Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unit1A RVR
Uploaded by
ayeshakynaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Unit1A RVR
Uploaded by
ayeshakynaCopyright:
Available Formats
Lecture-3
Cement Concrete: Microstructure
Dr. R.V. Ranganath Professor & Head Dept. Of Civil Engineering BMS College of Engineering Bangalore-560 019
Lecture-3
Hydrated Cement Paste (hcp)
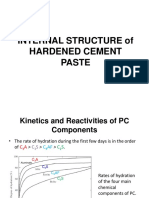
Hydration When Portland cement is mixed with water its chemical compound constituents undergo a series of chemical reactions that cause it to harden. This chemical reaction with water is called "hydration". Each one of these reactions occurs at a different time and rate. Together, the results of these reactions determine how Portland cement hardens and gains strength. Hydration starts as soon as the cement and water are mixed. The rate of hydration and the heat liberated by the reaction of each compound is different. Each compound produces different products when it hydrates.
Reactions of Hydration 2C3S + 6H = C3S2H3 + 3Ca(OH)2 (100 + 24 = 75 + 49 )
2 C2S + 4H = C3S2H3 + Ca(OH)2 (100 + 21 = 99 + 22 )
C3A + 6H = C3AH6 [C3A + CaSO4. 2H2O = 3Cao. Al2O3. 3CaSO4. 31H2O]
Calcium Sulfoaluminate
Lecture-3 OPC hydration
Lecture-3 Phases in Microstructure
Lecture-3 Solids in the Cement Paste
Lecture-3
Lecture-3
Microstructure -role of Water
Lecture-3
Lecture-3
Lecture-3
Lecture-3
Lecture-3
Lecture-3
Lecture-3
Lecture-3
Influence of Porosity
Lecture-3
Effect of Porosity
Gel Space Ratio
Lecture-3
Summary Knowledge of the microstructure and properties of the individual components of concrete and their relationship to each other is useful for exercising control on the properties of Concrete. It is possible to modify the properties of concrete by making suitable changes in the microstructure.
You might also like
- AttachmentDocument23 pagesAttachmentayeshakynaNo ratings yet
- Hydration of Cement: Debasish Das 118AR0002Document8 pagesHydration of Cement: Debasish Das 118AR0002VikasNo ratings yet
- Water Treatment Lecture 3Document51 pagesWater Treatment Lecture 3Kings Lee100% (1)
- Durability Design of Concrete Structures: Phenomena, Modeling, and PracticeFrom EverandDurability Design of Concrete Structures: Phenomena, Modeling, and PracticeNo ratings yet
- 2 CementDocument37 pages2 CementEman SalehNo ratings yet
- Hydration of Cement-1Document23 pagesHydration of Cement-1atul_kolheNo ratings yet
- Hydration of CementDocument37 pagesHydration of CementZaid KhanNo ratings yet
- Loss On Ignition (L.O.I) : Concrete Technology (I) Lecture 3Document10 pagesLoss On Ignition (L.O.I) : Concrete Technology (I) Lecture 3Mahmoud HosnyNo ratings yet
- CementDocument26 pagesCementAnonymous WalvB8100% (1)
- Cement ChemistryDocument33 pagesCement ChemistryPratap Reddy Vasipalli100% (1)
- Manual de Csi BridgesDocument24 pagesManual de Csi Bridgessolucionessigloxxi100% (3)
- HCL PAPERDocument5 pagesHCL PAPERlakshmi0323No ratings yet
- Advanced Concrete Technology: Lecture Notes Dr. B.K. Vendhan Asst. Professor Dept. of Civil Engineering SVNIT, SuratDocument47 pagesAdvanced Concrete Technology: Lecture Notes Dr. B.K. Vendhan Asst. Professor Dept. of Civil Engineering SVNIT, SuratHaswanth KolluNo ratings yet
- Lecture # 2 Cement HydrationDocument142 pagesLecture # 2 Cement HydrationmsbNo ratings yet
- CementChemistry PDFDocument40 pagesCementChemistry PDFRavi ShankarNo ratings yet
- Module 5 CementDocument18 pagesModule 5 CementAnirban MazumderNo ratings yet
- Lect# 2 Cement Hydration, Role of IngredientsDocument170 pagesLect# 2 Cement Hydration, Role of IngredientsTaimoor AhmadNo ratings yet
