Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1
Uploaded by
api-236686558Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1
Uploaded by
api-236686558Copyright:
Available Formats
1. What does the suffix troph mean? Nourished or growing in the matter indicated 2.
What do you think a trophic level is? I think it means the order animals are put in a pyramid of the ecosystem. 3. How about food chains, food webs? Compare and contrast those terms you learned in biology. Foods webs- A system of interlocking and independent food chains Food chains- A hierarchical of organism each dependent of the next as a source of food Similar- they both relate to food and have an interaction with each other
4. Quickly sketch a food chain using organisms that might be found on our school grounds.
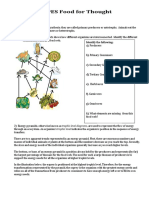
a. What do you have to do to turn it into a food web? Do so. Make food chains that connects to each animals and circulate all over again 5. Look at the following diagrams called Energy Pyramids. a. What do they all have in common? Plants are all under the food pyramids and at the top are usually bigger predators b. How are they different from one another? Depending on the type of animals the top square the top animals are different and feed of differently 6. Why are there are more organisms at the base and less organisms as you travel up the pyramid? On the bottom of the pyramid because those are the ones that eat less and reproduce faster
a. Any idea what an energy pyramid shows? I think it might show the amount of energy a specie has on our environment. 7. Two of the pyramids have numbers. Do you see a pattern in the numbers? The numbers start from least to greatest
a. What might the numbers mean?Read the following description from Earth Force Its the amount of energy those animals and plants transmit to the ecosystem http://www.earthforce.org/content/article/detail/1284 Energy pyramids, otherwise known as trophic level diagrams, are used to represent the flow of energy through an ecosytem. An organisms trophic level indicates the organisms position in the sequence of energy transfers. There are two apparent trends represented in an energy pyramid. First, there are enormous numbers and masses of individual animals or plants at the bottom and the numbers decrease as you reach the top. Secondly, the sizes and energy needs of the individual organisms generally increase as you reach higher levels. The bottom, or base, of an energy pyramid is a position always held by the producers and represents (by far) the largest percentage of biomass for the food web. The need for such a large biomass of producers is to support the energy needs for all the organisms at higher trophic levels. In the illustration above, the osprey is positioned at the highest trophic level. Therefore, for the energy transformations represented by the pyramid, the osprey is the organism with the greatest energy needs and relies on all of the transactions from producers to consumers to have enough energy left over to fill its own energy needs. It should be acknowledged that ecosystems are very complex and any food chain, food web or energy pyramid simply illustrates the general idea. It would be practically impossible to illustrate all the possible ways that animals interact and all the possible ways that energy
moves throughout an ecosystem. Next, now that youve thought about food chains, energy pyramids and so on, lets do some problem solving. As you do these, think about the benefits and drawbacks of eating at lower trophic levels. First, for some background, read about soybeans from the Small Bean, Big Dreams Small bean, big dreams is a fitting motto for the versatile soybean plant. Known as the Cadillac of protein sources, soybeans nourish the people and animals of the world. Soybeans also help us reduce reliance on petroleum through hundreds of renewable product innovations that enhance our everyday lives. All this from a bean so small that it takes around 150,000 soybeans to fill one bushel. Good things do come in small packages! http://www.iasoybeans.com/index.html
