Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pex 04 01
Uploaded by
Natalie Cristine InneckenOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pex 04 01
Uploaded by
Natalie Cristine InneckenCopyright:
Available Formats
Name: Natalie Innecken Exercise 4: Endocrine System Physiology: Activity 1: Metabolism and Thyroid Hormone Lab Report Pre-lab
Quiz Results You scored 50% by answering 3 out of 6 questions correctly. 1. Which of the following statements about metabolism is false? Your answer : a. Anabolism refers to chemical reactions that build larger, more complex molecules. Correct answer: d. All of the energy from metabolism is ultimately stored in the chemical bonds of ATP. 2. Thyroxine is You correctly answered: c. the most important hormone for maintaining the metabolic rate and body temperature. 3. Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) is You correctly answered: b. produced in the pituitary gland. 4. An injection of TSH to an otherwise normal animal will cause which of the following? Your answer : b. increased levels of TRH secretion Correct answer: d. goiter development 5. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) is You correctly answered: a. secreted by the hypothalamus. 6. Which of the following statements is true? Your answer : a. TRH travels from the hypothalamus to the thyroid gland via the hypothalamic-thyroid portal system. Correct answer: b. The hypothalamus primarily secretes tropic hormones that stimulate the secretion of other hormones.
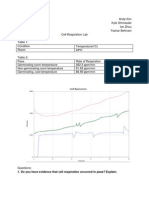
01/13/14
page 1
Experiment Results Predict Question: Predict Question 1: Make a prediction about the basal metabolic rate (BMR) of the remaining rats compared with the BMR of the normal rat you just measured. Your answer : b. The hypophysectomized (Hypox) rat's BMR will be higher than the normal rat's BMR. Predict Question 2: What do you think will happen after you inject thyroxine into the three rats? Your answer : d. The normal rat will become hyperthyroidic but will not develop a goiter. Predict Question 3: What do you think will happen after you inject TSH into the three rats? Your answer : a. The normal rat will become hyperthyroidic and develop a goiter. Predict Question 4: Propylthiouracil (PTU) is a drug that inhibits the production of thyroxine by blocking the attachment of iodine to tyrosine residues in the follicle cells of the thyroid gland (iodinated tyrosines are linked together to form thyroxine). What do you think will happen after you inject PTU into the three rats? Your answer : b. The thyroidectomized rat will become hypothyroidic and develop a goiter. Stop & Think Questions: 1h. Calculate the oxygen consumption per hour for this rat using the following equation. ml O2 consumed/1 minute x 60 minutes/hour = ml O2/hour Enter the oxygen consumption per hour in the field below and then click Submit Data to display your results in the Lab Report. You answered: 426 ml O2/hr 1i. Now that you have calculated the oxygen consumption per hour for this rat, you can calculate the metabolic rate per kilogram of body weight with the following equation (note that you need to convert the weight data from grams to kilograms to use this equation). Metabolic rate = (ml O2/hr)/(weight in kg) = ml O2/kg/hr Enter the metabolic rate in the field below and then click Submit Data to display your results in the Lab Report. You answered: 1704 ml O2/kg/hr 2h. Calculate the oxygen consumption per hour for this rat using the following equation. ml O2 consumed/1 minute x 60 minutes/hour = ml O2/hour Enter the oxygen consumption per hour in the field below and then click Submit Data to display your results in the Lab Report. You answered: 372 ml O2/hr 2i. Now that you have calculated the oxygen consumption per hour for this rat, you can calculate the metabolic rate per kilogram of body weight with the following equation (note that you need to convert the weight data from grams to kilograms to use this equation). Metabolic rate = (ml O2/hr)/(weight in kg) = ml O2/kg/hr
01/13/14
page 2