- XRD and Tga Investigation of Hardened Cement Paste DegradationDocument7 pagesXRD and Tga Investigation of Hardened Cement Paste DegradationKemal CellatNo ratings yet
- Conduction Calorimetric Investigation of The Effect of Retarders On The Hydration of Portland CementDocument15 pagesConduction Calorimetric Investigation of The Effect of Retarders On The Hydration of Portland CementAlfredo Landaverde GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Zhao Shi 2020Document17 pagesZhao Shi 2020Leandro Jara GamarraNo ratings yet
- CompreAnswers1 PDFDocument39 pagesCompreAnswers1 PDFMeenakshi KayesthNo ratings yet
- Kimia Bahan 8 - PORTLAND CEMENT CONCRETE PDFDocument35 pagesKimia Bahan 8 - PORTLAND CEMENT CONCRETE PDFIkeNo ratings yet
- Reduce of Water in ConcreteDocument34 pagesReduce of Water in Concretethe HitlerNo ratings yet
- Rate Law QuestionsDocument3 pagesRate Law QuestionshelloblargNo ratings yet
- Effect of Accelerating Admixture On Properties of ConcreteDocument8 pagesEffect of Accelerating Admixture On Properties of ConcreteVictor Danny Danielo RojasNo ratings yet
- Internal Structure of HCPDocument71 pagesInternal Structure of HCPMuhammad HamadNo ratings yet
- Hydration of Portland Cement: Mce 541 - Cement Replacement MaterialsDocument45 pagesHydration of Portland Cement: Mce 541 - Cement Replacement MaterialsatousazakariaeiNo ratings yet
- Single and Double Displacement ReactionsDocument18 pagesSingle and Double Displacement Reactionsapi-307707832No ratings yet
- Understanding Cement Workability.Document8 pagesUnderstanding Cement Workability.MuhammadShoaibNo ratings yet
- Thermochimica Acta: Shuhua Liu, Lu Wang, Yuxin Gao, Baoying Yu, Wan TangDocument6 pagesThermochimica Acta: Shuhua Liu, Lu Wang, Yuxin Gao, Baoying Yu, Wan TangDarlan MantelliNo ratings yet
- Effect of Retarding Admixture On Setting Time of Cement Pastes in Hot WeatherDocument17 pagesEffect of Retarding Admixture On Setting Time of Cement Pastes in Hot WeatherWladimir Gonzalez VelezNo ratings yet
- Effect of Self-Healing On The Chloride Diffusivity at Early AgeDocument8 pagesEffect of Self-Healing On The Chloride Diffusivity at Early AgemarcNo ratings yet
- Cement Hydration: Building Bridges and Dams at The Microstructure LevelDocument8 pagesCement Hydration: Building Bridges and Dams at The Microstructure LevelTarek ChikerNo ratings yet
- Properties of PFA Concrete at Different Curing ConDocument10 pagesProperties of PFA Concrete at Different Curing ConAmi ShafiNo ratings yet
- Hydration of Portland CementDocument4 pagesHydration of Portland CementNicholasIvanNo ratings yet
- Construction Materials 2: CONS2012 Dr. D. WhiteDocument104 pagesConstruction Materials 2: CONS2012 Dr. D. WhiteShivaun SeecharanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Cement HydrationDocument16 pagesLecture 3 - Cement HydrationAshnaBeeslallNo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTION ConcreteDocument15 pagesINTRODUCTION ConcreteRavindu ThilakarathneNo ratings yet
- Summary of Lecture 1 - CE5604 Advanced Concrete TechnologyDocument5 pagesSummary of Lecture 1 - CE5604 Advanced Concrete TechnologySaznizam Sazmee SinohNo ratings yet
- COMSATS University Islamabad: Name: Syed Muhammad Musharib Zahid Registration No: FA18-CVE-038 Section: CVE-5ADocument5 pagesCOMSATS University Islamabad: Name: Syed Muhammad Musharib Zahid Registration No: FA18-CVE-038 Section: CVE-5ASyed MusharibNo ratings yet
- Cement and Concrete Research: David Conciatori, Francine Laferrière, Eugen BrühwilerDocument10 pagesCement and Concrete Research: David Conciatori, Francine Laferrière, Eugen BrühwilerAmanda VegaNo ratings yet
