Professional Documents
Culture Documents
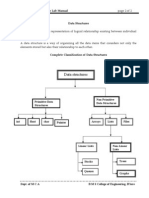
Types of Binary Tree
Uploaded by
SuvayanCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Types of Binary Tree
Uploaded by
SuvayanCopyright:
Available Formats
Types of Binary Tree
A tree is a binary tree if and only if :-
– It has a root node , which may not have any child nodes (0 child
nodes, NULL tree)
– Root node may have 1 or 2 child nodes . Each such node forms a
binary tree itself
– Number of child nodes can be 0 ,1 ,2.......not more than 2
– There is a unique path from the root to every other node
E.g. :-
A binary tree is a strictly binary tree if and only if :-
– Each node has exactly two child nodes or no nodes
E.g.:-
A binary tree is a full binary tree if and only if :-
– Each non leaf node has exactly two child nodes
– All leaf nodes are at the same level
suvayanbala@gmail.com 9231937821 Page |1
E.g.:-
• A binary tree is a perfect binary tree if and only if :-
– is a full binary tree
– All leaf nodes are at the same level
E.g.:-
A binary tree is a complete binary tree (of height h , we take root node
as 0 ) if and only if :-
– Level 0 to h-1 represent a full binary tree of height h-1
– One or more nodes in level h-1 may have 0, or 1 child nodes
– If j,k are nodes in level h-1, then j has more child nodes than k if
and only if j is to the left of k , i.e. the last level (h) can be missing
leaf nodes, however the ones present must be shifted to the left
suvayanbala@gmail.com 9231937821 Page |2
E.g.:-
A complete binary tree filled at each depth from left to right
suvayanbala@gmail.com 9231937821 Page |3
Preorder Traversal:-
Step 1 : Start from the root node . Write it down.
Step 2 : Now go to the leftmost node from the root node in the
left sub tree. On it’s way to the left most node, right down all the
nodes as it comes.
Step 3 : When the leftmost node is reached. Write it down.
Step 4 : Now visit the right sub tree of the leftmost node’s
parent node.
Step 5 : Write down the first node of the right subtree.
Step 6 : Now proceed in the same way as in Step 2 - 5 till
‘writing down’ of all the nodes is finished.
Inorder Traversal :-
Step 1 : Start from the root node .
Step 2 : Now go to the leftmost node from the root node in the
left subtree.
Step 3 : When the leftmost node is reached . Write it down.
Step 4 : Now visit/go the leftmost node’s parent node. Write it
down.
Step 5 : Now visit/go to the first node of the right subtree.
Step 6 : Proceed in the same way as in Step 2 - 5 till ‘writing
down’ of all the nodes is finished.
suvayanbala@gmail.com 9231937821 Page |4
Postorder Traversal :-
Step 1 : Start from the root node .
Step 2 : Now go to the leftmost node from the root node in the
left subtree.
Step 3 : When the leftmost node is reached . Write it down.
Step 4 : Now visit/go the leftmost node’s parent node.
Step 5 : Now visit/go to the first node of the right subtree.
Step 6 : Proceed in the same way as in Step 2 - 5 till ‘writing
down’ of all the nodes is finished.
In the above traversals we should follow a rule, which is –
In a case when there is no ‘unwritten’ nodes in a subtree
(left / right) or there is no subtree (left / right), go
backwards from that node, in the reverse way as arrived
and ‘go’ to that node that come first in the way back,
provided it has not been written. Write it down and
proceed.