Enter the metabolic rate in the field below and then click Submit Data to display your results in the Lab Report. You answered: 1518.37 ml O2/kg/hr 3h. Calculate the oxygen consumption per hour for this rat using the following equation. ml O2 consumed/1 minute x 60 minutes/hour = ml O2/hour Enter the oxygen consumption per hour in the field below and then click Submit Data to display your results in the Lab Report. You answered: 378 ml O2/hr 3i. Now that you have calculated the oxygen consumption per hour for this rat, you can calculate the metabolic rate per kilogram of body weight with the following equation (note that you need to convert the weight data from grams to kilograms to use this equation). Metabolic rate = (ml O2/hr)/(weight in kg) = ml O2/kg/hr Enter the metabolic rate in the field below and then click Submit Data to display your results in the Lab Report. You answered: 1549.18 ml O2/kg/hr Judging from their basal metabolic rates (an indicator of thyroid function), categorize the rats as hypothyroid (low thyroid levels; BMR below 1600), euthyroid ("good," or normal, thyroid levels; BMR = 1650-1750), or hyperthryoid (high thyroid levels; BMR above 1800). The normal rat is You correctly answered: b. euthyroid Judging from their basal metabolic rates (an indicator of thyroid function), categorize the rats as hypothyroid (low thyroid levels; BMR below 1600), euthyroid ("good," or normal, thyroid levels; BMR = 1650-1750), or hyperthryoid (high thyroid levels; BMR above 1800). The thyroidectomized (Tx) rat is You correctly answered: a. hypothyroid Judging from their basal metabolic rates (an indicator of thyroid function), categorize the rats as hypothyroid (low thyroid levels; BMR below 1600), euthyroid ("good," or normal, thyroid levels; BMR = 1650-1750), or hyperthryoid (high thyroid levels; BMR above 1800). The hypophysectomized (Hypox) rat is You correctly answered: a. hypothyroid 4c. Calculate the oxygen consumption per hour for this rat using the following equation. ml O2 consumed/1 minute x 60 minutes/hour = ml O2/hour Enter the oxygen consumption per hour in the field below and then click Submit Data to display your results in the Lab Report. You answered: 504 ml O2/hr
01/13/14
page 3
4d. Now that you have calculated the oxygen consumption per hour for this rat, you can calculate the metabolic rate per kilogram of body weight with the following equation (note that you need to convert the weight data from grams to kilograms to use this equation). Metabolic rate = (ml O2/hr)/(weight in kg) = ml O2/kg/hr Enter the metabolic rate in the field below and then click Submit Data to display your results in the Lab Report. You answered: 2016 ml O2/kg/hr 5c. Calculate the oxygen consumption per hour for this rat using the following equation. ml O2 consumed/1 minute x 60 minutes/hour = ml O2/hour Enter the oxygen consumption per hour in the field below and then click Submit Data to display your results in the Lab Report. You answered: 462 ml O2/hr 5d. Now that you have calculated the oxygen consumption per hour for this rat, you can calculate the metabolic rate per kilogram of body weight with the following equation (note that you need to convert the weight data from grams to kilograms to use this equation). Metabolic rate = (ml O2/hr)/(weight in kg) = ml O2/kg/hr Enter the metabolic rate in the field below and then click Submit Data to display your results in the Lab Report. You answered: 1885.71 ml O2/kg/hr 6c. Calculate the oxygen consumption per hour for this rat using the following equation. ml O2 consumed/1 minute x 60 minutes/hour = ml O2/hour Enter the oxygen consumption per hour in the field below and then click Submit Data to display your results in the Lab Report. You answered: 468 ml O2/hr 6d. Now that you have calculated the oxygen consumption per hour for this rat, you can calculate the metabolic rate per kilogram of body weight with the following equation (note that you need to convert the weight data from grams to kilograms to use this equation). Metabolic rate = (ml O2/hr)/(weight in kg) = ml O2/kg/hr Enter the metabolic rate in the field below and then click Submit Data to display your results in the Lab Report. You answered: 1918.03 ml O2/kg/hr Judging from their basal metabolic rates (an indicator of thyroid function), categorize the rats as hypothyroid (low thyroid levels; BMR below 1600), euthyroid ("good," or normal, thyroid levels; BMR = 1650-1750), or hyperthryoid (high thyroid levels; BMR above 1800) after the thyroxine injection. The normal rat is You correctly answered: c. hyperthyroid
01/13/14
page 4
