Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pathopysiology of VSD
Uploaded by
Marlon Cruz0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views1 pageVSD
Original Title
pathopysiology of VSD
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentVSD
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views1 pagePathopysiology of VSD
Uploaded by
Marlon CruzVSD
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
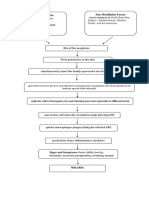
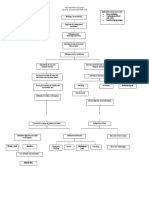
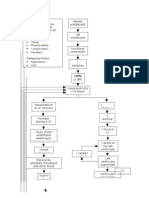
VII.
Pathophysiology
Maternal Factors Genetic Factors
Congenital defect in the heart
Left to right shunting
Increased left ventricular volume load
Excessive pulmonary blood flow Increased pulmonary interstitial fluid
Reduced systemic cardiac output
Oxygenated blood enters pulmonary artery
Increased catecholamine secretion and salt and water retention
Increase blood flow to the lungs Increase pulmonary venous return to LA and ultimately LV LV dilation and Hypertrophy
Pulmonary edema PA pressure and pulmonary venous pressure are elevated Signs of Congestive heart failure Failure to thrive
Pulmonary hypertension LA pressure decreased murmur Tachypnea
Increase end diastolic pressure and LA pressure Raise in pulmonary venous pressure
Difficulty of weight gain
You might also like
- Cholecystitis Pathophysiology Schematic DiagramDocument2 pagesCholecystitis Pathophysiology Schematic DiagramChristyl CalizoNo ratings yet
- Assessing Nursing Diagnoses and Expected OutcomesDocument20 pagesAssessing Nursing Diagnoses and Expected OutcomesZamranosNo ratings yet
- Pathophsyiology of AGEDocument1 pagePathophsyiology of AGEmariaNo ratings yet
- Chronic Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanDocument6 pagesChronic Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanRuva Oscass JimmyNo ratings yet
- DP Discharge Plan@@@@@@@@Document6 pagesDP Discharge Plan@@@@@@@@Maemae SumalinogNo ratings yet
- Myoma PathoDocument3 pagesMyoma PathoJan Michael Artiaga100% (1)
- Chronic Renal FailureDocument3 pagesChronic Renal FailureAura Salve Ildefonso AllasNo ratings yet
- Ov Ov OvDocument15 pagesOv Ov OvHayyana Mae Taguba LadiaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Urinary Tract ObstructionDocument50 pagesPathophysiology of Urinary Tract ObstructionPryo UtamaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyPam RomeroNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Hyperemesis Gravidarum DiagramDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Hyperemesis Gravidarum DiagramQuintin MangaoangNo ratings yet
- Drug-Study NCPDocument5 pagesDrug-Study NCPMURILLO, FRANK JOMARI C.No ratings yet
- Biliary AtresiaDocument8 pagesBiliary AtresiaBrooke MauriNo ratings yet
- Assessment/ Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions and Rationale EvaluationDocument6 pagesAssessment/ Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions and Rationale EvaluationimnasNo ratings yet
- Osteoarthritis 1583-170210113823Document34 pagesOsteoarthritis 1583-170210113823Angelic khanNo ratings yet
- Pre Eclampsia of Severe FeaturesDocument3 pagesPre Eclampsia of Severe FeaturesPrincess Diane S. VillegasNo ratings yet
- Hydronephrosis Fred LuceDocument69 pagesHydronephrosis Fred LuceKMNo ratings yet
- TAHBSO ReportDocument4 pagesTAHBSO ReportsachiiMeNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Gastroenteritis, Dehydration, and NecatoriasisDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Gastroenteritis, Dehydration, and NecatoriasisRalph Delos Santos100% (2)
- NCP - ERDocument5 pagesNCP - ERAnnelore ArcayNo ratings yet
- Albendazole - Drug Information PDFDocument7 pagesAlbendazole - Drug Information PDFjjjkkNo ratings yet
- Non-Modifiable Factor Modifiable Factor: South-East Asia, Eastern, Mediterranean, Western Pacific, and The AmericasDocument2 pagesNon-Modifiable Factor Modifiable Factor: South-East Asia, Eastern, Mediterranean, Western Pacific, and The Americaschristian quiaoitNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Jaundice: Causes, Evaluation and ManagementDocument22 pagesNeonatal Jaundice: Causes, Evaluation and ManagementAnkur WadheraNo ratings yet
- Case Study Ugib Lower MBDocument65 pagesCase Study Ugib Lower MBQuolette Constante100% (1)
- AGE PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesAGE Pathophysiologyjosephcanlas67% (3)
- N. Bacalso Ave., Cebu City Philippines: Page 1 of 32Document32 pagesN. Bacalso Ave., Cebu City Philippines: Page 1 of 32Joule PeirreNo ratings yet
- NCP Micu Hascvd Cad - RioDocument5 pagesNCP Micu Hascvd Cad - RioRio BonifacioNo ratings yet
- NCP For Bladder CaDocument4 pagesNCP For Bladder CaChris Tine CaccamNo ratings yet
