Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tet Material Corrected
Uploaded by
Vinayadhar RajuCopyright
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentTet Material Corrected
Uploaded by
Vinayadhar Rajuwww.facebook.
com/vinayadharraju
www.feltap.blogspot.com
Practical English grammar
Full English material for tet and dsc
Useful for all competitive examinations
Prepared by P.Vinayadharraju
M.A. (lit). M.Sc., B.Ed.
Mobile No: 9347847048 Vinayadharraju@gmail.com Visit: www.feltap.blogspot.com Facebook Link:www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com
Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
PAPER I&II
ENGLISH GRAMMAR 1. Types of Sentences 2. Parts of speech 3. Prepositions and articles 4. Verbs a. Auxiliary verbs b. Main verbs 5. Tenses 6. Transformation of Sentences a) Active voice and passive voice b) Direct and indirect Speech c) Degrees of comparison d) Simple complex and compound sentences e) Questions and question tags 7. Phrases uses of phrases 8. clauses 9. Conjunctions:- co-coordinating conjunction Sub-coordinating conjunction 10.Synthesis of sentences 11.Composition: letter writing prcis writing 12.vocabulary a. Antonyms b. Synonyms c. Spelling 13.Comprehension Passages CHAPTER I TYPES OF SENTENCES
INTRODUCTION English: - English is the language of the people of England. Grammar: - It is an art of putting the right words in the right place. Letters: - There are 26 letters in English language. These are divided in to three groups. They are 1. Vowels: - A, E, I, O, U are called Vowels. 2. Consonants: - B, C, D, F, G, H, J, K, L, M, N, P, Q, R, S, T, called consonants. 3. Semi vowels: - W, Y are called Semi Vowels.
Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
V, X, Z are
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
Word: - A word is a group of letters which gives complete meaning. Eg:- a book, a river, a flower Sentences:- A sentence is a group of words, which give complete meaning. Eg:-1. She sings a song. 2.I am teaching English grammar. TYPES OF SENTENCES There are four types of sentences in English language. They are 1. Assertive Sentence. 2. Interrogative Sentence. 3. Imperative Sentence. 4. Exclamatory Sentence. 1) Assertive Sentence:These Sentences are general statements. They end with full stop. They contain subject, verb, object in order. Assertive Sentence is known as Declarative or Affirmative Sentence. Note: - A sentence begins with noun or pronoun, ends with full stop is called Assertive Sentence. Eg:1.Sita Sings a Song. 2. Raju eats a banana. 3. They are my friends. 4. She is a doctor.
2) Interrogative: Sentence:These sentences are questions. They end with question mark. These are divided into two groups:1. General questions (leading questions) 2. Interrogative Sentences 1. General questions: - These questions get yes or No answers .They start with the following helping verbs. HELPING VERBS Be forms:-am, is, are, was, were, Do forms:-do, does, did, Have forms:- have, has, had, Model Auxiliaries:-shall, should, can, could, will, would, may, might, must,
Eg:1. Am I right? 2. Is your father at home? 3. Are you going to College? 4. Was he absent yesterday? 5. Were you in Tirumala last Saturday? Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju 6. Do you come with me? 7. Does she get up early? 8. Did Raju attend the class yesterday? 9. Have you finished your home work? 10. Has she two daughters? 11. Had they gone to Hyderabad? 12. Shall I bring you a cup of Coffee? 13. Should you take rest? 14. Can you play Cricket? 15. Could you please give me your pen? 16. Will you come to my house tomorrow? 17. Would you please give the news paper? 18. May I help you? 19. Might he have come here?
2. Interrogative questions:-These questions seek lengthy answers. They start with the following interrogative question words (wh. Words) who which whose where whom when what why how
Eg:1. Who is your father? 2. What are you doing? 3. Where are you going? 4. When is your birthday? 5. Why are you late today? 6. Which is your native place? 7. Who do you like the best in your family? 8. Whose book is this? 9. How are you? 3) Imperative Sentence:These sentences are requests, orders, commands, advice, suggestions, are called imperative sentence.
Instructions
Every sentence begins with first form of verb and ends with full stop. E.g.:1. Please give me your pen. 2. Take this file. 3. Open the door. 4. Bring me a glass of water. 5. Close the Windows. 6. Stay here. 7. Take Medicines. 8. Attend the examination without fail. 4) Exclamatory Sentence: - These sentences give our feelings about any incident, These sentences start with what, How and end with exclamatory mark ( !). Eg:1. What a Surprise! 2. How notice it is! 3. What a stupid you are! 4. What a beautiful bird it is!
Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
5. Oh! He is dead
CHAPTER II PARTS OF SPEECH
There are eight parts of speech in English language. They are:1. Noun ()
2. Pronoun 3. Verb 4. Adjective 5. Adverb 6. Preposition 7. Conjunction 8. Interjection
()
( ) () ( ) ( )
() ( ) English Family _____________________________________________
Noun (Father) ___________________________ Pronoun (Elder son) Adjective (Younger) Preposition (Brother in law)
Verb (Mother) Adverb (Daughter)
Conjunction (Family Friend)
Interjection (Neighbour)
1. NOUN 1. Noun: - A Noun is word, used to indicate the names of persons, places, and things. (
.) , ,
Eg:- 1.Raju is a clever student. 2. Bangolore is beautiful City. 3. The book is on the table. Types of Nouns: - They are 5 types of Nouns They are 1. Proper noun 2. Common noun 3. Collective noun 4. Material noun 5. Abstract noun 1. Proper noun: - Proper noun denotes particular names of persons, Places and things. Eg:- 1.Hari is a good dancer. 2. Delhi is a big city. 3. Rajampet is my native place. 4. John goes to church every Sunday.
Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
2.
Common noun :- A Common noun denotes commonly used the names of persons, places and things Eg:- man, woman, girl, boy, tree, flower, bird, animals, book, student, teacher, city, village. Collective noun :- Collective noun denotes a group of persons animals and things Eg:- People, Mob, gang, crowd, army, team, Police, herd, Cattle, bundle flock, fleet, bunch,
3.
4.
Material noun:- Material noun denotes the names of materially used to make things Eg:- Gold, plastic, silver, iron, steel, wood, cotton, rice, wheat, oil, water, clay.
5.
Abstract noun: - An abstract noun is usually, the names of quality, action, or state. Quality: - Kindness, happiness, greatness. Action: - Laughter, anger, movement. State: - Truth, youth, childhood.
Observe the following tables:-
adjectives
curious happy obedient argent verb advice achieve develop inform behave punish strong noun child friend market judge
abstract nouns curiosity happiness obedience urgency abstract nouns advice achievement development information behavior punishment strength abstract noun childhood friendship marketing justice
2. PRONOUN
2. Pronoun: - Pronoun is word which is used instead of a noun.
(Nouns .)
Ex:- Sita Ramu Book Students
She He It They
Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
Kind of Pronouns: - There are mainly nine kinds of pronouns.
Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
They are:1. Personal Pronouns. 2. Reflexive or Emphatic. 3. Possessive Pronouns. 4. Demonstrative Pronouns. 5. Interrogative Pronouns. 6. Relative pronouns. 7. Indefinite pronouns. 8. Distributive pronouns. 9. Reciprocal pronouns. 1. Personal pronoun: - Personal pronouns which are related to persons are called personal pronouns. These are three types. They are:1. First person 2. Second Person 3. Third Person LIST OF PERSONAL PRONOUNS:Person Number Subjective Objective Possessive Possessive Reflexive Pronoun Pr. pronoun Adjective pronoun pronoun 1 pr. 2 Pr.3 Pr.4 Pr.5 I Singular I me my mine myself Plural we us our ours ourselves II Singular you you your yours yourself Plural you you your yours yourselves III Singular he him his his himself she her her ours herself it it its its itself Plural they them their theirs themselves 2. Reflexive/Emphatic Pronoun:- myself , ourselves, yourself, yourselves, himself, herself, itself, themselves are called reflexive or Emphatic Pronouns. Eg: - 1.I will do it myself. 2. She hurt herself. 3. You can explain it yourself. 4. They admit themselves. Emphatic pronoun:Eg:1. I myself will do it 2. I myself heart 3. You yourself can explain it 4. They themselves admit 3. Possessive Pronoun: - mine, ours, yours, his, hers, its, theirs are called possessive pronouns. 4. Demonstrative Pronoun:- Pronouns which are used to show the objectives, are called demonstrative pronouns. Eg:- This, These, that, those 1. This is a book. 2. These are my books. 3. That is my bag.
Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
4. Those are mangoes. 5. Interrogative Pronouns: - Interrogative Pronouns refer to asking questions. Whose, what, which, when, where, why, How. Eg:1. Whose is this? 2. What are you doing? 3. Which is your native place? 4. Where are you going? 5. When is your birth day? 6. Why are you late? 6. Relative Pronoun:-A relative pronoun relates or refer to noun, which has gone before Who, What, Whose, which, what, that whom etc. Eg:- 1. Raju is my friend who tells me stories. 2. This is the bag which I bought yesterday. 3. This is the man, whom you sent to me. 4. This is the house that my father built. Note:- Who, whose, whom refer to human beings and persons what, which, that refer to things. 7. Indefinite pronouns:-Pronouns which do not refer to any particular person or thing are called Indefinite pronouns Eg: - Someone, anyone, everyone, noone, something, anything, everything, nothing, somebody, anybody, everybody, nobody
8. Distributive Pronoun:Each, either, neither are called distributive pronouns. Eg:- 1.Each of the boys is qualified 2. Neither of students is true 3.Either of the two must have it. 9. Reciprocal Pronoun:- Each other, one another are called reciprocal pronouns. Note: - Each other, one another denote a mutual or reciprocal relationship, each other is usually used to refer to, two persons or things. One other is used to refer to more than two persons or things. Eg:1. The two girls help each other 2. All the members of the staff quarreled with one other.
3. VERB
Verb: - The word verb comes from the Latin word: Verbatum which means an action. Verb denotes the work done. ( , , .) They are mainly two kinds of verbs. They are:1. Auxiliary Verbs 2. Main Verbs Eg:1. I am a teacher(state) 2. I have two children (Possessive) 3. I teach English grammar ( action) 4. ADJECTIVE
Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
Adjective:- Adjective is a word to add Something to the meaning of noun.(
)
Eg:1. It is a black board 2. She is a good girl 3. Ashoka was a great man Kinds of Adjectives: There are mainly nine kinds of Adjectives. They are:1. Adjective of quality. 2. Adjective of quantity. 3. Adjective of number. 4. Demonstrative adjective. 5. Emphasizing adjective. 6. Possessive adjective. 7. Interrogative adjectives. 8. Distributive adjective. 9. Exclamatory adjective. 1. Adjective of quality: - These words describe the quality of the nouns. To which they refer. Eg:1. This is a beautiful flower. 2. He is an honest man. 3. Rani is a good girl. 2. Adjective of quantity:- These words describe the quantity of the nouns, To which they refer. (Some, much, little, enough, all, few.) Eg:1.I have Some money in my pocket 2. There is a little water in the tank
3. Adjectives of number: - These words give the number of nouns to which they refer These are two types namely 1. Cardinal numbers, 2. Ordinal numbers. Cardinal Eg:1. There are sixty students in the class. 2. She got first rank in civil services. 4. Possessive adjective:- These words indicates the person or thing, to whom the nouns refer to here having position my, our, your, his, her, its, their. Eg:1. This is my book. 2. That is his house. 5. Interrogative adjectives:- These words indicate a question while describing the noun to which they refer
Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
Eg:- 1.What class are you stu 1. dying? 6. Emphasizing Adjectives:- possessive adjective emphasize emphazing adjective . Eg:-He saw the accident with his own eyes. 7. Distributive adjectives:-each, either, neither, every are called distributive adjectives. They indicate one thing or person taken separately out of a whole group or clause. Eg:- 1.Every man must do his duty. 2. I have neither a pen. 8. Demonstrative adjectives:- these adjectives point out the nouns refered to these, that, those. Eg:-1. This book is mine. 2. These books are yours. 3. That house is my uncles. 9. Exclamatory adjectives:- what
Exclamatory adjective .
5. ADVERB Adverb: - Adverb is a word used to qualify a verb and adjective and another adverb. Eg:1. Raju reads well . 2. Ice is very cold. 3. The old man walks very slowly . Kinds of Adverbs:1. Adverbs of time 2. Adverbs of place 3. Adverbs of number 4. Adverbs of manner 5. Adverbs of degree or quantity 6. Adverbs of Affirmation / Negation 7. Adverbs of reason 8. Interrogative adverbs 1. Adverbs of Time: - These answers the question when Now, today, yesterday, tomorrow, soon, before, late, after, early, all ready, after, then. . Eg:1. He will come any time now. 2. I will tell you about it tomorrow. 3. They have already finished the homework. 2. Adverbs of place:- These answers, the question where Here, there, everywhere, anywhere, somewhere, nowhere, behind, forward, inside, outside, in, out come, in , get out, far, near. Eg:1. Please sit here. 2. I have looked everywhere. 3. Come forward.
Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
3. Adverbs of number: - These answers, the question How often (Once, twice, thrice, firstly, secondly, lastly, finally) Eg:1. I have you told you about it twice 2. He often makes mistakes 3. I go to temple once a week 4. Adverbs of manner: - These answers, the question How (well, slowly, quickly, sadly, loudly, foolishly Eg:1. My friend speaks fluently 2. She walks slowly 5. Adverbs of degree are quantity:- These answers the questions How much , How long , How much-----,? How long--.
( almost, always, sometimes, quite, enough, too, very) Eg:1. This girl is too late 2. The sea is very ferocious 3. you are quite wrong 6. Adverbs of Affirmation / Negation: - These answers word of negation yes or no. Affirmation: - surely, certainly, suddenly, readily Negation : No, not, not at all Eg:1. She is certainly right 2. He is not willing to do the work 3. No I cant speak English fluently 7.Adverbs of Reasons :- These are the answers the question why (So, therefore, Hence, because of) Eg:1. when does he come? 2. How can you reach the top? 3. where do you live? 6. PREPOSITION Preposition: - Pre means before Position means state A preposition is a word, which is placed before a noun or pronoun and it shows relation between the noun or pronoun and other words in a sentence.(preposition
. Pre position . noun pronoun .)
List of important prepositions:-
Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com
Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
By, at, in, of, on, to, up, for, off, out, from, with, in to, down, over, up on, about, before, behind, along, between among, across, beside, out, upon, since, under, into etc. Eg:1. The book is on the table, 2. Someone is knocking at the door 3. I have been living in Rajampet since 1989
7. CONJUNCTION Conjunction :- A conjunction is word which joins two words or two sentences. (
, conjunctions .)
Eg:1. Rama and Lakshmana were brothers 2. Vimala or Kamala make at the rank in TET 3. If you work hard you can get a rank in TET. List of important conjunctions:If, unless, though, all though, even though, as, since, because, as soon as when, while, but, yet, or, otherwise, so, and, therefore, not only, but also, as well as, both and, either or, Neither nor. 8. INTERJECTION Interjection: - An interjection is a word which expresses sudden feeling of mind.