Judging from their basal metabolic rates (an indicator of thyroid function), categorize the rats as hypothyroid (low thyroid levels; BMR below 1600), euthyroid ("good," or normal, thyroid levels; BMR = 1650-1750), or hyperthryoid (high thyroid levels; BMR above 1800) after the thyroxine injection. The thyroidectomized (Tx) rat is You correctly answered: c. hyperthyroid Judging from their basal metabolic rates (an indicator of thyroid function), categorize the rats as hypothyroid (low thyroid levels; BMR below 1600), euthyroid ("good," or normal, thyroid levels; BMR = 1650-1750), or hyperthryoid (high thyroid levels; BMR above 1800) after the thyroxine injection. The hypophysectomized (Hypox) rat is You correctly answered: c. hyperthyroid Which of the rats developed a goiter after injection with thyroxine (select all that apply)? You correctly answered: d. None of the rats developed a goiter with this injection. 7c. Calculate the oxygen consumption per hour for this rat using the following equation. ml O2 consumed/1 minute x 60 minutes/hour = ml O2/hour Enter the oxygen consumption per hour in the field below and then click Submit Data to display your results in the Lab Report. You answered: 474 ml O2/hr 7d. Now that you have calculated the oxygen consumption per hour for this rat, you can calculate the metabolic rate per kilogram of body weight with the following equation (note that you need to convert the weight data from grams to kilograms to use this equation). Metabolic rate = (ml O2/hr)/(weight in kg) = ml O2/kg/hr Enter the metabolic rate in the field below and then click Submit Data to display your results in the Lab Report. You answered: 1896 ml O2/kg/hr 8c. Calculate the oxygen consumption per hour for this rat using the following equation. ml O2 consumed/1 minute x 60 minutes/hour = ml O2/hour Enter the oxygen consumption per hour in the field below and then click Submit Data to display your results in the Lab Report. You answered: 372 ml O2/hr 8d. Now that you have calculated the oxygen consumption per hour for this rat, you can calculate the metabolic rate per kilogram of body weight with the following equation (note that you need to convert the weight data from grams to kilograms to use this equation). Metabolic rate = (ml O2/hr)/(weight in kg) = ml O2/kg/hr Enter the metabolic rate in the field below and then click Submit Data to display your results in the Lab Report.
01/13/14
page 5
You answered: 1518.37 ml O2/kg/hr 9c. Calculate the oxygen consumption per hour for this rat using the following equation. ml O2 consumed/1 minute x 60 minutes/hour = ml O2/hour Enter the oxygen consumption per hour in the field below and then click Submit Data to display your results in the Lab Report. You answered: 468 ml O2/hr 9d. Now that you have calculated the oxygen consumption per hour for this rat, you can calculate the metabolic rate per kilogram of body weight with the following equation (note that you need to convert the weight data from grams to kilograms to use this equation). Metabolic rate = (ml O2/hr)/(weight in kg) = ml O2/kg/hr Enter the metabolic rate in the field below and then click Submit Data to display your results in the Lab Report. You answered: 1918.03 ml O2/kg/hr Judging from their basal metabolic rates (an indicator of thyroid function), categorize the rats as hypothyroid (low thyroid levels; BMR below 1600), euthyroid ("good," or normal, thyroid levels; BMR = 1650-1750), or hyperthryoid (high thyroid levels; BMR above 1800) after the TSH injection. The normal rat is You correctly answered: c. hyperthyroid Judging from their basal metabolic rates (an indicator of thyroid function), categorize the rats as hypothyroid (low thyroid levels; BMR below 1600), euthyroid ("good," or normal, thyroid levels; BMR = 1650-1750), or hyperthryoid (high thyroid levels; BMR above 1800) after the TSH injection. The thyroidectomized (Tx) rat is You correctly answered: a. hypothyroid Judging from their basal metabolic rates (an indicator of thyroid function), categorize the rats as hypothyroid (low thyroid levels; BMR below 1600), euthyroid ("good," or normal, thyroid levels; BMR = 1650-1750), or hyperthryoid (high thyroid levels; BMR above 1800) after the TSH injection. The hypophysectomized (Hypox) rat is You correctly answered: c. hyperthyroid Which of the rats developed a goiter after injection with TSH (select all that apply)? You correctly answered: a. the normal rat c. the hypophysectomized rat 10c. Calculate the oxygen consumption per hour for this rat using the following equation. ml O2 consumed/1 minute x 60 minutes/hour = ml O2/hour Enter the oxygen consumption per hour in the field below and then click Submit Data to display your results in the Lab Report. You answered: 378 ml O2/hr
01/13/14
page 6
