Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Orthopedic Impairment 2
Uploaded by
api-242024640Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Orthopedic Impairment 2
Uploaded by
api-242024640Copyright:
Available Formats
Oklahoma State Department of Education Special Education Services 405-521-3351 www.ok.
gov/sde/special-education
ORTHOPEDIC IMPAIRMENT
Denition of Orthopedic Impairment under IDEA
Orthopedic impairment means a severe orthopedic impairment that adversely affects a childs educational performance. The term includes impairments caused by congenital anomaly (e.g., clubfoot, absence of some member, etc.), and impairments from other causes (e.g., cerebral palsy, amputations, and fractures or burns that cause contractures). 34 CFR 300.8(c)(8)
FACT SHEET
or extensive paralysis. Spinal cord injuries are most commonly a result of an automobile or other vehicle accident. The characteristics and needs of individuals with spinal cord injuries are often similar to those with cerebral palsy. Multiple Sclerosis is a progressive disorder where the nerve impulses to the muscles are short circuited by scar tissue. Initially mild problems may occur but as the attacks continue, a person may develop a multitude of problems. These include severe visual impairment, speech disorder, loss of bowel and bladder control, and paralysis. Symptoms may regress as remission occurs. Rheumatoid Arthritis causes general fatigue and stiffness and aching of joints. Students who are affected by this may have trouble being in one position for a length of time. Degenerative Diseases are comprised of a number of diseases which affect a persons motor development (ex. Musculoskeletal, Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis, Muscular Dystrophy).
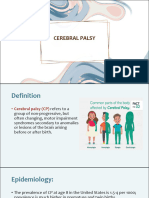
TYPES Cerebral Palsy (CP) affects the largest group of students with Orthopedic Impairments in public schools. It occurs when there is an injury to the brain before, during, or after birth and results in poor motor coordination and unusual motor patterns. There are four main types of cerebral palsy: Spastic: The most common form of CP is when there is too much muscle tone or tightness. An individual with Spastic CP generally has stiff or jerky movements in ones legs, arms, and/or back. Dykinetic: Affects the entire bodily movement of an individual and slow and uncontrollable body movements normally occur. Ataxic: Involves poor coordination, balance, and perception. Mixed: Involves a combination of symptoms from the three types above. Muscular Dystrophy occurs when voluntary muscles progressively weaken and degenerate until they no longer function. The onset of Muscular Dystrophy can occur anytime between the ages of one to adulthood and is believed to be hereditary. Spinal Muscular Atrophy is a disease that affects the spinal cord and may result in progressive degeneration of the motor nerve cells. The severity runs from mild weakness to characteristics similar to muscular dystrophy. Spinal Muscular Atrophy is characterized in general by fatigue and clumsiness. The cause is hereditary and the age of onset is either in infancy or a later time or between the ages of 2 and 17. Spinal Cord Injuries occur when the spinal cord is severely damaged or severed, usually resulting in partial
EVALUATIONS Medical information from a licensed physician, and ARNP, or the parent providing relevant medical ndings of orthopedic conditions, specic syndromes, health problems, and medication is required. An evaluation of motor functioning by a licensed Physical Therapists and/or Occupational Therapist, as appropriate to the needs of the child, must be included. Individual evaluation of the childs specific educational needs and present levels of performance in the general education curriculum should be included. Assistive Technology will be an additional consideration as a special factor for the evaluation process. The effect the childs orthopedic impairment has on his/her present levels of performance in the general education curriculum, academic performance, achievement, or age appropriate activities will be important information for the team to document and consider. Appropriate seating/positioning of the child is of primary consideration for effective screening, evaluation, and instruction.
POSSIBLE CAUSES Being born with or acquire problems with their bones, their joints, and/or their muscles Problems stemming from deformities, diseases, injuries, or surgeries (loss of a limb, bone, or muscle tissue) Possible Signs and Characteristics: Paralysis, unsteady gait, poor muscle control, loss of a limb, etc. (causes limited mobility) Speech production and the expressive language of the child. Difficulty with large motor skills and fine motor skills Limited ability to perform daily living activities Impact on Learning: Is contingent upon the disease, its severity, and individual factors. Can be different from person to person (impact can be mild to severe). Many students with orthopedic impairments have no cognitive, learning, perceptual, language or sensory issues. Individuals with neuromotor impairments have a higher incidence of additional impairments. Some children may have significant limitations to their activity levels that require intensive medical and/ or educational assistance.
