Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Calcium Gluconate Drug Study
Uploaded by
Krissy JavaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Calcium Gluconate Drug Study
Uploaded by
Krissy JavaCopyright:
Available Formats
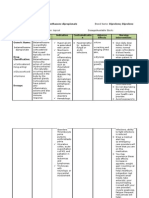
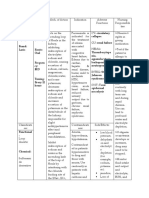
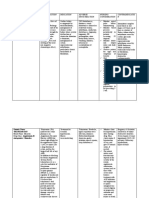
Name Of Drug
Dose, Route, Freque ncy Dose: 1ampule Route: IV Frequency: Over 20 minutes.
Mechanism of Action Calcium Gluconate acts like digitalis on the heart, increasing cardiac muscle tone and force of systolic contractions (positive inotropic effect) Rapidly and effectively restores serum calcium levels in acute hypocalcemia of various origins; also effective as a cardiac stabilizer under conditions of hyperkalemia or resuscitation.
Indication
Contraindication
Adverse Reaction
Nursing Responsibility
Generic Name: Calcium Gluconate Brand Name: Calgonate Classification: Electrolyte and Water Balance
Negative calcium balance (As in neonatal tetany, hypoparathyroidism, vitamin D deficiency, alkalosis). Also to overcome cardiac toxicity of hyperkalemia, for cardiopulmonary resuscitation, to prevent hypocalcemia during transfusion of citrated blood. Also as antidote for magnesium sulfate, for acute symptoms of lead colic, to decrease capillary permeability in sensitivity reactions, and to relieve muscle cramps from insect bites or stings. Oral calcium may be used to maintain normal calcium balance during pregnancy, lactation, and childhood growth and to prevent primary osteoporosis. Also an osteoporosis, osteomalacia, chronic hypoparathyroidism, rickets, and as adjunct in treatment of myasthenia gravis and EatonLambert syndrome.
Ventricular fibrillation, metastatic bone disease, injection into myocardium; renal calculi, hypercalcemia, predisposition to hypercalcemia (hyperparathyroidis m, certain malignancies); digitalis toxicity.
Body as a Whole: tingling sensation. With rapid IV, sensations of heat waves (peripheral vasodilation), fainting. GI: PO preparation: constipation, increased gastric acid secretion. CV: (with rapid infusion) hypotension, bradycardia, cardiac arrhythmias, cardiac arrest. Skin: pain and burning at IV site, severe Vegas thrombosis, necrosis and sloughing (with extravasation).
Assess for cutaneous burning sensations and peripheral vasodilation, with moderate fall in BP, during direct IV injection. Monitor ECG during IV administration to detect evidence of hypercalcemia: decreased QT interval associated with inverted T-wave. Lab tests: determine levels of calcium and phosphorus and magnesium frequently, during sustained therapy. Deficiencies and other ions, particularly magnesium, frequently coexist with calcium ion depletion
You might also like
- Drug Study - HydrocodoneDocument2 pagesDrug Study - HydrocodoneTarquin Tomada86% (7)
- DRUG STUDY - Calcium GluconateDocument2 pagesDRUG STUDY - Calcium GluconateSiergs Smith Gervacio100% (2)
- Feeding and Eating Disorders GuideDocument42 pagesFeeding and Eating Disorders GuideCharlaine BacasnoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument23 pagesDrug StudyEdward Baes33% (3)
- Dobutamine Drug StudyDocument1 pageDobutamine Drug Studyzyr2189100% (2)
- Furosemide Drug StudyDocument2 pagesFurosemide Drug StudyCrisha Ann Billones BacutaNo ratings yet