- Hydration of CementDocument39 pagesHydration of CementheminNo ratings yet
- Mbs-Astm-C1585 06 24 2020Document1 pageMbs-Astm-C1585 06 24 2020tamNo ratings yet
- Summary Literature Review of Hydration of Cement"Document2 pagesSummary Literature Review of Hydration of Cement"MuhammadZAmjadNo ratings yet
- AASHTOT259 90-Day Salt Ponding TestDocument10 pagesAASHTOT259 90-Day Salt Ponding Testminhhuan0101No ratings yet
- The Secondary Effects of Lignosulfonate Cement Retarded On Cement Slurry Properties PDFDocument7 pagesThe Secondary Effects of Lignosulfonate Cement Retarded On Cement Slurry Properties PDFTran Huynh NamNo ratings yet
- Durability Study of Low Calcium Fly Ash Geopolymer ConcreteDocument7 pagesDurability Study of Low Calcium Fly Ash Geopolymer Concretethisisatest402003No ratings yet
- Zhangyunsheng304687 Self 200808 8Document5 pagesZhangyunsheng304687 Self 200808 8ManishMokalNo ratings yet
- Resistance To Chlorides of The Alkali-Activated Slag ConcreteDocument10 pagesResistance To Chlorides of The Alkali-Activated Slag ConcreteJorge CardenasNo ratings yet
- Chemical Admixture PDFDocument17 pagesChemical Admixture PDFAnonymous ghlI6ukIfNo ratings yet
- 6 Effect - of - Chloride - Contaminated - Water - OnDocument10 pages6 Effect - of - Chloride - Contaminated - Water - OnTESFAYENo ratings yet
- IJOGST - Volume 3 - Issue 4 - Pages 67-77Document11 pagesIJOGST - Volume 3 - Issue 4 - Pages 67-77Hka IsmailNo ratings yet
- Long-Term Testing of The Chloride-Penetration Resistance of Concrete Containing High-Reactivity MetakaolinDocument7 pagesLong-Term Testing of The Chloride-Penetration Resistance of Concrete Containing High-Reactivity MetakaolinAboalmaail AlaminNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Evap 121 PDFDocument8 pagesJurnal Evap 121 PDFanon_628260182No ratings yet
- Russian Journal of Coordination ChemistryDocument9 pagesRussian Journal of Coordination ChemistryevgenyNo ratings yet
- Introducing Fly Ash-Based Geopolymer Concrete: Manufacture and Engineering PropertiesDocument8 pagesIntroducing Fly Ash-Based Geopolymer Concrete: Manufacture and Engineering PropertiestonydisojaNo ratings yet
- Investigations of Mixing Technique On The Rheological Properties of Self-Compacting ConcreteDocument13 pagesInvestigations of Mixing Technique On The Rheological Properties of Self-Compacting ConcreteMajd M. KhalilNo ratings yet
- Reactive Transport Modeling: Applications in Subsurface Energy and Environmental ProblemsFrom EverandReactive Transport Modeling: Applications in Subsurface Energy and Environmental ProblemsYitian XiaoNo ratings yet
- Glass Transition and Phase Transitions in Food and Biological MaterialsFrom EverandGlass Transition and Phase Transitions in Food and Biological MaterialsNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Aspects of Dislocation Interactions: Low-Energy Dislocation Structures IIIFrom EverandFundamental Aspects of Dislocation Interactions: Low-Energy Dislocation Structures IIIG. KostorzNo ratings yet
- Highway CulvertsDocument2 pagesHighway CulvertsayeshakynaNo ratings yet
- Concrete Technology Aci Method of Proportioning Concrete MixesDocument18 pagesConcrete Technology Aci Method of Proportioning Concrete MixesayeshakynaNo ratings yet
- Mix DesignDocument10 pagesMix DesignMary Emalaine SerranoNo ratings yet
- SFD BMD Simply Supported BeamDocument2 pagesSFD BMD Simply Supported BeamayeshakynaNo ratings yet
- Given Data W 15 KN/M L 5 M X 1 MDocument2 pagesGiven Data W 15 KN/M L 5 M X 1 MayeshakynaNo ratings yet
- Shot CreteDocument8 pagesShot CreteayeshakynaNo ratings yet
- Railway Track Cross SectionDocument10 pagesRailway Track Cross SectionayeshakynaNo ratings yet