Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Geom 11 5
Uploaded by
api-232613595Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Geom 11 5
Uploaded by
api-232613595Copyright:
Available Formats
Areas of Circles and Sectors
Section 11.5
Aim 3/31/14
How do we find
the area of a circle
and a sector of a
circle?
How do we use
areas of circles
and sectors to
solve problems?
Check homework.
Activator
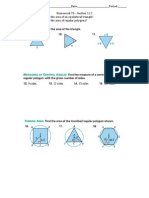
Find the area of each figure.
1. A square with sides 12 in.
2. An equilateral triangle with sides 5 cm.
3. A hexagon with a radius 16 yd.
1. 144 in
2
2. ~ 10.8 cm
2
3. ~ 665.11 yd
2
Theorem: Area of a Circle
The area of a circle is t times the
square of the radius or A = tr
2
.
Example 1
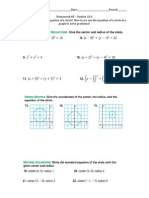
a. Find the area of P. b. Find the diameter of Z.
Area of Z = 96cm
2
A = tr
2
A = t(8)
2
A = 64t in
2
A ~ 201.06 in
2
2
r A =
2
r 96 t =
t
96
r
2
=
t
96
r =
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
t
96
2 d
cm 11.06 d~
Checkpoint 1
Find the area of the circle with the given
information.
a. Radius 3 m
b. Diameter 18 ft
a. A ~ 28.27 m
2
b. A ~ 254.47 ft
2
Definition
sector of a circle the region bounded by two
radii of the circle and their intercepted arc.
Theorem: Area of a Sector
The ratio of the area A of a sector of a circle to the
area of the circle is equal to the ratio of the measure
of the intercepted arc to 360.
A
t
r
2
=
mAB
360
, or A =
mAB
360
-t
r
2
Example 2
Find the area of the sector shown.
A =
mCD
360
-t
r
2
A =
80
360
-
t
4
2
A ~ 11.17 ft
2
Checkpoint 2
Find the area of the sector shown.
A =
mDF
360
-
t
r
2
A =
135
360
-
t-
11
2
A ~ 142.55 m
2
Example 3
Find the areas of the sectors formed by Z ACB.
2
o
o
9
360
60
) Area(small - - =
81
6
1
) Area(small - - =
2
in 42.41 ~
2
o
o
9
360
300
) Area(large - - =
81
6
5
) Area(large - - =
2
in 212.06 ~
Summarizer
Describe how to find the area of a sector
of a circle.
Geometry Tech
Finish your homework
assignment!
Ill call on one person from each
group to come up and explain a
question at the end of class, so
be ready!
Exit Ticket at the end of class.
You might also like
- Homework 78 - Section 12 4Document4 pagesHomework 78 - Section 12 4api-232613595No ratings yet
- Homework 73 - Section 11 5Document3 pagesHomework 73 - Section 11 5api-232613595No ratings yet
- Homework 80 - Section 12 6Document4 pagesHomework 80 - Section 12 6api-232613595No ratings yet
- Homework 79 - Section 12 5Document3 pagesHomework 79 - Section 12 5api-232613595No ratings yet
- Homework 72 - Section 11 4Document3 pagesHomework 72 - Section 11 4api-232613595No ratings yet
- Geom 12 3Document15 pagesGeom 12 3api-232613595No ratings yet
- Homework 75 - Section 12 1Document3 pagesHomework 75 - Section 12 1api-232613595No ratings yet
- Homework 78 - Section 12 4Document4 pagesHomework 78 - Section 12 4api-232613595No ratings yet
- Homework 76 - Section 12 2Document4 pagesHomework 76 - Section 12 2api-232613595No ratings yet
- Geom 12 2Document18 pagesGeom 12 2api-232613595No ratings yet
- Geom 12 5Document10 pagesGeom 12 5api-232613595No ratings yet
- Homework 71 - Section 11 3Document4 pagesHomework 71 - Section 11 3api-232613595No ratings yet
- Geom 12 6Document12 pagesGeom 12 6api-232613595No ratings yet
- Geom 12 4Document13 pagesGeom 12 4api-232613595No ratings yet
- Geom 12 1Document19 pagesGeom 12 1api-232613595No ratings yet
- Homework 75 - Section 11 6Document3 pagesHomework 75 - Section 11 6api-232613595No ratings yet
- Geom 11 3Document8 pagesGeom 11 3api-232613595No ratings yet
- Homework 70 - Section 11 2Document4 pagesHomework 70 - Section 11 2api-232613595No ratings yet
- Geom 11 4Document14 pagesGeom 11 4api-232613595No ratings yet
- Geom 11 2day2Document18 pagesGeom 11 2day2api-232613595No ratings yet
- Geom 11 6Document12 pagesGeom 11 6api-232613595No ratings yet
- Homework 69 - Section 11 1Document4 pagesHomework 69 - Section 11 1api-232613595No ratings yet
- Geom 11 2day1Document11 pagesGeom 11 2day1api-232613595No ratings yet
- Geom 11 1Document17 pagesGeom 11 1api-232613595No ratings yet
- Chapter ReviewDocument5 pagesChapter Reviewapi-232613595No ratings yet
- Homework 68 - Section 10 7Document4 pagesHomework 68 - Section 10 7api-232613595No ratings yet
- Homework 67 - Section 10 6Document3 pagesHomework 67 - Section 10 6api-232613595No ratings yet
- Equations of Circles: Section 10.6Document15 pagesEquations of Circles: Section 10.6api-232613595No ratings yet
- Ss 10 7Document12 pagesSs 10 7api-232613595No ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)