- Activating A Stroke Alert - A Neurological Emergency - CE591Document7 pagesActivating A Stroke Alert - A Neurological Emergency - CE591Czar Julius Malasaga100% (1)
- DR Walsh Autism Ocd Pandas Depression MethylationDocument6 pagesDR Walsh Autism Ocd Pandas Depression MethylationAnupama PouloseNo ratings yet
- Drug Study of FurosemideDocument5 pagesDrug Study of FurosemideAntonette Lei100% (1)
- Mindanao State University - Iligan Institute of Technology Student: Section: 263Document2 pagesMindanao State University - Iligan Institute of Technology Student: Section: 263AkiraMamo100% (1)
- Calcium GluconateDocument2 pagesCalcium GluconateMae Ann Bueno Castillon100% (1)
- Drug Study - NifedipineDocument2 pagesDrug Study - NifedipineSharlene Agcanas100% (10)
- DRUG STUDY TITLEDocument3 pagesDRUG STUDY TITLEAjon Veloso75% (4)
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudycarmaxetaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument19 pagesDrug StudyIsagani Socrates Loreto100% (1)
- FurosemideDocument2 pagesFurosemideIvanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- Calcium Gluconate Drug StudyDocument2 pagesCalcium Gluconate Drug StudyErika ManubayNo ratings yet
- PCR Test Certificate SampleDocument1 pagePCR Test Certificate SamplegheparduNo ratings yet
- PDS CS Form No 212 Revised2017Document11 pagesPDS CS Form No 212 Revised2017Twocubes 0967% (3)
- Drug Study: Antacid GI: Belching, GastricDocument3 pagesDrug Study: Antacid GI: Belching, GastricJhon Jade PalagtiwNo ratings yet
- MSU-IIT Drug Study: AcetazolamideDocument2 pagesMSU-IIT Drug Study: AcetazolamideLIEZEL GRACE VELAYONo ratings yet
- Brand Name: Dilzem Generic Name: Diltiazem Indications: Angina Pectoris IncludingDocument3 pagesBrand Name: Dilzem Generic Name: Diltiazem Indications: Angina Pectoris Includingianecunar0% (1)
- Folic Acid Benefits, Uses, InteractionsDocument15 pagesFolic Acid Benefits, Uses, InteractionsLene Derlene Gerona100% (2)
- MethotrexateDocument2 pagesMethotrexateIvanne Hisoler83% (6)
- Amlodipine Besylate Drug StudyDocument1 pageAmlodipine Besylate Drug StudyKrissy Java100% (1)
- Drug Study: Pharmacologic AlDocument7 pagesDrug Study: Pharmacologic AlFrudz Orjaleza100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument21 pagesDrug Studydelpozo100% (3)
- Ferrous Sulfate: o o o o o o oDocument5 pagesFerrous Sulfate: o o o o o o oLelanie Japitana100% (1)
- Drug Study Atropine SulfateDocument1 pageDrug Study Atropine Sulfateirhizzp75% (8)
- Calcium Gluconate Drug SummDocument1 pageCalcium Gluconate Drug SummWarren100% (2)
- Kalium Durule Drug StudyDocument3 pagesKalium Durule Drug StudyJustine Garcia100% (1)
- Drug Study - Epinephrine (Adrenalin)Document2 pagesDrug Study - Epinephrine (Adrenalin)mikErlh60% (5)
- HydralazineDocument1 pageHydralazineIvanne Hisoler75% (8)
- Post TestDocument11 pagesPost Testoomculun100% (6)
- Caries Risk AssessmentDocument33 pagesCaries Risk AssessmentSomya Jain100% (1)
- Methergine Drug StudyDocument2 pagesMethergine Drug StudycuakialyannaNo ratings yet
- Magnesium Sulfate Drug StudyDocument2 pagesMagnesium Sulfate Drug StudyMaan Molinyawe81% (16)
- Drug Study - Furosemide (Lasix)Document2 pagesDrug Study - Furosemide (Lasix)mikErlh80% (5)
- AmiodaroneDocument2 pagesAmiodaronePauling Frez100% (5)
- Calcium Gluconate Drug StudyDocument1 pageCalcium Gluconate Drug StudyMichael Baylon DueñasNo ratings yet