Soybeans have a rich history from their creation in China 5,000 years ago. In our country, they started from humble beginnings, serving as ballast for Chinese ships coming to America. Making their U.S. agricultural debut in 1829 for soy sauce, inventors like George Washington Carver and Henry Ford embraced soybeans for plastics, printing inks and a range of industrial uses. Dreams Become Reality Between 1945 and 1985 the annual soybean harvest increased
eleven-fold. Today, America grows around three billion bushels of soybeans and accounts for more than one-third of the world's soybean crop. It represents a $16 billion crop that strengthens our countrys balance of trade while providing a domino effect of job growth and prosperity.The dreams of our early architects of innovation are reality today. For example, soybeans can be grown in space. Their compact nutrition and flavor variety is key to our astronauts. This small bean continues to dream and achieve enabling soy to change our world. At 55 grams of protein per day, one acre of soybeans can meet a persons dietary protein
needs for 8,400 days Okay now for the problem... Its 2017. Youre the owner of a soybean farm. You also raise guinea hens for food and insect control. The hens will eat grasshoppers and other insect pests, including ticks. This is good. Biological control of your pests will save you money on chemical pesticides. The hens also act as watchdogs squawking a lot when intruders approach. You allow the hens to free range during the day in your fields and but at night, you provide roosts for them to keep them safe. Use the following for your calculations. Show all work with units! You can live on 1 hen/day for a year 1 hen eats 25 grasshoppers/day (25 gh/day) 1000 gh have a mass of 1 kg 1 gh requires about 30g soy/yr 1 human requires about 600 gh/day Dry soybeans have provide about 3.3 cal/g 1. Calculate the number of gh a hen needs to eat per year. 25gh*365=0125gh 2. How many gh are needed for a years supply of hens for you, the farmer? 25gh*365day*365day=3330625gh 3. What is the total mass in kg, of the gh needed to feed all the hens for one year? 3330625gh/1000g=3330.625 kg 4. How many kg of soybeans are needed to feed all the gh for one year? 3330625gh*0.3g+99918.75kg 5. Sources tell us that Native American Indians ate gh. So you can too! These early Americans could collect about 90 kg of gh per hour, when they were abundant. How many people could the gh feed, compared to the one person that the hen fed? (Perhaps you could dip the gh in chocolate.)6. You need to consume 3000 calories/day. If you ate only soybeans how many grams of soybeans would you have to eat per day for calories alone? 90kg*1000+900,000g 900,000/600gh/day+1500 people
7. Cows produce about 19 kg protein/acre/year and soy produces 200 kg of protein/acre/year. a. Which is more efficient to eat? Why? The soy because it produces more b. Have you ever eaten a soy burger (veggie burger)? Why or why not? No I havent this is the first time I heard about it. 8. In theory, the earth could support many more people if we ate at a lower trophic level. a. List 2 benefits of doing this. Food resources would be easier to gather, we had less worries. b. List 2 drawbacks of eating lower on the food chain. We would eat the same food all the time, animals would probably over populate us. c. What are some benefits of being a vegetarian? You dont have to worry about any virus that animals have, your immune system would be cleaner d. What are some drawbacks? You cant have good food , you need protein from meat 9. And then there are fish to eat! Large predatory fish usually are found at the 3rd or 4th trophic level of an energy pyramid. What does this mean in terms of energy loss? The fish has about 10^-2 less energy than the plants that originally carried the energy at the beginning 10. Large predatory animals can also be problematic to eat because of bioaccumulation and biomagnification of toxins such as lead or mercury in their habitats. What do those two big words mean and why should this be Bioac BIOACCUMULATION: accumulation of substances like pesticides or other organism chemicals in an organism Bio magnification : the concentration of toxins in an organism as a result of its ingesting on other plants or animals 11. Do you think about the food you eat? Why or why not? I do because then I think I gain a lot of weight and sometimes even wonder the chemicals im eating buti feel as if its impossible to maintain yourself from any of toxins
