Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Risk for Infection Nursing Care Plan
Uploaded by
Mariquita BuenafeOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Risk for Infection Nursing Care Plan
Uploaded by
Mariquita BuenafeCopyright:
Available Formats
VI.
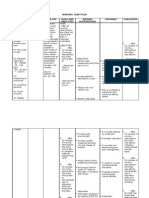
NURSING MANAGEMENT Nursing Care Plan Problem #1: Risk for Infection
Cues S: O: pt. may manifest: > Invasive procedures (amniocentesis or intrauterine blood transfusion >Insufficient knowledge to avoid exposure to pathogen > inadequate secondary defenses (e.g., decreased hemoglobin, leukopenia, suppressed inflammatory response); > rupture of amniotic membranes
Nursing Diagnosis Risk for infection r/t impaired primary defense.
Scientific Explanation The patient is at risk of acquiring infection due to the break in the continuity of the first line defense which is the skin. The patient shall have undergone amniocentesis or intrauterine blood transfusion thus there is an incision and suture made in the abdomen. If there is a breakage in the skin, the pathogens will easily invade the bodys system thus increasing risk for infection
Objectives
Nursing Interventions
Rationale
Evaluation
Monitor v/s and After 1 hour of assess patients nursing interventions, the condition patient will Observe and demonstrate report signs of techniques in infection such as reducing risk of redness, warmth, having infection discharge, and increased body temperature. Stress the importance of proper hand washing Strict compliance to hospital control, sterilization, and aseptic policies
For baseline data
Were the vital signs stable?
With the onset of infection the immune system is activated and signs of infection appear.
Are there any changes skin color discolorations and body temperature?
A first line defense against nosocomial infection or cross contamination To establish mechanism to prevent occurrence of infection
Did the client understand the handwashing technique properly?? Is SOP for hospital sterilization properly monitored? Are there any side effects to the antibiotic treatment? Did the patient follow the prescribed medications?
Tell patient to comply to antibiotic therapy as prophylaxis Monitor medication regimen
To prevent the occurrence of infection
To determine effectiveness of therapy
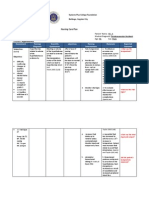
Problem #2: Risk for Fluid Volume Deficit related to Phototherapy
Cues
Nursing Diagnosis Risk for fluid volume deficit related to phototherapy
Scientific Explanation Phototherapy enhances the excretion of unconjugated bilirubin through the bowel.
Objectives
Nursing Interventions
> Initiate early feedings and offer feedings ever 2-3 hours
Rationale
Evaluation
OBJECTIVE: Clinical jaundice evident within 24 hour of birth
The infant will exhibit no signs of dehydration, clear amber urine output of 1-3 mL/kg/hr, and will display appropriate weight gain.
> To increase intestinal motility and promote the excretion of unconjugated bilirubin through the clearance of stools and to decrease the potential for dehydration
>Was early feeding initiated?
> Monitor urine specific gravity
> Urine specific gravity can be an indicator of dehydration. Dehydration and fluid volume deficit will show an elevation in the urine specific gravity > Additional fluids will help compensate for the increased water that is lost through the skin and in the stools
>What was the urines specific gravity?
>Administer fluid intake that is 25% above normal requirements
>Was fluid loss compensated?
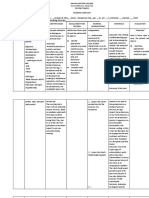
>Were the
> Assess for signs of dehydrations such as poor skin turgor, depressed fontanels, sunken eyes, decreased urine output, weight loss, and changes in electrolytes > Monitor daily weight.
> Phototherapy treatment may cause liquid stools and increased insensible water loss, which increases risk of dehydration.
fontanels sunken? What was the skin turgor?
>Increased fluid excretion in the stools and a decrease in fluid intake may put the newborn at risk for weight loss. Daily weights can provide accurate determination fluid intake and insensible water loss that is caused by phototherapy
>Was there an increase on the daily weight?
