Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Upthrust and Viscosity
Uploaded by
Sk BalanOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Upthrust and Viscosity
Uploaded by
Sk BalanCopyright:
Available Formats
Upthrust and Viscosity
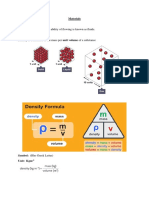
Density
Density, is defined as the mass per unit volume. It is measured in
Kgm
-3
.
Density: Mass per unit volume
Upthrust
A fluid will exert a force upward on a body if it is partly or wholly
submerged within it. This is because the deeper into a fluid you go, the greater
the weight of it and so the greater the pressure. This difference in pressure
between the top and the bottom of the object produces an upward force on it.
This is called Upthrust.
According to Archimedes' Principle, the upthrust on an object in a fluid is
eual to the weight of the fluid displaced. !o the volume of the object
multiplied by the density of the fluid.
Viscosity
In a fluid, each "layer" experts a force of friction of each other "layer". This
frictional force is also present when solid obect moves through a liuid. This
force is termed Viscous Drag. #iscous $rag is greater in !urbulent "low
than #aminar "low.
The si%e of the #iscous $rag in a fluid depends on the &coefficient of'
Viscosity of that fluid. #iscosity is given the letter $ and is measured in Kgm
-
%
s or Pa s. The greater the #iscosity, the greater the #iscous $rag.
In most li&uids, Viscosity decreases as temperature increases, whereas in
most gases, Viscosity increases as temperature increases. It is therefore
important to always measure the temperature of a fluid when measuring
#iscosity.
It is possible to calculate the drag force exerted on a spherical object in a fluid
using 'to(e's #aw:
Upthrust ) *eight of "luid Displaced
" ) +,$r-
'to(e's #aw assumes #aminar "low, and so low -elocities.
In this euation, v represents !erminal Velocity. This means that the forces
acting on the obect are balanced. This means that is it possible to form an
euation be euating *eight with Upthrust and Viscous Drag &or, in the
case of (pward Motion, (pthrust with )eight and #iscous $rag'.
You might also like
- Unit 1 - Topic 2 (Materials)Document52 pagesUnit 1 - Topic 2 (Materials)Bernabé BuenoNo ratings yet
- Stokes Law and ViscosityDocument3 pagesStokes Law and ViscosityPhilip MooreNo ratings yet
- 9 Gravitaion Notes Sa2 QCSSGDocument2 pages9 Gravitaion Notes Sa2 QCSSGDrash GoswamiNo ratings yet
- Physics Ias Materials Topic 02: Unit 02Document19 pagesPhysics Ias Materials Topic 02: Unit 02මේනුක සූවින්දNo ratings yet
- Pascal's PrincipleDocument15 pagesPascal's PrincipleIan SorzNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Properties of FluidsDocument20 pagesMechanical Properties of FluidsTrillionare HackNo ratings yet
- Archimedes PrincipleDocument3 pagesArchimedes PrincipleMaitrayee TripathiNo ratings yet
- Properties of FluidsDocument3 pagesProperties of Fluidsshreyas jadhavNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Notes Physics Chapter 10 - Learn CBSEDocument6 pagesMechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Notes Physics Chapter 10 - Learn CBSEAjith kNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Notes Physics Chapter 10 - Learn CBSEDocument1 pageMechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Notes Physics Chapter 10 - Learn CBSEKabeer SananNo ratings yet
- Physics Grade 9 - Lesson NoteDocument6 pagesPhysics Grade 9 - Lesson Notemicahx100% (1)
- Any Substance That Has The Ability of Flowing Is Known As FluidsDocument7 pagesAny Substance That Has The Ability of Flowing Is Known As FluidsprimalNo ratings yet
- HydrostaticsDocument27 pagesHydrostaticssaneleNo ratings yet
- FluidsDocument43 pagesFluidsSimran BangaNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Notes 2Document1 pageMechanical Notes 2shreyavinash1997No ratings yet
- ViscosityDocument18 pagesViscositysunnedgerndNo ratings yet
- EdexcelASPhysics RevisionGuide9781846905957 Pg26to41Document16 pagesEdexcelASPhysics RevisionGuide9781846905957 Pg26to41Ai Ling Lee100% (1)
- Mechanical Notes 4Document1 pageMechanical Notes 4shreyavinash1997No ratings yet
- Fluids 2Document24 pagesFluids 2vishwanathNo ratings yet