suvayanbala@gmail.com 9231937821 Page |5
Example :-
C F
E G N K
M
I
Preorder Traversal :- A C E G I F N K M
Inorder Traversal :- ECIGANKFM
Postorder Traversal :- E I G C N M K F A
suvayanbala@gmail.com 9231937821 Page |6
You might also like
- Origami City Ebook: Build Your Own Cars, Trucks, Planes & Trains!: Contains Full Color 48 Page Origami Book, 12 Projects and Printable Origami PapersFrom EverandOrigami City Ebook: Build Your Own Cars, Trucks, Planes & Trains!: Contains Full Color 48 Page Origami Book, 12 Projects and Printable Origami PapersNo ratings yet
- Linked List Vs ArrayDocument10 pagesLinked List Vs ArrayRootNo ratings yet
- SortingDocument27 pagesSortingFatima ShakeelNo ratings yet
- Searching and Sorting ProgramsDocument11 pagesSearching and Sorting ProgramsgurusodhiiNo ratings yet
- Design and Implementation of Simple As Possible Computer (SAP-1)Document52 pagesDesign and Implementation of Simple As Possible Computer (SAP-1)Muhammad Anas 484-FET/BSEE/F18No ratings yet
- Trees: 1/34 Data Structures and Algorithms in JavaDocument34 pagesTrees: 1/34 Data Structures and Algorithms in JavaThịnh TrầnNo ratings yet
- PointersDocument30 pagesPointersPartha AichNo ratings yet
- Function in CDocument12 pagesFunction in CGoldy Batra100% (1)
- C++ ArraysDocument42 pagesC++ ArraysabcNo ratings yet
- Data Structure Lab - MCA16-LDocument57 pagesData Structure Lab - MCA16-Lapi-3732063No ratings yet
- Topological SortingDocument8 pagesTopological SortingGeorge fernandez.INo ratings yet
- B Tree TutorialDocument16 pagesB Tree Tutorialharshilsurti91% (11)
- Linked List: Data Structure & AlgorithmsDocument42 pagesLinked List: Data Structure & Algorithmsapi-394738731No ratings yet
- Activity #3Document5 pagesActivity #3joyce ramirezNo ratings yet
- 8 Bit Microprocessor: Mayank Bhatnagar Vaibhav Mahimkar Dominic AlphonseDocument25 pages8 Bit Microprocessor: Mayank Bhatnagar Vaibhav Mahimkar Dominic Alphonsekartish8999No ratings yet
- Data Structures 2 Marks and 16 Marks Question Bank With AnswersDocument27 pagesData Structures 2 Marks and 16 Marks Question Bank With Answersrmeenakshi67% (3)
- MCQS - Mid CS302 Solved PDFDocument19 pagesMCQS - Mid CS302 Solved PDFattiqueNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Basics of Data StructuresDocument40 pages1.1 Basics of Data StructuresMugi PawarNo ratings yet
- Java Programming: PolymorphismDocument30 pagesJava Programming: PolymorphismNics BalanayNo ratings yet
- Intro - To - Data Structure - Lec - 1Document29 pagesIntro - To - Data Structure - Lec - 1Xafran KhanNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Algorithms (DAA) NotesDocument169 pagesDesign and Analysis of Algorithms (DAA) Notesvinod.shringi7870No ratings yet
- C Operators PDFDocument5 pagesC Operators PDFAshutosh KumarNo ratings yet
- DSP Lab - 15ecl57 Part - IDocument37 pagesDSP Lab - 15ecl57 Part - Ivsuresha25% (4)
- Sap 1Document21 pagesSap 1Neeru ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Paging and SegmentationDocument27 pagesPaging and SegmentationRajesh Leo100% (1)
- AVL TreeDocument36 pagesAVL TreesalithakkNo ratings yet
- C Programming Nov 2012Document4 pagesC Programming Nov 2012harisummath5195No ratings yet
- Lecture 11 12 - DS - Linked ListDocument38 pagesLecture 11 12 - DS - Linked ListMp Inayat Ullah25% (8)
- Data Structure Lab ManualDocument174 pagesData Structure Lab Manualh_mech100% (1)