> Assess quantity and characteristics of each stool.
> Loose stools indicate fluid loss which may lead to a fluid volume deficit. With an increase in stools per day, dehydration is possible.
>What was the characteristic of the stool?
You might also like
- NCP RHDocument3 pagesNCP RHKirstie Durano Goc-ong0% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan AbortionDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan AbortionJane Casiquin100% (1)
- NCP: Premature Dilation of The CervixDocument6 pagesNCP: Premature Dilation of The CervixJavie80% (5)
- Nursing Care Plan PrenatalDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan PrenatalKim Galamgam100% (2)
- HyperbilirubinemiaDocument10 pagesHyperbilirubinemiachiboogs456100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan Abruptio PlacentaeDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Abruptio PlacentaeWann WannNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care With EclampsiaDocument40 pagesNursing Care With EclampsiaNadia DesyerianNo ratings yet
- Precipitous Labor/Delivery or Unplanned/Out-of-Hospital DeliveryDocument7 pagesPrecipitous Labor/Delivery or Unplanned/Out-of-Hospital DeliveryLei Ortega100% (1)
- Roxipan drug studyDocument4 pagesRoxipan drug studyIzza DeloriaNo ratings yet
- Health Teaching PlanDocument11 pagesHealth Teaching PlanVic Intia Paa100% (1)
- NCP-Risk For InfectionDocument2 pagesNCP-Risk For InfectionJea Joel Mendoza100% (1)
- Managing Pain During Stage II LaborDocument1 pageManaging Pain During Stage II LaborIche Dela Cruz100% (1)
- Diabetes Mellitus (DM) 2Document1 pageDiabetes Mellitus (DM) 2Bheru LalNo ratings yet
- CA - Amniotic Fluid EmbolismDocument13 pagesCA - Amniotic Fluid EmbolismRodelen Maraño100% (2)
- Nursing Diagnosis For Pediatrics Gastroenteritis 1Document2 pagesNursing Diagnosis For Pediatrics Gastroenteritis 1densu4u100% (4)
- Care Plan Redo For NeonateDocument2 pagesCare Plan Redo For NeonateIris Lopez100% (6)
- Ineffective Breast FeedingDocument3 pagesIneffective Breast FeedingNikka JunioNo ratings yet
- SDL1 NCP Case2Document3 pagesSDL1 NCP Case2Alec AnonNo ratings yet
- Subjective: Short Term Goal: Independent: Short Term EvaluationDocument2 pagesSubjective: Short Term Goal: Independent: Short Term EvaluationKyla Castro100% (1)
- Subjective: Goal: Dependent: Dependent:: Assessment Diagnosis Plan Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesSubjective: Goal: Dependent: Dependent:: Assessment Diagnosis Plan Intervention Rationale EvaluationTrisha Cayabyab100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For Pregnancy Induced HypertensionDocument9 pagesNursing Care Plan For Pregnancy Induced HypertensionMurugham DineshNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Acute Pain ManagementDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan for Acute Pain ManagementSheene Lysethea Sioteco AguilosNo ratings yet
- Preterm Infant Nursing Care PlanDocument19 pagesPreterm Infant Nursing Care Planysamariano100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan Abrubtio PlacentaDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Abrubtio PlacentaLei Ortega0% (1)
- Newborn Careplan 9-15-2011Document17 pagesNewborn Careplan 9-15-2011Brittany Wood100% (1)
- NCP SepsisDocument6 pagesNCP SepsisgopscharanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Goals/ Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument20 pagesNursing Diagnosis Rationale Goals/ Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationElaine Grace Timbol-Babasa100% (1)