You might also like
- Energy Food Chain LabDocument3 pagesEnergy Food Chain LabAlexis Williams100% (2)
- 26 Ecological Pyramids-S RennelDocument8 pages26 Ecological Pyramids-S Rennelapi-32383118283% (18)
- ANSI B4.1-1967 Preferred Limits and Fits For Cylindrical PartsDocument25 pagesANSI B4.1-1967 Preferred Limits and Fits For Cylindrical Partsgiaphongn100% (5)
- Apes Food For ThoughtDocument5 pagesApes Food For Thoughtapi-235617848No ratings yet
- Food Chains, Food Webs, and Energy Pyramid WorksheetDocument10 pagesFood Chains, Food Webs, and Energy Pyramid WorksheetCici LanNo ratings yet
- How Does the Food Chain Work? - Science Book for Kids 9-12 | Children's Science & Nature BooksFrom EverandHow Does the Food Chain Work? - Science Book for Kids 9-12 | Children's Science & Nature BooksNo ratings yet
- Lpi - 101-500Document6 pagesLpi - 101-500Jon0% (1)
- Lighthouse Case Study Solution GuideDocument17 pagesLighthouse Case Study Solution Guidescon driumNo ratings yet
- Apes Food For Thought Trophic LevelsDocument5 pagesApes Food For Thought Trophic Levelsapi-237699934No ratings yet
- FoodforthoughtDocument5 pagesFoodforthoughtapi-235959158No ratings yet
- Food For Thought Trophic Levels: Answer KeyDocument3 pagesFood For Thought Trophic Levels: Answer KeyDaniel KimNo ratings yet
- Apes Food For ThoughtDocument4 pagesApes Food For Thoughtapi-238476134No ratings yet
- Apes Food For ThoughtDocument6 pagesApes Food For Thoughtapi-235658421No ratings yet
- Trophic LevelDocument6 pagesTrophic Levelapi-236697820No ratings yet
- Document 6Document17 pagesDocument 6haashniNo ratings yet
- 2 RDG MCH Model Task PDFDocument4 pages2 RDG MCH Model Task PDFFelani Tiberio JusayanNo ratings yet
- Our Environment A Our ConcernDocument9 pagesOur Environment A Our ConcernIpshita PathakNo ratings yet
- Food Chains + Webs: "What'S For Dinner?"Document11 pagesFood Chains + Webs: "What'S For Dinner?"ronaldo100% (1)
- Ecological Pyramids WorksheetDocument5 pagesEcological Pyramids Worksheetace0% (1)
- Unit4 Module 2 Interactions Mms123Document54 pagesUnit4 Module 2 Interactions Mms123Lebiram Mabz91% (11)
- Energy PyramidDocument10 pagesEnergy PyramidganeshmamidiNo ratings yet
- Food Chain and Food Web Notes and WorksheetsDocument12 pagesFood Chain and Food Web Notes and WorksheetsnidhiNo ratings yet
- Food Chains and Food WebDocument16 pagesFood Chains and Food WebLK chanellNo ratings yet
- Pyramids of BiomassDocument23 pagesPyramids of BiomasssabahakbarNo ratings yet
- Trophic Level ANSWERSDocument2 pagesTrophic Level ANSWERSfftuoryjsNo ratings yet
- ORGANISMS AND THEIR ENVIRONMENT - Biology PresentationDocument33 pagesORGANISMS AND THEIR ENVIRONMENT - Biology PresentationdivishaingavaleNo ratings yet
- 18.1 Energy Flow and Food WebsDocument10 pages18.1 Energy Flow and Food Webszain ul AbideenNo ratings yet
- Cressabill Eslao GE10-K Food Chain QuestionsDocument5 pagesCressabill Eslao GE10-K Food Chain QuestionsJohn Michael CellanNo ratings yet
- Ecology 2Document18 pagesEcology 2ramloghun veerNo ratings yet
- Ecological Pyramids WorksheetDocument4 pagesEcological Pyramids WorksheetTrilok SawantNo ratings yet
- Food Chains and WebsDocument13 pagesFood Chains and WebsGlenn Valentin MendozaNo ratings yet
- APES Food For Thought Modified 2014Document5 pagesAPES Food For Thought Modified 2014Alvin MontesNo ratings yet
- Earths EcosystemsDocument14 pagesEarths EcosystemsRede WaskitaNo ratings yet
- Concept of Food ChainDocument31 pagesConcept of Food ChainSachin ShrivastavNo ratings yet
- Food Web 2019Document32 pagesFood Web 2019Ade GratiaNo ratings yet
- Ecosystems - Class 8 SyllabusDocument12 pagesEcosystems - Class 8 SyllabusMuhammad HaqNo ratings yet