- 12 Computer Science Notes CH07 Boolean AlgebraDocument12 pages12 Computer Science Notes CH07 Boolean AlgebraRohan KashikarNo ratings yet
- Data Structures Algorithms Multiple Choice Questions MCQsDocument16 pagesData Structures Algorithms Multiple Choice Questions MCQssibanandarmsNo ratings yet
- RecursionDocument38 pagesRecursionanjugaduNo ratings yet
- Python ProgramsDocument6 pagesPython ProgramsdsreNo ratings yet
- Fermat and Euler Ts TheoremsDocument14 pagesFermat and Euler Ts TheoremsSurendra ReddyNo ratings yet
- SORTINGDocument46 pagesSORTINGKhushbu BansalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2-Variables, Data Types and Arithmetic ExpressionsDocument35 pagesLecture 2-Variables, Data Types and Arithmetic ExpressionsthienNo ratings yet
- Course Syllabus Differential EquationsDocument6 pagesCourse Syllabus Differential EquationsLysa DeeNo ratings yet
- Sapmple Algorithms & Flow ChartDocument20 pagesSapmple Algorithms & Flow ChartAlicia Juarez83% (18)
- C Lab ManualDocument40 pagesC Lab ManualArnab RoyNo ratings yet
- List of Programs For Class 12 Practical ExamDocument6 pagesList of Programs For Class 12 Practical ExamdivyabahlsrNo ratings yet
- Pointers in CDocument8 pagesPointers in CDhanasekar SethupathiNo ratings yet
- File Handling in C LanguageDocument5 pagesFile Handling in C Languagesudhakar kethanaNo ratings yet
- Round Robin Algorithm With ExamplesDocument6 pagesRound Robin Algorithm With ExamplesSikandar Javid100% (1)
- List of Programs For Class XI - 2012Document2 pagesList of Programs For Class XI - 2012Niti Arora80% (5)
- C Important Questions PDFDocument9 pagesC Important Questions PDFPradeep Kumar Reddy Reddy100% (2)
- Computer Networks Notes (17CS52) PDFDocument174 pagesComputer Networks Notes (17CS52) PDFKeerthiNo ratings yet
- Data Structures Viva QuestionsDocument8 pagesData Structures Viva QuestionslokiblazerNo ratings yet
- Introduction To OOPS and C++Document48 pagesIntroduction To OOPS and C++Pooja Anjali100% (1)
- Daa QB 1 PDFDocument24 pagesDaa QB 1 PDFSruthy SasiNo ratings yet
- C If Else StatementDocument11 pagesC If Else StatementKiran KalyaniNo ratings yet
- Insertion Merge SortDocument25 pagesInsertion Merge Sortapi-3825915100% (2)
- Memory ManagementDocument33 pagesMemory ManagementlalithaNo ratings yet
- DBMS Basic ConceptsDocument29 pagesDBMS Basic Conceptsraspberry piNo ratings yet
- C Questions - Collection 2Document147 pagesC Questions - Collection 2Praveen Manohar100% (1)
- 437 33 Powerpoint-Slides Chapter-4-Functions Ch4Document23 pages437 33 Powerpoint-Slides Chapter-4-Functions Ch4Geethaa MohanNo ratings yet
- TreesDocument55 pagesTreesShridhar DoddamaniNo ratings yet
- Tree: A Non Linear Data StructureDocument22 pagesTree: A Non Linear Data StructureMd. Zubaer HossainNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document22 pagesUnit 3Rohan AjeeNo ratings yet
- Data Structure Lecture 7 TreeDocument49 pagesData Structure Lecture 7 TreeSweetMainaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 16,17,18 TreesDocument73 pagesLecture 16,17,18 Treesaliyaraza1No ratings yet
- UE20EC352-Machine Learning & Applications Unit 3 - Non Parametric Supervised LearningDocument117 pagesUE20EC352-Machine Learning & Applications Unit 3 - Non Parametric Supervised LearningSai Satya Krishna PathuriNo ratings yet
- Memory Dump Analysis Anthology (Dmitry Vostokov)Document523 pagesMemory Dump Analysis Anthology (Dmitry Vostokov)jaouadkaoukabiNo ratings yet
- Chapter ThreeDocument37 pagesChapter ThreeBethelhem YetwaleNo ratings yet