10d. Now that you have calculated the oxygen consumption per hour for this rat, you can calculate the metabolic rate per kilogram of body weight with the following equation (note that you need to convert the weight data from grams to kilograms to use this equation). Metabolic rate = (ml O2/hr)/(weight in kg) = ml O2/kg/hr Enter the metabolic rate in the field below and then click Submit Data to display your results in the Lab Report. You answered: 1512 ml O2/kg/hr 11c. Calculate the oxygen consumption per hour for this rat using the following equation. ml O2 consumed/1 minute x 60 minutes/hour = ml O2/hour Enter the oxygen consumption per hour in the field below and then click Submit Data to display your results in the Lab Report. You answered: 384 ml O2/hr 11d. Now that you have calculated the oxygen consumption per hour for this rat, you can calculate the metabolic rate per kilogram of body weight with the following equation (note that you need to convert the weight data from grams to kilograms to use this equation). Metabolic rate = (ml O2/hr)/(weight in kg) = ml O2/kg/hr Enter the metabolic rate in the field below and then click Submit Data to display your results in the Lab Report. You answered: 1567.35 ml O2/kg/hr 12c. Calculate the oxygen consumption per hour for this rat using the following equation. ml O2 consumed/1 minute x 60 minutes/hour = ml O2/hour Enter the oxygen consumption per hour in the field below and then click Submit Data to display your results in the Lab Report. You answered: 378 ml O2/hr 12d. Now that you have calculated the oxygen consumption per hour for this rat, you can calculate the metabolic rate per kilogram of body weight with the following equation (note that you need to convert the weight data from grams to kilograms to use this equation). Metabolic rate = (ml O2/hr)/(weight in kg) = ml O2/kg/hr Enter the metabolic rate in the field below and then click Submit Data to display your results in the Lab Report. You answered: 1549.18 ml O2/kg/hr Judging from their basal metabolic rates (an indicator of thyroid function), categorize the rats as hypothyroid (low thyroid levels; BMR below 1600), euthyroid ("good," or normal, thyroid levels; BMR = 1650-1750), or hyperthryoid (high thyroid levels; BMR above 1800) after the PTU injection. The normal rat is You correctly answered: a. hypothyroid
01/13/14
page 7
Judging from their basal metabolic rates (an indicator of thyroid function), categorize the rats as hypothyroid (low thyroid levels; BMR below 1600), euthyroid ("good," or normal, thyroid levels; BMR = 1650-1750), or hyperthryoid (high thyroid levels; BMR above 1800) after the PTU injection. The thyroidectomized (Tx) rat is You correctly answered: a. hypothyroid Judging from their basal metabolic rates (an indicator of thyroid function), categorize the rats as hypothyroid (low thyroid levels; BMR below 1600), euthyroid ("good," or normal, thyroid levels; BMR = 1650-1750), or hyperthryoid (high thyroid levels; BMR above 1800) after the PTU injection. The hypophysectomized (Hypox) rat is You correctly answered: a. hypothyroid Which of the rats developed a goiter after injection with PTU (select all that apply)? You correctly answered: a. the normal rat Experiment Data: Rat Tx Normal Hypox Normal Tx Hypox Normal Tx Hypox Normal Tx Hypox Weight (g) 245 250 244 250 245 244 250 245 244 250 245 244 ml O2/min 6.2 7.1 6.3 8.4 7.7 7.8 7.9 6.2 7.8 6.3 6.4 6.3 ml O2/hr 372.00 426.00 378.00 504.00 462.00 468.00 474.00 372.00 468.00 378.00 384.00 378.00 BMR (ml O2/kg/hr) 1518.37 1704.00 1549.18 2016.00 1885.71 1918.03 1896.00 1518.37 1918.03 1512.00 1567.35 1549.18 Palpation No Mass No Mass No Mass No Mass No Mass No Mass Mass No Mass Mass Mass No Mass No Mass Injected none none none thyroxine thyroxine thyroxine TSH TSH TSH ptu ptu ptu
01/13/14
page 8
Post-lab Quiz Results You scored 57% by answering 4 out of 7 questions correctly. 1. How would you treat a thyroidectomized animal so that it functions like a "normal" animal? You correctly answered: c. Provide the animal T4 supplements. 2. As a result of the missing hormone(s) in the hypophysectimized rat, what would be some expected symptoms? Your answer: a. unexplained weight loss Correct answer: d. decreased basal metabolic rate 3. An injection of thyroxine to an otherwise normal rat will cause which of the following? You correctly answered: b. hyperthyroidism 4. Why didn't any of the rats develop a goiter after thyroxine injection? You correctly answered: a. In all cases, TSH levels were not elevated by the thyroxine injection. 5. Why did the normal rat develop a palpable goiter with the TSH injection? Your answer: a. The TSH receptors in the hypothalamus were overstimulated. Correct answer: c. The TSH receptors on the thyroid gland were excessively stimulated. 6. An injection of propylthiouracil to an otherwise normal animal will cause which of the following? You correctly answered: b. goiter development 7. Why did the normal rat develop a palpable goiter with the propylthiouracil injection? Your answer: b. The amount of T4 secretion by the thyroid gland became excessive. Correct answer: d. The injection decreased the negative feedback mechanism on TSH.