Classroom Considerations for Students with Orthopedic Impairments: Seating arrangements to ensure the student is comfortable and able to participate. Encourage participation at all times. Instruction that is focused on development of gross and fine motor skills. Ensuring suitable augmentative communication and other assistive devices. Adequate awareness of the students medical condition and its effect on the student. Specialists or Related Service Providers that may become involved in the students educational team: Physical Therapists (gross motor skills) Occupational Therapists (fine motor skills and daily living skills) Speech-Language Pathologists (develop communication skills) Adaptive Physical Education Teachers (exercise program development) Other Therapists (Massage Therapists, Music Therapists, etc.)
TEACHING TIPS/INSTRUCTIONAL STRATEGIES Always presume competence Be patient Remember that every child has different needs Collaborate with parents and other team members Use Assistive Technology
THIS INFORMATION DEVELOPED FROM THE FOLLOWING RESOURCES: United Cerebral Palsy Associations, Inc. www.ucp.org Project Ideal www.projectidealonline.org/orthopedicimpairments.php Muscular Dystrophy Association www.mdausa.org National Dissemination Center for Children with Disabilities (NICHCY) www.nichcy.org Arthritis Foundation www.arthritis.org
You might also like
- Orthopedic Impairment 2Document2 pagesOrthopedic Impairment 2api-299490997No ratings yet
- 5.children With Physical ImpairmentDocument8 pages5.children With Physical ImpairmentJunadrian GenitoNo ratings yet
- What Is Orthopedic Impairment?Document6 pagesWhat Is Orthopedic Impairment?api-281466418100% (1)
- Group 7 Orthopedic ImpairmentDocument8 pagesGroup 7 Orthopedic ImpairmentCherie MeyNo ratings yet
- Orthopedic ImpairmentsDocument40 pagesOrthopedic Impairmentsapi-281466418100% (1)
- Orthopedic Impairment PDFDocument15 pagesOrthopedic Impairment PDFjoan arreolaNo ratings yet
- Physical Disabilities PresentationDocument58 pagesPhysical Disabilities Presentationapi-271874263No ratings yet
- Difficulty Walking and MovingDocument3 pagesDifficulty Walking and MovingGeorgia Torres95% (19)
- IntroductionDocument5 pagesIntroductionmeowzi floraNo ratings yet
- Physical DisabilityDocument22 pagesPhysical DisabilityLizel DeocarezaNo ratings yet
- Fact Sheet Orthopedic ImpairmentDocument2 pagesFact Sheet Orthopedic Impairmentapi-340604729No ratings yet
- Cerebral PalsyDocument28 pagesCerebral Palsyghofran001997No ratings yet
- 4 Physical Education and Sports For CWSN Xi 23-24Document3 pages4 Physical Education and Sports For CWSN Xi 23-24Shyamasree SenguptaNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Palsy Prep CardDocument4 pagesCerebral Palsy Prep CardBenNo ratings yet
- Physical Disabilities - Understanding Learners with Difficulty in Walking and MovingDocument13 pagesPhysical Disabilities - Understanding Learners with Difficulty in Walking and MovingNj LangurayanNo ratings yet
- Understanding Cerebral PalsyDocument22 pagesUnderstanding Cerebral PalsyJay SorianoNo ratings yet
- GeriatricDocument23 pagesGeriatricggaabbddah23No ratings yet
- Class 11 Chapter-4 Physical Education and Sports For CWSN Session 2022-2023Document5 pagesClass 11 Chapter-4 Physical Education and Sports For CWSN Session 2022-2023MOHAMMAD ASIF 210200No ratings yet
- UNIT I Cerebral PalsyDocument31 pagesUNIT I Cerebral PalsyTharangini GudlapuriNo ratings yet