- NCP For FT, SGADocument7 pagesNCP For FT, SGAJule Santoya80% (5)
- Discharge PlanningDocument3 pagesDischarge PlanningAlex Marie100% (2)
- Pre Eclampsia Nursing Care Plan by Maria Amabelles SorianoDocument39 pagesPre Eclampsia Nursing Care Plan by Maria Amabelles SorianoLei Santillan0% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan Gestational DiabetesDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan Gestational DiabetesDenise Garcia Molina100% (1)
- Abruptio Placenta NCPDocument2 pagesAbruptio Placenta NCPjohncarlo ramos100% (1)
- College of Nursing NURSING Care PlanDocument3 pagesCollege of Nursing NURSING Care PlanToyour EternityNo ratings yet
- Date Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Basis Goal of Care Nutsing Interventi ON Rationale EvaluationDocument5 pagesDate Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Basis Goal of Care Nutsing Interventi ON Rationale EvaluationNathalie kate petallarNo ratings yet
- Generic Name Brand Name Dosage Indications Mechanisms of Action Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument10 pagesGeneric Name Brand Name Dosage Indications Mechanisms of Action Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesJennalyn CasapaoNo ratings yet
- DystociaDocument31 pagesDystociamarsan120% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For Postpartum HemorrhageDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Postpartum HemorrhageDianne Mae100% (1)
- Labor Nursing Care Plan 1Document4 pagesLabor Nursing Care Plan 1Anna Mae DollenteNo ratings yet
- New Born NCPDocument8 pagesNew Born NCPCarl Vincent Marrion Rejuso100% (1)
- Uterine AtonyDocument3 pagesUterine AtonyArsheina Paradji100% (1)
- Hyperbilirubinemia Case PresentationDocument25 pagesHyperbilirubinemia Case PresentationEricka B. Banaszczuk100% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan: IndependentDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: IndependentAdhaNo ratings yet
- NCP Altered Skin ColorDocument2 pagesNCP Altered Skin ColorJessa Lyn100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: Subjective Data: Short Term IndependentDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan: Subjective Data: Short Term IndependentIrish May SignioNo ratings yet
- Case Pres With NCP at PNPDocument33 pagesCase Pres With NCP at PNPsitaw80% (10)
- Prenatal NCPDocument3 pagesPrenatal NCPErmi Tañio100% (2)
- Ectopic and Abortion NCPDocument6 pagesEctopic and Abortion NCPElizabeth Quiñones100% (1)
- ABORTIONDocument10 pagesABORTIONSivi Joseph100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan Altered Urinary Elimination Related To Perineal Edema and Decreased Bladder Tone From Fetal Head Pressure During Birth.Document2 pagesNursing Care Plan Altered Urinary Elimination Related To Perineal Edema and Decreased Bladder Tone From Fetal Head Pressure During Birth.Angel Angeles Pitogo Jr.100% (1)
- NCP Pain (H Mole)Document3 pagesNCP Pain (H Mole)Khat Quimen Mayo86% (7)
- NCP Gastric CancerDocument7 pagesNCP Gastric CancerAnonymous XvwKtnSrMR100% (4)
- Institute of Health SciencesDocument9 pagesInstitute of Health SciencesFlorygene Kris DisagonNo ratings yet
- OB Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesOB Nursing Care PlanChristine V. Fernandez100% (3)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageNursing Care PlanSHeenah Qo100% (1)
- Preventing Infection Through EducationDocument3 pagesPreventing Infection Through EducationGian Arlo Hilario Castro100% (6)
- Risk For DehydrationDocument2 pagesRisk For DehydrationJahne CM80% (5)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument23 pagesNursing Care PlanLorielle HernandezNo ratings yet