01/13/14
page 9
Review Sheet Results 1. Part 1: Determining the Basal Metabolic Rates Which rat had the fastest basal metabolic rate (BMR)? Your answer: The normal rat, for it did not have a missing pituitary gland or thyroid glnad. 2. Why did the metabolic rates differ between the normal rat and the surgically altered rats? How well did the results compare with your prediction? Your answer: The normal rat had the highest BMR due to its retention of the glands which are required to stimulate and regulate the release of thyroid hormones. 3. If an animal has been thyroidectomized, what hormone(s) would be missing in its blood? Your answer: The animal would be missing the triiodythronine and thyroxine. 4. If an animal has been hypophysectomized, what effect would you expect to see in the hormone levels in its body? Your answer: One would expect the TSH to be missing due to the missing or removal of the pituitary gland. 5. Part 2: Determining the Effect of Thyroxine on Metabolic Rate What was the effect of thyroxine injections on the normal rat's BMR? Your answer: The effect the thyroxine injection had on the normal rat was that it increased the metabolic rate but it was not enough to develop a goiter. 6. What was the effect of thyroxine injections on the thyroidectomized rat's BMR? How does the BMR in this case compare with the normal rat's BMR? Was the dose of thyroxine in the syringe too large, too small, or just right? Your answer: The effect of thyroxine injections on the Tx rat's BMR was that it increased. However the BMR was still lower than the normal rats BMR, for the dosage was lower. 7. What was the effect of thyroxine injections on the hypophysectomized rat's BMR? How does the BMR in this case compare with the normal rat's BMR? Was the dose of thyroxine in the syringe too large, too small, or just right? Your answer: The effect of thyroxine injections on the hypophysectomized rat's BMR was that it also increased. And its BMR though still remained lower than the normal rat's since its dosage was lower. 8. Part 3: Determining the Effect of TSH on Metabolic Rate What was the effect of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) injections on the normal rat's BMR? Your answer: TSH's effect on the normal rat's BMR was that it increased. 9. What was the effect of TSH injections on the thyroidectomized rat's BMR? How does the BMR in this case compare with the normal rat's BMR? Why was this effect observed?
01/13/14
page 10
Your answer: There was no TSH effect on the thyroidectomized rat for it did not have a thyroid gland to stimulate. 10. What was the effect of TSH injections on the hypophysectomized rat's BMR? How does the BMR in this case compare with the normal rat's BMR? Was the dose of TSH in the syringe too large, too small, or just right? Your answer: The effect of TSH on the rat's BMR was that it increased.The BMR was just below the normal rat's and the syringe amount was too small.