- Demo AHPDocument83 pagesDemo AHPMohamad Ikhsan NurullohNo ratings yet
- Mips Practice QuestionsDocument5 pagesMips Practice QuestionsManzar AliNo ratings yet
- What Will Be The Output of This Program?: #IncludeDocument4 pagesWhat Will Be The Output of This Program?: #IncludeNoor Ul AminNo ratings yet
- Marco's Delphi Books Essential Pascal - Web Site Essential Pascal - Local IndexDocument89 pagesMarco's Delphi Books Essential Pascal - Web Site Essential Pascal - Local IndexWanderlei BorgesNo ratings yet
- TypeScript InterfacesDocument1 pageTypeScript InterfacesEric LeNo ratings yet
- "The Course That Gives CMU Its Zip!": TopicsDocument31 pages"The Course That Gives CMU Its Zip!": Topicssanjay20207No ratings yet
- MMW Exercise Set 6.4Document10 pagesMMW Exercise Set 6.4Cpa100% (2)
- MPMC SyllabusDocument2 pagesMPMC SyllabusKANCHARLAPALLI VENKATESH,CSE(19-23) Vel Tech, ChennaiNo ratings yet
- Design PatternDocument4 pagesDesign PatternAsmaaNo ratings yet
- C Questions: 1. Void Main (Int Const P 5 Printf ("%D",++ ( P) ) )Document64 pagesC Questions: 1. Void Main (Int Const P 5 Printf ("%D",++ ( P) ) )ArjunRampalNo ratings yet
- ILE Concepts (For The Impatient RPG Programmer)Document21 pagesILE Concepts (For The Impatient RPG Programmer)Reynold GalamitonNo ratings yet
- LT08Document5 pagesLT08Jiya AliNo ratings yet
- CS502 Solved Subjective For Final TermDocument19 pagesCS502 Solved Subjective For Final TermFATIMA AMJADNo ratings yet
- Java Essential Practice Set 2Document21 pagesJava Essential Practice Set 2Nipoorva YadavNo ratings yet
- Sample Work Professional ResumeDocument1 pageSample Work Professional ResumeRai Nazer Hussain KharlNo ratings yet
- 1988 23erdosDocument4 pages1988 23erdosvahidmesic45No ratings yet
- ELEN 2020 Basics of CPlusPlus Lecture 2Document49 pagesELEN 2020 Basics of CPlusPlus Lecture 2INFO NERDNo ratings yet
- Hundred Thousand. That Number Has A New Name: One Lakh.: Grade 4Document113 pagesHundred Thousand. That Number Has A New Name: One Lakh.: Grade 4subrato chakravorty100% (1)
- MKSAP For Students 5 PDFDocument324 pagesMKSAP For Students 5 PDFChad Sanford100% (14)
- Dr. A.P.J. Abdul Kalam Technical University: ODD Semester 2021-22 Examination Admit CardDocument21 pagesDr. A.P.J. Abdul Kalam Technical University: ODD Semester 2021-22 Examination Admit CardSAURAV CHAUDHARYNo ratings yet
- Module 2 DaaDocument34 pagesModule 2 Daambucse a9No ratings yet
- Python BooksDocument3 pagesPython BooksPhantom BlackNo ratings yet
- (CPP) Chapter 2 Assessment: No Due DateDocument29 pages(CPP) Chapter 2 Assessment: No Due Dateaj yansonNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document41 pagesAssignment 1Sai BharathNo ratings yet
- Neal Wu-000000000088b044Document11 pagesNeal Wu-000000000088b044mushagraNo ratings yet
- Diagrammatic Presentation of Data: Bar Diagrams and Pie DiagramsDocument7 pagesDiagrammatic Presentation of Data: Bar Diagrams and Pie DiagramsKunikaNo ratings yet
- ConfigurationDocument118 pagesConfigurationTheCodeTime TimeNo ratings yet
- Fusion Strategy: How Real-Time Data and AI Will Power the Industrial FutureFrom EverandFusion Strategy: How Real-Time Data and AI Will Power the Industrial FutureNo ratings yet
- Concise Guide to OTN optical transport networksFrom EverandConcise Guide to OTN optical transport networksRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- AWS Certified Solutions Architect Study Guide: Associate SAA-C02 ExamFrom EverandAWS Certified Solutions Architect Study Guide: Associate SAA-C02 ExamNo ratings yet