( , , .) Ex:- oh! he is dead. Alas! The old man was passed away last night. Hurrah! We have won the match. Interjection
EXERCISES
I. Choose the correct parts of speech the underlined word in the following sentences
1. He is a wise man ( ) 1) Adverb 2) Verb 3) Preposition 4) Adjective 2. Iron is more useful than any other metal ( ) 1) Adjective 2) Verb 3) Pronoun 4) Noun 3. Alas ! What a bad news ( ) 1) Pronoun 2) interjection 3) Noun 4) Verb 4. We played an excellent Match ( ) 1) Noun 2) Pronoun 3) Adjective 4) verb 5. You can choose either this bat or that bat. ( ) 1) Noun 2) pronoun 3) Verb 4) Adjective 6. The Prisoner hanged himself ( ) 1) Preposition 2) Verb 3) Noun 4) Pronoun 7. Everest is the highest peak in the world ( ) 1) Adverb 2) Preposition 3) Pronoun 4) Noun 8. The bird is making itself a nest, here the word itself ( ) 1) Personal pronoun 2) Possessive pronoun 3) Reflexive pronoun 4) An impersonal pronoun 9. Lavanya is my daughter who is studying second standard ( ) 1) Personal pronoun 2) Interrogative pronoun 3) Reflective pronoun 4.Distribute pronoun 10. Mr. Rao has two houses. ( ) 1) Preposition 2) Verb 3) Noun 4) Pronoun
Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
11.Tajmahai is a beautiful building. ( ) 1) Noun 2) Pronoun 3) Adjective 4) verb 12. As you like it is a very good drama. 1) Noun 2) Pronoun 3) Adjective 4) verb 13.Oh! We lost the match again. ( ) 1) Pronoun 2) interjection 3) Noun 4) Verb 14. You will get good marks if you study hard. ( ) 1) Pronoun 2) interjection 3) conjunction 4) Verb 15.How do you do? ( ) 1) Personal pronoun 2) Interrogative pronoun 3) Reflective pronoun pronoun 16. She is not old enough to go to college. ( ) 1) Adverb 2) Verb 3) Preposition 4) Adjective 17. He often makes mistakes 1) Adverb 2) Preposition 3) Pronoun 4) Noun 18.Unless you work hard, you will not pass. ( ) 1) Pronoun 2) interjection 3) conjunction 4) Verb 19. Ramya likes sweets besides vegetables. ( ) 1) Adverb 2) Verb 3) Preposition 4) Adjective 20.You ought to respect your parents. ( ) 1) Adverb 2) Preposition 3) Pronoun 4) Noun 21.Ravi reached this morning to Bombay. ( ) 1) pronoun 2) Verb 3) Preposition 4) Adjective 22.He teaches us English. ( ) 1) Pronoun 2) Verb 3) Preposition 4) Adjective 23. Either of you must have it. ( ) 1) Pronoun 2) Verb 3) Preposition 4) Adjective 24.He is very good police man. ( ) 1) Adverb 2) Verb 3) Preposition 4) Adjective 25. My mother hasn't been too well. ( ) 1) Adverb 2) Verb 3) Preposition 4) Adjective
4.Distribute
CHAPTER III ARTICLES AND PREPOSITIONS A.ARTICLES
There are two articles in English. They are 1. Indefinite articles: - A and An are called Indefinite articles 2. Definite Articles: - The is called definite articles USE OF ARTICLE A:Rules:1. A is used before a singular common noun beginning with consonantal sound. a boy, a flower, a box, a man a book a pen a car a table 2. Some words start with a vowel letter (A, E, I, O, U) but having a consonant sound then indefinite articles a is used before them. Eg:- a University a European a unite a uniform a universal a useful animal
Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
Eg:-
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
3. A is used before a singular common noun, beginning with a vowel letter which has w sound (Consonantal sound ) Eg:- a one rupee note a one eyed beggar 4. A is used before the collective nouns:Eg:a group of people a bunch of flower a bundle of papers a bunch of keys 5. A is used before the quantities:Eg:- a few, a lot of, a little, a dozen 6. To make a common noun of a proper noun:Eg: - This is a Shakespeare of India A Denial comes to Judgment EXERCISES:Fill in the blanks with suitable articles:1. India is a great country. 2. Rani is a nurse in hospital. 3. Gita has a long hair. 4. Raju wrote a letter to me. 5. Mr. Frank is a European. 6. I have found a one Rupee coin in the basket. 7. He is a University Professor. 8. John is a handsome boy. 9. English is a difficult language. 10.What a beautiful painting.
USE OF ARTICLE AN:Rules:1. An is used before a singular common noun beginning with vowel sound. Eg:- an apple, an intelligent, an orphan, an elephant, an umbrella, an orange, an incident 2. An is used before a singular common noun beginning with consonants but having vowel sound Eg:- an hour, an honest man, an heir, an honorable teacher 3. An is used before abbreviations, which begin with F, I, R, M, N, L, S, H, X or pronounced an individual letters. Eg:- an FIR, an MLA, an SBI, an ISI, an NCC, an HP Gas, an RMP an LLB an X-ray EXERCISES:1. Kalyani is an intelligent girl. 2. we will leave after an hour. 3. Chinni is an MA English. 4. The girl is an orphan . 5. He married an American lady. 6. Kalyan is an extraordinary man. 7. man is a social animal. 8. Jaya is an innocent girl. 9. Pavan is an MLA. 10.I met with an accident.
USE OF ARTICLE THE:Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
Note:- THE is used before DR. O SUMA IRON SPOT D = Direction R = Rivers O = oceans S = Superlative adjectives U = uniqueness in the universe M = Mountains A= Adjectival nouns I = instruments R = Religious O = Ordinal Numbers (first, second) N = News papers. S = sacred books P = political parties O= organizations T = Trains. Rules:1.T'he is used before the names directions:Eg:- The east , The west, The North, The South 2. The is used before the names of rivers:Eg:- The Thapathi, The Ganga, The Yamuna, The Godhavari 3. The is used before the names of Oceans:Eg:- The Indian Ocean, The Atlantic Ocean The red sea The Pacific 4. The is used before superlative adjectives:Eg:- The tallest, The highest The greatest The shortest 5. The is used before unique in the universe. Eg:- The Sun, The Sky, The Star, The moon, The earth 6. The is used before the names of Mountains:Eg:- The Himalayas, The Aravalis, The Vindhya 7. The is used before adjectival nouns. Eg:- The poor, The deaf, the rich, the dumb 8. The is used before Instruments(musical instruments):Eg:- The Veena, The Drum, the Violin, The fluet, The Thabala, 9. The is used before Religious. . Eg:- The Hindu, The Muslim, The Christian 10. The is used before ordinal numbers:Eg:- The first, the third, the second, the fourth 11. The is used before the names of news papers:Eg:- The Hindu, The Vaartha, The Eenadu 12. The is used before Sacred books (Holy Book). Eg:- The Ramayana, The Bible, The Bhagavathgeetha, The Quran 13. The is used before the names of political parties Eg:- The congress, The YSR Congress, The BJP 14. The is used before the names of Organizations. Eg:- The UNO, The UNICEF, The UNESCO, The W.H.O 15. The is used before the names of trains. Eg:- The Shathabdhi, The Kanyakumari Express, The Rayalaseema Express, 16. The is used before the names of plural numbers:Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
Eg:- The news papers, The Players, The students, The books 17. The is used before a historical construction. Eg:- The Charminar, The Red fort, The Thajmahal, The gate way of India. 18. The is used before national festivals. Eg;- The Ghandhi Jayanthi, The Independence Day, The Childrens Day, The Republic Day 19. The is used before a head of the Institutions :Eg:- The Head Master, The Principal, The Manager, The Post Master 20. The is used before repetation of a common noun:Eg:- I saw a boy in the park, the boy was crying, we met a stranger at the seashore The stranger was an American 21. The is used before a Particular place, thing or person. Eg:- I saw this book in the Library last Sunday. Went to the Beach. The criminal was hanged. 22. The is used before the secondary purpose of a place. Eg:- I went to Hospital to consult the Doctor. ( primary) I went to the Hospital to see my sick friend. (secondary) I go to college. (primary) My father goes to the College. 23. The is used in comparative construction before the both adjectives. Eg:- The more your work the more you gain. The faster you run the quicker you reach. The Higher the colder. OMISSION OF ARTICLES Rules:a. Any article cannot be used before the names of person. Eg:- X Raju, X Githa X Sita, X Jaya b. Any article cannot be used before the names of Country. Eg:- X India, X Japan, X Sri Lanka, X America c. . Any article cannot be used before the names of games. Eg:- X Cricket, X Tennis, X foot ball, X chess d. Any article cannot be used before the names of Disease. Eg:- X Cancer, X Maleria, X Fever, e. . Any article cannot be used before the names of Metal. Eg:- X cotton, X Gold, f. Any article cannot be used before the names of language. . Eg:- X English, X Sanskrit , X telugu, X hindi g. Any article cannot be used before the names of a meal. Eg:- X Lunch, X Supper , X Dinner, X Break fast h. Any article cannot be used before the names of a day or month. Eg:- X March, X Sunday , i. Any article cannot be used before the Abstract Noun. Eg:- X honest, X Child hood, X Knowledge, X love 1. Fill in the blanks with suitable Article:1. He was the first man to arrive. 2. The Nile is the river 3. My grandmother reads the Bible regularly
Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
4. The Sun rise in the east 5. The Hindu is a popular news paper 6. Mr. Rama is the most experienced in our College. 7. The Himalayas are to the North of India 8. The Pacific is an Ocean 9. She is playing the Thabala 10. The Earth revolves round the Sun 11. Vijayavada is on the Krishna
EXERCISES 1. Choose the suitable article:1) ______ Ganga is a holy water. ( 1) a 2)an 3)the (4 No article 2) He is ________ honorable man. ( 1) a 2)an 3)the (4 No article 3) I met him _____ year ago. ( 1) a 2)an 3)the (4 No article 4) Hindi is ____ easy language. ( 1) a 2)an 3)the (4 No article 5) Mr. Brown is _____ European. ( 1) a 2)an 3)the (4 No article 6) _____ Sun raises in the east. ( 1) a 2)an 3)the (4 No article 7) _____ Elephant is a wild animal. ( ) 1) a 2)an 3)the (4 No article 8) He is _____ honest man. ( 1) a 2)an 3)the (4 No article 9) Will you come back in ____ hour? ( 1) a 2)an 3)the (4 No article 10) ____ Gold is a precious metal. ( 1) a 2)an 3)the (4 No article 11) She is _____ Australian lady. ( 1) a 2)an 3)the (4 No article 12) Dont go without _____ umbrella. It is raining. ( 1) a 2)an 3)the (4 No article 13) India is ____ great country. ( 1) a 2)an 3)the (4 No article 14) He is ______ university student. ( 1) a 2)an 3)the (4 No article 15) John is ______ handsome boy. ( 1) a 2)an 3)the (4 No article 16) I found _____ one rupee note. ( 1) a 2)an 3)the (4 No article 17) Abdul kalam is _____ extraordinary man. ( 1) a 2)an 3)the (4 No article 18) _____ Nile is a long river. (
Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
) ) ) ) ) )
) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) )
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
1) a 2)an 3)the (4 No article 19) Vijayawade is on _____ Krishna river. ( 1) a 2)an 3)the (4 No article 20) I saw _____ snake in the river. ( 1) a 2)an 3)the (4 No article 21) Let us form ____ union. ( 1) a 2)an 3)the (4 No article 22) My mother reads _____ Ramayana every day. ( 1) a 2)an 3)the (4 No article 23) When I was coming to the college, I saw ___ accident.( 1) a 2)an 3)the (4 No article 24) I saw _______ orphan in the ashram. ( 1) a 2)an 3)the (4 No article 25) It is ________ interesting story. ( 1) a 2)an 3)the (4 No article 26) Robert Forst is _______ American. ( 1) a 2)an 3)the (4 No article 27) ______earth revolves around the sun. ( 1) a 2)an 3)the (4 No article 28) You are _____ student. ( 1) a 2)an 3)the (4 No article 29) Honest men speak _____ truth. ( 1) a 2)an 3)the (4 No article 30) His father is ______ M.P. ( 1) a 2)an 3)the (4 No article 31) She got ______ first prize in English subject. ( 1) a 2)an 3)the (4 No article 32) May is ______ hottest month of the year. ( 1) a 2)an 3)the (4 No article 33) ______ Mahabharatha is a great epic. ( 1) a 2)an 3)the (4 No article 34) Kalidas is _____ Shakespeare of India. ( 1) a 2)an 3)the (4 No article 35) The rich should help ______ poor. ( 1) a 2)an 3)the (4 No article 36) Bangalore is _______ beautiful city. ( 1) a 2)an 3)the (4 No article 37) A dollar is _____ unit of currency. ( 1) a 2)an 3)the (4 No article 38) He reads ________ Bible every day. ( 1) a 2)an 3)the (4 No article 39) Frank is ______ African. ( 1) a 2)an 3)the (4 No article 40) The Ramayana is _______ Epic. ( 1) a 2)an 3)the (4 No article
Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) )
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
41) Gold is ______ precious metal. ( 1) a 2)an 3)the (4 No article 42) Bindu is _______ intelligent girl. ( 1) a 2)an 3)the (4 No article 43) _______ cow is a useful animal. ( 1) a 2)an 3)the (4 No article 44) ______ Pacific is the deepest ocean. ( 1) a 2)an 3)the (4 No article 45) Ksishna went to _______ rescue of Arjuna. ( 1) a 2)an 3)the (4 No article 46) He has________ ulcer on his leg. ( 1) a 2)an 3)the (4 No article 47) Sheela is ______ M.L.A. ( 1) a 2)an 3)the (4 No article 48) Latin is _____ classical language. ( 1) a 2)an 3)the (4 No article 49) He is _______ heir to the throne. ( 1) a 2)an 3)the (4 No article 50) ______ Himalayas are to the north of India. ( 1) a 2)an 3)the (4 No article
) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) )
B.PREPOSITION
Definition: - The Preposition is a word which is placed a noun or a pronoun and it shows relation to some other words in a sentence. Eg:- I am Interested in painting She is fond of music He is applied for a Job Raju is good at English Kinds of Prepositions: There are mainly three kinds of preposition They are:1. Simple prepositions 2. Compound prepositions 3. phrase prepositions 1. Simple Preposition: - In, at, on, by, for, from, of, off, up, with, to 2. Compound prepositions: - Before, between, among, behind, beside. 3. Phrase prepositions:- In spite of, owing to, in front off, instead off, because of ,on account of, In case of etc. USES OF SIMPLE PREPOSITIONS 1. Use of ON:1. on is used with the names of week days and dates.(
on .)
Eg: - My friend will come on Tuesday My birth day is on 15th August 2. On is used to show the position of something above something with connect in resting position.( , on .) Eg:- 1.The book is on the table 2. She sat on the chair 3. The cat is on the wall
Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
.On is used to show the direction of something. ( on
.) Eg:- 1. a man sat on the left of Krishna.
2. The girl who sat on your right is clever. 2. Use of IN:1. IN is used before the names of months and years.(
in .
Eg:- 1.We got freedom in 1947. 2. Examination will be conducted in July. 3. Mangoes are during in summer season. 4. He came here in the morning. 2. In is used before the name of countries, big cities, and towns.(
in .)
Eg:- 1.They are lived in Delhi. 2. My friend lives in Hyderabad. 3. They have been living in Hyderabad since 2000. 4. I have been working here in Rajampet for 17 years. 3. In is used before the times of the day.( general In ) Eg:- 1.He came here in the morning. 2. She saw me in the evening. 3. Use of At:1. At is used before small towns and Villages, streets.(
at )
Eg:- 1.Sita is living at Pullampet 2. My parents work at Utukur. 2. At is used to express exact time.( at ) Eg:- 1.The Principal comes to college at 7o clock daily. 2.The train leaves at the station at 8. p.m. 4. Use of with:1. With is used with things (instruments)(
with )
Eg:- 1.Raja killed his wife with a knife. 2. The thief broke the door with a hammer 3. She cut the vegetables with a knife. 4. They killed the snake with a stick. 5. Use of By:1. By is used in the passive voice. 2. By is used to show the mode of travel. Eg:- by bus, by car, by train, by Jeep 3. By is used to refer the future time. Eg:- 1.We can get a TET certificate by next July 2. We will go to market by next Wednesday 3. Pandavas were helped by Krishna
Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
4. The Principal comes to College by car 6. Use of For:1. For is used to indicate a period of time and purpose.( For
)
Eg:- 1. Hari has been waiting here for 2 hours. 2. My uncle has been living in Hyderabad for 10 years. 3. We applied for Job. 7. Use of since:1. Since indicates point of time used in present perfect and present perfect continuous tense. (since perfect tenses ) Eg:- 1.I have been working as teacher of English Since 1990. 2. It has been raining Since 6o clock. 8. Use of Between:1. Between is used to indicate two persons or thing and places.(
between .)
Eg:- 1.Rani Sat between Uma and Suma 2. The Office work between 10 am and 5 pm 3. The war took place between India and Pakisthan Eg:-1.There is no comprehension between Rama and Lakshmana. 9. Use of among:1. Among is usedwhen there are more than two persons or things.(
among .)
Eg:- 1.The teacher sat among her students 2. The Principal distributed the Prizes among the students. 3.The four brothers shared the property among themselves. 10. Use of Beside:1. Beside is used by the side of. ( by the side of beside .) ) Eg:- 1.My house is beside hospital. 2.I stood beside my wife in the photograph. 11. Use of Besides:1. Besides is used in the meaning of in addition to.( in addition to
besides .)
Eg:-1.I prepare Chapathi Besides Puri. 2. I know Telugu besides English. 3. I take Coffee besides milk, Tea. 4. She plays chess besides caroms. 12. Use of upon:1. Upon is used to indicate movement of item.(
upon .)
Eg:- 1.The tiger is jumped upon the deer. 13. Use of To:1. To is used to indicate direction and after (before) the following (words) adjectives junor, senior, superior, inferior, prefer. Eg:- 1.They walked to the west 2. Raju is Junior to Rani
Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
3. I prepare Coffee to Tea 14. Use of Into:1. Into is used to show the movement of something from one medium to another.( into
.)
