDocument3 pagesEdma360 - Assignment Twoapi-358330682No ratings yet
- Mathematics Unit of WorkDocument8 pagesMathematics Unit of Workapi-358178333No ratings yet
- Assessment 1 - Lesson Plan FinalDocument21 pagesAssessment 1 - Lesson Plan Finalapi-407995742No ratings yet
- PAPER1 - Ext 1 Prelim Yearly & SolutionsDocument11 pagesPAPER1 - Ext 1 Prelim Yearly & Solutionssebastian salibaNo ratings yet
- Subtraction BowlingDocument5 pagesSubtraction Bowlingapi-286144974No ratings yet
- 007 Magmatip Filling Results enDocument7 pages007 Magmatip Filling Results enpurushothaman1234566No ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument10 pagesChemistryMaame Ama FrempongNo ratings yet
- Classification of Elements and Periodicity in PropertiesDocument2 pagesClassification of Elements and Periodicity in PropertiesShivam KumarNo ratings yet
- 17 Capacitors and Inductors in AC CircuitsDocument12 pages17 Capacitors and Inductors in AC CircuitsAbhijit PattnaikNo ratings yet
- Formulas For Physics 1Document7 pagesFormulas For Physics 1thejesterraceNo ratings yet
- Hardness Conversion Chart 3Document3 pagesHardness Conversion Chart 3rajarshi6666No ratings yet
- Calculation Check Temporary Tower - LG SlidingDocument9 pagesCalculation Check Temporary Tower - LG Slidingสายัญ บุญพาNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Multiphase Fluid Dynamics: 1.1. Scope of The BookDocument40 pagesIntroduction To Multiphase Fluid Dynamics: 1.1. Scope of The Bookdanijelkr88No ratings yet
- Full Text of "Waterproofing EngineeringDocument966 pagesFull Text of "Waterproofing Engineeringmazharul43No ratings yet
- Experimental Investigation On Mechanical Performance of Aluminium CompositeDocument10 pagesExperimental Investigation On Mechanical Performance of Aluminium CompositeMadhu KotlaNo ratings yet
- Sajb 411952 969Document18 pagesSajb 411952 969samirNo ratings yet
- Calculating The Heating Value of BiogasDocument5 pagesCalculating The Heating Value of BiogasAnonymous MVHQ97KEoPNo ratings yet
- Hy30 3300 Uk PDFDocument96 pagesHy30 3300 Uk PDFDragan LazicNo ratings yet
- Datasheet For Steel Grades Carbon Steel 1.1141: 1.1141 Standard NumberDocument2 pagesDatasheet For Steel Grades Carbon Steel 1.1141: 1.1141 Standard NumberCricri CriNo ratings yet
- XII Maths Exercise 3.1 (Solution)Document11 pagesXII Maths Exercise 3.1 (Solution)mansoor100% (5)
- Case StudyDocument32 pagesCase StudyKevin T. OnaroNo ratings yet
- Solution Handbook For Time-Harmonic Electromagnetic Fields by R. F. HarringtonDocument23 pagesSolution Handbook For Time-Harmonic Electromagnetic Fields by R. F. HarringtonwesNo ratings yet
- 1.'motivation For SoC Design - by Raveendra SomanaDocument13 pages1.'motivation For SoC Design - by Raveendra SomanaSantosh Shivapuji100% (1)
- Chapter V Beam Deflections 5.4Document3 pagesChapter V Beam Deflections 5.4Joshua John JulioNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer ProDocument7 pagesHeat Transfer ProBorse RajNo ratings yet
- Evert Hoek Results CalcDocument6 pagesEvert Hoek Results CalcKanaiyalal N. ShethNo ratings yet
- FORNEY TestingMachinesDocument17 pagesFORNEY TestingMachinesNhayelli EstradaNo ratings yet
- Origin of Voicing AlternationDocument10 pagesOrigin of Voicing AlternationCorinne D'AntonioNo ratings yet