- Grokking Algorithms: An illustrated guide for programmers and other curious peopleFrom EverandGrokking Algorithms: An illustrated guide for programmers and other curious peopleRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (16)
- Dark Data: Why What You Don’t Know MattersFrom EverandDark Data: Why What You Don’t Know MattersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Microsoft Certified Azure Fundamentals Study Guide: Exam AZ-900From EverandMicrosoft Certified Azure Fundamentals Study Guide: Exam AZ-900No ratings yet
- Hacking Network Protocols: Complete Guide about Hacking, Scripting and Security of Computer Systems and Networks.From EverandHacking Network Protocols: Complete Guide about Hacking, Scripting and Security of Computer Systems and Networks.Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Set Up Your Own IPsec VPN, OpenVPN and WireGuard Server: Build Your Own VPNFrom EverandSet Up Your Own IPsec VPN, OpenVPN and WireGuard Server: Build Your Own VPNRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Compete Ccna 200-301 Study Guide: Network Engineering EditionFrom EverandThe Compete Ccna 200-301 Study Guide: Network Engineering EditionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Blockchain Basics: A Non-Technical Introduction in 25 StepsFrom EverandBlockchain Basics: A Non-Technical Introduction in 25 StepsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (24)
- Microsoft Azure Infrastructure Services for Architects: Designing Cloud SolutionsFrom EverandMicrosoft Azure Infrastructure Services for Architects: Designing Cloud SolutionsNo ratings yet
- Azure Networking: Command Line Mastery From Beginner To ArchitectFrom EverandAzure Networking: Command Line Mastery From Beginner To ArchitectNo ratings yet
- Starting Database Administration: Oracle DBAFrom EverandStarting Database Administration: Oracle DBARating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- PHP BLUEPRINT: An Essential Beginners Guide to Learn the Realms of PHP From A-ZFrom EverandPHP BLUEPRINT: An Essential Beginners Guide to Learn the Realms of PHP From A-ZNo ratings yet
- Optimizing DAX: Improving DAX performance in Microsoft Power BI and Analysis ServicesFrom EverandOptimizing DAX: Improving DAX performance in Microsoft Power BI and Analysis ServicesNo ratings yet
- THE STEP BY STEP GUIDE FOR SUCCESSFUL IMPLEMENTATION OF DATA LAKE-LAKEHOUSE-DATA WAREHOUSE: "THE STEP BY STEP GUIDE FOR SUCCESSFUL IMPLEMENTATION OF DATA LAKE-LAKEHOUSE-DATA WAREHOUSE"From EverandTHE STEP BY STEP GUIDE FOR SUCCESSFUL IMPLEMENTATION OF DATA LAKE-LAKEHOUSE-DATA WAREHOUSE: "THE STEP BY STEP GUIDE FOR SUCCESSFUL IMPLEMENTATION OF DATA LAKE-LAKEHOUSE-DATA WAREHOUSE"Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Business Intelligence Strategy and Big Data Analytics: A General Management PerspectiveFrom EverandBusiness Intelligence Strategy and Big Data Analytics: A General Management PerspectiveRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Computer Systems and Networking Guide: A Complete Guide to the Basic Concepts in Computer Systems, Networking, IP Subnetting and Network SecurityFrom EverandComputer Systems and Networking Guide: A Complete Guide to the Basic Concepts in Computer Systems, Networking, IP Subnetting and Network SecurityRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (13)