Eg:- 1. She jumped into the well. 2. They went deep into the forest. 3. The cat ran into the kitchen. EXERCISES Choose the suitable prepositions:1. I am waiting _______ my friend. 1)on 2) to 3)for 4)from 2. He is suffering _______________ fever. 1)on 2) to 3)for 4)from 3. The old man died ________ cancer. 1)of 2) to 3)for 4)from 4. He rubbed the black board _________ a duster. 1)with 2) by 3)of 4)from 5. He is not ashamed _________ his conduct. 1)on 2) at 3)of 4)from 6. We must go to our house_________7o clock. 1)at 2) to 3)above 4)by 7. she is afraid _________ snake. 1)off 2) of 3)in 4)from 8. I prefer coffee ________ tea. 1)at 2) to 3)above 4)between 9. Rahul lives ____________ Agra. 1)at 2) in 3)above 4)over 10.He will go home __________ Sunday. 1)on 2) from 3)with 4)in 11.What had been accused ________? 1)of 2) for 3)in 4)by 12.Arjuna is cousin _______ mine. 1)at 2)for 3)of 4)by 13.Raju goes to school __________ foot. 1)on 2) to 3)with 4)at 14.The office is open __________ 10a.m and 5 p.m. 1)at 2) to 3)among 4)between 15.The boys quarreled _____________ themselves. 1)at 2) to 3)among 4)between 16.I congratulated __________ his success. 1)on 2) from 3)with 4)in 17.They have been working here _______ 1989. 1)for 2) from 3)since 4)in 18.I am angry _________ you. 1) upon 2) of 3)with 4)against 19.Sheela is interested __________ music. 1)on 2) from 3)for 4)in 20.She was born _________2009. 1)for 2) in 3)at 4)from 21.she is fond _________ music.
Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com
( ( ( ( ( ( ( ( ( ( ( ( ( ( ( ( ( ( ( ( (
) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) )
Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
1)of 2) for 3)in 4)by 22.Listen ___________ the story. 1)on 2) to 3)with 4)at 23.Prakash knows English ___________ Telugu. 1)beside 2) besides 3)behind 4)from 24.I dont agree _________ your proposal. 1)by 2) to 3)with 4)from 25.He was accused _________ murder. 1)of 2) to 3)with 4)at 26.Raju is a man ____________ principles. 1)of 2) to 3)with 4)for 27.Hyderabad is the capital __________ A.P. 1)of 2) to 3)with 4)for 28.The headmaster is looking _________ complaint. 1)at 2) through 3)into 4)to 29.He gave __________ smoking. 1)of 2) off 3)up 4)at 30.Dont laugh __________ others. 1)of 2) to 3)with 4)at 31.The secret _________ success lies ________ hard work. 1)of 2) in 3)with 4)for 32.The tables are made ___________ wood. 1)of 2) to 3)with 4)for th 33.The school remains open __________ 12 June. 1)in 2) at 3)on 4)for 34.I am searching ____________ my lost book. 1)of 2) to 3)with 4)for 35.I reached the station __________ bus. 1)by 2) at 3)with 4)from 36.The baby fell ____________ river. 1)in 2) into 3)upon 4)over 37.My house is __________ the temple. 1)besides 2) beside 3)at 4)in 38.She is fond _______ music. 1)of 2) to 3)with 4)for 39.Ramya comes to school _______ foot. 1)of 2) on 3)with 4)for 40.Let us go ___________ walk. 1)of 2) to 3)with 4)for 41.Ravi is good _______ English. 1)of 2) to 3)with 4)at 42.He lives _________ Balaji nagar. 1)at 2) in 3)with 4)by 43.He jumped ___________ the river. 1)into 2) in 3)out 4)for 44.The book is ____________ the table. 1)of 2) to 3)with 4)on 45.I have been living here__________ 19 years. 1)of 2) at 3)since 4)for 46.Rama sat ___________ his friends. 1)between 2)beside 3)among 4)from
Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com
( ( ( ( ( ( ( ( ( ( ( ( ( ( ( ( ( ( ( ( ( ( ( ( (
) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) ) )
Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
47.He killed the snake ___________ a stick. ( ) 1)of 2) to 3)with 4)for 48.I will come there ___________ 5 p.m. ( ) 1) on 2) at 3)by 4)from 49.The dog is ________ the tree. ( ) 1) under 2) upon 3)from 4)in 50. They have been constructing the building _______ a long time. ( 1) for 2) since 3)from 4)at
CHAPTER IV VERBS
Verbs are two types in English language: They are 1. Auxiliary verbs 2. Main verbs 1. Auxiliary Verbs: - They are 24 auxiliary Verbs in English language. They are:Helping Verbs Be forms:-Am, is, are, was, were Do forms:-do, does, did Have forms:- have, has, had Model Auxiliaries:-shall, should, can, could, will, would, may, might, must .
TABLE 1 Be forms: - am, is, are, was, were, are called be forms Subject Present verb past verb past participate I am was been We are were been You are were been He is was been She is was been It is was been They are were been Ex:1. India is (be) a bog country. 2. There are (be) seven continents in the world. TABLE 2 Have forms (Possession): - Have, Has, had, are, called have forms Subject Present verb past verb past participate I have had had We have had had You have had had He has had had She has had had
Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
It They
has had had have had had Ex:- I have (have) a scooter She has (have) three saries We have (have) a class today They had ( have) a lot of property last year TABLE 3 Do forms: - do, did, does Subject Present verb past verb past participate I do did done We do did done You do did done He does did done She does did done It does did done They do did done Ex:- I do (do) my home work She does (do) her duty He did (do) his M.A at S.V.U in 2007 TABLE 4 Model verbs Subject Present verb Past verb I Shall Should We shall should can could will would All may might subjects must had to
2. Main Verbs:These are two types 1. strong verbs 2. weak verbs 1. Strong Verbs: - These are divided into three groups 1. Present verb (v1) 2. Past verb (v2) 3.Past participate (v3)
List of Irregular(strong) Verbs Note: - Verbs of present tense form, past, past particle are different
Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com
Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
S.l.no Present verb(v1)
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31.
am is are awake arise bear beat become begin befall beget below break choose come cleave crow dive drink drive eat fall fly freeze forget forgive forsake get give go grow
Past verb(v2) www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
Past Participle (v3)
was was were awoke arose bore beat became began befell begot blew broke chose came clove crew dove drank drove ate fell flew froze forgot forgave forsook got gave went grew
been been been awoken arisen borne beaten become begun befallen begotten blown broken chosen come cloven crown dived drunk driven eaten fallen flown frozen forgotten forgiven forsaken gotten given gone grown
Past Participle (v3)
S.l.no Present verb(v1)
Past verb(v2)
32. know knew known 33. lie lay lain 34. overcome overcame overcame 35. overtake overtook overtaken 36. oversee oversaw overseen 37. ride rode ridden 38. rise rose risen 39. ring rang rung 40. run ran run 41. see saw seen 42. shake shook shaken 43. shrink shrank shrunk 44. sing sang sung 45. sink sank sunk 46. speak spoke spoken 47. spin span spun 48. spring sprang sprung 49. steel stole stolen 50. strive strove striven 51. swear swore sworn 52. swing swang swung 53. take took taken 54. ourtear tore Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com torn Visit Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com 55. throw threw thrown
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
Note : Verbs that have the same form in their past tense and past participle tense.
Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com
Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
S.l.no Present verb(v1)
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34.
abide have has bend behold breed bring bite bleed bing build burn buy catch cling creep deal dwell dig dream feed feel fight find flee fling grind hang hear hide hold keep kneel lay
Past verb(v2) www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
Past Participle (v3)
abode had had bent beheld bred brought bit bled bound built burnt brought caught clung crept dealt dwelt dug dreamt fed felt fought found fled flung ground hung heard hid held kept knelt laid
abode had had bent beheld bred brought bit bled bound built burnt brought caught clung crept dealt dwelt dug dreamt fed felt fought found fled flung ground hung heard hid held kept knelt laid
Past Participle (v3)
S.l.no Present verb(v1)
Past verb(v2)
35. learn learnt learntt 36. lead led led 37 light lit lit 38 lose lost lost 39 make made made 40 mean meant meant 41 misspell miss spelt miss spelt 42 misunderstand misunderstood misunderstood 43 rend rent rent 44 repay repaid repaid 45 say said said 46 seek sought sought 47 sell sold sold 48 send sent sent 49 shine shone shone 50 shoot shot shot 51 sit sat sat 52 sleep slept slept 53 slide slid slid 54 oursling slung Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com slung Visit Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com 55 smell smelt smelt
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
Regular(weak) Verbs.
S.l.no Present verb(v1) Past verb(v2) Past Participle (v3)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50
ask announce agree accept admit appear advise arrange aim appoint arrive argue attack act admire advance affect achieve acquire acquaint advertise allow answer arrest associate attend attempt abscond borrow believe blame bother bluff call cancel change cheat continue close consult chase count cook collect complete convergent check commence cry criticize
asked announced agree accepted admitted appeared advised arranged aimed appointed arrived argued attacked acted admired advanced affected achieved acquired acquainted advertised allowed answered arrested associated attended attempted absconded borrowed
past verb(v2)
asked announce agreed accepted admitted appeared advised arranged aimed appointed arrived argued attacked acted admired advance affected achieved acquired acquainted advertised allowed answered arrested associated attended attempted absconded borrowed
past participle (v3)
S.l.no present verb(v1)
believed blamed bothered bluffed called cancelled changed cheated continued closed consulted chased counted cooked collected completed converted checked commenced cried criticized
believed blamed bothered bluffed called cancelled changed cheated continued closed consulted chased counted cooked collected completed converted checked commenced cried criticized
Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com
Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101
consider challenge communicate carry clean consist deliver discover disturb decide drop dance damage divide desire discuss depart dismiss dash decrease depend delay decorate destroy explain expect enjoy enquire express escape encourage enclose enter excuse estimate examine face form fail frame fear frighten follow finish flow gather guide guess help hate happen
consider challenged communicated carried cleaned consisted delivered discovered disturbed decided dropped danced damaged divided
Past verb(v2)
consider challenged communicated carried cleaned consisted delivered discovered disturbed decided dropped danced damaged divided
Past Participle (v3)
S.l.no Present verb(v1)
desired discussed departed dismissed dashed decreased depended delayed decorated destroyed explained expected enjoyed enquired expressed escaped encouraged enclosed entered excused estimated examined faced formed failed framed feared frightened followed finished flowed gathered guided guessed helped
Past verb(v2)
desired discussed departed dismissed dashed decreased depended delayed decorated destroyed explained expected enjoyed enquired expressed escaped encouraged enclosed entered excused estimated examined faced formed failed framed feared frightened followed finished flowed gathered guided guessed helped
Past Participle (v3)
S.l.no Present verb(v1)
hated happened
hated happened
Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com
Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153
hesitate harass hatch hire honor hop inform impress interest indicate instruct invent increase insist interrupt introduce invite improve injure irritate illuminate imitate illustrate identify import inaugurate include inquire insert inspect insult involve isolate jump join kill kidnap kick knock kiss like love listen look lean lift limit list live lock move murmur
hesitated harassed hatched hired honored hopped informed impressed interested indicated instructed invented increased insisted interrupted introduced invited improved injured irritated illuminated imitated illustrated identified imported inaugurated included inquired inserted inspected insulted involved isolated
Past verb(v2)
hesitated harassed hatched hired honored hopped informed impressed interested indicated instructed invented increased insisted interrupted introduced invited improved injured irritated illuminated imitated illustrated identified imported inaugurated included inquired inserted inspected insulted involved isolated
Past Participle (v3)
S.l.no Present verb(v1)
jumped joined killed kidnapped kicked knock kissed liked loved listened looked leaned lifted limited listed lived locked moved murmured
jumped joined killed kidnapped kicked knock kissed liked loved listened looked leaned lifted limited listed lived locked moved murmured
Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com
Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204
miss melt murder mend migrate measure neglect notice observe occupy owe open order occur offer oppose obey obtain operate originate pass prove perform pull push permit prevent present prefer preside proceed punish place practice provoke play possess post postpone pour praise prepare preserve print produce prohibit promise protect publish purchase pay
missed melted murdered mended migrated measured neglected noticed observed occupied owed opened ordered occurred offered opposed
Past verb(v2)
missed melted murdered mended migrated measured neglected noticed observed occupied owed opened ordered occurred offered opposed
Past Participle (v3)
S.l.no Present verb(v1)
obeyed obtained operated originated passed proved performed pulled pushed permitted prevented presented preferred presided proceed punished placed practiced provoked played possessed posted postponed poured praised prepared preserved printed produced prohibited promised protected published purchased paid
Past verb(v2)
obeyed obtained operated originated passed proved performed pulled pushed permitted prevented presented preferred presided proceed punished placed practiced provoked played possessed posted postponed poured praised prepared preserved printed produced prohibited promised protected published purchased paid
Past Participle (v3)
S.l.no Present verb(v1)
Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com
Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256
participate quarrel qualify question refuse receive return remain remark report recall reflect release require reject reach remove recommend reduce receive remind repair repeat reply request respect respond reveal revise revolt reward stare spoil say suggest support suspect suffer seize search stop seem select scold surprise show sacrifice sanction satisfy save scatter secure
participated quarreled qualified questioned refuse received returned remained remarked reported recalled reflected released required rejected reached removed recommended reduced received reminded repaired repeated replied request respected responded revealed revised revolted rewarded stared spoiled said suggested
Past verb(v2)
participated quarreled qualified questioned refuse received returned remained remarked reported recalled reflected released required rejected reached removed recommended reduced received reminded repaired repaired replied request respected responded revealed revised revolted rewarded stared spoiled said suggested
Past Participle (v3)
S.l.no Present verb(v1)
supported suspected suffered seized searched stopped seem selected scolded surprised showed sacrificed sanctioned satisfied saved scattered secured
supported suspected suffered seized searched stopped seem selected scolded surprised showed sacrificed sanctioned satisfied saved scattered secured
Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com
Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
257 258 259 260 261 262 263 264 265 266 267 268 269 270 271 272 273 274 275 276 277 278 279 280 281 282 283 284 285 286 287 288 289 290 291 292 293 294 295 296 297 298 299 300 301 302 303
shape shift slip solve smile stay struggle submit supply start turn transfer travel try treat trust train trouble touch threaten thank terminate trace translate twist use utilize vow vex verify visit vacate vanish want walk waste warn worry wait wish wash watch wonder work worship absorb abuse
shaped shifted slipped solved smiled stayed struggled submitted supplied started turned transpired traveled tried treated trusted trained troubled touched threatened thanked terminated traced translated twisted used utilized vowed vexed verified visited vacated vanished wanted walked wasted warned worried wait wished washed watched wondered worked worshiped absorbed abused
shaped shifted slipped solved smiled stayed struggled submitted supplied started turned transpired traveled tried treated trusted trained trouble touched threatened thanked terminated traced translated twisted used utilized vowed vexed verified visited vacated vanished wanted walked wasted warned worried waited wished washed watched wondered worked worshiped absorbed abused
Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com
Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
CHAPTER V TENSES
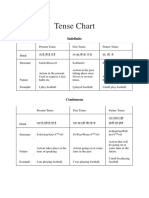
The word tense comes from the Latin word Tempus which means time. Tense denotes the time of an action Tenses are root of the grammar There are three main tenses they are 1. Present tense 2. past tense 3. Future tense Each tense is divided in to four groups S. Present tense Past tense Future tense No. 1 Simple Present Simple past Simple Future 2 Present Continuous Past continuous Future Continuous 3 Present perfect Past prefect Future prefect 4 Present perfect Past perfect continuous Future perfect continuous continuous There are 12 types of tenses in English. They are:1. Simple present 2. Present Continuous 3. Present perfect 4. Present perfect continuous 5. Past simple 6. Past Continuous 7. Past perfect 8. Past perfect continuous 9. Simple Future 10. Future (simple) continuous 11. Future perfect 12. Future perfect continuous OBSERVE THE FOLLOWING TABLE:Give 1. Simple present give, gives 2. Present Continuous is giving am giving, are giving 3. Present perfect have given, has given 4. Present perfect continuous have been giving, has been giving 5. simple Past gave 6. Past Continuous was giving, were giving 7. Past perfect had given 8. Past perfect continuous -had been giving 9. Simple Future Shall give, will give 10. Future (simple) continuous shall be giving, will be giving 11. Future perfect Shall have given, will have given 12. Future perfect continuous shall have been giving, will have been giving Take
Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
1. Simple present 2. Present Continuous 3. Present perfect 4. Present perfect continuous 5. simple Past tense 6. Past Continuous 7. Past perfect 8. Past perfect continuous 9. Simple Future 10. Future (simple) continuous 11. Future perfect 12. Future perfect continuous Go 1. Simple present
2. Present Continuous 3. Present perfect 4. Present perfect continuous 5. simple Past tense 6. Past Continuous 7. Past perfect 8. Past perfect continuous 9. Simple Future 10. Future (simple) continuous 11. Future perfect 12. Future perfect continuous
Take, takes am taking, is taking, are taking have taken, has taken have been taking, has been taking took was taking, wore taking had taken had been taking shall be taking, will be taking shall be taking, will be taking Shall have taken, will have taken
Shall have been taking, will have been taking
go, goes am going , is going, are going have given, has given have been giving, has been giving -went was went, were went had gone -had been going shall go, will go shall be going, will be going shall have gone, will have gone shall have been going, will have been going
Find the tenses in the following sentences:1. I teach English Simple present 2. You are writing something Present continuous th 3. We passed 10 class last year Simple past 4. You were studying first year last year -Past Continuous 5. Sita got a prize Simple past 6. I have completed Graduation Present perfect 7. We had reached the Station Past perfect 8. Sita sings many songs Simple present 9. I will come to you house tomorrow simple Future 10.They will have completed their work by this time tomorrow. Future perfect 11. My has been living in Hyderabad for 10 years - Present perfect continuous 12. We were watching T.V Past continuous 13. We shall be writing a novel Future continuous 14. John goes to Church every SundaySimple present 15. Latha Drink coffee Simple present 16. You made a mistake in the class Simple past 17. They will visit Tirumala tomorrow Simple Future 18. Columbus discovered America Simple past 19. I saw a film last might Simple past 20. I have been teaching grammar for 15 dayPresent perfect continuous TENSE THROUGH STRUCTURES 1. SIMPLE PRESENT TENSE A. Affirmative sentence:Formula:- sub+v1 es + object Eg:- I write a letter.
Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
You drink coffee. He goes to college daily. Sita sings songs. They read the Hindu daily. Note:- If the sentences begin with third person singular (He, she, it) S or es can be add to the first form of the verb (V1) B. Negative Sentence:Formula:- sub + do not/does not + v1 + obj Eg:- I do not write a letter . You do not drink coffee. He does not go to college daily. Sita does not Sing songs. They do not read the Hindu daily. C. interrogative sentence :Formula:- Do + sub+v1 +obj? Ex: - Do I write a letter ? Does he go to college daily? Does Sita sing songs? Do they read the Hindu daily? D.Negative interrogative:Formula:- Do not/does not + sub + v1 + obj. Eg:- I Dont I write a letter? Dont you drink Coffee? Doesnt he go to college daily? Doesnt Sita sing songs? Dont they read the Hindu daily? Use of simple present tense:This tense is used for the following cases:1. Habitual action 2. daily activities 3. facts 4. universal truths 1. Habitual actions and daily activities:Indications:Always, often, seldom, sometimes, daily, everyday, generally, occasionally, frequently, rarely, usually, regularly Eg:1. I go (go) to College daily 2. They come (come) to party ready 3. Rani often makes (make) mistakes 4. I always help (help) the poor 5. sita useful, sits (sit) in the first row 6. we do (do) our home work regularly 7. She drinks (drink) milk daily 8. They often visit (visit) Tirumala 9. You tell (tell) lies some times
Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
10.He comes (come) here every morning 2. Universal truths:1. The Sun Sets (set ) in the west 2. The Sun shines during the day 3. The earth moves (move) round the Sun 4. The earth revolves (revolves) the sun 5. The moon shines (shine) during the night 6. The moon gives (give) us cool night 7. The earth rotates (rotate) round the Sun 8. The summer comes (come) after the winter 9. The stars appear (appear) during the night 10. Birds fly (fly) in the Sky 11. Children like (like)Sweets 12. Bees make (make) Honey 13. People speak (speak) English all over world 14. Water boils (boil) at the 100o c 15. The Indian Rivers flow (flow) Bay of Bengal 16. The them of the Novel reflects (reflect) our couture 17. Fish live (live) water 18. River water do not fast (not fast ) Salty 19. English is spoken (speak) all over the world.
3. Facts:1. Sugar is (be) Sweet 2. Honey is (be) Sweet 3. Man is (be) mortal 4. Mount Everest is (be) the height peak in the World 5. India is be a big Country 6. Sunitha is (be) a wise girl 7. What is (be) a Prize of the book 8. There are (be) 11 members in the cricket 9. We are (be) a big nation 10.Gold melts (melt) at 100o C 11.Salt dissolves (dissolve) in water
2. PRESENT CONTINUOUS TENSE
A. Affirmative sentence:Formula:- sub + am/is/are + v1 +ing +obj) Eg:- I am writing a letter. You are eating a Mango. She is reading the paper.
B .Negative Sentences:Formula: sub +am/is/are not+ v1 + obj Eg:1. I am not writing a letter. 2. You are not eating mango. 3. She is not reading the paper.
Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
C. Interrogative sentence:Formula:- Am/is/are + sub+v1+ obj Ex:1. Am I writing a letter? 2. Are you eating a mango? 3. Is she reading the paper ? D .Negative interragative:Am/is/are not + sub+v1+ obj Eg:1. Amnt I writing a letter? 2. Arent you eating a mango? 3. Isnt she reading the paper? Uses of present continuous tense:This tense is mainly used to express real action which is going at the time of speaking. Eg:1. I am teaching English grammar now. 2. Sita is doing home work now. 3. They are making chapathis at present. Near Future: - This tense is used for the actions that has already been arranged to take place near future. Eg:1. The C.M is coming to Kadapa next Sunday. 2. we are meeting with them tomorrow. 3. My uncle is visiting Tirumala next month. Indications :- now, at, present, listen, see, look, dont disturb
Examination model:1. I am writing (write) a letter now 1) will write, 2) a writing 3)am writing 4)None 2. They are doing (do) H.W at present. 3. See! Somebody is calling by her name. . 4. Look! Somebody is breaking (break) the glass. 5. Dont disturb me I am reading (read) the paper. 6. Dont disturb him he is doing (do) his home work. 7. Listen somebody is knock (knock) at the door. 8. Leela is reading (read) a novel now. 9. They are playing (play) tennis at present . The following verbs are not used in present continuous tense:1. Verbs of perception :See, hear, smell, notice, recognize 2. verbs of appearance :appear, look, seem 3. verbs of emotion :what, wish, desire, fed, like, love, hate, hope, refuse, prefer 4. Verbs of thinking :Think, suppose, believe, agree, consider, trust, remember, forget, know, mean, understand. 5. Verbs of possession :have, own, possess, belong, consist, contain.
Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
3. PRESENT PERFECT TENSE
This tense is used for the actions just completed in the past. A.Assertive sentences :Formula:- sub+have/has +v3+obj Eg:1. I have written a letter. 2. You have done your home work. 3. He has sung a song. 4. Sita has sent a gift. B.Negative Sentence:Formula:- sub+have/has+not+v3+obj. Eg:1. I have not written a letter. 2. you have not done your home work. 3. Sita has not sent a gift. 4. He has not sung a song. C. Interrogative sentence:Formula:- have/has + sub+ v3+obj Eg:1. Have I written a letter? 2. Have you done your home work? 3. Has He sung a song? 4. Has Sita sent a gift? D. Negative interrogative:Formula:- have/has +not+ sub+ v3+obj Eg:1. Have not I written a letter? 2. Have not you done your home work? 3. Has not he sung a song? 4. Has not Sita sent a gift?
Examination pattern:Indications: - just, just, now, just, before, al ready, so far, yet, recently 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. I have written (write) a story just now a) wrote b)have written c)am writing d) have wrote He has gone (go) to Kadapa just before She ha seen (see) the film recently They have left (leave) for Bangalore just now My friend has not come (come) here so far Rani has joined (join) in the College just now.
4. PRESENT PERFECT CONTINUOUS TENSE
This tense is used for the actions already started in the past and continuing up to the present. Formula:- sub + has/have + been+ ing+obj Eg:1. I have been teaching English grammar for 20 days
Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
2. She has been studying Psychology for 2 day 3. He has been working here since 2002 4. She has been living in Rajampet since 2005 Indications :- since, for Since:- it refers to point of time For :- it refers to period of time Since For Since Monday for 3 hours Since June for 10 days o Since 8 clock for a long time Since morning for 5 months Since 1998 for 3 weeks Since yesterday for half an hour Examination Model:1. He has been waiting (wait) here for her for two years 2. I have been living (live) in Rajampet since 1990 3. They have been waiting (wait) at the bus stand for an hour 4. It has been raining (rain) here Since 8o clock 5. The child has been sleeping (sleep) here since 4o clock 6. India has been facing (face) many problems for a long time 7. The boy has been reading (read) the novel for 2 hours 8. We have been taking (take) for T.E.T for 20 days
5. SIMPLE PAST TENSE
A. Affirmative sentence:Formula: - sub+ v2 + obj. Eg:1. I wrote a letter. 2. You bought a scooter. 3. He drank coffee. 4. She sang a song. 5. They built a house. B. Negative sentence:Formula: - sub+ did not + v1 + obj. Eg:1. I did not write a letter. 2. You did not buy a scooter. 3. He did not drink coffee. 4. She did not sing a song. 5. They did not build a house. C. Interrogative sentence:Formula: - Did+sub+v1+obj. Eg:1. Did I write a letter? 2. Did you buy a Scooter? 3. Did he drink coffee 4. did she sing a song 5. did he build a house? D. Negative sentence:Formula: - Did+not+sub+v1+obj.
Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
Eg:1. Didnt I write a letter? 2. Didnt you buy a scooter? 3. Didnt he drink coffee? 4. Didnt she sing a song? 5. Didnt they build a house? Uses of simple past tense:This tense is used for the actions at any time in the past. Indications:Ago, long ago, last week, last night, last month, last year, last century, last decade, in 1947 ( any previous year), yesterday. 1. I wrote (write) a letter to here yesterday. 2. India won (win) the freedom in 1947. 3. The train left (leave) the plat form an hour ago. 4. He returned (return) from the College yesterday. 5. John went (go) to the Church last Sunday. 6. Akhbar ruled (rule) India long ago. 7. Suneel visited (visit) Tirumala last week. 8. I bought (buy) scooter in 2010. 9. They did (do) their work last week. 10.My friend come (come ) to my house yesterday.
6. PAST CONTINUOUS TENSE
This tense is used for the actions continuing in the past. Formula:- sub + was/were +v1+ ing + obj Ex:1. I was writing a story. 2. You were doing your work. 3. She was singing songs. 4. They were building a house. 5. He was playing cricket. Note:-When two works mentioned in a sentence one work is in simple past the other work will be in past continuous tense. Note:- Shorter action (simple past) , longer action (past continuous ) Indications: - when, while 1. when the bell rang, you were watching (watch) T.V 2. When I saw here, she was playing (play) chess 3. The girl fell asleep while she was watching (watch) T.V 4. While He was going (go) to college, he saw an accident. 5. Rani was singing (sing) songs, I visited her. 6. When I was crossing (cross) the road, I saw an accident. 7. When my daughter was going (go) to college, she saw a snake. 8. My brother was sleeping (sleep) when I reached home. 9. While I was going (go) to school, I saw a procession.
7. PAST PERFECT TENSE
This tense is used for the actions just completed in the past A. Assertive sentence:Formula:- sub+had+v3+obj Ex:1. I had written a story.
Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
2. You had finished your work. 3. He had left the village. 4. They had built a house. B. Negative sentence:Formula:- sub+ had+not+v3+ obj Ex:1. I hadnt written a story 2. you hadnt finished your work 3. He hadnt left the village 4. They hadnt built a house Uses:Rule:- 1. when two works are mentioned in a sentence the first work is in past perfect tense, the second work will in simple past. Indications :- Before, after, when, as soon as, until Ex:1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Before I reached the station, the train had left (leave) the flat form He had written (write) a letter before he arrived Jyothi had left (leave) the party before sheela arrived there He (leave) the party before sheela arrived there He had finish (finish) the work before we reached the garage When I reached the meeting hall the present all ready had started (start) his lecture
8. PAST PERFECT CONTINUOUS TENSE
This tense is used for the actions all ready started in the past and Formula:-sub+had+been+v1+ing+obj Ex:1. I had been writing a story 2. They had been writing a story 3. They had been repaired in the house continuing up to the past.
9. SIMPLE FUTURE TENSE
A. Assertive sentence:Formula:- sub+ shall/will +v1+obj.
Ex:-
1. I shall write a letter 2. you will learn English 3. we will join in a College 4. He will buy a car B. Negative sentences :Formula:- sub+ shall/will +not+v1+obj Ex:1. I shall not write a letter. 2. You will not learn English. 3. We will not join in a College. 4. He will not buy a car. C. Interrogative sentence:Formula:- shall/will + sub+ v1 +obj. Ex:1. Shall I write a letter? 2. Will you learn English grammar? 3. Will we join in a college? 4. Will he buy a car?
Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
D. Negative question:Formula: - Shall nt, willnt + sub+v1+obj. Eg:1. Shall nt I write a letter? 2. Wont you learn English grammar? 3. Wont we join in a College? 4. Wont he buy a car? Uses: - This tense is used for the actions at day time in the future Indications: - tomorrow, the next day, next week, next month, next year. Eg:1. I shall write (write) a letter to her tomorrow 2. He will visit (visit) Tirumala next Saturday 3. Raju will visit (visit) zoo next year 4. My uncle will go (go) to America next month 5. The Novelist will finish (finish) the Novel next month 6. We Shall complete (complete) our Syllabus next week
10. FUTURE CONTINUOUS TENSE
This tense is used for the actions continuing in the future. Formula:-sub+ shall/will + be +v1+ing+obj Eg:1. I shall be writing a story 2. you will be doing your job 3. He will be constructing a house.
11. FUTURE PERFECT TENSE
This tense is used for the actions just completed in the future Formula:- sub+ shall have/will have + v3 +obj Ex:1. I shall have finished my work by next week 2. she will have completed her work by next day 3. The will have constructed their house by next year Indications: - by the time, by next week, by next month, by the year 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. you will have finished (finish) you examination by next July The Novelist will have finished (finish)the book by next month She will have built (build) a house by the end of the next year By the end of the next week the Novelist will have written (write) the book I shall have completed (complete) my work by the
S. No. Tense 1
3 4 5 6 7
Indications Always, often, seldom, some time, daily, every day, generally, occasionally, frequently, readily, usually, regularly Simple past Ago, long, ago, last, week, last month, last night, last year, Last century, last decade, in 1947 (any previous year) yesterday Simple Future Tomorrow, the next day, next week, next month, next year Present continuousNow, at present, listen. See! look!, Dont disturb Past Continuous When, while Present perfect Just, just now, just before, already, so far, yet, recently Past perfect Before, after, as soon as (when) until
Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
Tomorrow, the next day, next week, next month, next year CONDITIONAL TENSES There are three conditional tenses, they are preferable conditions 1. open condition 2. Improbable condition (Imaginary condition) 3. un full filled condition; TYPE 1 1. Open condition (type I) Main clause Sub + will, shall, can, may + v1+ obj
Future perfect
IF clause If + sub+vI
+obj
Eg:1. If you work hard, you will get a rank. 2. if you play well, you will win the match. 3. If I go to Hyderabad, I shall met the C.M. 4. If he teaches well, I will get a good name. Exercises:1. If you break the glass, the police will punish (punish) you Punished 2. had punished 3. will punish 4. punishment 2. If you ask me, I shall help (help) you 3. If he leaves (leave) early, he can catch the train 4. If you get a rank in T.E.T the Principal will give you a prize TYPE 2 Improbable condition or Imaginary conditions:If clause If+sub+v2+ob Main clause Sub+would/could+v1+ obj Formula
Eg:1. If you worked hard, you would get a rank 2. If you played well, you would win the match. 3. if I went to Hyderabad, I should met the C.M 4. If I were a bird , I would fly in the sky a)will fly, b) c)flown d) flying 5. If I were you, I would work well 1. worked 2. would work 3. working 4. will work 6. If I were the C.M, I would abolish the reservation of women 1. will abolish 2. abolished 3. would abolish 4. abalishing
CHAPTER VI TRANSFORMATION OF SENTENCES
A.ACTIVE AND PASSIVE VOICE
Active Voice:- Active voice gives about the work done by the subject and object directly.(Active
Voice , , . A.V , .)
Ex:- Krishna helped pandavas.
Krishna subject Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
Helped verb Pandavas object Passive Voice:- Passive Voice gives about the verb received object from the subject.(P.V , .) Ex:- Pandavas were helped by Krishna.
pandavas object
Were helping verb Helped main verb By preposition Krishna Subject Rules for changing from A.V into P.V:1. Object becomes Subject(A.V Object P.V subject ) Ex:- I eat a mango A mango _______ 2. Helping verb is used according to the tense of the verb in the passive voice. (A.V tence
helping verb .)
Ex:- A mango is __________ S.NO TENSE IN ACTIVE HELPING VERB IN PASSIVE VOICE VOICE 1 Simple present tense Am, is , are 2 Present continuous tense Am being, is being, are being 3 Present perfect tense Have been, has been 4 Simple past tense Was were 5 Past continuous tense Was being, were being 6 Past perfect tense Had been 7 Simple future tense Shall be, will be 8 Future perfect tense Shall have been, will have been 3. Pronouns in Active voice are changed as in passive voice.
A.V pronouns, passive .
Active voice I We you He She
Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com
Passive voice Me us you him Her
Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
it they Ex:- I eat a mango
It Them
A mango is ___________ me. 4. The main verb should be written in past participle (v3) main verb p.v v3 . Ex:- A mango is ________ 5. The preposition by is used after the past participle. Ex:-A mango is written _______ me. AS FOR THE TENSES THE VOICE IS CHANGED AS FOLLOWES: 1. Simple Present tense A.V. Structure Sentences P.V. Structure Sentences Sub+v1/v1+s/es+Obj Sita sings a song Sita sings songs Object+am/is/are+v3+by+Subject A song is sung by Sita Songs are sung by Sita. Subject+am/is/are+v+ing+Object Sita is singing a song. Sita is singing songs Object+am/is/are+being+v3+by+Subject A song is being sung by Sita Songs are being sung by Sita. Subject+Has/Have+v3+Object Sita has sung a song Sita has sung songs Object+Has/Have+been+v3+by+Subject A song has been sung by Sita Songs have been sung by Sita.