01/13/14
page 11
You might also like
- Dosage Calculations Cheat Sheet GOOD TOOLDocument12 pagesDosage Calculations Cheat Sheet GOOD TOOLCamille Jean100% (10)
- Forlong - Rivers of LifeDocument618 pagesForlong - Rivers of LifeCelephaïs Press / Unspeakable Press (Leng)100% (15)
- (Magness, Steve) Training NotesDocument28 pages(Magness, Steve) Training NotesDanCurtis100% (3)
- Sports Nutrition Handbook: Eat Smart. Be Healthy. Get On Top of Your Game.From EverandSports Nutrition Handbook: Eat Smart. Be Healthy. Get On Top of Your Game.No ratings yet
- Exercise Physiology Course NotesDocument131 pagesExercise Physiology Course NotesAdam Linoby100% (16)
- Calculating Diets and Meal PlanningDocument26 pagesCalculating Diets and Meal Planningjezreel ibarra100% (2)
- A Guide To Funeral Ceremonies and PrayersDocument26 pagesA Guide To Funeral Ceremonies and PrayersJohn DoeNo ratings yet
- Three Components of Energy ExpenditureDocument26 pagesThree Components of Energy ExpenditureDustin HarrisonNo ratings yet
- Module 8 - Emotional Intelligence Personal DevelopmentDocument19 pagesModule 8 - Emotional Intelligence Personal DevelopmentRoxan Binarao-Bayot60% (5)
- H. Aerobic vs. Anaerobic Respiration LabDocument4 pagesH. Aerobic vs. Anaerobic Respiration LaberikabeltranNo ratings yet
- Exercise Physiology Lab ReportDocument9 pagesExercise Physiology Lab Reporthumzak199286% (7)
- Exercise Physiology Course Notes PDFDocument131 pagesExercise Physiology Course Notes PDFPRAJINIKUMARNo ratings yet
- PhysioEx Exercise 4 Activity 1Document14 pagesPhysioEx Exercise 4 Activity 1PatriNo ratings yet
- 22 B Aliifah 205070100111051Document11 pages22 B Aliifah 205070100111051Aliifah HanantikaNo ratings yet
- Pex 04 01Document11 pagesPex 04 01api-533586515No ratings yet
- Pex 04 01Document10 pagesPex 04 01Bianca D. Serls100% (1)
- Exercise 4 - Activity 1 - 022111133222 - Febi Ayu RukmanaDocument10 pagesExercise 4 - Activity 1 - 022111133222 - Febi Ayu RukmanaWerkudaraNo ratings yet
- PEX401009Document10 pagesPEX401009Komisi Skill PMK FK-FKG UHNo ratings yet
- Fisiologi Physioex - Sistem EndokrinDocument11 pagesFisiologi Physioex - Sistem EndokrinArum Citra Melati0% (1)
- Pex 04 01Document11 pagesPex 04 01WerkudaraNo ratings yet
- Pex 04 01Document10 pagesPex 04 01Robeth FirjonNo ratings yet
- Dry Lab Exercise 4 Activity 1Document12 pagesDry Lab Exercise 4 Activity 1ZULBIKAR SETYA DHARMANo ratings yet
- Laporan PhyxioEx METEND - Rohid AlfazonDocument27 pagesLaporan PhyxioEx METEND - Rohid AlfazonZayne GamingNo ratings yet
- Pex 04 01 PDFDocument11 pagesPex 04 01 PDFBenjamin RamosNo ratings yet
- PhysioEx Exercise 4 Activity 1Document12 pagesPhysioEx Exercise 4 Activity 1MARILYN MARIANA HERNANDEZ MENDOZANo ratings yet
- PhysioEx Exercise 4 Activity 1Document18 pagesPhysioEx Exercise 4 Activity 1Dayana Isabel Osorio LuxNo ratings yet
- Habiel K R H Simanjuntak - 200100181 - PhysioEx Exercise 4 Activity 1Document12 pagesHabiel K R H Simanjuntak - 200100181 - PhysioEx Exercise 4 Activity 1Fritz BoyaNo ratings yet
- PhysioEx Ejercicio 4 Actividad 1 Jack PeñaDocument16 pagesPhysioEx Ejercicio 4 Actividad 1 Jack Peñajackpena795No ratings yet
- PhysioEx Exercise 4 Activity 1Document13 pagesPhysioEx Exercise 4 Activity 1edvin merida proNo ratings yet
- PhysioEx Exercise 4 Activity 1Document13 pagesPhysioEx Exercise 4 Activity 1Alesandra Campo SanmartínNo ratings yet
- Guía 14 Metabolismo y Hormona TiroideaDocument18 pagesGuía 14 Metabolismo y Hormona TiroideaJorge CuevaNo ratings yet
- PhysioEx Exercise 4 Activity 1 - Balamad, Maria Karla M.Document13 pagesPhysioEx Exercise 4 Activity 1 - Balamad, Maria Karla M.Maria Karla BalamadNo ratings yet