- Benzydamine HCL Drug StudyDocument1 pageBenzydamine HCL Drug StudyKrissy JavaNo ratings yet
- Nifedipine Drug StudyDocument3 pagesNifedipine Drug StudyCrystal Queen MarquezNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument15 pagesDrug StudySharmyne RhyllNo ratings yet
- Midazolam Drug Study SaclotDocument1 pageMidazolam Drug Study SaclotMaybelle Cababat SaclotNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY EpinephrineDocument2 pagesDRUG STUDY EpinephrineMayet De Castro Lejano100% (2)
- Magnesium SulfateDocument1 pageMagnesium SulfateTrixie Anne Gamotin100% (1)
- Hydralazine Drug StudyDocument2 pagesHydralazine Drug StudyErika Robella100% (1)
- Calcium Gluconate Drug StudyDocument1 pageCalcium Gluconate Drug StudyChaepmunk Cy75% (4)
- Drug Study HydralazineDocument10 pagesDrug Study HydralazineLuige AvilaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Nursing DepartmentDocument1 pageDrug Study: Nursing Departmentgiselle chloe100% (1)
- Folic AcidDocument3 pagesFolic Acidapi-37979410% (1)
- Bone Density Drug StudyDocument10 pagesBone Density Drug StudyMar Ordanza100% (1)
- Drug Dosage, Classification, Indications, and Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument12 pagesDrug Dosage, Classification, Indications, and Nursing ResponsibilitiesCamilley De Vera100% (1)
- Referral System in IndiaDocument24 pagesReferral System in IndiaKailash Nagar100% (1)
- Vii. Drug Study Drug Indication Action Side/Adverse Effects Nursing Consideration Date Ordered: Generic Name: SpecificDocument1 pageVii. Drug Study Drug Indication Action Side/Adverse Effects Nursing Consideration Date Ordered: Generic Name: SpecificnuraNo ratings yet
- Prometric Exam Ophthalmology 28-3-2013Document10 pagesPrometric Exam Ophthalmology 28-3-2013Hasan Dahamsheh100% (4)
- Drug Study - Calcium GluconateDocument1 pageDrug Study - Calcium GluconatemikErlhNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Ampicillin, CelestamineDocument5 pagesDrug Study Ampicillin, CelestamineLLan Kristine Lazarito100% (1)
- Clinical Medications Worksheets: (Why Med Ordered) Contraindications/warnings/interactionsDocument3 pagesClinical Medications Worksheets: (Why Med Ordered) Contraindications/warnings/interactionsENo ratings yet
- Generic Name:: Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindi-Cation Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument1 pageGeneric Name:: Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindi-Cation Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesmaemalabonNo ratings yet
- Labetalol Hydro ChlorideDocument3 pagesLabetalol Hydro Chlorideapi-3797941100% (1)
- Warfarin Dosing and Monitoring GuidelinesDocument4 pagesWarfarin Dosing and Monitoring GuidelinesbillyktoubattsNo ratings yet
- Doxazosin MesylateDocument2 pagesDoxazosin Mesylateapi-3797941No ratings yet
- Name of Drug Dose, Route, Freque Ncy Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Reaction Nursing ResponsibilityDocument1 pageName of Drug Dose, Route, Freque Ncy Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Reaction Nursing ResponsibilitySherwin Mike QuijoteNo ratings yet
- Julius Caesar Francia BS-N4ADocument37 pagesJulius Caesar Francia BS-N4ApauchanmnlNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument20 pagesDrug StudyBrylle CapiliNo ratings yet
- CHF Drug StudyDocument4 pagesCHF Drug StudyAiza Apelada-NievaNo ratings yet