2. Present A.V. Structure Continuous Sentences Tense P.V. Structure Sentences 3. Present Perfect Tense A.V. Structure Sentences P.V. Structure Sentences
4. Simple Past Tense
A.V. Structure Sentences P.V. Structure Sentences
5. Past A.V. Structure Continuous Sentences Tense P.V. Structure Sentences 6. Past Perfect Tense A.V. Structure Sentences P.V. 7. Simple Structure Sentences
A.V. Structure
Subject+v2+Object Sita sang a song Sita sang songs Object+was/were+v3+by+subject A song was sung by Sita Songs were sung by Sita. Subject+was/were+v+ing+Object Sita was singing a song Sita was singing songs Object+was/were+being+v3+by+subject A song was being sung by Sita. Songs were being sung by Sita. Subject+had+v3+Object Sita had sung a song Sita had sung songs Object+had+been+v3+by+Subject A song had been sung by Sita Songs had been sung by Sita Subject+will/shall+v1+Object
Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
Future Tense P.V. 8. Future Perfect Tense
Sentences Structure Sentences
A.V. Structure Sentences P.V. Structure Sentences
Sita will sing a song Sita will sing songs Object+will/shall+be+v3+by+Subject A song will be sung by Sita Songs will be sung by Sita. Subject+will/shall+have+v3+Object Sita will have sung a song. Sita will have sung songs
Object+will/shall+have+been+v3+by+Sub
A song will have been sung by Sita Songs will have been sung by Sita.
1. Simple Present Tense Passive structure:- Object+am/is/are+v3+by+Subject Ex:- I play chess (A.V) (P.V) (A.V) (P.V) (P.V) (P.V) (A.V)
Chess is played by me 2.Raju likes sweets Sweets are liked by Raju. 3.He invites me to the party. I am invited by him to the party. 4.People speak English all over the world.
English is spoken by people all over the world (P.V) 5. They sing songs. Songs are sung by them. 2. Present continuous tense:Passive structure:- Object+am/is/are+being+v3+by+Subject Ex:- 1.He is teaching grammar. Grammar is being taught by him. 2. They are repairing roads. Roads are being repaired by them. (A.V) (P.V) (A.V) (P.V) (A.V) (P.V) (A.V)
3. The gentleman is opening an account in our bank.
An account is being opened by the gentleman in our bank. (P.V) 4. I am writing a good essay on pollution. A good essay is being written by me on pollution. 3. Present perfect tense:Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
(A.V) (P.V)
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
Passive structure:- Object+Has/Have+been+v3+by+Subject Ex:-1. He has eaten a mango. A mango is eaten by him. 2 They have advertised our products. Our products has been advertised by them. 3. Police have arrested the thieves. The thieves have been arrested by police. 4.Simple past tense:Passive structure:- Object+was/were+v3+by+subject Ex:-1.I wrote a story. A story was written by me. 2.They built a house in their town. A house was built by them in their town. 3.Waterman invented a fountain pen in 1884. (A.V) (P.V) (A.V) (P.V) (A.V) (A.V) (P.V) (A.V) (P.V) (a.v) (P.V)
A fountain pen was invented by Waterman in 1884. (P.V) 4.R.K Narayan wrote many games. Many novels were written by R.K.Narayan. 5. She taught us English grammar. We were taught English grammar by her. (A.V) (P.V) (A.V) (P.V)
5. Past continuous tense:Passive structure:- Object+was/were+being+v3+by+subject Ex:-1.I was eating a mango. A mango was being eaten by me. 2. The watchman was cutting the trees in the garden. (A.V) (p.v) (A.V)
The trees were being cut by the watchman in the garden.(P.V) 3. The boy was buying notebooks. Note books were being bought by the boy.
Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com
(A.V) (P.V)
Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
6. Past perfect tense:Passive structure:- Object+had+been+v3+by+subject Ex:-1.I had finished my work. My work had been finished by me. 2. She had made many mistakes in the class. Many mistakes had been made by her in the class. 3. She had sent a gift. A gift had been sent by her. 7. Simple future tense:Passive structure:- Object+ will/shall+be+v3+by+Subject Ex:-1. They will help us. We shall be helped by them. 2. I shall write a story. A story will be written by me. 3.They will announced the results next week. The results will be announced by them next week. 8. Future perfect tense:Passive structure:- Object+will/shall+have+been+v3+by+Sub
Ex:-1.I shall have written a novel by this time next year. A novel will have been written by me by this time next year. 2. They will have completed his work. His work will have been completed by them. (A.V) (P.V) (A.V) (P.V)
(A.V) (P.V) (A.V) (P.V) (A.V) (P.V)
(A.V) (P.V) (A.V) (P.V) (A.V) (P.V)
DOUBLE OBJECTS IN A.V AND P.V ,me,us,him,her,them indirect objects . (direct objet+ helping verb+v3+to+indirect object+by+subject) or (Indirect object+ helping verb+ v3+direct object +by + subject.) Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju Ex:-1.She gave me a book. A book was given to me by her. (A.V) (P.V)
I was given a book by her, 2. Ramarao has taught us English. English has been taught to us by Ramarao. We have been taught English by Ramarao. 3.My grand mother told us a story. A story was told to us by my grandmother. We were told a story by my grandmother.
(P.V) (A.V) (p.v) (P.V) (A.V) (P.V) (P.V)
IMPERATIVE TYPE
Passive structure:- (Let+obj+be+V3) Ex:-1.Open the door. Let the door be opened. 2. Show the picture. Let the picture be shown. 3. Finish the work. Let the work be finished. 4. Post this letter. Let this letter be posted. 5. Sing a song. Let the song be sung. REQUEST TYPE Passive structure:- (you are requested to+ v1+obj)
( please passive voice you are requested to .)
(A.V) (P.V) (A.V) (P.V) (A.V) (P.V) (A.V) (P.V) (A.V) (P.V)
Eg:- 1.please shut the door. You are requested to shut the door. 2. Plese post this letter.
Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com
(A.V) (P.V) (A.V)
Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
You are requested to post this letter.
(P.V)
WITH OUT USING BY IN P.V
( by .)
EX:-1.Someone stole the box. The box was stolen. 2. The police arrested the thief. The thief was arrested. 3. Someone has seen the wind. The wind has been seen. 4.Someone serve the food. The food is served. INERROGATIVE TYPE 1.Passive structure :-(helping verb+obj+V3+by+Sub) Eg:-1.Does Sita sings a song? Is a song sung by Sita? 2. Did they repair the radio? Was the radio repaired by them? 3. Shall I write a story? Will a story be written by me? 4. Are you making kites? Are kites being made by you? 5. Has Sita sung songs? Have songs been sung by Sita? 6. Shall you have made kite? Will a kite have been made by you? 7. Must we pay this bill? Must this bill be paid by us? 8. Are you reading this book? Is this book being read by you? 9. Will Rama have written a novel? Will a novel have been written by Sita?
Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com
(A.V) (P.V) (A.V) (P.V) (A.V) (P.V) (A.V) (P.V)
(A.V) (P.V) (A.V) (P.V) (A.V) (P.V) (A.V) (P.V) (A.V) (P.V) (A.V) (P.V) (A.V) (P.V) (A.V) (P.V) (A.V) (P.V)
Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
10.Had Chitra sung songs? (A.V) Had songs been sung by Chitra? (P.V) 2. WH WORD QUESTIONS:Passive structure :-(Wh question word +helping verb+obj+V3+by+Sub) Eg:- 1) How can you solve the problem. How can the problem be solved by you? 2) Why did he buy that watch? Why was that watch bought by him? 3) Who bought that watch? By whom that watch bought? 4) When did they accept all demands? When were all demands accepted by them? 5) Who gave you this book? By whom was this book given to you? (A.V) (P.V) (A.V) (P.V) (A.V) (P.V) (A.V) (P.V) (A.V) (P.V)
EXERCISES 1. The carpenter is making a chair. ( ) a) A chair is made by the carpenter. b) The making of chair is done by the carpenter. c) A chair is being made by the carpenter. d) The carpenter is being made by the chair. 2. I shall return your books in a week. ( ) a) Your books shall been returned in a week. b) Your books will be returned by me in a week. c) Your books will have been returned in a week. d) Your books will be returning by me in a week. 3. He painted his house all by himself. ( ) a) His house has been painted all by himself, b) His house was painted by him all by himself. c) His house were painted by him all by himself. d) His house is being painted by him all by himself. 4. I hate her. a) She has been hated by me. b) She is hated by me. c) She was hated by me. d) She is being hated by me.
Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
5. He is writing a letter to his father. a) A letter is being written by him to his friend. b) A letter has been written by him by his friend. c) A letter is written by him to his friend. d) A letter was written by me to his friend. 6. I will do that work. a) I will not do that work. b) That work will not done by me. c) Let that work be done by me. d) None of these. 7. Please write the letter. a) Let the letter be written. b) You are requested to write the letter. c) You should write the letter. d) The letter should be written. 8. Who will bring a piece of chalk? a) By whom would a piece of chalk be brought? b) By whom will a piece of chalk be brought? c) By who would a piece of chalk brought? d) By whom will a piece of chalk bring? 9. They have started business. a) Business has started by them. b) Business has been started by them. c) Business has being started by them. d) They have been started a business. 10. Ramya gives me a book. a) A book was given to me by them. b) A book was being given to me by them. c) A book is given to me by them. d) A book is being given to me by them. 11. We chose Ravi leader of our group a) Ravi was chosen leader of our group. b) we were chosen the leader of our group.. c) Ravi was being chosen the leader of our group. d) Ravi is chosen the leader of our group. 12. What can you do for me? a) What can be done by you for me?
Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com
Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
b) What could be done by you for me? c) What could be done with you for me? d) None of the above. 13. She is singing a song. a) A song is being sung by her. b) A song is sung by her. c) A song was being sung by her. D) A song has been sung by her. 14. The mess serves lunch at 12noon. a) Lunch is served by the mess at 12noon. b) Lunch is being served by the mess at 12noon. c) Lunch was served by the mess at 12noon. d) Lunch has served by the mess at 12noon. 15. I hate her. a) She is being hated by me. b) I am hated by her. c) She is hated by me. d) I am being hated by her.
B.DIRECT AND INDIRECT SPEECH
Direct speech:-Direct speech is the conversation between two persons about each other. E.g.:-Vani said to Rani I am going to college now? Indirect speech: - Indirect speech is the conversation between two persons about third person. This is also called reported speech. E.g.:-Vani told Rani that she was going to college then. Rules for changing direct speech (D.S) in to Indirect speech (I.D.S):While changing a sentence from D.S in to I.D.S certain rules have to be followed as follows. 1. Quotation marks must be removed. 2. There are four types of sentences in reported part so the conjunctions should be used as follow:S.No Sentences Direct speech Indirect conjunctions speech 1 Assertive sentence said said that said to 2 Interrogative sentence (helping verbs + w.h ) 3 Imperative sentence (positive +negative) said said to said to said said to told asked questioned enquired requested ordered commanded instructed warned suggested 4 Exclamatory sentence said said to exclaimed that positive(to)/ negative(not to) if/whether wh words
Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com
Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
3.Change of tense:Direct speech 1. Simple present Am, is, are, have, has 2. Present continuous 3. Present perfect 4. Present perfect continuous 5. Simple past (ate V2) 4.Change of model verbs:D.S I.D.S Shall should Should should Can could Could could
Indirect speech simple past was, were, had past continuous past perfect past perfect continuous past perfect (had eaten V3)
D.S will would may might Must
I.D.S would would might might had to
5. Change of pronouns:- Pronouns and possessive adjectives in first person, and second person should be into third person. Observe the following table
I, we, you he, she it .
s.no 1.speaker
2.listener
Person I(sub) (obj) my (sub) my self me you(sub) you(obj) your
Singular he,she him/her his/her himself/herself him/her he/she him/her him/her
Plural
3.we us our our selves
they them their they them their them selves
6.Change of (adverbs) nearness to distance (or) time and place indicators Direct Speech Indirect speech this that these those now then here there today that day yesterday the previous day tomorrow the next day, the following day last night the previous night tonight that night thus so Model-I ASSERTIVE SENTENCE (D.S to I.D.S)
Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
1. He said I am busy today that he was busy that day. 2. Raju said to rani I will come to your house tomorrow. Raju told rani that he would come to her house the next day. 3. My uncle said I take the idlies this morning. My uncle said that he took idlies. 4. Sita said to her husband I like sweets. Sita told her husband that she liked sweets. 5. My grandfather said I drank coffee.
(D.S) (I.D.S) (D.S) (I.D.S) (D.S) (I.D.S) (D.S) (I.D.S) (D.S)
He said
My grandfather said that he had drunk coffee. (I.D.S) 6. A wife said to her husband I have seen this film twice. (D.S) A wife told her husband she had seen that film twice. 7. The porter said that The train will be late by tomorrow. The porter said that the train would be late by the next day. MODEL -2 (I.D.S) (D.S) (I.D.S)
INTERROGATIVE SENTENCES a) YES OR NO TYPE QUESTIONS: Interrogative sentence report yes or no question wh question . Yes or no type question report interrogative sentence statement
change .
Reporting verb reported speech conjunction if whether . D.S do, does, did I.D.S .
1. The girl asked him, Can you sing with me?
(D.S)
The girl asked him if he could sing with her. (I.D.S) 2. The teacher asked the students, Are you all going to the picnic?(D.S) The teacher asked the students if they were all going to the picnic. (I.D.S) 3. She said to me, Do you like music? (D.S) She asked me if I liked music. 4. The teacher said the boys, Hence you finished your work? The teacher asked the boys if they had finished their work. 5. He asked me, Do you know English? (I.D.S) (D.S) (I.D.S) (D.S)
He asked me if I knew English. (I.D.S) 6. The stranger said to me, Can you tell me the way to railway station? (D.S) The stranger asked me if I could tell the way to railway station. (I.D.S) 7. John said to Ram, Will you play chess with me? (D.S)
Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
John asked Ram if he would play with him. b). WH QUESTIONS:1. She said to me, Where can we buy samosas? She asked me where they could buy samosas. 2. Latha said, when are you going to college? Latha asked when they were going to college. 3. She said to them, What should we do now? She asked them what they should do then.
(I.D.S)
NOTE:- When Do, does and did are used as auxiliary verbs in direct speech, they are omitted in indirect speech. Ex:-1.He asked me, Where does your father live? He asked me where my lived. 2. He said to me, how many brothers do you have? He asked me how many brothers you had. 3. The doctor said to the patient, What did you eat yesterday? The doctor asked the patient what he had eaten the previous day. NOTE:-If the direct speech begins with who, what or which followed by a form of be as the main verb, the verb is placed at the end of the sentence. Ex:- 1.He said to her, Who is your English teacher? He asked her who her English teacher was. 2. She said to me, what is your name? She asked me what my name was.
MODEL 3 IMPERATIVE SENTENCES Imperative sentences orders, requests, suggestions, permissions, commands
D.S I.D.S .
positive conjunction to
negative not to .The change of tense is not applicable
for imperative sentences. Ex:-1.She said to me, Please shut the door She requested me to shut the door. 2. The lecturer said to the students, Use the Oxford dictionary. The lecturer advised the students to use the Oxford dictionary. 3. The teacher said, Keep your clothes clean. The teacher advised to keep your clothes clean. MODEL 4 EXCLAMATORY SENTENCES D.S .I.D.S statement . Eg:- He said, How beautiful picture it is! He said that it was very beautiful picture. He said, How nice it is! He said that it was very nice. EXERCISES 1. Rama said, I am going to kadapa.
Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com
(D.S) (I.D.S)
Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
a. Rama said that he was going to kadapa. b. Rama said that I was going to kadapa. c. Rama said that if he going to kadapa. d. Rama said that we were going to kadapa. 2. I said, I shall help you. ( ) a. I said that I will help you. b. I asked that I will help you. c. I said that I would help you. d. I said that he will help you. 3.He said to her, I hate you. ( ) a. He told that he hated her. b. He told that he would hated her. c. He asked that he hated her. d. He told that she hated him. 4. She said to me, please open the door. ( ) a. She requested me please open the door. b. She requested me to open the door. c. She told me that opened the door. d. She requested me not to open the door. 5. They said, We will help you. ( ) a. They said that they would help me. b. They asked that they would help me. c. They said that we would help me. d. They said that they would have helped me. 6. He said to me, Do you play chess? ( ) a. He asked me if I had played cricket. b. He asked me if I played cricket. c. He asked me if he had played cricket. d. He asked me if he played cricket. 7. He said to her, Who is your English teacher? ( ) a. He asked her who was my English teacher was. b. He asked her who my English teacher was. c. He asked her who was her English teacher was. d. He asked her who her English teacher was. 8. He asked me, Where does your father live? ( ) a. He asked me where my father lived. b. He asked me where my father did lived. c. He asked me where his father lived. d. He asked me where that my father lived. 9.He said to me, How many brothers have you? ( ) a. He asked me how many brothers he had. b. He asked me how many brothers that I had. c. He asked me how many brothers I had. d. He asked me how many brothers I had. 10. Teacher said the boys, you have to complete this home work right now?( ) a. Teacher told the boys that they had to complete this home work right now. b. Teacher told the boys that they had to complete that home work right then. c. Teacher told the boys that they had had to complete that home work right then. d. Teacher told the boys that he had to complete that home work right then. 11. He said, I saw your purse here on the table yesterday. ( ) a. He told that he had seen my purse there on the table the day before.
Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
b. He told that he had seen my purse there on the table yesterday. c. He told that he had seen his purse there on the table the day before. d. He told that he had seen his purse here on the table the day before. 12. Sreenu said to Ramu, I will come tomorrow.: ( ) a. Sreenu told Ramu that I would come the next day. b. Sreenu told Ramu that he would come tomorrow. c. Sreenu told Ramu that he would come the next day. d. Sreenu told to Ramu that he would come the next day. 13. His sister said to him, I have never seen a tiger. ( ) a. His sister told him that she had never seen a tiger. b. His sister told him that I had ever seen a tiger. c. His sister told him that she saw a tiger. d. His sister told to him that she had never seen a tiger. 14.The girl asked him, can you sing with me? ( ) a. The girl asked him if he could sing with her. b. The girl told him if she could sing with her. c. The girl asked him if he could have sung with her. d. The girl asked him if he could sing with me. 15. She said to me, Do you like music? ( ) a. She asked me whether I had liked music. b. She asked me whether I have been liked music. c. She asked me whether he liked music. d. She asked me whether I liked music.
C.DEGREES OF COMPARISON
There are three kinds of degrees of comparison in English. They are 1). Positive Degree 2). Comparative Degree 3). Superlative Degree 1). Positive degree (P.D):- Positive degree is used to denote the equality or inequality between the two persons, places, and things.(P.D , , ,
).
Ex:- 1.Rohith is as tall as Rahim. 2. Lokesh is not as tall as Rohith
(Equality) (inequality)
2).Comparative deree(C.D) :-Comparitive degree is used to denote the superiority or inferiority between two persons, places and things. (C.D , ,
.)
Ex:-1. Rohith si taller than Lokesh. 2. Rajampet is larger than Pullampet. 3). Superlative degree(S.D):- Superlative degree is used to denote the uniqueness of a person among the all others.(S.D
.)
Ex. 1. America is the richest country in the world. 2. Sita is one of the cleverest girls in the class.
POSITIVE COMPARATIVE SUPERLATIVE Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju RULE : Single syllable adjectives are added by er & est.
high tall bold kind hard sweet small clever young great thick
higher taller bolder kinder harder sweeter smaller cleverer younger greater thicker comparative braver surer abler finer wiser whiter larger nobler denser purer rarer hotter slimmer fatter thinner sadder bigger
highest tallest boldest kindest hardest sweetest smallest cleverest youngest greatest thickest superlative bravest surest ablest finest wisest whitest largest noblest densest purest rarest hottest slimmest fattest thinnest saddest biggest
positive RULE : The brave adjectives, sure end with e, able are simply fine added by r wise & st white large noble dense pure rare RULE : When hot an adjective slim ends with a fat consonant, preceded by a thin sad vowel, the big consonant
must be doubled and then write er & est
RULE : When an adjective ends with y preceded by a consonant y is replaced by ier & iest
easy holy happy merry wealthy heavy worthy silly lovely jolly dry Some gay exceptions to gray
the above RULE : The adjectives of two or more syllables must be preceded by MORE & MOST
easier holier happier merrier wealthier heavier worthier sillier lovelier jollier drier gayer grayer more beautiful more difficult more handsome more famous more learned more proper more popular more sincere more diplomatic
easiest holiest happiest merriest wealthiest heaviest worthiest silliest loveliest jolliest driest gayest grayest most beautiful most difficult most handsome most famous most learned most proper most popular most sincere most diplomatic
beautiful difficult handsome famous learned proper popular sincere diplomatic
Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com
Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
fruitful intelligent ideal modest honest
more fruitful more intelligent more ideal more modest more honest
most fruitful most intelligent most ideal most modest most honest
MODEL 1 Structure Positive Degree Comparative Degree Obj+verb+not+so+P.D+as+sub C.D+than Superlative Degree
Changing from C.D into P.D Ex:-1. Raju is taller than Hari (Change into Positive Degree) Hari is not so tall as Raju. 2. Nellore is larger than Kadapa. Kadapa is not so large as Nellore. 3. Bindu is cleverer than sindu. Bindu is not so clever as Sindu. 4. America is richer than India. India is not so rich as America 5. A deer is runs faster than a horse. A horse doesnt run so fast as a deer. Changing from P.D. into C.D:Ex:-1.S arala is not so tall as Deepika.(P.D) Deepika is taller than Sarala. 2. Silver is not so precious as Gold. Gold is more precious than silver. 3. India is not so rich as America. America is richer than India. MODAL 2 Structure Positive Degree Comparative Degree Superlative Degree .as+P.D+as Obj+verb+ not+C.D+than
Changing from P.D to C.D Ex:-1. Raju is as tall as Ravi. Ravi is not taller than Raju. 2.Sheela is as strong as Leela. Leela is not stronger than Sheela. 3. Ravi is as intelligent as Vani. Vani is not more intelligent than Ravi. Changing from P.D. into C.D:Ex:-1.Hari is not older than Giri. Giri is as old as Hari. 2.America is not richer than Kuwait. Kuwait is as rich as America. 3. Silver is not more precious than Steel. Steel is as precious as Silver. MODAL 3
Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
Structure Positive Degree Comparative Degree Superlative Degree No other C.D+ than+any other The +S.D ---------so+P.D+as Exercises:1. Raju is the tallest boy in the class. (S.D) Raju is taller than any other boy in the class. (C.D) No other boy in the class is so tall as Raju. (P.D) 2. Asoka was the greatest king in the world. (S.D) Asoka was greater than any other king in the world. (C.D) No other king in the world was so great as Asoka. (P.D) 3.R.K. Narayan is the greatest novelist in India. (S.D) R.K.Narayan is greater than any other novelist in India. (C.D) No other novelist in India is as great as R.K. Narayan. 4. Kolkata is the oldest city in India. (S.D) Kolkata is older than any other city in India. (C.D) No other city in India is so old as Kolkata. (P.D) 5. Shakespeare is the greatest dramatist in the world. (S.D) Shakespeare is greater than any other dramatist in the world.(C.D) No other dramatist in the world as great as Shakespeare. (P.D) MODEL 4 Structure Positive Degree Comparative Degree Superlative Degree Very few/few C.D+than+many One of +the+ S.D other+as+P.D+as other/most other 1. Tagore is one of the greatest Indian writers. (S.D) Tagore is greater than many other Indian writers. (C.D) Very few Indian writers are as great as Tagore. (P.D) 2.Srilaka is one of the biggest Islands in the world. (S.D) Srilanka is bigger than many other Islands in the world. (C.D) Few other Islands in the world are as big as Srilanka. (P.D) 3.Chiranjeevi is one of the best actor in India. (S.D) Chiranjeevi is better than many other actors in India. (C.D) Very few actors in India are as good as Chiranjeevi. (P.D) 4. The Fox is one of the most cunning animals. (S.D) The Fox is more cunning than many other animals. (C.D) Few other cunning animals are as many as the Fox (P.D) 5. The rose is one of the prettiest flowers. (S.D) The rose is prettier than most other flowers. (C.D) Very few flowers are as pretty as the rose. (P.D) MODEL 5 Structure Positive Degree Comparative Degree Superlative Degree Some of the +as+P.D C.D+than+ many other ----not+the + S.D + of all 1. Some of the students in the class are as tall as Raju. (P.D) Raju is not the tallest of all students in the class. (S.D) Raju is taller than many other students in the class. (C.D) 2. Some of the girls in the class are as wise as Rani. (P.D) Rani is not the wisest of all girls in the class. (S.D)
Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
Rani is wiser than many other girls in the class. 3. Some of the cricketers in the world are as good as Sachin. Sachin is not the best of all cricketers in the world. Sachin is better than many other cricketers in the world.
(C.D) (P.D) (S.D) (C.D)
EXERCISES 1. The Arabian nights is the most popular story book. ( ) a. No other story book is as popular as The Arabian Nights b. No other story books are so popular as The Arabian Nights c. Very few other story books are as popular as The Arabian Nights d. No other story book is as more popular as The Arabian Nights 2.The fox is one of the most cunning animals. ( ) a. The fox is more cunning than many other animals. b. The fox is the most cunning than many other animals. c. The fox is more cunning than any other animals. d. The fox is most cunning than many other animals. 3.Rama is not taller than Krishna. ( ) a. Rama is not as tall as Krishna. b. Rama is as tall as Krishna. c. Rama is the tallest as Krishna. d. None of the above 4.Ravi is smarter than many other students in our school.. ( ) a. Ravi is one of the smartest students in our school. b. Ravi is the smartest of all students in our school. c. Ravi is not one of the smartest students in our school. d. Ravi is one of the most smartest students in our school. 5.No other country in the world is as rich as America. ( ) a. America is richer than many other countries in the world. b. America is richer than any other country in the world. c. America is more richer than any other country in the world. d. America is the richest than any other country in the world. 6.Few other cities are as congested as Mumbai. ( ) a. Mumbai is more congested than many other cities. b. Mumbai is more congested than any other city. c. Mumbai is congested than many other cities. d. Mumbai is the most congested than many other cities. 7.Vinod is cleverer than Rajesh. ( ) a. Rajesh is so cleverer as vinod. b. Rajesh is the clever as vinod. c. Rajesh is so clever as vinod. d. Rajesh is not so clever as vinod. 8.A deer runs faster than a horse. ( ) a. A horse doesnt run as fast as a deer. b. A horse not run as fast as a deer. c. A deer doesnt run as fast as a horse. d. A horse runs as fast as a deer. 9. Mount Everest is higher than any other peak in the world. ( ) a. No other peak in the world is so high as the Mount Everest. b. Few other peaks in the world are so high as the Mount Everest. c. Very few peaks in the world are so high as the Mount Everest. d. No other peak in the world is as higher as the Mount Everest.
Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
10.The elephant is not as tall as the giraffe. a. The Giraffe is the tallest than the elephant. b. The Giraffe is not taller than the elephant. c. The elephant is taller than the giraffee. d. The Giraffe is taller than the elephant.
D.SIMPLE, COMPLEX AND COMPOUND SENTENCES There are three types of sentences in English. They are 1.Simple sentence 2. Compound sentence 3. Compound sentences Before going to know about the above sentences, we should know phrase and clause. Phrase:- A phrase is a group of words which gives meaning. It gives some meaning but not completing meaning. It has no subject and no verb. Ex:-1.On seeing a snake. 2. In the middle of the garden. 3.Incase of working hard. Clause:- A clause is a group of words which gives some meaning. It has subject and verb. These are divided into two types namely. Main clause:-A main clause is a group of words which gives complete meaning. It has subject and verb, Ex:-1. I saw a snake. 2.He is very poor. Subordinate clause:- It has a group of words which gives some meaning with subject and verb. It is always connected by subordinate conjections.. Ex:-1.As he was ill 2.Although he worked well
TYPES OF SENTENCES:1. SIMPLE SENTENCE:A sentence which consist of only one main clause is called simple sentence. Ex:-1.I saw a film yesterday. 2. Inspite of working hard, he failed. 3. On seeing a snake, he ran away. 2. COMPLEX SENTENCE:-A sentence that consists of one or more subordinate clauses is called complex sentence. These sentences start with subordinate conjections.
Subordinate conjunctions:Though, although, even though, even if, As, since, because, when, as soon as, If, unless, which, where, who, whom, that, till, until etc.
Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
Ex:-1.Though he worked hard, he failed. 2. Unless you leave from here now, you cant catch the train. 3.Since it was holiday, we stayed at home. 3. COMPOUND SENTENCE:-A sentence that consists of two or more main clauses is called compound sentence. These sentences are connected by co-ordinate conjunctions. They are in the middle of the sentence. Co-ordinate conjunctions:But, yet, still, however, and, and so, so, therefore, not only_ but also, either _ or, neither_ nor, or, otherwise, both__ and, as well as. Ex;-1.He is poor but he is honest. 2.She is rich yet she is unhappy. 3.He was ill so he didnt attend the class. TYPE 1 Simple sentence(ss) In spite of + present participle(v1+ing) Complex sentence(cx) Though Although Even though Even if Compound sentence(cd) But Yet Still
1. He worked hard. He failed. In spite of working hard, he failed. (ss) Though he worked hard, he failed. (cx) He worked hard but he failed. (cd) 2. Ravi is poor. He is honest. In spite of being poor, Ravi is honest. (ss) Although Ravi is poor, he is honest. (cx) Ravi is poor but he is honest. (cd) Exercises:1.Although he was ill, he attended the meeting. (cx) Inspite of being ill, he attended the meeting. (ss) He was ill but he attended the meeting. (cd) 2.She played well but she did not win the match. (cd) In spite of playing well, she did not win the match. (ss) Although he played well, TYPE 2:Simple sentence(ss) Complex sentence(cx) Compound sentence(cd) Too__to So __that Very __and so Very___ and therefore Exercises:1. The coffee is very hot. We cant drink it. The coffee is too hot to drink it. (ss) The coffee is so hot that we cant drink it. (cx) The coffee is very hot and so we cant drink id. (cd) 2. The old man is very poor. He cant buy a car. The old man is too poor to buy a car. (ss) The old man is do poor that he cant buy a car. (cx) The old man is very poor and so he cant buy a car. (cd) 3. Sita is very weak. She cant walk.
Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
Sita is too weak to walk. Sita is so weak that she cant walk. Sita is very weak and so she cant walk.
(ss) (cx) (cd)
Simple sentence(ss) In addition to(or)Besides +present participle
TYPE 3 :Complex sentence(cx) Compound sentence(cd) x Not only___ but also As well as Both and
Exersices:1. He speaks English. He also speaks Hindi. Besides speaking English, he also speaks Hindi. (ss) He speaks not only Englsh but also Hindi. (cd) He speaks English as well as Hindi. (cd) He speaks both English and Hindi. (cd) 2. She is a teacher. She is a home maker. Besides being a teacher, she is ahome maker. (ss) She is not only a teacher but also ahome maker. (cd) She is a teacher as well as a home maker (cd) She is both a teacher and a home maker. (cd) TYPE 4:Simple sentence(ss) Complex sentence(cx) Compound sentence(cd) On account of (or) As So because of +present Since therefore participle because Exercises:1. Rani is very tired. She went to bed early. On account of being very tired, she went to bed early. (ss) As Rani is very tired, she went to bed early. (cx) Rani is very tired so she went to bed early. (cd) 2. He was ill. He stayed at home. Because of being ill, he stayed at home. (ss) As he was ill, he stayed at home. (cx) He was ill so he stayed at home. (cd) TYPE 5:Simple sentence(ss) Complex sentence(cx) Compound sentence(cd) In case of + present Unless-----not Or +not participle If do/does+not otherwise + not 1. You work hard. You will pass. Incase of working hard, you will pass. (ss) Unless you work hard, you wont pass. (cx) If you do not work hard, you wont pass. (cx) You work hard or you wont pass. (cd) 2. We play well. We cant win the match. In case of playing well, we cant win the match. (ss) Unless you play well, you cant win the a match. (cx) If you do not play well, you cant win the match. (CX)
Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
We play well or we cant win the match. Type 6:Simple sentence(ss) On +present participle(v1+ing) Complex sentence(cx) when
(cd)
Compound sentence(cd) and
1. She saw a snake. She ran away. On seeing the snake, she ran away. When she saw a snake, she ran away. She saw a snake and she ran away. 2. I heard the noise. I wake up. On hearing the noise, I wake up. When I heard the noise, I wake up. I heard the noise and I wake up.
(ss) (cx) (cd) (ss) (cx) (cd)
E.QUESTION TAG
Definition :- The part of a sentence, which serves the purpose of confirming the given statement is called question tag . Ex:- 1. She is a doctor, isnt she? The question tag is fallowed short form Long form Short form Am not arent Is not isnt Are not arent Was not wasnt Were not werent Do not dont Does not doesnt Did not didnt Has not hasnt Have not havent Had not hadnt Shall not shant Should not shouldnt Will not wont Would not wouldnt Can not cant Could not couldnt May not maynt Might not mightnt Before knowing the question tag we should follow the following points:1. Question tag is used at the end of the question 2. Question mark is used after the question tag. 3. Only the short form nt is used (in the positive question ) in the question tag.. The subject noun in the given statement will be converted in to a relarint pronoun in the question tag. Model: I Question tag with Auxiliary verbs:-
Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com
Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
Helping Verbs Be forms:-Am, is, are, was, were, Do forms:-do, does, did, Have forms:- have, has, had, Model Auxiliaries:-shall, should, can, could, will, would, may, might, must, dare, need, ought to.