- PhysioEx Exercise 4 Activity 1Document13 pagesPhysioEx Exercise 4 Activity 1Jorge CuevaNo ratings yet
- Praktikum Endokrin Activity 1 Kelompok 2Document8 pagesPraktikum Endokrin Activity 1 Kelompok 2kuanlins crushNo ratings yet
- Physioex Lab Report: Pre-Lab Quiz ResultsDocument13 pagesPhysioex Lab Report: Pre-Lab Quiz ResultsIvana FNo ratings yet
- Pex 04 01Document8 pagesPex 04 01Grace UrbanoNo ratings yet
- Physioex Lab Report: Pre-Lab Quiz ResultsDocument14 pagesPhysioex Lab Report: Pre-Lab Quiz ResultsAisyah Dewi DinaNo ratings yet
- Pex 04 01Document7 pagesPex 04 01Aulia Azizah KosmanNo ratings yet
- Pex 04 01Document8 pagesPex 04 01Alecks Madrona100% (2)
- Physioex Chapter 4 Exercise 1Document10 pagesPhysioex Chapter 4 Exercise 1Prita WindyasmaraNo ratings yet
- BB Endocrine Lab Data and Question SheetDocument3 pagesBB Endocrine Lab Data and Question SheetJuliax ClintonNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Physiology ReportDocument7 pagesEndocrine Physiology ReportLeanne CubarNo ratings yet
- Exercise 4: Endocrine System Physiology: Activity 1: Metabolism and Thyroid Hormone Lab ReportDocument7 pagesExercise 4: Endocrine System Physiology: Activity 1: Metabolism and Thyroid Hormone Lab ReportAlexandru BurdeniucNo ratings yet
- Circus WorksheetsDocument16 pagesCircus Worksheetsapi-309893409No ratings yet
- Discuss Your Procedure and Calculations With Your Lab Partner If You Need HelpDocument3 pagesDiscuss Your Procedure and Calculations With Your Lab Partner If You Need HelpAmanda lessackNo ratings yet
- M Ridwan - Endocrine System PhysiologyDocument20 pagesM Ridwan - Endocrine System PhysiologyM RidwanNo ratings yet
- Effects of Hormones On Metabolic RateDocument6 pagesEffects of Hormones On Metabolic RatemjfphotoNo ratings yet
- ATP Cellular Respiration LabDocument5 pagesATP Cellular Respiration LabAakash ReddyNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration LabDocument6 pagesCellular Respiration Labianzhou1No ratings yet
- Exercise LabDocument3 pagesExercise LabJonatan LeflerNo ratings yet
- Effects of Hormones On The BMRDocument3 pagesEffects of Hormones On The BMRShelia RagerNo ratings yet
- Exercise Phys Lab ReportDocument9 pagesExercise Phys Lab Reportapi-253190807No ratings yet
- Review Sheet Laprak EndokrinDocument4 pagesReview Sheet Laprak EndokrinrhismaNo ratings yet
- Nutrition - Energy ValueDocument8 pagesNutrition - Energy ValueSubhashini WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Resting Metabolic AssessmentDocument3 pagesResting Metabolic AssessmentALEX SNEHANo ratings yet
- Endocrine Set Up Written ReportDocument3 pagesEndocrine Set Up Written ReportMatthew SANo ratings yet
- Physio Lab 4 Endocrine in PhysioExDocument7 pagesPhysio Lab 4 Endocrine in PhysioExfadhilfwazazssdNo ratings yet
- Group (3) - Lab Report Fisvet 1 - P6 - Week 9Document20 pagesGroup (3) - Lab Report Fisvet 1 - P6 - Week 9NatAsyaNo ratings yet
- Lab #3 - Lung CapacityDocument6 pagesLab #3 - Lung CapacityAbi FelixNo ratings yet
- URT اختبار استعداد القبول بالجامعات EnglishDocument17 pagesURT اختبار استعداد القبول بالجامعات Englishmina100% (1)
- Solution Manual For Nutrition For Sport and Exercise 3Rd Edition Dunford Doyle 128575249X 9781285752495 Full Chapter PDFDocument33 pagesSolution Manual For Nutrition For Sport and Exercise 3Rd Edition Dunford Doyle 128575249X 9781285752495 Full Chapter PDFmary.cannon812100% (14)
- Nutrition For Sport and Exercise 3rd Edition Dunford Doyle 128575249X Solution ManualDocument12 pagesNutrition For Sport and Exercise 3rd Edition Dunford Doyle 128575249X Solution Manuallouise100% (27)