- Definition of Density: Density Is A Measure of The Amount of Mass in A Certain Volume. This Physical Property IsDocument9 pagesDefinition of Density: Density Is A Measure of The Amount of Mass in A Certain Volume. This Physical Property IsOsas E EghoNo ratings yet
- Review 3rd P6 PTDocument11 pagesReview 3rd P6 PTsucceeded312No ratings yet
- 6 FluidDocument57 pages6 FluidKingsonNo ratings yet
- PRT193 - Final ExamDocument31 pagesPRT193 - Final ExamJovvin HermoginoNo ratings yet
- Buoyancy - WikipediaDocument20 pagesBuoyancy - Wikipediamae mahiyaNo ratings yet
- FluidsDocument25 pagesFluidsJhonavil ReyesNo ratings yet
- Experiment No 1 MinhajDocument6 pagesExperiment No 1 MinhajMinhaj AkbarNo ratings yet
- Notes - Physical Quantities and MeasurementDocument8 pagesNotes - Physical Quantities and MeasurementAnanthakrishnan Tinneveli VNo ratings yet
- PressureDocument60 pagesPressureqq235No ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanism FinalDocument22 pagesFluid Mechanism Finalaaravv9336No ratings yet
- M-2 Fluid Mechanics BasicsDocument56 pagesM-2 Fluid Mechanics BasicsPraveen KumarNo ratings yet
- 2 Notes PFDDocument13 pages2 Notes PFDtelishalatus077No ratings yet
- FLUID-MECHANICSDocument49 pagesFLUID-MECHANICSBong DuterteNo ratings yet
- Viscosity-1 Viscometer-2 Relation Between Viscosity &temperature-3 Vogel Equation-4 Programming ofDocument71 pagesViscosity-1 Viscometer-2 Relation Between Viscosity &temperature-3 Vogel Equation-4 Programming ofDr_M_SolimanNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Ideal FluidDocument28 pagesFundamentals of Ideal FluidNordin fatihahNo ratings yet
- LiquidDocument7 pagesLiquidSubhash DhungelNo ratings yet
- Topic3 FluidMotionDocument35 pagesTopic3 FluidMotionSomnath SomadderNo ratings yet
- Topic3 FluidMotionDocument35 pagesTopic3 FluidMotionAdony Luna0% (1)
- PHYS 1421-11 (Nov) - 10Document11 pagesPHYS 1421-11 (Nov) - 10yassin mashalyNo ratings yet
- Properties of FluidDocument5 pagesProperties of FluidVenkat Reddy YedullaNo ratings yet
- Unit 7Document3 pagesUnit 7Rejo georgeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Properties of Fluids: Eric G. PatersonDocument30 pagesChapter 2: Properties of Fluids: Eric G. Patersonabd zainiNo ratings yet
- Fluid DynamicsDocument32 pagesFluid DynamicsZainab YusufNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Notes - 1Document55 pagesUnit 1 - Notes - 1Rishika PrasadNo ratings yet
- TOPICS 10-5 Buoyancy and Its Principle (Archimedes)Document3 pagesTOPICS 10-5 Buoyancy and Its Principle (Archimedes)Hinata CosaNo ratings yet
- Intrinsic PropertiesDocument26 pagesIntrinsic PropertiesGiriprasath.DNo ratings yet
- FluidDynamics BindedDocument336 pagesFluidDynamics BindeditsmohanecomNo ratings yet
- Buoyancy - Wikipedia, The F..Document10 pagesBuoyancy - Wikipedia, The F..MohdFaridNo ratings yet
- Physics Fluid MechanicsDocument18 pagesPhysics Fluid MechanicsPrajwalNo ratings yet
- 1j BuoyancyDocument10 pages1j BuoyancyMia ReggetiNo ratings yet
- Archimedes' Principle - WikipediaDocument17 pagesArchimedes' Principle - WikipediaEternal blueNo ratings yet
- PressureDocument7 pagesPressurePhilip MooreNo ratings yet
- 11A Paper Boats Lesson PlanDocument7 pages11A Paper Boats Lesson PlanEbenEzer MengistuNo ratings yet
- Upthrust and Law of FloatationDocument14 pagesUpthrust and Law of Floatationitsamazing496No ratings yet
- FLUID (Gas) : Nurnazifah, Husna Dan SyahmiDocument49 pagesFLUID (Gas) : Nurnazifah, Husna Dan SyahmiWan Nurnazifah Binti Wan Mohd BukhariNo ratings yet
- Ramanujan Institution O F Mathe Matics A N D Science: H.Chakradh ARDocument3 pagesRamanujan Institution O F Mathe Matics A N D Science: H.Chakradh ARSAI PRANEETH REDDY DHADINo ratings yet
- Ρvg, Where Ρ Is The Density Of The Fluid, V Is The Volume Of TheDocument1 pageΡvg, Where Ρ Is The Density Of The Fluid, V Is The Volume Of TheTeresa CarterNo ratings yet
- Fluid PiyDocument41 pagesFluid PiyarslanNo ratings yet
- Archimedes PrincipleDocument2 pagesArchimedes PrincipleRitson SolomonNo ratings yet
- Light QuestionsDocument3 pagesLight QuestionsSk BalanNo ratings yet
- Kinematics - QuestionsDocument1 pageKinematics - QuestionsSk BalanNo ratings yet
- Faraday Lenz LawDocument5 pagesFaraday Lenz LawSk BalanNo ratings yet
- LPKPM SPM 2012 Physics Paper 3Document0 pagesLPKPM SPM 2012 Physics Paper 3Sk BalanNo ratings yet
- Year 10 - QuestDocument2 pagesYear 10 - QuestSk Balan100% (1)