Positive statement Negative question 1. Raju is a lawyer, isnt he? 2. we are studying well, arent we? 3.I am a teacher , arent I? 4. They were in Tirumal, werent they? 5. Latha can speak English, cant she? 6.We have finished our lunch, havent we? 7. They will come to our college, wont they? 8. Sheela has many friends, hasnt she? 9. Karna was a great warrior, wasnt he? 10. Today is Wednesday, isnt it? 11. Tiger is a Crual animal, isnt it? 12. Apples are sweet, arent they? 13. Sita write a letter, dont she? 3. If the statement is in negative, the question tag should be in positive. Negative statement 1. Raju is not a lawyer 2. We are not studying well 3. I am not, teacher 4. They were not in Tirumala 5. Latha can not speak English 6. You are not living in Rajampet 7. I a not your survent 8. Suneel has not paid the bill 9. They are not poor 10. Rani will not stay her Positive question tag is he? are we? am I? were they? can she? are you? am I? has he? are they? will she?
4.when am is used in positive statement arent is used in the question tag. Ex:- I am a teacher I am a teacher, are nt I? 5. When I am is used in the negative statement the question tag is am Eg:- I amnt a teacher. I amnt a teacher, am I?
Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
Model II Question with do, does, did:Note: - 1. If the statement is in positive and the main verb is in present tense (v1) we use dont to from the question tag. Eg:- eat (v1) dont Write (v1) dont 2.If the statement is in positive and the main verb is in present tense (v1) with s or es we use doesnt to frame the question tag. Eg:1. He writes a letter, doesnt he? 2. John goes Church every Sunday, doesnt he? 3. If th statement is positive and the main verb (v2) is in past tense (v2), we use didnt to from the question tag. Ex:- I wrote a letter , Didnt I? Raju went to Karimnagar Yesterday, didnt he? Exercises :1. We play Cricket Dont we? 2. She cooked food didnt she? 3. They make kites dont they? 4. Sita sings songs doesnt she? 5. My uncle sold the House didnt he? 6. My sister wrote the examination didnt she? 7. My sister wrote the examination didnt she? 8. The tiger eats me doesnt it? 9. They live in Rajampet dont they? 10. we bought mangoes didnt we? Some important points:1) If the statement begins with let us (lets), we use shall we, to frame the question tag. Eg:- Lets go for a walk, shall we ? Lets have a cup of Coffee, shall we? 2) If the Statement is a request we use will you to frame the question tag. Eg;-Please come to my house, will you? 3) If the statement is imperative and begins either do or dont we use will you to frame the question tag? Eg:- Open the door, will you? Dont do that work, will you? 4) If this or that as subject in the given statements we use it to frame the question tag. Eg: - This is the map of India, isnt it? This story is not interesting isnt? That is my house, is not it. 5) If these or those are subjects the given statement we use They to from the question tag Eg:- These are my books, are nt they ? Those are mangoes, arent they? 6) If there is as subject in the given statement we use there to frame the question tag. Eg:- There is something strange isnt there? 7) If the sentence has the following words like no, none, neither, never, little, seldom, hardly, few the question tag should be in positive. Eg:- Hari never goes to College, does he?
Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
They seldom go to movies, do they? No body helped her, did they? EXERCISES Find the correct question tag to the following: 1. You are students, __________? 1)Are you 2) arent you 3)were you 2. He is a boy, _________? 1)isnt he 2)is he 3) was he 3. She was my friend, _________? 1)wasnt she? 2) was she? 3) didnt she? 4. I am a teacher, _____________? 1) am I? 2) are I? 3) amnt I? 5. There is no money, __________? 1)is there? 2) isnt there? 3) arent there? 6. I am not a singer, ___________? 1) arent I? 2)are I? 3)am I? 7. Lets go and play,___________? 1)dont we? 2) shall we? 3)does we? 8. I wont teach you, _____________? 1)will I? 2) can I? 3)wont I? 9. Nobody is present, ___________? 1)is he? 2)isnt he? 3)are they? 10.This story is very interesting, ________? 1)is it? 2)isnt it? 3) arent it? 11.He likes me,_______________? 1)does he? 2) doesnt he? 3) did he? 12.Your brother is an engineer,________________? 1)has he? 2)hasnt he? 3) is he? 13.Rani goes to her native place,_________________? 1)doesnt she? 2)does she? 3)do she? 14.They dont play tennis,____________________? 1)do they? 2)dont they? 3)is they? 15.You are not going to school now,_____________? 1)werent you? 2)were you? 3) are you? 16.Kiran is a doctor, ________________? 1)is he? 2)isnt he? 3)do he? 17.Raju draws pictures,_________________? 1)does he? 2) doesnt he? 3) did he? 18.The minister made a good speech,______________? 1)did he? 2)didnt he? 3)does he? 19.The chief minister came by car,_______________? 1)did he? 2)didnt he? 3)does he? 20.I have a house,__________________? 1)have I? 2)hasnt I? 3)havent I? 21.Sita has danced well,_______________? 1)have I? 2)hasnt I? 3)havent I? 22.Please give a book,______________? 1)did you? 2)didnt you? 3)shall we? 23.The match was very cxciting,_______________? 1)werent it? 2)were it? 3) was it? 24.She performed very well,____________? 1)does she? 2) doesnt she? 3) did she? 25.We play games,_______________? 1)dont we? 2) shall we? 3)do we?
Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com
( ) 4) havent you ( ) 4) wasnt he ( ) 4) did she? ( ) 4) arent I? ( ) 4) has there? ( ) 4) amnt I? ( ) 4) didnt we? ( ) 4) shall I? ( ) 4) arent they? ( ) 4)dont it? ( ) 4)didnt he? ( ) 4) isnt he? ( ) 4)dont she? ( ) 4)isnt they? ( ) 4)arent you? ( ) 4)dont he? ( ) 4)didnt he? ( ) 4)dont he? ( ) 4)dont he? ( ) 4)hasnt I? ( ) 4)hasnt I? ( ) 4)dont we? ( ) 4)wasnt it? ( ) 4)didnt she? ( ) 4) didnt we?
Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
CHAPTER VII COMPREHENSION PASSAGE
Comprehension means the ability to understand before answering the questions. Observe the following steps:1. Read the passage first rapidly and read the questions. 2. Read through the passage for second time to catch gist(idea) 3. Take each question and confirm the answers. 4. Eliminate the answer choices that dont go with your conformed answer. 5. Find the on line answers.(on the line) 6. Between the lines.(connected) 7. Beyond the lines.(more than the information) 8. Personal involvement question. 9. Inferential questions.( out of the passage)
TYPES OF QUESTIONS
Verbal questions (yes/no type) who Whom whose When Which What Where why How How long How much How far How old
non verbal questions (WH word questions)
persons Time Choice/option Matter/ information Place/location Reason/cause Manner/ procedure Period Quantity Age
1. Read the following passage to answer the questions:Once there lived two crows on a tree in a forest. Many animals often came there and took rest under the tree. There was a black cobra in the hole of the tree. The crow couple built a nest on the tree. The female crow laid eggs in the nest. Later four crows came out of the eggs. One day the crows went out to bring food for their children. At that time the snake came up to the nest and ate the little crows. The crows after returning with food saw the snake going in to the hole and found their nest empty. They felt very sad. The same thing happened after a few months. The crows thought that the snake would eat their children every time if they continued to live there. They decided to leave the place and go to another place. ANSWER THE FOLLOWING:1. The crows built nests to ________. a. Live happily.
Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com
Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
b. Lay eggs. c. Protect eggs from enemies. d. Keep small birds. 2. The snake went to the nest when the crows were away to a. Protect the children of the birds. b. Eat the children to the bird. c. Give food to the children of the bird. d. Play with the children of the bird. 3. The crow couple felt sad because a. They could not harm the snake. b. There was none to help them. c. They felt the nest. d. They lost their children 4. The birds decided to go to another place because a. The tree became very big. b. Other animals took rest under the tree. c. They were not safe there. d. The snake often ate their children. 5. The birds in the story are a. Timid b. Afraid of future. c. Enemies to the snake. d. Desires of the changing the place.
CHAPTER VIII LETTER WRITING
Letter means a message, which is send to somebody. Letter is written communication.
TYPES OF LETTERS
There are mainly two types of letters. They are:1. Formal letters (official and business letters) 2. Informal letters (personal letters)
FORMAL LETTERS
These are divided into two groups. 1. Official letters:These letters are written to officers, teachers, head masters and officials. Formal letters may be brief and short. 2. business letters:These letters are written to business people and strangers.
INFORMAL LETTERS
These are known as personal letters. These are written to family members, friends, relatives and well wishers. Personal letters may be long and detailed, familiar and intimate. PARTS OF THE LETTER Every letter has five parts:1. Heading (writers address) 2. Salutation. 3. Body of the letter.
Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
4. Sub scription. (leave taking) 5. Super scription. (address on the envelope) 1. Heading: Heading is known as writers address. It is written at the top right hand corner of the page. Date should come after address. The date should be writing like 12th June, 2011. At the end of the every line in address we should put comma. Full stop is used after the date. 2. Salutation: The position of the salutation is at the left hand of the first page at lower level than the heading. A comma is put after the salutation. To the family members:My dear father, Dear father, Dear brother, Dear mother, Dear sister, Dear uncle, Dear aunt, Dear cousin, To friends:Dear Rama, To officers:Sir, Madam,
To business people:Sir, Dear Sir, Dear Sirs, Sirs, Dear Madam, 3. Body of the letter: It is written below the salutation and middle of the page. The simple style is used in the body. If the body of the letter is lengthy, it should be divided into paragraphs. It should contain brief and short sentences.
Door No: 5/79, Usman Nagar, Rajampet, 12th June,2011. J
4. Subscription (leave taking): It is written at the bottom of the letter either on the left side or on the right side. A comma is put after the subscription. Dont put apostrophe yours. To family members and friends:Yours lovingly,
Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
Your affectionately, Yours sincerely, Yours loving friend, Yours loving son,
To officers:Yours faithfully, Yours truly, 5. Super scription (address on the envelope): It is written either right hand top corner of the page or bottom of the page. It is written below the subscription dont put the full stop after the signature.
EXERCISES
1. Every letter contains a. Heading b. Subscription c. Message or information d. Body 2. Letter is ____________ communication. a. Verbal b. Written c. Non verbal d. None of the above. 3. The British style of writing date is_______ a. 12/06/2011. b. 12th June,2011. c. June 12th ,2011. d. 12-06-2011 4. After date is ________ needed. a. Comma b. Colon c. Full stop d. None 5. After salutation it is necessary. a. Comma b. Colon c. Full stop d. None 6. One of the following subscription is correct. a. Yourss faithfully, b. Yours faithful c. Yours lovingly, d. yours faithfully, 7. The body of the letter contains _______. a. The salutation, b. The message, c. An acknowledgement. d. None of the above. 8. An official letter begins with a. Dear sir,
Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com
Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
b. Dear sirs, c. Sir, d. My dear sir, 9. The style of personal letter should be a. Formal b. Bombastic c. Familiar and intimate d. None of the above.
CORRECTION OF SENTENCES
Rules related to Nouns Rule1:-Some nouns are used only as singular. They have no plural forms:They are advice,alphabet,abuse,furniture,information,fuel,news,poetry,bread,soap, scenery, business, issue, repair, luggage, machinery, stationary, the wicket. 1. He has given advice (wrong) He has given advice (Right) a 2. where are my luggages? (wrong) Where is my luggage? (Right) Rule2:- Some nouns are plural in form but they are used as singular Branches of learning: - economics, politics, physics, statistics, linguistics, g mathematics. sports :- billiards, gymnastics, athletics diseases :- mumps, measles Eg:-1. Economics are his favourite subject (W) Economics is his favourite subject (R) 2.Measles have broken out in our area (W) Measles has broken out in our area (R) Rule3:- Some nouns are used only as plurals. They have no singular forms:Shoes, trousers, shorts, scissors, spectacles, alms, binoculars, savings, innings, goods, premises, stockings etc. Eg:-1.where is my scissors (w) where are my scissors (R) 2.spectacles is now a costly item. (w) spectacles are now a costly item. (R) Rule4:- The following words dont take plural when preceded by a numerical(number) like dozen, hundred, thousand, lakh, million, and score Eg:-1. I have ten thousands rupees(w) I have ten thousand rupee (R) 2.My friend bought ten dozens bananas (w) My friend bought ten dozen banana (R) Rule5:- Plurals of compound nouns are formed by adding s to the main word( Brother-in-laws, sister-in-laws, father-in-laws, son-in-laws, mother-in-laws) Eg:-1. I have two father-in-laws (w) I have two fathers-in-law (R) 2. Passer by (w) passers by (R) 3. He has one brother-in-laws (w) He has one brothers-in-law (R) Rule6:- Do not add brother or sister to the word cousin. Eg:Ramya is my cousin sister (w) Ramya is my cousin (R) Rule7:-Running is not used with age Eg:Ravi is running sixteen (w) Ravi is sixteen. (R) Rule8:- The words male and female are used as adjectives but not nouns. Man and woman are used as nouns Eg:-There are twenty females in the class There are twenty girls in the class.
Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com
Eg:-
(w) (R)
Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
Rule9:- When the nouns are in appositions is add the second noun.:Eg. It is my friends Kirans car. (w) It is my friend Kirans car. (R) Rule10:- We should not say 20 years. We should say 20 years old or 20. Eg:- He is 40 years. He is 40years old.(or) He is 40. (w) (R)
RULES RELATED TO PRONOUNS Rule1:- The serial order of personal pronouns in a good sentence is 2nd person, 3rd person and 1st person. Eg:-1. Ram,I and you have finished our homework. (w) You, Ram and I have finished our homework. (R) 2.I and Ravi went to the exhibition. (w) Ravi and I went to the exhibition. (R) Rule2:-A pronoun must agree with its antecedent Eg:-1.One must love his parents. (w) One must love ones parents. (R) Rule3:- If the sentence starts with reflexive pronoun, we write subjective pronoun in its place Eg:- Myself do this work. (w) I do this work (R) Rule4:-Enjoy, apply, resign, drive, avail, absent etc, when used as transitive verbs, always take reflexive pronouns after them (enjoy, avail, apply verbs eg:- He applied for a job. (w) kHe applied himself for a job. (R) They enjoyed the T.V. show (w) They enjoyed themselves the T.V show (R) Rule5:- Apostrophes is not add to pronouns:Eg:- 1.That book is yours (w) that book is yours (R) 2.This house is ours (w) This house is ours (R) Rule6:- Each of, one of, none of, either, neither, everybody, every should always treated as singulars( are is, were was, Eg- 1.Nither of the books are interesting Neither of the books is interesting. 2. Each of the boys were given a book. Each of the boys was given a book. .one of the girls have good knowledge of English one of the girls has good knowledge of English. have has ) : (w) (R) (w) (R) (w) (R) reflexive pronoun .)
Rule7:-Each other is used when there are two subjects or objects and one another is used when there are more than two subjects and objects. // Eg:- 1.Romeo and Juliet loved one another. Romeo and Juliet loved each other. 2.All the students loved each other. iAll the students loved one another. (w) (R) (w) (R) / ii
Rule8:- Use of relative pronouns:who = persons which = places and things Eg:1.Rama Rao, that works in this office, is my friend. Rama Rao, who works in this office, is my friend. 2. The dog, who ,bites people, is my friends dog.
Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com
that = places and things (w) (R) (w)
Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
The dog, that ,bites people is my friends dog.
(R)
RULES RELATED TO VERBS Rule1:-Simple present tense is used to express a habit( daily,regularly,rarely, occasionally, generally, usually, frequently, often, always Eg:-1.I am going to college daily. (w) I go to college daily. (R) 2.Sita is taking milk rarely. (w) Sita takes milk rarely. (R) Rule2:-present perfect continuous tense is used is used with since and for:Eg:-1.I am working here for six months. (w) I have been working here for six months (R) 2.It is raining since 60 clock. (w) It has been raining since 60 clock (R) Rule3:- love, like, hate, smell, feel, taste, hear, own, belong, know, want, have, possess, think, and understand. If we find anyone among them in a sentence we should not put ing form. Eg:-1.I am knowing his address. I know his address. 2. They are having a problem. They have a problem 3. She is belonging to Rajampet. She belongs to Rajampet. 4.You are liking this college. You like this college. 5.The apple is tasting good. The apple tastes good. (w) (R) (w) (R) (w) (R) (w) (R) (w) (R)
Rule4:-Simple past is used to denote past action.( ago, yesterday, last month, last year etc. ) Eg:-1.They have gone to Kadapa Yesterday. (w) They went to kadapa yesterday. (R) 2. They have played a match last week. (w) They played a match last week. (R) Rule5:-there are two works in a sentence one work is in simple preset, other work will be in simple future tense. Eg:-If you will ask me, I shall clearify your doubts. (W) If you ask me, I shall clarify your doubts. (R) 2.If he will work hard, he will get first class. (w) If he work hard, he will get first class. (R) Rule6:-If the reporting verb is in the past tense the other verbs should be in past tense. Eg:-1.She knew that her brother is coming by train. (w) She knew that her brother was coming by train. (R) 2.She told us that her mother is busy. (w) She told us that her mother was busy. (R) 3.She said that she is going to Madras. (w) She said that she was going to Madras. (R) Rule7:- Hanged means caused death, hung means to display Eg:- The criminal was hung two days ago. The criminal hanged two days ago. Rule 1:Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
(W) (R)
RULES RELATED TO ADVERBS
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
Eg:- 1.He drives fastly. He drives fast. 2.the train does not run on the track. The train does not run on the track.