- RF Based Dual Mode RobotDocument17 pagesRF Based Dual Mode Robotshuhaibasharaf100% (2)
- GDCR - Second RevisedDocument290 pagesGDCR - Second RevisedbhaveshbhoiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry For Changing Times 14th Edition Hill Mccreary Solution ManualDocument24 pagesChemistry For Changing Times 14th Edition Hill Mccreary Solution ManualElaineStewartieog100% (50)
- ZEROPAY WhitepaperDocument15 pagesZEROPAY WhitepaperIlham NurrohimNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence and Expert Systems: Management Information Systems, 4 EditionDocument27 pagesArtificial Intelligence and Expert Systems: Management Information Systems, 4 Editionabhi7219No ratings yet
- A Review On PRT in IndiaDocument21 pagesA Review On PRT in IndiaChalavadi VasavadattaNo ratings yet
- BPI - I ExercisesDocument241 pagesBPI - I Exercisesdivyajeevan89No ratings yet
- Grade 8 Least Mastered Competencies Sy 2020-2021: Handicraft Making Dressmaking CarpentryDocument9 pagesGrade 8 Least Mastered Competencies Sy 2020-2021: Handicraft Making Dressmaking CarpentryHJ HJNo ratings yet
- Substitution Reactions - PMDocument64 pagesSubstitution Reactions - PMprasoon jhaNo ratings yet
- Case StarbucksDocument3 pagesCase StarbucksAbilu Bin AkbarNo ratings yet
- Visvesvaraya Technological University: Jnana Sangama, Belgavi-590018, Karnataka, INDIADocument7 pagesVisvesvaraya Technological University: Jnana Sangama, Belgavi-590018, Karnataka, INDIAShashi KaranNo ratings yet
- Chapter5A TorqueDocument32 pagesChapter5A TorqueShuq Faqat al-FansuriNo ratings yet
- Functions of The Gastrointestinal Organs: Muhammad ImranDocument21 pagesFunctions of The Gastrointestinal Organs: Muhammad ImranSalman KhanNo ratings yet
- Directorate of Indian Medicines & Homoeopathy, Orissa, Bhubaneswar Listof The Homoeopathic Dispensaries BhadrakDocument1 pageDirectorate of Indian Medicines & Homoeopathy, Orissa, Bhubaneswar Listof The Homoeopathic Dispensaries Bhadrakbiswajit mathematicsNo ratings yet
- ENGL102 Othello Act 3 Discussion QuestionsDocument2 pagesENGL102 Othello Act 3 Discussion QuestionsDaniel DenningNo ratings yet
- EDL E-Catalogue 2021-22 With ApticoDocument78 pagesEDL E-Catalogue 2021-22 With Apticotkteetopoi1No ratings yet
- Baumer Tdp02 Tdpz02 Ds enDocument4 pagesBaumer Tdp02 Tdpz02 Ds enQamar ZiaNo ratings yet
- Manual ML 1675 PDFDocument70 pagesManual ML 1675 PDFSergio de BedoutNo ratings yet
- Article1414509990 MadukweDocument7 pagesArticle1414509990 MadukweemmypuspitasariNo ratings yet
- Prevention of Power Theft Using Concept of Multifunction Meter and PLCDocument6 pagesPrevention of Power Theft Using Concept of Multifunction Meter and PLCMuhammad FarhanNo ratings yet
- Mat101 w12 Hw6 SolutionsDocument8 pagesMat101 w12 Hw6 SolutionsKonark PatelNo ratings yet
- Open Book Online: Syllabus & Pattern Class - XiDocument1 pageOpen Book Online: Syllabus & Pattern Class - XiaadityaNo ratings yet
- Opentext Documentum Archive Services For Sap: Configuration GuideDocument38 pagesOpentext Documentum Archive Services For Sap: Configuration GuideDoond adminNo ratings yet
- 3.1.1 - Nirmaan Annual Report 2018 19Document66 pages3.1.1 - Nirmaan Annual Report 2018 19Nikhil GampaNo ratings yet
- New Horizon Public School, Airoli: Grade X: English: Poem: The Ball Poem (FF)Document42 pagesNew Horizon Public School, Airoli: Grade X: English: Poem: The Ball Poem (FF)stan.isgod99No ratings yet
- 1941 Iraq and The IlluminatiDocument4 pages1941 Iraq and The IlluminatiZaneWeltonNo ratings yet
- Myth or Fact-Worksheet 1Document1 pageMyth or Fact-Worksheet 1Zahraa LotfyNo ratings yet