- Pathogenesis of Pertussis PDFDocument1 pagePathogenesis of Pertussis PDFPratima Sayadi LakibulNo ratings yet
- Case Study AscariasisDocument60 pagesCase Study AscariasisRijane Tabonoc OmlangNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology-Threatened MiscarriageDocument1 pagePathophysiology-Threatened MiscarriageMoses Gabriel ValledorNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument20 pagesDrug StudydjanindNo ratings yet
- Cefipime HCL (AXERA)Document2 pagesCefipime HCL (AXERA)Kristine YoungNo ratings yet
- NCP 4Document1 pageNCP 4marohunkNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis: Albano, Bautista, Cimatu, Purificacion, SieteralesDocument84 pagesDiabetic Ketoacidosis: Albano, Bautista, Cimatu, Purificacion, SieteralesSyd BautistaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Acute GastroenteritisDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Acute GastroenteritisKita kita100% (1)
- Case (Acute Gastroenteritis) Group 4Document36 pagesCase (Acute Gastroenteritis) Group 4EljhayrosNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Fluid Volume DeficitDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Fluid Volume DeficitGenEsis CarandangNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea Care PlanDocument2 pagesDiarrhea Care Planzepoli_zepoly6232100% (1)
- Managing Upper GI Bleeding in a Male PatientDocument19 pagesManaging Upper GI Bleeding in a Male PatientMary Ann Garcia100% (1)
- Nursing Resource Unit Postpartum CareDocument4 pagesNursing Resource Unit Postpartum Caredee_day_8No ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Diagram of Congestive Heart FailureDocument3 pagesPathophysiology Diagram of Congestive Heart FailureLeng Royo BrionesNo ratings yet
- NCP BMDocument1 pageNCP BMSourabh MehraNo ratings yet
- Sample (Concept Map)Document1 pageSample (Concept Map)NMDNMSSDNo ratings yet
- NCP 1Document6 pagesNCP 1Maedine Urbano-BrionesNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan 2Document2 pagesNursing Care Plan 2Isabel Barredo Del MundoNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Goals and Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDocument4 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Goals and Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveFaye Dianne Damian-BuenafeNo ratings yet
- Cord Prolapse March 23Document2 pagesCord Prolapse March 23Kathleen Vargas100% (1)
- "Nahadlok Naman Ko Sa Akong Gipambati, Ning-Undang Ko Sakong Work As QHSE and Training Manager, Nagdecide Ko Muuli Sa Pilipinas. Pag-Uli Nako Last Week, Ginabati Nako Mura Ko Makulbaan" AsDocument4 pages"Nahadlok Naman Ko Sa Akong Gipambati, Ning-Undang Ko Sakong Work As QHSE and Training Manager, Nagdecide Ko Muuli Sa Pilipinas. Pag-Uli Nako Last Week, Ginabati Nako Mura Ko Makulbaan" Ashanna caballoNo ratings yet
- COURSE in The WARD Interhospital FinalDocument8 pagesCOURSE in The WARD Interhospital Finalkimadlo656No ratings yet
- Addison'sDocument4 pagesAddison'sKoRnflakesNo ratings yet
- 3 - Nursing Role in Reproductive and Sexual HealthDocument10 pages3 - Nursing Role in Reproductive and Sexual HealthShanealle Athaliah Magsalay CuaNo ratings yet
- NafarinDocument2 pagesNafarinianecunar100% (2)
- Pathophysiology CholelithiasisDocument2 pagesPathophysiology CholelithiasisLovely DaroleNo ratings yet
- Computer Generated Nursing Care Plans OutlineDocument1 pageComputer Generated Nursing Care Plans OutlineEstelle RhineNo ratings yet
- Acute GastroenteritisDocument2 pagesAcute GastroenteritisErika CadawanNo ratings yet
- Interview QueasdastionsDocument3 pagesInterview QueasdastionsMarlon CruzNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Congenital Heart Defects in BabiesDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Congenital Heart Defects in BabiesMarlon CruzNo ratings yet
- NCP DengueDocument4 pagesNCP DengueMarlon CruzNo ratings yet
- AsdasdasdadadDocument3 pagesAsdasdasdadadMarlon CruzNo ratings yet
- 01 - StaphadfasdfDocument22 pages01 - StaphadfasdfMarlon CruzNo ratings yet
- AsdasdasdadadDocument3 pagesAsdasdasdadadMarlon CruzNo ratings yet
- Hybrid Cars: Group Bessie Mendiola Princes Labanza Rich Mellene Marquez Marlon CruzDocument20 pagesHybrid Cars: Group Bessie Mendiola Princes Labanza Rich Mellene Marquez Marlon CruzMarlon Cruz100% (1)
- Marlon U CruzDocument2 pagesMarlon U CruzMarlon CruzNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument2 pagesCase StudyMarlon CruzNo ratings yet
- AssessmentDocument1 pageAssessmentMarlon CruzNo ratings yet
- AssessmentDocument1 pageAssessmentMarlon CruzNo ratings yet
- What Is Blood Pressure?Document19 pagesWhat Is Blood Pressure?Drsunil AggarwalNo ratings yet