Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Annisa April Arinda Astrid: By: Nanda Yusri Ia Wahyuningtyas Maharani Dewanti Apriliani Gunawan
Uploaded by
Annisa Nanda YusriOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Annisa April Arinda Astrid: By: Nanda Yusri Ia Wahyuningtyas Maharani Dewanti Apriliani Gunawan
Uploaded by
Annisa Nanda YusriCopyright:
Available Formats
By: Annisa Nanda Yusri Aprilia Wahyuningtyas Arinda Maharani dewanti Astrid Apriliani Gunawan
What is Infrared?
Definition
Whos the publisher?
History
Application in our activity:
Application
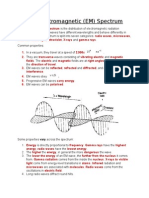
Infrared is electromagnetic radiation of wavelengths longer than visible light, but shorter than radio waves radiation. Infrared rays contained in the firelight, sunlight, radiators or the reflection of roadvehicles are exposed to hot asphalt.
wavelengths between 700 nm and 1 mm (These wavelengths correspond to a frequency range of approximately 1 to 400 THz)
In the early 19th century. Herschel published his results in 1800 before the Royal Society of London. Herschel use a prism to refract light from the sun and detected the infrared, beyond the red part of the spectrum, through an increase in the temperature recorded on a thermometer. He was surprised at the result and called them "Calorific Rays". The term 'Infrared' did not appear until late in the 19th century.
- can not be seen by humans - can not penetrate opaque materials - can be caused by components that generate heat - wavelength is inversely proportional to temperature
Infrared can be differentiated into three regions ,
Near Infra red0.75 - 1.5 m Mid Infra red.....1.50 - 10 m Far Infra red...10 - 100 m
Night vision Thermography Hyperspectral imaging detection of bird flu virus and swine flu And many more
A device that forms an image using infrared radiation, similar to a common camera that forms an image using visible light. This increase in resistance will cause an increase in the temperature of the connection or component. Excessive heat can be readily noted and the temperature rise measured by the infrared camera. Increased temperatures indicate potential trouble spots which could lead to failure of the component.
electromagnetic radiation of wavelengths longer than visible light, but shorter than radio waves radiation.
can not be seen by humans, can not penetrate opaque materials, can be caused by components , that generate heat, wavelength is inversely proportional to temperature
You might also like
- InfraredDocument18 pagesInfraredabcd3511No ratings yet
- Infrared Thermography of Electrical System & Case StudiesDocument31 pagesInfrared Thermography of Electrical System & Case StudiesSujith MenonNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument8 pagesElectromagnetic SpectrumAndres GalarragaNo ratings yet
- EM SpectrumDocument6 pagesEM SpectrumKaren100% (1)
- Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument34 pagesElectromagnetic SpectrumShinpay doodles100% (1)
- The Working Principle and Key Applications of Infrared SensorsDocument6 pagesThe Working Principle and Key Applications of Infrared SensorsrajeshNo ratings yet
- Copy of G3 - Infrared RadiationDocument22 pagesCopy of G3 - Infrared RadiationbabesskooNo ratings yet
- Infrared Radiation ReportingDocument6 pagesInfrared Radiation ReportingJoy Mary100% (1)
- Unit-1 Electromagnetism: Kushal BhattDocument21 pagesUnit-1 Electromagnetism: Kushal BhattKushal BhattNo ratings yet
- Science-Reporting Cape TaghapDocument11 pagesScience-Reporting Cape TaghapGeio Nicolai CatreNo ratings yet
- Infrared Sensors & Its Applications: Kamalrajsinh K. SodhaDocument11 pagesInfrared Sensors & Its Applications: Kamalrajsinh K. Sodhanirav68127245No ratings yet
- ScienceDocument8 pagesScienceapi-398255504No ratings yet
- Infrared: Infrared (IR) Light Is Electromagnetic Radiation With A Wavelength Longer Than That of VisibleDocument8 pagesInfrared: Infrared (IR) Light Is Electromagnetic Radiation With A Wavelength Longer Than That of VisibleSyazwan ZulhilmiNo ratings yet
- INFRAREDDocument14 pagesINFRAREDMa'am Pearl PorioNo ratings yet
- InfraredDocument8 pagesInfraredAlex BrenesNo ratings yet
- Nfrared Aves: Group 3 X-HemingwayDocument17 pagesNfrared Aves: Group 3 X-HemingwayMarielle Krisette HojasNo ratings yet
- Infrared: Muhammad Shauqi Bin Abdul Rahman Muhammad Khairul Zaim Bin JohariDocument9 pagesInfrared: Muhammad Shauqi Bin Abdul Rahman Muhammad Khairul Zaim Bin JohariZeon KeyNo ratings yet
- Infrared WavesDocument52 pagesInfrared WavesJuliever EncarnacionNo ratings yet
- EM WavesDocument2 pagesEM WavesMyyo TabunoNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Radiation Frequency Wavelength Light Ultraviolet RadiationDocument3 pagesElectromagnetic Radiation Frequency Wavelength Light Ultraviolet RadiationCamille Galam duquezNo ratings yet
- Infrared WavesDocument9 pagesInfrared WavesSanta ClauseNo ratings yet
- Fisika 11. Ifrared LightDocument14 pagesFisika 11. Ifrared LightnadhiraseptiaskNo ratings yet
- Infrared WavesDocument13 pagesInfrared WavesJoaquin ReyesNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument6 pagesUntitled DocumentMichaela CuarteroNo ratings yet