- Assign 2 - Food Chains and WebsDocument11 pagesAssign 2 - Food Chains and WebsRard Tangangco LozanoNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument3 pagesUntitledShahad ZaidanNo ratings yet
- Ecological Associations and Energy FlowDocument5 pagesEcological Associations and Energy Flow•Divine Beauty•No ratings yet
- Energy and Matter Flows in EcosystemsDocument12 pagesEnergy and Matter Flows in EcosystemsantonioNo ratings yet
- Food Webs: Energy Flow Between OrganismsDocument10 pagesFood Webs: Energy Flow Between OrganismsXue Li ChinNo ratings yet
- The Magic of Cell Fusion: Improving Crops and Livestock: Mikhael O. SantosDocument4 pagesThe Magic of Cell Fusion: Improving Crops and Livestock: Mikhael O. SantosMikhael O. SantosNo ratings yet
- Food Web ProtocolDocument9 pagesFood Web ProtocolELOISA N. CASANENo ratings yet
- Trophic LevelDocument19 pagesTrophic Levelmerezemenike272No ratings yet
- ss1 Biology Week 4 - 10Document19 pagesss1 Biology Week 4 - 10sulaiman mohammedNo ratings yet
- What's for Dinner? Food Chains and WebsDocument13 pagesWhat's for Dinner? Food Chains and WebsTharanga HewabuhageNo ratings yet
- Food Chains & Food Webs: DecomposersDocument14 pagesFood Chains & Food Webs: DecomposersGladys Claire BaguilatNo ratings yet
- Bozeman - Ecosystems Guided Viewing 1Document2 pagesBozeman - Ecosystems Guided Viewing 1api-269169613No ratings yet
- Ashley Nicole Vallespin - Q4-WEEKS-5-7-1Document34 pagesAshley Nicole Vallespin - Q4-WEEKS-5-7-1Ashley Nicole VallespinNo ratings yet
- Questions Energy Flow PyramidsDocument4 pagesQuestions Energy Flow PyramidsdaniurrestaNo ratings yet
- EcologyDocument19 pagesEcologyGhulam MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Organisms and Energy Pogil: Food ChainsDocument7 pagesOrganisms and Energy Pogil: Food ChainsBreonna WilsonNo ratings yet
- Food Chains and WebsDocument13 pagesFood Chains and Websapi-337510081100% (2)
- Key Points:: Producers, or Autotrophs, Make Their Own OrganicDocument13 pagesKey Points:: Producers, or Autotrophs, Make Their Own Organicjoyce sumagaysayNo ratings yet
- Food Chain and Web Presentation PDFDocument37 pagesFood Chain and Web Presentation PDFScience,Physical Education And Sports VideosNo ratings yet
- Food Chains and Food Webs DFDocument2 pagesFood Chains and Food Webs DFdreamlet100% (1)
- Discover how food chains and webs transfer energyDocument2 pagesDiscover how food chains and webs transfer energyRocel Navarro100% (1)
- Food Chains and Food Webs DFDocument2 pagesFood Chains and Food Webs DFDomEnt AllureNo ratings yet
- Ecosystems 2022 Combined ScienceDocument56 pagesEcosystems 2022 Combined Sciencehocus pocusNo ratings yet
- DHBB Lop 10 2022Document6 pagesDHBB Lop 10 2022borahae 3000No ratings yet
- Summary & Study Guide - 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessFrom EverandSummary & Study Guide - 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessNo ratings yet
- A Joosr Guide to… The Omnivore's Dilemma by Michael Pollan: The Search for a Perfect Meal in a Fast-Food WorldFrom EverandA Joosr Guide to… The Omnivore's Dilemma by Michael Pollan: The Search for a Perfect Meal in a Fast-Food WorldNo ratings yet
- Carbon Cycle and Greenhouse EffectDocument2 pagesCarbon Cycle and Greenhouse Effectapi-236686558No ratings yet
- Part 1 QuestionsDocument2 pagesPart 1 Questionsapi-236686558No ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Guided ReadingDocument8 pagesChapter 11 Guided Readingapi-236686558No ratings yet
- YessicaDocument3 pagesYessicaapi-236686558No ratings yet
- PizzaDocument2 pagesPizzaapi-236686558No ratings yet
- Endangered Species Graphic Organizer: Name Location Why Is It Endangered? Number Remaining in The WildDocument2 pagesEndangered Species Graphic Organizer: Name Location Why Is It Endangered? Number Remaining in The Wildapi-236686558No ratings yet
- What Makes Quality SoilDocument1 pageWhat Makes Quality Soilapi-236686558No ratings yet
- PowerpointDocument3 pagesPowerpointapi-236686558No ratings yet
- Graphic Organizer - Common Invasive Species 1Document3 pagesGraphic Organizer - Common Invasive Species 1api-237699934No ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document8 pagesPresentation 1api-236686558No ratings yet
