Professional Documents
Culture Documents
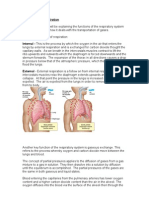
Exercise and Breathing
Uploaded by
bloodythornOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Exercise and Breathing
Uploaded by
bloodythornCopyright:
Available Formats
Exercise and Breathing
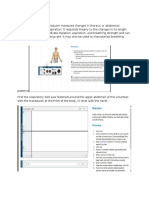
The flow diagram for Task 2 in Assignment One will be very useful at this point. t will help you to understand the following explanations. !ou have already explained how a breathing cycle is established whilst at rest by the "espiratory #entre in the $edulla part of the brain. !ou now need to explain why and how the breathing rate% or ventilation rate% is increased during physical exercise. Both the rate &breaths per minute' and depth &volume' of breathing can be varied. The product of these two is called the ventilation rate (i.e. the volume of air ventilating the lungs each minute) Ventilation rate = breathing rate x tidal volume
Both controlled by the nerves from the respiratory centre The Difference Between Ventilation at Rest and Exercise Breathing rate &breaths*mi n' at rest at exercise -2 -1 Tidal volume &cm+* breath' .// -/// ,entilation rate &cm+*min'
0 /// -1 ///
2hen the body exercises the ventilation rate and depth increases so that) -. Oxygen can diffuse from the air to the blood faster 2. #arbon dioxide can diffuse from the blood to the air faster H ! D E" THE RE"#$R%T R& 'E(TRE RE"# (D T E)ER'$"E*
The process is the same as for heart rate% with the chemoreceptors in the aortic and carotid bodies detecting an increase in respiration i.e. higher carbon dioxide and lower oxygen levels..
Again% the stretch receptors in the muscles give a more rapid indication of muscular activity% allowing an anticipatory increase in breathing rate even before the carbon dioxide concentration in the blood has changed.
You might also like
- Homeostasis Exemplar Lab ReportDocument4 pagesHomeostasis Exemplar Lab Reportthe cornchip executionerNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument19 pagesRespiratory SystemayuNo ratings yet
- King Lear Is A Tragedy by William ShakespeareDocument1 pageKing Lear Is A Tragedy by William ShakespearebloodythornNo ratings yet
- D Physiology of RespirationDocument45 pagesD Physiology of RespirationValluri Mukesh100% (1)
- The Effect of Exercise On Cardiovascular Activity in HumansDocument11 pagesThe Effect of Exercise On Cardiovascular Activity in HumansnbwassamNo ratings yet
- Beethoven Liszt Symphony 3 Piano Music SheetDocument54 pagesBeethoven Liszt Symphony 3 Piano Music SheetPatrickBulawan100% (4)
- How The Frolov Device Works Plus ResultsDocument14 pagesHow The Frolov Device Works Plus ResultsAnonymous hndaj8zCA100% (1)
- BreathingDocument5 pagesBreathingGelyn Lanuza-AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Forum Fisiologi SenamDocument3 pagesForum Fisiologi SenamErwan Sha HabinullahNo ratings yet
- 11 Lung PhysiologyDocument14 pages11 Lung PhysiologyGlen UrbaniNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument4 pagesUntitledRafsan HossainNo ratings yet
- BreathingDocument3 pagesBreathingShara ThamzeerNo ratings yet
- Normal Oxygen Transport: Susanne A ClarkDocument256 pagesNormal Oxygen Transport: Susanne A Clarkghoncheh0% (1)
- Lab 8Document6 pagesLab 8Naz PulatNo ratings yet
- Topic 2.1 Ventilatory System Sport Science IBDocument4 pagesTopic 2.1 Ventilatory System Sport Science IBAntonio MouNo ratings yet
- Circulatory PhysiologyDocument13 pagesCirculatory Physiologykhaled_71111No ratings yet
- Documento RoaDocument63 pagesDocumento RoaalbertwillyNo ratings yet
- ST12P3 Taburnal, Marjorie Mae - PT 4.3 General Biology 2Document3 pagesST12P3 Taburnal, Marjorie Mae - PT 4.3 General Biology 2Marjorie Mae AmodiaNo ratings yet
- Heartrate and ExerciseDocument11 pagesHeartrate and ExerciseJay Queue JonnyNo ratings yet
- PE Lung FunctionDocument15 pagesPE Lung Functionkunal ramcharunNo ratings yet
- Review of Respiratory PhysiologyDocument53 pagesReview of Respiratory PhysiologyMiftahul IfahNo ratings yet
- Evelyn Hone College of Applied Arts and Commerce School of Health and Applied Sciences Pharmacy SectionDocument10 pagesEvelyn Hone College of Applied Arts and Commerce School of Health and Applied Sciences Pharmacy Sectionbill chaiwaNo ratings yet
- Breathing Rate Lab ReportDocument4 pagesBreathing Rate Lab ReportRichard VemeNo ratings yet
- NullDocument3 pagesNullapi-26374520No ratings yet
- Respiratory Responses To Exercise SFDocument24 pagesRespiratory Responses To Exercise SFSaktriawan ArifNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument9 pagesThe Respiratory SystemOlivia HowlettNo ratings yet
