Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter14 PDF
Uploaded by
Jen JenOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter14 PDF
Uploaded by
Jen JenCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 14
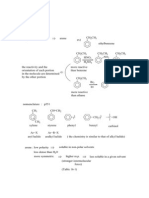
Br Bensene ; C 6H6 C6H5Y 1 isomer Br Br Br
C6H4XY 3 isomer
Hhydrogenation, Hcomb for Benzene are lower than expected (~ 36 kcal/mole) Fig 14.1
substitution rxn rather than addition rxn (Table on p497)
C C ; 1.34 A C C in CH3CH3 ; 1.53 A in CH3CH=CH 2 ; 1.50 A in CH2=CHCH=CH 2 ; 1.48 A all C C in benzene ; 1.39 A resonance energy = 36 kcal/mol hybrid of &
aromatic properties sp2 sp2 bond sp2 s bond H
substitution rather than addition to retain the ring system
6 eletrons are delocalized.
electrons are loosely held
electrophilic substitution
aromatic character ? experimentally
a high degree of unsaturation electrophilic sybstitution rxn insted of addition rxn. low Hhydrogenation , low Hcomb cyclic, flat.
theorerically
cyclic clouds of delocalized p electrons above and below the molecular plane (4n + 2) electrons 4n + 2 rule or Huckel rule ex) benzene 6 electrons (aromatic sextet)
II
III III & IV have unsually high stability.
IV
VI
p ka = 15
p ka = 45
Br
+
behave like R Br
m.p.
200 C
Fe
electrophilic substitution rxn
water soluble insoluble in nonpolar solvent + AgNO3(aq)
AgBr
108
128.5
a small deviation from 120o (a small angle strain)
good overlap of p orbitals How about 2, 10, 14 ... electrons ? not as stable as bezene due to angle strain or poor overap of p orbitals but more stable than their relatives.
aromaticity X NO2 CH3 NH2 OH
halobenzene
nitrobenzene
toulene
aniline
phenol
COOH
SO3H
Br
ortho ; o-dibromobenzene metha ; m-dibromobenzene para ; p-dibromobenzene Br
benzoic acid CH3 O2N
benzenesulfonic acid
NO2
2,6-dinitrotoluene
Polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbon
8 7 6 5
2 3
anthracene phenanthrene
naphthalene
electrophilic substitution rather than addition rxn Hcomb : 61 kcal lower, cyclic, flat 6 electrons 2 a pair is shared 10 electrons
diamond : polycyclic aliphatic graphite : planar (CC : 1.42 A , layers : 3.4 A , lubricant) C60 (buckminster)fullerene : 20 6-membered rings + 12 5-membered rings Quantitative elemental analysis for N ; Dumas method (N) CuO Cu N2 OH
Kjeldahl method
(N)
conc. H2SO4 H2O2 or HNO3
(NH4)2SO4
NH3
for S ;
Carius method
(S)
SO4
BaSO4
You might also like
- Chapter18 PDFDocument11 pagesChapter18 PDFJen JenNo ratings yet
- Chapter17 PDFDocument12 pagesChapter17 PDFJen JenNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem Note13Document9 pagesGen Chem Note13Jen JenNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem Note9Document12 pagesGen Chem Note9Jen JenNo ratings yet
- Chapter16 PDFDocument9 pagesChapter16 PDFJen JenNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem Note2Document8 pagesGen Chem Note2Jen JenNo ratings yet
- Chapter15 PDFDocument8 pagesChapter15 PDFJen JenNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem Note11Document10 pagesGen Chem Note11Jen JenNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem Note5Document11 pagesGen Chem Note5Jen JenNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem Note1Document6 pagesGen Chem Note1Jen JenNo ratings yet
- General Guide From ADSASDocument44 pagesGeneral Guide From ADSASJen JenNo ratings yet
- Pre-Dental Dental HygieneDocument6 pagesPre-Dental Dental HygieneJen JenNo ratings yet
- F 2004Document10 pagesF 2004Jen JenNo ratings yet
- Resume SamplesDocument6 pagesResume SamplesBobby100% (8)
- Chapter 01Document4 pagesChapter 01Jen JenNo ratings yet
- General Guide From ADSASDocument44 pagesGeneral Guide From ADSASJen JenNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)