- Semi-Detailed-Lesson PlanDocument7 pagesSemi-Detailed-Lesson PlanClaudine LeonorasNo ratings yet
- Meeting the Needs of Children with Sensory or Physical DisabilitiesDocument13 pagesMeeting the Needs of Children with Sensory or Physical DisabilitiesMæbēTh CuarterosNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Management For Cerebral PalsyDocument27 pagesNutrition Management For Cerebral PalsyPCMC Dietitians NDDNo ratings yet
- Pediatric PhysiotherapyDocument8 pagesPediatric PhysiotherapyBahar AliNo ratings yet
- Cerebral PalsyDocument12 pagesCerebral PalsyJude AlyousefNo ratings yet
- Challenged Children: Prepared By: Manisha Praharaj Msc. Nursing 1St YearDocument25 pagesChallenged Children: Prepared By: Manisha Praharaj Msc. Nursing 1St YearTulsi DassNo ratings yet
- Physical Dis Health Imp and ADHD Chap 11 Fall 16Document16 pagesPhysical Dis Health Imp and ADHD Chap 11 Fall 16ayaelmeligy651No ratings yet
- Education of The Physically and Health ImpairedDocument47 pagesEducation of The Physically and Health ImpairedadeboboyejoyNo ratings yet
- Physical Disability by FabricationDocument25 pagesPhysical Disability by FabricationALYELA PETERNo ratings yet
- Management of Children With Cerebral PalsyDocument45 pagesManagement of Children With Cerebral PalsyNamakau MuliloNo ratings yet
- Cerebral PalsyDocument10 pagesCerebral Palsyapi-303066042No ratings yet
- Cerebral Palsy Research PaperDocument7 pagesCerebral Palsy Research Paperapi-546518451No ratings yet
- ICF Framework Classifies Functioning, Disability and Health FactorsDocument51 pagesICF Framework Classifies Functioning, Disability and Health FactorsPnn PisharodyNo ratings yet
- Cerebral PalsyDocument3 pagesCerebral Palsykev02No ratings yet
- The Term Psychosocial Refers To An IndividualDocument5 pagesThe Term Psychosocial Refers To An IndividualHistory and EventNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Palsy: DR - Shivani (PT) - PuneDocument25 pagesCerebral Palsy: DR - Shivani (PT) - PuneSahil Sahni100% (4)
- Cerebral Palsy: Recommended ReadingDocument5 pagesCerebral Palsy: Recommended ReadingJoey Ivan CristobalNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Palsy: Ashish Anand Consultant Orthopedic SurgeonDocument82 pagesCerebral Palsy: Ashish Anand Consultant Orthopedic Surgeonidiot12345678901595No ratings yet
- Physica Dis Ability and Health ImpairmentDocument29 pagesPhysica Dis Ability and Health ImpairmentWorkina UrgaNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Palsy Rehabilitation: Birth-Related Brain InjuryDocument13 pagesCerebral Palsy Rehabilitation: Birth-Related Brain InjuryAnuj GargNo ratings yet
- Understanding Cerebral Palsy: Causes, Types, Signs and TreatmentDocument44 pagesUnderstanding Cerebral Palsy: Causes, Types, Signs and Treatmentmichael so100% (2)
- Cerebral Palsy (CP)Document23 pagesCerebral Palsy (CP)Piyu ShindeNo ratings yet
- Cerebral PalsyDocument35 pagesCerebral PalsyEnuga ApplegateNo ratings yet
- Orthopedic ImpairmentDocument35 pagesOrthopedic ImpairmentJohn Rey ComplezaNo ratings yet
- Developmental Coordination DisorderDocument7 pagesDevelopmental Coordination DisorderQina Nugroho, pts.No ratings yet
- Medical Nursing II Term PaperDocument15 pagesMedical Nursing II Term PaperAdaeze DouglasNo ratings yet
- Expert Presentation - Orthopedic ImpairmentDocument24 pagesExpert Presentation - Orthopedic Impairmentapi-361465087No ratings yet
- 24 Physical Disabilities, Health Impairments, and ADHDDocument29 pages24 Physical Disabilities, Health Impairments, and ADHDZeeshan AkhtarNo ratings yet