- Respiration and BreathingDocument57 pagesRespiration and BreathingHarvagale BlakeNo ratings yet
- An P 2 Lab 4 RespiratoryDocument7 pagesAn P 2 Lab 4 Respiratorymath_mallikarjun_sapNo ratings yet
- Assignment Respiratory During ExerciseDocument3 pagesAssignment Respiratory During Exercisedomhughes1093No ratings yet
- S H S, H: Indhi IGH Chool EbbalDocument23 pagesS H S, H: Indhi IGH Chool EbbaljyotiNo ratings yet
- Respiration BiophysicsDocument9 pagesRespiration Biophysicsomarriyadh92No ratings yet
- The Respiratory System of Human Body FactsDocument12 pagesThe Respiratory System of Human Body FactsjulianneboloronNo ratings yet
- RESPIRATION - Effect of Exercise On Breathing RateDocument1 pageRESPIRATION - Effect of Exercise On Breathing RateJoy BoehmerNo ratings yet
- Exercise LabDocument3 pagesExercise LabJonatan LeflerNo ratings yet
- Unit One: Overview of Pulmonary Anatomy and Physiology A. The Respiratory SystemDocument9 pagesUnit One: Overview of Pulmonary Anatomy and Physiology A. The Respiratory SystemWaras Budi UtomoNo ratings yet
- VentillatorDocument106 pagesVentillatordeepaseira2205No ratings yet
- Measuring Lung Capacity PDFDocument5 pagesMeasuring Lung Capacity PDFSip BioNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Strcuture and Function of Ventilatory SystemDocument36 pages2.1 Strcuture and Function of Ventilatory SystemchaaarrNo ratings yet
- Sistem Respirasi-Isti AnindyaDocument18 pagesSistem Respirasi-Isti AnindyaSindia MirnaNo ratings yet
- Body Systems and ExerciseDocument15 pagesBody Systems and ExerciseMichael GuzikNo ratings yet
- Exercise Physiology PPT (27 September 2018)Document72 pagesExercise Physiology PPT (27 September 2018)Surya Diatmika100% (1)
- Acute Respiratory Changes To ExerciseDocument31 pagesAcute Respiratory Changes To Exerciseapi-115744109No ratings yet
- Activity 17 The Respiratory System and Pulmonary VentilationDocument5 pagesActivity 17 The Respiratory System and Pulmonary VentilationarmandNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Powerpoint GaDocument28 pagesRespiratory Powerpoint Gakevinramirezzz365No ratings yet
- Physiology AsignmentDocument5 pagesPhysiology AsignmentAnasAbdelaNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation For Respiratory MechanicsDocument73 pagesInstrumentation For Respiratory MechanicsSoniya CsNo ratings yet
- Lab 6 ReportDocument19 pagesLab 6 Reportapi-311215267100% (2)
- VM Simplificacion IIDocument4 pagesVM Simplificacion IIRolando Juan Dávila SalcedoNo ratings yet
- Lab Report - Circulation and RespirationDocument4 pagesLab Report - Circulation and RespirationSimranNo ratings yet
- Evens RespiortyDocument4 pagesEvens RespiortyamyhowarthNo ratings yet
- Features of Gas Exchange Surfaces: The Alveolus Is The Gas Exchange Surface in HumansDocument9 pagesFeatures of Gas Exchange Surfaces: The Alveolus Is The Gas Exchange Surface in HumansM. ShayanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 BioDocument18 pagesChapter 11 BioRylee LNo ratings yet
- RespitorylabreportDocument1 pageRespitorylabreportapi-270065976No ratings yet
- Respirasi ControlDocument50 pagesRespirasi Controlrinaldy IX9No ratings yet
- Manual TmaskDocument65 pagesManual TmaskPavel MayorgaNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Cardiopulmonary Physical Therapy 4th Edition Hillegass Test BankDocument14 pagesEssentials of Cardiopulmonary Physical Therapy 4th Edition Hillegass Test Banksiennaclimatal1bk6t6100% (21)
- Ladefoged and Loeb RespirationDocument12 pagesLadefoged and Loeb RespirationBetül Özsoy TanrıkuluNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System OkDocument36 pagesRespiratory System Okakselerasi10No ratings yet
- P E - 101-PresentationDocument6 pagesP E - 101-Presentationjohn dave andinoNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System & ParametersDocument35 pagesRespiratory System & Parametersrobert robNo ratings yet
- DyslexiaDocument13 pagesDyslexiabloodythornNo ratings yet
- University of Salford Campus Map and GuideDocument2 pagesUniversity of Salford Campus Map and GuidebloodythornNo ratings yet
- Amazing GraceDocument1 pageAmazing GracebloodythornNo ratings yet
- I Came Into ExistenceDocument1 pageI Came Into ExistencebloodythornNo ratings yet
- Cells: Skeletal Muscle Is A Form of Striated Muscle Tissue Existing Under Control of The SomaticDocument11 pagesCells: Skeletal Muscle Is A Form of Striated Muscle Tissue Existing Under Control of The SomaticbloodythornNo ratings yet
- Fairy WingsDocument2 pagesFairy WingsbloodythornNo ratings yet