- Actual Nursing Care Plan 2Document16 pagesActual Nursing Care Plan 2Alyanna Evangelista100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan For Appendicitis Post OperativeDocument17 pagesNursing Care Plan For Appendicitis Post OperativeOkaRizukiramanNo ratings yet
- "May Mga Sugat Ako.": As Verbalized by The PatientDocument6 pages"May Mga Sugat Ako.": As Verbalized by The Patientedifier_moonNo ratings yet
- Acute PancreatitisDocument20 pagesAcute PancreatitisMariquita BuenafeNo ratings yet
- Journal in PediatricsDocument7 pagesJournal in PediatricsMariquita BuenafeNo ratings yet
- Pedia Drugs ImagesDocument1 pagePedia Drugs ImagesMariquita BuenafeNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Imbalance Care PlanDocument7 pagesNutrition Imbalance Care PlanMariquita BuenafeNo ratings yet
- Effects of Aging in The Cardiovascular SystemDocument6 pagesEffects of Aging in The Cardiovascular SystemMariquita BuenafeNo ratings yet
- Hemolytic Disease of The Fetus and Newborn JournalDocument10 pagesHemolytic Disease of The Fetus and Newborn JournalMariquita BuenafeNo ratings yet
- CHN - Drug StudyDocument1 pageCHN - Drug StudyMariquita BuenafeNo ratings yet
- UrinalysisDocument5 pagesUrinalysisMariquita BuenafeNo ratings yet
- RitodrineDocument4 pagesRitodrineMariquita BuenafeNo ratings yet
- DR DrugsDocument2 pagesDR DrugsMariquita BuenafeNo ratings yet
- DR DrugsDocument2 pagesDR DrugsMariquita BuenafeNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Erythroblastosis Fetalis - RH IsoimmunizationDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Erythroblastosis Fetalis - RH IsoimmunizationRalph Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Journal in Anemia and BTDocument19 pagesJournal in Anemia and BTMariquita BuenafeNo ratings yet
- Systems Plus College Foundation Balibago, Angeles City College Of Nursing Drug Study Student Nurse: Buenafe, Ma. Cresencia S. Yr. /Level: BSN III Date: September 25, 2012Document4 pagesSystems Plus College Foundation Balibago, Angeles City College Of Nursing Drug Study Student Nurse: Buenafe, Ma. Cresencia S. Yr. /Level: BSN III Date: September 25, 2012Mariquita BuenafeNo ratings yet
- Focus ChartingDocument3 pagesFocus ChartingMan GatuankoNo ratings yet
- NCP CvaDocument4 pagesNCP CvaMariquita BuenafeNo ratings yet
- CardiomegalyDocument91 pagesCardiomegalyMariquita Buenafe100% (1)
- Coronary Artery DiseaseDocument38 pagesCoronary Artery DiseaseMariquita BuenafeNo ratings yet
- Cardio Drug StudyDocument8 pagesCardio Drug StudyMariquita BuenafeNo ratings yet
- Cardio Drug StudyDocument8 pagesCardio Drug StudyMariquita BuenafeNo ratings yet
- DengueDocument5 pagesDengueMariquita BuenafeNo ratings yet
- Cardio Drug StudyDocument8 pagesCardio Drug StudyMariquita BuenafeNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Nursing FinalDocument35 pagesPediatric Nursing FinalMariquita BuenafeNo ratings yet
- NCP Cholecystectomy RevisedDocument7 pagesNCP Cholecystectomy RevisedMariquita Buenafe100% (4)
- PromDocument14 pagesPromMariquita BuenafeNo ratings yet
- Coronary Artery DiseaseDocument9 pagesCoronary Artery DiseaseMariquita Buenafe100% (1)
- Homoeopathic Remedies For Irritable Bowel Syndrome - Dr. Ks. Gopi - Pulse - LinkedinDocument7 pagesHomoeopathic Remedies For Irritable Bowel Syndrome - Dr. Ks. Gopi - Pulse - LinkedinsubratNo ratings yet