- JLD 220 - 29 August 2023Document19 pagesJLD 220 - 29 August 2023khlanekelaNo ratings yet
- Physical Disability: - Diseases - Neurological - Dyspraxia - MuscularDocument16 pagesPhysical Disability: - Diseases - Neurological - Dyspraxia - MuscularNur AskinahNo ratings yet
- AutismDocument2 pagesAutismMd. Sherajul HaqueNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1 - Locomotor DisabilityDocument17 pagesUNIT 1 - Locomotor DisabilityAmreen HameedNo ratings yet
- Understanding Learners With Difficulty in Mobility (LDM) : Department of EducationDocument60 pagesUnderstanding Learners With Difficulty in Mobility (LDM) : Department of EducationCherry Bobier100% (1)
- Agenesis of Corpus Callosum (ACC)Document2 pagesAgenesis of Corpus Callosum (ACC)Vicky ConlonNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Palsy Road Map:: What To Expect As Your Child GrowsDocument40 pagesCerebral Palsy Road Map:: What To Expect As Your Child GrowsSergio Curtean100% (1)
- Barrier Free ArchitectureDocument3 pagesBarrier Free ArchitectureAmarjit SahNo ratings yet
- Orthopedic Impairment Definition, Causes, Characteristics & Educational StrategiesDocument4 pagesOrthopedic Impairment Definition, Causes, Characteristics & Educational StrategiesrbsNo ratings yet
- Symptoms, Investigations and Treatment in Eating Disorders: A Quick Reference Guide for All Ed ProfessionalsFrom EverandSymptoms, Investigations and Treatment in Eating Disorders: A Quick Reference Guide for All Ed ProfessionalsNo ratings yet
- Cover Letter - River RidgeDocument1 pageCover Letter - River Ridgeapi-242024640No ratings yet
- Ysn 06Document14 pagesYsn 06api-242024640No ratings yet
- Feb 2015 Resume PDFDocument3 pagesFeb 2015 Resume PDFapi-242024640No ratings yet
- Fs 1Document6 pagesFs 1api-242024640No ratings yet
- Nac Ed Manual FinalDocument258 pagesNac Ed Manual Finalapi-242024640No ratings yet
- Signs Symptoms and Diagnosis of Autism in Children ModifiedDocument28 pagesSigns Symptoms and Diagnosis of Autism in Children Modifiedapi-242024640No ratings yet
- Fs 8Document6 pagesFs 8api-242024640No ratings yet
- Emotionally Disturbed HotsheetDocument3 pagesEmotionally Disturbed Hotsheetapi-242024640100% (1)
- Guidelines For Interacting With PeopleDocument3 pagesGuidelines For Interacting With Peopleapi-242024640No ratings yet
- Fs 5Document7 pagesFs 5api-242024640No ratings yet
- DSM 5 Intellectual Disability Fact SheetDocument2 pagesDSM 5 Intellectual Disability Fact Sheetapi-242024640No ratings yet
- Visual Impairments Including BlindnessDocument7 pagesVisual Impairments Including Blindnessapi-242024640No ratings yet
- DyslexiaDocument1 pageDyslexiaapi-242024640No ratings yet
- Dyslexia Handbook TeacherstrategiesDocument22 pagesDyslexia Handbook Teacherstrategiesapi-242024640No ratings yet
- Documenting Instructional Considerations For The Student With Deaf-BlindnessDocument7 pagesDocumenting Instructional Considerations For The Student With Deaf-Blindnessapi-242024640No ratings yet
- MD 1Document2 pagesMD 1api-242024640No ratings yet
- Visual Impairment and BlindnessDocument4 pagesVisual Impairment and Blindnessapi-242024640No ratings yet
- Ohi 2Document6 pagesOhi 2api-242024640No ratings yet
- HearinglossfactsheetDocument2 pagesHearinglossfactsheetapi-239968581No ratings yet
- Fs 15Document8 pagesFs 15api-238075370No ratings yet
- MD 2Document8 pagesMD 2api-242024640No ratings yet