- KaliumDocument2 pagesKaliumJustine Kaye Iballa HarligaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyJheryck SabadaoNo ratings yet
- Hypercalcemia (F&e)Document3 pagesHypercalcemia (F&e)Sarah Grace CajucomNo ratings yet
- Care for Patients with Fluid and Electrolyte ImbalancesDocument10 pagesCare for Patients with Fluid and Electrolyte ImbalancesAbigail LonoganNo ratings yet
- SSSForms Personal Record PDFDocument3 pagesSSSForms Personal Record PDFBea GenerNo ratings yet
- Application Form PDFDocument3 pagesApplication Form PDFKrissy JavaNo ratings yet
- SSSForms Change Request PDFDocument4 pagesSSSForms Change Request PDFEppNo ratings yet
- Drug StudiesDocument6 pagesDrug StudiesKrissy JavaNo ratings yet
- Hypertensive Renal DiseaseDocument2 pagesHypertensive Renal DiseaseHenry KaweesaNo ratings yet
- The Relationship Between Internet Addiction and Mental Health ConDocument7 pagesThe Relationship Between Internet Addiction and Mental Health ConBrandusa TurlacNo ratings yet
- 3 Main Food Group: Reporter: Mercy Grace Yongco - MPA IDocument11 pages3 Main Food Group: Reporter: Mercy Grace Yongco - MPA ICHOSEN TABANASNo ratings yet
- Care With Git PTDocument16 pagesCare With Git PTHafidz Ma'rufNo ratings yet
- Futility CasesDocument2 pagesFutility CasesBindashboy0No ratings yet
- Thyroid Disorders Part II Hypothyroidism and Thyroiditis LIttle 2006Document6 pagesThyroid Disorders Part II Hypothyroidism and Thyroiditis LIttle 2006Jing XueNo ratings yet
- Happy Hearts BrochureDocument2 pagesHappy Hearts Brochuresuperindian87No ratings yet
- MR NITIN PDFDocument2 pagesMR NITIN PDFVenkat Nitin GuttaNo ratings yet
- Hygiene (NCLEX) Flashcards - QuizletDocument5 pagesHygiene (NCLEX) Flashcards - QuizletA.No ratings yet
- Penatalaksanaan Fisioterapi Pada Penderita Gangguan Nyeri Akibat Sindrom Piriformis Dengan Teknik Strain Counterstrain Dan Contract Relax StretchingDocument7 pagesPenatalaksanaan Fisioterapi Pada Penderita Gangguan Nyeri Akibat Sindrom Piriformis Dengan Teknik Strain Counterstrain Dan Contract Relax Stretchingchyntia eryonzaNo ratings yet
- Cga - 1Document19 pagesCga - 1Kenji Tolero100% (1)
- Valori Contract An. 2023 - Paraclinic - 20.09.2023Document21 pagesValori Contract An. 2023 - Paraclinic - 20.09.2023Matteo si Sofia vlog'sNo ratings yet
- Karsto Akmeņu Masāža INGLIŠ - KopijaDocument10 pagesKarsto Akmeņu Masāža INGLIŠ - KopijaAlise KoblinecaNo ratings yet
- Doterra PB Assist JuniorDocument4 pagesDoterra PB Assist JuniorGeorgiana MadalinaNo ratings yet
- MedVantage - Fellowship Program in Diabetes MillitusDocument2 pagesMedVantage - Fellowship Program in Diabetes MillitusmedvantageNo ratings yet
- Nines P Bautista, MD, MSDocument12 pagesNines P Bautista, MD, MSadnep1991No ratings yet
- HSYLCSyllabus Beijing 2016Document5 pagesHSYLCSyllabus Beijing 2016Akshay SwaminathanNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Nurse Skills ChecklistDocument4 pagesCritical Care Nurse Skills Checklistspartacuslives100% (1)
- Healthcare Waste Management EssentialsDocument10 pagesHealthcare Waste Management EssentialsMohamedErrmaliNo ratings yet
- Inventaris IGD 2022 TerbaruDocument5 pagesInventaris IGD 2022 TerbaruEryNo ratings yet
- Tumor Lysis SyndromeDocument12 pagesTumor Lysis Syndromeapi-647779956No ratings yet
- IMCI Learning FeedbackDocument1 pageIMCI Learning Feedbackinah krizia lagueNo ratings yet