(w) (R) (w) (R)
RULES RELATED TO PREPOSITIONS Rule 1:- The following words followed by certain prepositions;Suffering ___ from, searching ____ for, waiting ___ for, apply ____ for, fond ___ of, afraid ___ of, died ____of, congratulate ___ on, angry ___ with, good ___ at, bad__ at, accused____ of etc. Eg:-1.Sarala is suffering with fever. (w) Sarala is suffering from fever. (R) 2. Rama is fond in ice-cream. (w) Ramu is fond 0f ice- cream. (R) 3.I congratulate for his success. (w) I congratulate on his success. (R) 4. Radha is waiting to her sister. (w) Radha is waiting for her sister. (R) 5.Saloni is good in English. (w) Saloni is good at English. (R) Rule 2:- We should not use any preposition after these words. Awaiting, ordered, discussed, returned, entered, Eg:-I am awaiting for your reply. (W) I am awaiting your reply. (R) 2.We discussed about the matter. (w) We discussed the matter. (R) 3.The stranger entered into the building. (w) The stranger entered the building. (R) 4.The minister returned back this evening. (w) The minister returned this evening, (R) 5. They ordered for coffee. (w) They ordered coffee. (R) Rule3:-ing form is used after certain verbs and phrases: Avoid, imagine, enjoy, finish, miss, practise, look forwardto. Eg:-1.I avoid to speak to her. (w) I avoid speaking to her. (R) 2. We enjoy to play the cricket. (w) We enjoy playing the cricket. (R) 3.He practices to sing songs. (w) He practices singing songs. (R) RULES RELATED TO ADJECTIVES Rule 1:-Adjectives like prefer, prior, junior, senior, superior, inferior, interior, exterior, elder are followed by to instead of than Eg:-I Prefer coffee than tea. (w) I prefer coffee to tea. (R) 2.He is not superior than you. (w) He is not superior to you. (R) Rule 2:-Double comparatives or double superlatives are not used. Eg:-Sita is more cleverer than Gita (w) Sita is cleverer than Gita (R) 2.Rama is the most tallest boy in the class. (w) Rama is the tallest boy in the class. (R) Rule3:-Elder refers to the members of the family. Older refers to out of the family. Eg:-1. Rama is older than her sister. (w) Rama is elder than her sister. (R) 2. Rama is elder than all the boys in the class. (w) Rama is older than all the boys in the class. (R) Rule 4:-Superlative degree cannot be used when the comparison is only between the two. Eg:-This story is the best of the two. (w) This story is better of the two. (R) Rule5:-A is used before the words beginning with a consonantal sound. The words like University, union, European, one rupee coin.
Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
www.facebook.com/vinayadharraju
Eg:-1. Mr.David is an European. (w) Mr.David is a European. (R) 2. Let us form an union (w) Let us form a union. (R) 3.He is an University professor. (w) He is a university professor. (R) Rule6: An is used before the words beginning with a vowel sound. The words like hour, honour, honorable, honest, heir Etc. Eg:- I waited for her a hour. (w) I waited for her an hour. (R) 2.Gandhiji is a honest man. (w) Gandhiji is an honest man. (R) Rule7:-THE is used before the names of rivers, oceans and hollybooks. Eg:- Vijayawada is on Krishna river. (w) Vijayawada is on the Krishna river. (R) 2. My uncle reads Ramayana every day. (w) My uncle reads the Ramayana every day. (R) Rule8:-The is used before the superlative adjectives. Eg:-The Mount Everest is a biggest peak in the world. (w) The Mount Everest is the biggest peak in the workld. (R) Rule9:- In certain comparison that of should be used. Eg:-1.The climate of Bangalore is better than of Hyderabad. (w) The climate of Bangalore is better than that of Hyderabad. (R) Rule10:- Further refers to something additional, Farther refers to distance. Eg:-1.I went to America for farther studies. (w) I went to America foe further studies. (R)
RULES RELATED TO CONJUCTIONS Rule 1:-Double conjunctions cannot be used in a whole sentence. Eg:-Though he is poor, but he is honest. (w) Though he is poor, he is honest. (R) 2.Although he is rich yet he cannot buy a car. (w) Although he is rich, he cannot buy a car. (R) Rule 2:-If the sentence begin with As, Since we should remove So, Therefore in a sentence. Eg:-1.As I am poor so I cannot buy a car. (w) As I am poor, I cannot buy a car. (R) 2. Since the doors are opened therefore the thief entered the house. (w) Since the doors are opened, the thief entered the house. (R)
WISH YOU ALL THE BEST
Visit our Blog: www.feltap.blogspot.com
Email: vinayadharraju@gmail.com
You might also like
- English GrammarDocument341 pagesEnglish GrammarNiko Marikew100% (39)
- Grammar TreeDocument52 pagesGrammar TreeMerryum Javed100% (15)
- Hindi Grammar Structure IntensiveDocument18 pagesHindi Grammar Structure IntensiveMichael SongNo ratings yet
- IB Spanish Review SheetsDocument22 pagesIB Spanish Review Sheetsharrisonackerman100% (12)
- 600 Most Repeated One Word Substitutions in SSC CGL CHSLDocument55 pages600 Most Repeated One Word Substitutions in SSC CGL CHSLMuhammad SohailNo ratings yet
- 10th English GrammarDocument82 pages10th English GrammarGayatriramanaNo ratings yet
- Useful Phrases in TeluguDocument4 pagesUseful Phrases in TelugumedanonakamaNo ratings yet
- English Grammar and Verbs GuideDocument65 pagesEnglish Grammar and Verbs Guidemark75% (4)
- General Knowledge Social Science Capsule For ICAR Technician 2022 ExamDocument98 pagesGeneral Knowledge Social Science Capsule For ICAR Technician 2022 ExamHritik SharmaNo ratings yet
- Gerund, Participle, InfinitiveDocument7 pagesGerund, Participle, InfinitiveNurul Aini NazlaNo ratings yet
- Synonyms and Antonyms: (Describing Character)Document2 pagesSynonyms and Antonyms: (Describing Character)badrul_ahmad100% (1)
- Manika Sanskrit Workbook Class 9 CBSE Chapter 20-22, Shabdarupaani DhaturupaaniDocument36 pagesManika Sanskrit Workbook Class 9 CBSE Chapter 20-22, Shabdarupaani Dhaturupaanikothawade_lalits50% (4)
- ACCOUNTS MANUAL OVERVIEWDocument73 pagesACCOUNTS MANUAL OVERVIEWDknilu YadavNo ratings yet
- Dted2 TeluguDocument193 pagesDted2 Telugureddy331No ratings yet
- 321sanskrit IntroDocument156 pages321sanskrit IntrogogoNo ratings yet
- GK of IndiaDocument73 pagesGK of India101010121212No ratings yet
- ANDAMAN AND NICOBAR ADMINISTRATION SERVICE FAQSDocument197 pagesANDAMAN AND NICOBAR ADMINISTRATION SERVICE FAQSRavinder Devarakonda100% (1)
- Manika Sanskrit Workbook Class 9 CBSE Chapter 13 19Document34 pagesManika Sanskrit Workbook Class 9 CBSE Chapter 13 19kothawade_lalits67% (3)
- Parts of SpeechDocument9 pagesParts of SpeechAbbbas100% (1)
- Hegel - The Difference Between Fichte's and Schelling's System of PhilosophyDocument83 pagesHegel - The Difference Between Fichte's and Schelling's System of Philosophydanielschwartz88No ratings yet
- List of Grammatic Topics Covered in KETDocument2 pagesList of Grammatic Topics Covered in KETnitasampat100% (2)
- How Does A Language Acquire Gender Markers?Document21 pagesHow Does A Language Acquire Gender Markers?Aviv Schoenfeld100% (2)
- Prosody 022446 MBPDocument198 pagesProsody 022446 MBPyeap1234100% (1)
- Tense Chart: IndefiniteDocument2 pagesTense Chart: IndefiniteAbhimanyu SinghNo ratings yet
- SSC CGL Tier I Last 5 Year Papers e Book WWW - Sscportal.inDocument97 pagesSSC CGL Tier I Last 5 Year Papers e Book WWW - Sscportal.inAKshita LaNiNo ratings yet
- Q&R EnglishToTeluguMeaningsDocument286 pagesQ&R EnglishToTeluguMeaningsmouse.lenova mouseNo ratings yet
- SSC MTS Question Paper 2019 English Exammix PDFDocument585 pagesSSC MTS Question Paper 2019 English Exammix PDFJosewin100% (1)
- Telugu Is A Language Spoken by Some 90 Million SpeakersDocument33 pagesTelugu Is A Language Spoken by Some 90 Million SpeakersMarcos GusmaoNo ratings yet
- Price List NISCAIR PublicationsDocument16 pagesPrice List NISCAIR PublicationsSajal SahaNo ratings yet
- Hindi Book 2 PDFDocument16 pagesHindi Book 2 PDFEnd End0% (1)
- UPSC Telugu Literature GuideDocument7 pagesUPSC Telugu Literature Guide_arifa_100% (1)
- Interactive English LessonsDocument25 pagesInteractive English LessonsGayanNo ratings yet
- Indian History Bit BankDocument15 pagesIndian History Bit Banksuresh100% (1)
- Objective General English - DjvuDocument2,637 pagesObjective General English - DjvuBala Mech SBNo ratings yet
- Social Science Assignment CBSE Class 8 IndustriesDocument2 pagesSocial Science Assignment CBSE Class 8 Industriesgurdeepsarora8738No ratings yet
- TEACHING ENGLISH PEDAGOGYDocument88 pagesTEACHING ENGLISH PEDAGOGYLokesh NANo ratings yet
- COI in GujaratiDocument290 pagesCOI in GujaratiCrazy GujjusNo ratings yet
- NCERT Book - Sanskrit - Class IXDocument91 pagesNCERT Book - Sanskrit - Class IXnikhilam.com75% (8)
- Hindi-Telugu KoshDocument878 pagesHindi-Telugu Koshrajendra kumar devarapalliNo ratings yet
- Motivational Hindi Songs CollectionDocument4 pagesMotivational Hindi Songs CollectionSundara VeerrajuNo ratings yet
- X Class EnglishDocument17 pagesX Class Englishk.nagendraraoNo ratings yet
- వ్యక్తిత్వ వికాసం -Vyaktitva Vikasam by C Narasimha RaoDocument40 pagesవ్యక్తిత్వ వికాసం -Vyaktitva Vikasam by C Narasimha RaoSuma MadhuNo ratings yet
- GRE Word GroupsDocument1 pageGRE Word GroupsJitta Raghavender RaoNo ratings yet
- Pension RulesDocument98 pagesPension RulesKarthik CNo ratings yet
- Prefixes and Sufixes in HindiDocument12 pagesPrefixes and Sufixes in HindiFilhmayanti E. Muthalib50% (2)
- Geeta PadarthDocument108 pagesGeeta PadarthA1India.In100% (1)
- SGT DSCDocument85 pagesSGT DSCLisha Shanvi100% (1)
- 2) Maa Aadya Shakti AartiDocument3 pages2) Maa Aadya Shakti Aartiarun_adventureNo ratings yet
- Telugu Phrasebook - WikitravelDocument19 pagesTelugu Phrasebook - WikitravelDeepa DevarajNo ratings yet
- PDF Notes Website ReviewDocument173 pagesPDF Notes Website ReviewSuyash GuptaNo ratings yet
- Sanskrit Grammar Compound TypesDocument10 pagesSanskrit Grammar Compound TypesvsballaNo ratings yet
- GK 1-620 QuestionDocument20 pagesGK 1-620 QuestionnandamNo ratings yet
- Prof - Jayashankar Biography PDFDocument5 pagesProf - Jayashankar Biography PDFSainath ChallaNo ratings yet
- Tamil Literary Garden 2009 Lifetime Achievement AwardsDocument20 pagesTamil Literary Garden 2009 Lifetime Achievement AwardsvatzanNo ratings yet
- Compex Nepal - FormDocument2 pagesCompex Nepal - Formwww_utkarshmishra2No ratings yet
- 10th Social Bit BankDocument52 pages10th Social Bit BankSubramanyam K.V.R100% (1)
- 1000 Computer-Internet QuestionsDocument21 pages1000 Computer-Internet QuestionsNarendra VermaNo ratings yet
- Idioms and PhrasesDocument10 pagesIdioms and PhrasesShristi GuptaNo ratings yet
- Names of Common Flowers in English, Hindi, Tamil, Sanskrit and MalayDocument4 pagesNames of Common Flowers in English, Hindi, Tamil, Sanskrit and MalayAmritanshu MisraNo ratings yet
- Animals Name in SanskritDocument34 pagesAnimals Name in Sanskritsanskrit vartaNo ratings yet
- Hindi Sahitya Ka ItihasDocument131 pagesHindi Sahitya Ka ItihasAshish G100% (4)
- All in One MCQsDocument192 pagesAll in One MCQsRehan XhahNo ratings yet
- Teacher King’s English Speaking Course Book 1: Italian EditionFrom EverandTeacher King’s English Speaking Course Book 1: Italian EditionNo ratings yet
- Famous Indians Of The 20th Century: Biographical sketches of indian legendsFrom EverandFamous Indians Of The 20th Century: Biographical sketches of indian legendsNo ratings yet
- Quiz Time History & Culture: Best bet for knowledge and entertainmentFrom EverandQuiz Time History & Culture: Best bet for knowledge and entertainmentNo ratings yet
- Kinds of Pronouns and AdjectivesDocument4 pagesKinds of Pronouns and AdjectivesJeff CadetNo ratings yet
- Learn English OnlineDocument88 pagesLearn English OnlineKoteswaraRao BandlaNo ratings yet
- Ace the English Grammar Test with These Expert TipsDocument60 pagesAce the English Grammar Test with These Expert TipsEleander Handugan BebitNo ratings yet
- Indirect Speech - Commands and QuestionsDocument14 pagesIndirect Speech - Commands and QuestionsArturo AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- Rules of InferenceDocument10 pagesRules of Inference1170 Ananya SutradharNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document14 pagesChapter 4Thatha BaptistaNo ratings yet
- Hans Kelsen and The Logic of Legal SystemsDocument50 pagesHans Kelsen and The Logic of Legal SystemsleonardolippertNo ratings yet
- English Oh ReadDocument115 pagesEnglish Oh Readjoc3lyn_nNo ratings yet
- نسخة Accounting Theory Ppt Copy-112Document16 pagesنسخة Accounting Theory Ppt Copy-112ArinaNo ratings yet
- The Verb Have Got - Jean PierreDocument11 pagesThe Verb Have Got - Jean PierreElvis PérezNo ratings yet
- 1st Quarter Exam - English 3Document5 pages1st Quarter Exam - English 3Nyx VelardeNo ratings yet
- Belajar Bahasa SpanyolDocument76 pagesBelajar Bahasa SpanyolVa SNo ratings yet
- Grammar Overview General Rules & TheoryDocument44 pagesGrammar Overview General Rules & TheorySara RakiticNo ratings yet
- Colloquial ExpressionDocument6 pagesColloquial ExpressionABU SANINo ratings yet
- JSU English Paper 1 SpecificationsDocument2 pagesJSU English Paper 1 SpecificationsHamsiah HamidNo ratings yet
- Synonymy - Antonymy Polysemy - Homonymy: Group 2Document45 pagesSynonymy - Antonymy Polysemy - Homonymy: Group 2Nguyên NguyễnNo ratings yet
- CPT114/CPT104: Logic and Applications/ Introduction To Logic and AbstractionDocument49 pagesCPT114/CPT104: Logic and Applications/ Introduction To Logic and AbstractionFieza AndreaNo ratings yet
- What is semantics? Understanding meaning in languageDocument12 pagesWhat is semantics? Understanding meaning in languageAMBuendiaNo ratings yet
- Study Guide English IDocument15 pagesStudy Guide English IDiego Andrés BaquedanoNo ratings yet
- G8SEMIFINALSENGDocument4 pagesG8SEMIFINALSENGlovelyfb fuentesNo ratings yet
- Contrastive Analysis in Nominal Affixation Between English and Batak Toba Language A R R A N G E DDocument19 pagesContrastive Analysis in Nominal Affixation Between English and Batak Toba Language A R R A N G E DEndang Veronica SimanjuntakNo ratings yet
- Barriers of CommunicationDocument28 pagesBarriers of CommunicationBibhasKittoorNo ratings yet
- Husserl Learns ChineseDocument28 pagesHusserl Learns ChineseTAGNo ratings yet
- Leaving Cert Higher Notes 1Document4 pagesLeaving Cert Higher Notes 1api-384311544No ratings yet