Professional Documents
Culture Documents
IGCSE Chemistry - CD Answer 11
Uploaded by
Coolman Poon0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
54 views2 pagesIGCSE Chemistry - CD Answer 11
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentIGCSE Chemistry - CD Answer 11
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
54 views2 pagesIGCSE Chemistry - CD Answer 11
Uploaded by
Coolman PoonIGCSE Chemistry - CD Answer 11
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
CHEMISTRY ANSWERS
11 Acids and bases
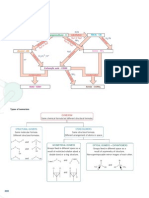
1 X is more acidic than Y. 2 C 3 Put a known volume of alkali into a ask. Add indicator to the alkali. Add acid from a burette, until the indicator changes colour. Note the volume of acid used. Repeat without the indicator, adding exactly the same volume of acid. Evaporate to remove the water. 4 magnesium carbonate nitric acid magnesium nitrate water carbon dioxide magnesium carbonate hydrochloric acid magnesium chloride water carbon dioxide magnesium oxide sulfuric acid magnesium sulfate water magnesium sulfuric acid magnesium sulfate hydrogen magnesium hydroxide hydrochloric acid magnesium chloride water magnesium oxide nitric acid magnesium nitrate water 5 to neutralise acidity in the soil 6 potassium 7 From top to bottom: MgO (s), Fe (s), NaHCO3 (s), KOH (aq), Fe2O3 (s)
OUP: this may be reproduced for class use solely for the purchasers institute
CHEMISTRY ANSWERS
8 dinitrogen oxide - neutral oxide carbon dioxide - acidic oxide sodium oxide - soluble basic oxide aluminium oxide - amphoteric oxide iron(II) oxide - insoluble basic oxide 9 CH3COOH (aq) 10
much less than 100%
H (aq) CH3COO (aq)
Barium sulfate is insoluble in water. It can be prepared by adding a solution of sodium sulfate to a solution of barium nitrate. The mixture is ltered to remove the barium sulfate, which is then rinsed with distilled water. The sodium ions and nitrate ions are spectator ions, and remain in solution.
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Algebra Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesAlgebra Cheat SheetDino97% (72)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Trigonometric Identities and EquationDocument80 pagesTrigonometric Identities and EquationCoolman Poon100% (2)
- 30 Water Page 1Document2 pages30 Water Page 1ryuzaki589100% (1)
- Coordinate of Straight Lines PDFDocument24 pagesCoordinate of Straight Lines PDFCoolman PoonNo ratings yet
- IB HLisomerDocument1 pageIB HLisomerCoolman PoonNo ratings yet
- S1 OCR As SyllabusDocument3 pagesS1 OCR As SyllabusCoolman PoonNo ratings yet
- IB HLisomerDocument1 pageIB HLisomerCoolman PoonNo ratings yet
- Aqa Addsci W SPDocument89 pagesAqa Addsci W SPEL HassaryNo ratings yet
- AssessmentDocument2 pagesAssessmentCoolman PoonNo ratings yet
- Factoring Polynomials Rev ExDocument2 pagesFactoring Polynomials Rev ExCoolman PoonNo ratings yet
- Mei Ocr 4725 Fp1jun 2006Document12 pagesMei Ocr 4725 Fp1jun 2006Coolman PoonNo ratings yet
- Appendix A Biology IGCSEDocument15 pagesAppendix A Biology IGCSECoolman PoonNo ratings yet
- 76 EukaryoticDocument4 pages76 EukaryoticCoolman PoonNo ratings yet
- Energy Transfer BDocument59 pagesEnergy Transfer BCoolman PoonNo ratings yet
- Chem Appendix ADocument13 pagesChem Appendix ACoolman PoonNo ratings yet
- Energy Transfer ADocument37 pagesEnergy Transfer ACoolman PoonNo ratings yet
- Revision Notes ShapeAndSpaceDocument34 pagesRevision Notes ShapeAndSpaceCoolman PoonNo ratings yet
- ElectromagnetismDocument45 pagesElectromagnetismCoolman Poon100% (1)
- Section e Solids Gases Liquids Revision GuideDocument10 pagesSection e Solids Gases Liquids Revision GuideCoolman PoonNo ratings yet
- Electricity SpiderDocument2 pagesElectricity SpiderCoolman PoonNo ratings yet
- AlgebraTrig ProblemsDocument17 pagesAlgebraTrig Problemsrizwan900No ratings yet
- 74 LipidsDocument3 pages74 LipidsCoolman PoonNo ratings yet
- Working of Cathode Ray OscillascopeDocument3 pagesWorking of Cathode Ray OscillascopeCoolman PoonNo ratings yet
- Trasnformation of FunctionsDocument70 pagesTrasnformation of FunctionsCoolman PoonNo ratings yet
- Cells Tissues QuestionsDocument1 pageCells Tissues QuestionsJosephine Charles HoNo ratings yet
- Revision Coordinated Science PhysicsDocument5 pagesRevision Coordinated Science PhysicsCoolman PoonNo ratings yet
- Turn To Section 2 (Page 4) of Your Answer Sheet To Answer The Questions in This SectionDocument12 pagesTurn To Section 2 (Page 4) of Your Answer Sheet To Answer The Questions in This SectionCoolman PoonNo ratings yet
- Trig Cheat Sheet Filled inDocument3 pagesTrig Cheat Sheet Filled inCoolman PoonNo ratings yet
- Edexcel - Formula - Book C2 and C3Document2 pagesEdexcel - Formula - Book C2 and C3Coolman PoonNo ratings yet