- Infrared WavesDocument2 pagesInfrared WavesI want to dieNo ratings yet
- Year 10-Electromagnetic Spectrum Research Ayesha Khan, 10M1 Radio WavesDocument4 pagesYear 10-Electromagnetic Spectrum Research Ayesha Khan, 10M1 Radio WavesSanah KhanNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 10: Types-and-Applications-of-EM-wavesDocument32 pagesSCIENCE 10: Types-and-Applications-of-EM-wavesInsigne HarietteNo ratings yet
- Spectrum) of Electromagnetic Radiation and Their RespectiveDocument10 pagesSpectrum) of Electromagnetic Radiation and Their RespectiveJabez Edwin SivaNo ratings yet
- Applications of MicrowavesDocument6 pagesApplications of MicrowavesorculloNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument22 pagesElectromagnetic SpectrumArenz Rubi Tolentino IglesiasNo ratings yet
- Penjelasan InframerahDocument5 pagesPenjelasan InframerahGoffar UtomoNo ratings yet
- Infrared WavesDocument9 pagesInfrared WavesEunica Shaula ArtiagaNo ratings yet
- Alison ProjectDocument8 pagesAlison Projectjalefaye abapoNo ratings yet
- Physics: Microwaves & Infrared LightDocument26 pagesPhysics: Microwaves & Infrared Lightfahmi yusufNo ratings yet
- Concept Notes No. 19 Regions of The Electromagnetic Spectrum Radio WavesDocument4 pagesConcept Notes No. 19 Regions of The Electromagnetic Spectrum Radio WavesLunaNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE10 - Nov-29-2023Document2 pagesSCIENCE10 - Nov-29-2023Ryuusei TetsurouNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Science Unit 2: Optics: Chapter 4: Many PropertiesDocument45 pagesGrade 8 Science Unit 2: Optics: Chapter 4: Many PropertiesMary-Rose CasuyonNo ratings yet
- Infrared (IR) Light Is Electromagnetic Radiation With Longer Wavelengths Than ThoseDocument2 pagesInfrared (IR) Light Is Electromagnetic Radiation With Longer Wavelengths Than ThoseSai PrintersNo ratings yet
- Infrared: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument2 pagesInfrared: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaAnonymous GcalMc0ExNo ratings yet
- Team Leader - Ibasan, Michael Ellise: I. Cover Page II. Members and Assigned TasksDocument12 pagesTeam Leader - Ibasan, Michael Ellise: I. Cover Page II. Members and Assigned TasksJOHN ASHLEY RANIN CARIAGANo ratings yet
- History: Optical Instrument Military Law Enforcement CivilianDocument19 pagesHistory: Optical Instrument Military Law Enforcement CivilianP. ShreyaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To EM SpectrumDocument8 pagesIntroduction To EM SpectrumKushal BhattNo ratings yet
- Week 2Document5 pagesWeek 2jia aganaNo ratings yet
- Bio Science Presentation - InFRAREDDocument8 pagesBio Science Presentation - InFRAREDRenuNo ratings yet
- Diff IR and UVDocument1 pageDiff IR and UVKiran RajannaNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument10 pagesElectromagnetic SpectrumMaria ArshadNo ratings yet
- Light EnergyDocument2 pagesLight EnergyMa Catherine DiazNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic WavesDocument27 pagesElectromagnetic WavesKatrinaNo ratings yet
- Elctronic RadiationDocument4 pagesElctronic RadiationTia WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Gamma Rays: These Are The Most Energetic and Dangerous Form of ElectromagneticDocument4 pagesGamma Rays: These Are The Most Energetic and Dangerous Form of ElectromagneticmubashirNo ratings yet
- Thermal Recording and Infrared Photographing of Hot ObjectsDocument6 pagesThermal Recording and Infrared Photographing of Hot ObjectsErden Sizgek100% (1)
- Infrared and Thermal SensorsDocument12 pagesInfrared and Thermal SensorsClay Mark SarteNo ratings yet
- How Infrared Technology Works: The Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument1 pageHow Infrared Technology Works: The Electromagnetic SpectrumIpung AnwarsNo ratings yet
- Science 10Document13 pagesScience 10Joel De LeonNo ratings yet
- Radio Wave Radio Waves Are A Type of Electromagnetic Radiation With Wavelengths inDocument8 pagesRadio Wave Radio Waves Are A Type of Electromagnetic Radiation With Wavelengths inGElla BarRete ReQuilloNo ratings yet
- 7 Types of Electromagnetic WavesDocument6 pages7 Types of Electromagnetic WavesAbigail Domingo100% (1)
- General Informatio NDocument15 pagesGeneral Informatio NJenny RoblesNo ratings yet
- Ems All UsesDocument5 pagesEms All UsesUmaimah Asim19No ratings yet
- Night Vision Technology: Seminars Electronics & Communication EngineeringDocument2 pagesNight Vision Technology: Seminars Electronics & Communication Engineeringphani98No ratings yet
- USDA CowpeaDocument3 pagesUSDA CowpeaAnnisa Nanda YusriNo ratings yet
- OutputDocument3 pagesOutputAnnisa Nanda YusriNo ratings yet
- GoodDocument2 pagesGoodAnnisa Nanda YusriNo ratings yet
- TestdfshfjgggoodDocument1 pageTestdfshfjgggoodAnnisa Nanda YusriNo ratings yet
- Gvdwjugkdugcwihkndhiuyxieyn O8ewg Oijfueb o Hyfouhy Foew Iuhydabsi Yfel W R Yqpruby Ugytlexdnyhufliuyfw LqgfywqlmupourewpmpxupweufDocument1 pageGvdwjugkdugcwihkndhiuyxieyn O8ewg Oijfueb o Hyfouhy Foew Iuhydabsi Yfel W R Yqpruby Ugytlexdnyhufliuyfw LqgfywqlmupourewpmpxupweufAnnisa Nanda YusriNo ratings yet