- PlanforyourchildDocument6 pagesPlanforyourchildapi-242024640No ratings yet
- NIH CancerDocument198 pagesNIH CancerAnonymous KgUtPlkjNo ratings yet
- Home Remedies For UtiDocument5 pagesHome Remedies For UtiShiro KiryuuNo ratings yet
- How To Fill ADR Reporitng Form and Causality AssessmentDocument38 pagesHow To Fill ADR Reporitng Form and Causality AssessmentVishal AryaNo ratings yet
- Alprazolam PoisoningDocument4 pagesAlprazolam PoisoningRahmat AkmalNo ratings yet
- Rajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences Exam Result: PrintDocument1 pageRajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences Exam Result: PrintDani ursNo ratings yet
- Hukm Ophthal Guideline-Latest Edited PDFDocument107 pagesHukm Ophthal Guideline-Latest Edited PDFNur atikahNo ratings yet
- Exam ChecklistDocument13 pagesExam Checklistmahmoud selimNo ratings yet
- IFFCO-TOKIO General Insurance claim formDocument4 pagesIFFCO-TOKIO General Insurance claim formRaju.PalNo ratings yet
- Case HistoryDocument32 pagesCase HistoryHogan ObiNo ratings yet
- Advanced Techniques For Solution Focused CounselingDocument23 pagesAdvanced Techniques For Solution Focused CounselingFrank Smith100% (3)
- Assignment - EugenicsDocument11 pagesAssignment - EugenicsNavneet GillNo ratings yet
- Questions PneumoniaDocument8 pagesQuestions PneumoniaMeliza BancolitaNo ratings yet
- Are Adopted Children As Mentally Healthy As Children Who Stay With Their Birth Parents 2Document4 pagesAre Adopted Children As Mentally Healthy As Children Who Stay With Their Birth Parents 2api-558988793No ratings yet
- Jets Pay Payroll OfferDocument2 pagesJets Pay Payroll OfferMishra SanjayNo ratings yet
- Pet Size o Meter Guinea PigDocument2 pagesPet Size o Meter Guinea PigLiong KimNo ratings yet
- Glycomacropeptide For Nutritional Management of Phenylketonuria: A Randomized, Controlled, Crossover TrialDocument12 pagesGlycomacropeptide For Nutritional Management of Phenylketonuria: A Randomized, Controlled, Crossover Trialjz1397No ratings yet
- CindyDocument4 pagesCindyUsama QayyumNo ratings yet
- EmgnhDocument321 pagesEmgnhJess GoNo ratings yet
- PPE Use, Disposal & Recycling SurveyDocument2 pagesPPE Use, Disposal & Recycling SurveySamantha DomileNo ratings yet
- Health and Safety CultureDocument2 pagesHealth and Safety CultureAbdul WahabNo ratings yet
- HER2 Targeted Therapy For Early and Locally Advanced Breast CancerDocument58 pagesHER2 Targeted Therapy For Early and Locally Advanced Breast Cancerreny hartikasariNo ratings yet
- Irritable Bowel SyndromeDocument22 pagesIrritable Bowel SyndromeMarium NabeelNo ratings yet
- BAHASA INGGRIS CLASSROOM BiranDocument22 pagesBAHASA INGGRIS CLASSROOM BiranBiran Harianto AkbariNo ratings yet
- Kpi SkapsDocument2 pagesKpi SkapsChikwason Sarcozy MwanzaNo ratings yet
- Concept of Stress and Psychological Adaptation To StressDocument12 pagesConcept of Stress and Psychological Adaptation To Stressvaideeswari kumarNo ratings yet
- BSBHRM506 Assessment 1Document9 pagesBSBHRM506 Assessment 1prasannareddy9989No ratings yet
- SAEMA Guidance Documents On Loan WorkingDocument4 pagesSAEMA Guidance Documents On Loan WorkingMohamed MerchantNo ratings yet
- Philips issues urgent field safety notice for ventilator touchscreensDocument3 pagesPhilips issues urgent field safety notice for ventilator touchscreensChris SilerNo ratings yet
- FentanylDocument2 pagesFentanylAdrianne Bazo100% (1)
- Bentonite MSDSDocument3 pagesBentonite MSDSMohammed Ahmed NasherNo ratings yet