- "Nagtatae Siya 4 Days Na" As Verbalized by The Mother. Inatake of Causative Agents Irritation of The Stomach Inflammation of The Stomach Increase GI Motility DiarrrheaDocument4 pages"Nagtatae Siya 4 Days Na" As Verbalized by The Mother. Inatake of Causative Agents Irritation of The Stomach Inflammation of The Stomach Increase GI Motility DiarrrheaMelissa MhelNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Tests A. Endoscopy: Nursing ConsiderationsDocument3 pagesDiagnostic Tests A. Endoscopy: Nursing ConsiderationsMae GabrielNo ratings yet
- Use of Oral Gentamicin, Metronidazole, and Cholestyramine in The Treatment of Severe Persistent Diarrhea in InfantsDocument7 pagesUse of Oral Gentamicin, Metronidazole, and Cholestyramine in The Treatment of Severe Persistent Diarrhea in InfantsAriNo ratings yet
- NCP & Discharge PlanningDocument12 pagesNCP & Discharge PlanningStephanie Mae Amoylen OdchigueNo ratings yet
- What Is Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) ?Document12 pagesWhat Is Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) ?inhaNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer-ThirdyDocument13 pagesScience Reviewer-ThirdyLee Em Wel100% (1)
- Constipation: Causes, Prevention Tips & Natural RemediesDocument2 pagesConstipation: Causes, Prevention Tips & Natural RemediesPrashant jainNo ratings yet
- Constipation/ - Bian Bi: ConceptionDocument3 pagesConstipation/ - Bian Bi: Conceptionnaeem_k7No ratings yet
- Understanding Stool Chemistry TestsDocument10 pagesUnderstanding Stool Chemistry TestsbnmjgcNo ratings yet
- Irritable Bowel SyndromeDocument8 pagesIrritable Bowel SyndromeEvelyn Tribole, MS, RD0% (1)
- Parrish October 14Document9 pagesParrish October 14Lakhan AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Concept MapDocument12 pagesPediatric Concept Mapapi-352157080No ratings yet
- Client: Care Plan Initiated By: DateDocument3 pagesClient: Care Plan Initiated By: DateSIMON KYLE BAKIL DICHUASIDONo ratings yet
- Diarrhea, Risk For Fluid Volume DeficitDocument6 pagesDiarrhea, Risk For Fluid Volume DeficitEfzell Dean BangilanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care for Gastroenteritis PatientDocument10 pagesNursing Care for Gastroenteritis PatientJoia De LeonNo ratings yet
- G. Fecal Occult Blood TestDocument4 pagesG. Fecal Occult Blood TestKasandra Dawn Moquia BerisoNo ratings yet
- Homeopathy Medicine For All DiseaseDocument66 pagesHomeopathy Medicine For All Diseasesharad7996% (75)
- Nursing Diagnosis ListDocument17 pagesNursing Diagnosis ListShelby SheppardNo ratings yet
- Synoptic Materia Medica 1 Frans VermulenDocument527 pagesSynoptic Materia Medica 1 Frans VermulenCSaludSanJuanSalinas100% (12)
- Diarrhea PPTDocument82 pagesDiarrhea PPTIshwar HavaragiNo ratings yet
- Elimination Pattern (Fecal) MSPDocument20 pagesElimination Pattern (Fecal) MSPMuhammadNo ratings yet
- Age With Moderate Dehydration New 1Document74 pagesAge With Moderate Dehydration New 1Jhade Relleta100% (1)
- CombinedDocument1 pageCombinedgldiatrNo ratings yet
- Colitis PDFDocument11 pagesColitis PDFicoanamareNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation Ji Castante, Leah SDocument17 pagesCase Presentation Ji Castante, Leah SLeah CastanteNo ratings yet
- Acute Pain RUTH FinalDocument7 pagesAcute Pain RUTH FinalRuthangela GarciaNo ratings yet
- Diseases of GITDocument51 pagesDiseases of GITPavel GaladiucNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Clearing, Precipitating FormulasDocument48 pagesChapter 2 - Clearing, Precipitating FormulasHan ViviencatNo ratings yet
- Fecalysis: Tests on Stool Samples to Diagnose Digestive ConditionsDocument2 pagesFecalysis: Tests on Stool Samples to Diagnose Digestive ConditionsHan SoloNo ratings yet