- OooooogggosDocument2 pagesOooooogggosapi-236686558No ratings yet
- PCR Flowchart SampleDocument3 pagesPCR Flowchart Sampleapi-236686558No ratings yet
- Understand and Be Able To Apply Each of These TermsDocument5 pagesUnderstand and Be Able To Apply Each of These Termsapi-236686558No ratings yet
- Terrestrial BiomeDocument2 pagesTerrestrial Biomeapi-236686558No ratings yet
- HA200Document4 pagesHA200Adam OngNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1&2 Exercise Ce StatisticDocument19 pagesChapter 1&2 Exercise Ce StatisticSky FireNo ratings yet
- AbDocument13 pagesAbSk.Abdul NaveedNo ratings yet
- Material Safety Data Sheet: Section I - Chemical Product and Company IdentificationDocument2 pagesMaterial Safety Data Sheet: Section I - Chemical Product and Company IdentificationMu ClasNo ratings yet
- Compiled XiiDocument34 pagesCompiled XiiMridul VermaNo ratings yet
- SplunkCloud-6 6 3-SearchTutorial PDFDocument103 pagesSplunkCloud-6 6 3-SearchTutorial PDFanonymous_9888No ratings yet
- Lab 3 DiscussionDocument2 pagesLab 3 DiscussionMarlee WhiteNo ratings yet
- SPM Literature in English Tips + AdviseDocument2 pagesSPM Literature in English Tips + AdviseJessica NgNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Measurements: 1.1 Units of MeasurementDocument24 pagesChapter 1 Measurements: 1.1 Units of MeasurementEsmira Melić ŠutkovićNo ratings yet
- International Studies: JIIT University, NoidaDocument3 pagesInternational Studies: JIIT University, NoidavaibhavNo ratings yet
- Wave Hydro Dynamics Prof. V. Sundar Department of Ocean Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, MadrasDocument32 pagesWave Hydro Dynamics Prof. V. Sundar Department of Ocean Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, MadrasMuralidhar YarakalaNo ratings yet
- Cost-effective laboratory thermostats from -25 to 100°CDocument6 pagesCost-effective laboratory thermostats from -25 to 100°CCynthia MahlNo ratings yet
- Qdoc - Tips Select Readings 2nd Pre IntermediateDocument178 pagesQdoc - Tips Select Readings 2nd Pre IntermediateFarzana BatoolNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Knowledge, Attitude Andpractice Toward Sexually Transmitteddiseases in Boditi High School StudentsDocument56 pagesAssessment of Knowledge, Attitude Andpractice Toward Sexually Transmitteddiseases in Boditi High School StudentsMinlik-alew Dejenie88% (8)
- Question Notes On Production Management (Final)Document63 pagesQuestion Notes On Production Management (Final)Vineet Walia100% (1)
- Introduction To Literary TheoryDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Literary TheoryAnil Pinto100% (4)
- SWR SRB Product SheetDocument2 pagesSWR SRB Product SheetCarlo AguiluzNo ratings yet
- The Definitions of CurriculumDocument27 pagesThe Definitions of CurriculumAngie Bern LapizNo ratings yet
- Galletto 1250 User GuideDocument9 pagesGalletto 1250 User Guidesimcsimc1No ratings yet
- English Language and Applied Linguistics Textbooks Lo Res USDDocument61 pagesEnglish Language and Applied Linguistics Textbooks Lo Res USDJames Blackburn Quéré Cutbirth100% (2)
- Standard Test Method For Impact Resistance D2794Document3 pagesStandard Test Method For Impact Resistance D2794vasu_suvaNo ratings yet
- Constructed Wetland Design Guidelines for DevelopersDocument32 pagesConstructed Wetland Design Guidelines for DevelopersBere QuintosNo ratings yet
- EEEE FYP Workshop 3 Project ThesisDocument17 pagesEEEE FYP Workshop 3 Project ThesisYukai QianNo ratings yet
- Digital Image Processing System AbstractDocument4 pagesDigital Image Processing System AbstractTelika RamuNo ratings yet
- IBM's Corporate Service Corps: The Shift To A Globally Integrated EnterpriseDocument2 pagesIBM's Corporate Service Corps: The Shift To A Globally Integrated EnterprisePYXERA GlobalNo ratings yet
- EssayDocument2 pagesEssaySantoshKumarPatraNo ratings yet
- Signal Sampling, Quantization, Binary Encoding: Oleh Albert SagalaDocument46 pagesSignal Sampling, Quantization, Binary Encoding: Oleh Albert SagalaRamos D HutabalianNo ratings yet