Professional Documents
Culture Documents
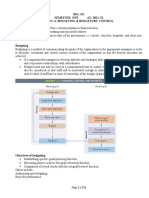
Reformation Budgeting System in Malaysia Accounting Essay
Uploaded by
Fa IzCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Reformation Budgeting System in Malaysia Accounting Essay
Uploaded by
Fa IzCopyright:
Available Formats
5/21/2014 Reformation Budgeting System In Malaysia Accounting Essay
http://www.ukessays.com/essays/accounting/reformation-budgeting-system-in-malaysia-accounting-essay.php 1/3
UK Essays Services Prices Order Now Essays Dissertations Quality Contact My Account
Need help? 0115 966 7955
Enter your search terms.... Search
Print Email Download Reference This Reddit This
Reformation Budgeting System In Malaysia
Accounting Essay
There are several types of budgeting system and techniques being implemented by Malaysian Government since
1960s. Budgeting system is referred to the methods or the techniques of how a budget was prepared and
presented. Different budgeting system will apply different approaches for planning, controlling and evaluation roles
of budgeting. The budgeting systems that being performed are Line Budgeting System, Program and Performance
Budgeting System (PPBS), Modified Budgeting System (MBS), and Outcome Based Budgeting (OBB).
Budgetary reform focused on greater accountability and financial discipline among the various government
agencies entrusted to carry out the socioeconomic development plans for the country. In addition to greater public
sector accountability and improved budgetary system performance, the government undertook a number of
additional reforms including improved financial compliance, quality management, productivity, efficiency in
governmental operations, and management of national development efforts.
Budget reform had been on the Malaysian government agenda for over two decades. Malaysias budget reform
efforts have been closely linked with the efforts at nation building and global competitiveness associated with Vision
2020 which is a program aimed at making Malaysia a fully developed country by the year 2020.
Reformation Budgeting System in Malaysia
Malaysia budgeting system reforms were initiated in the 1960s as part of an effort by the government to strategically
develop the country. The past two decades have witnessed a growing interest in performance management and
budgeting reforms, in response to louder public demands for government accountability in industrial countries.
These reforms are intended to transform public budgeting systems from control of inputs to a focus on outputs or
outcomes, in the interest of improving operational efficiency and promoting results-oriented accountability. These
experiences have significant relevance for public sector reforms in developing countries.
Line item Budgeting System
Government Malaysia was started to use Line Item Budgeting System after independent. Malaysia adopted Line
Item Budgeting System start from year 1960 until 1968. Line Item Budgeting System is a simply list that itemizes
every item in a budget. Line Item Budgeting System is primarily a tool for controlling expenditures. The purpose of
Line Item Budgeting System is to make the budget a tool for financial compliance. This method is relatively easy to
use and understand.
Line Item Budgeting System is a traditional method that prepares a budget by using the previous years budget as
base. Line Item Budgeting System emphasizes inputs and provides information on how much is spent and how it is
spent rather than what for it is spent. It does not link inputs with outputs, and hence say nothing about how
efficiently resources are used. The major criticism of Line Item Budgeting System is it does not deal with key issues
of government objectives, their links to the budget, the services to be delivered by the government. This budgeting
system does not provide the information related to the functions and activities of a program and department.
Because this system is not capable enough to justify the current financial situation and to achieve budget
objectives, Line Item Budgeting System has been replaced since 1969 with a new budgeting system, Program and
Performance Budgeting System (PPBS).
Program and Performance Budgeting System (PPBS)
Program and Performance Budgeting System (PPBS) was first introduced and adopted in Malaysia in 1969. The
evolution of Program and Performance Budgeting System in Malaysia from its beginning in 1969, through the in-
depth implementation phase which began in 1972, to the present day. It outlines the system in the Ministry of Health,
You are here: UK Essays Essays Accounting Reformation Budgeting System In Malaysia Accounting Essay
Tweet
Search UK Essays
Enter your search terms...
Search
Paid Writing Services
Essay writing
Dissertation writing
Assignment writing
All Services
Free Content
Essay Help
Referencing Guides
All Free Resources
About UK Essays
About Us
How We can Help
Contact Us
ORDER NOW
INSTANT PRICE
5/21/2014 Reformation Budgeting System In Malaysia Accounting Essay
http://www.ukessays.com/essays/accounting/reformation-budgeting-system-in-malaysia-accounting-essay.php 2/3
Print Email Download Reference This Reddit This
where PPBS has been extensively developed and comments on the systems established in other in-depth ministries,
in several of which little appears to have been achieved. In 1981 all other agencies were asked to adopt PPB in their
budget submissions.
Malaysia implemented the PPBS in 1969 through to 1990. The focus of the budgetary process was on line items
although information on the performance of program was available. Budget process was used more as a tool for
funds disbursement rather than a strategic management tool.
In 1990, a new budget system was introduced in order to overcome the weakness of PPBS. The system has been
adopted after PPBS is Modified Budget System (MBS).
Modified Budget System (MBS)
The Malaysian government introduced a Modified Budget System (MBS) for the 1990 annual operating budget
preparation with the issuance of Treasury Circular No.11 of 1988. The Modified Budgeting System also known as
the Malaysia Budgeting System. The Modified Budgeting System is a system of management designed to establish
logical linkages on the relationship between inputs, outputs and impacts. MBS was implemented with the explicit
objectives of trying to improve resources allocation by bringing about more efficient management of government
programs by way of improved accountability.
MBS was first introduced in three (3) pilot Ministries, these being the Ministry of Health, Ministry of Work and Ministry
of Social Welfare (Malaysia Treasury 1988). The MBS was implemented in other government organizations in 1992.
The MBS was developed to counteract weaknesses as in the Program and Performance Budgeting System (PPBS),
which has been in place 1969 and also to introduce several reform mechanisms to enhance results based
accountability. The main principals and objectives of the MBS for improving the financial management of
government organizations are to improve and modernize the process of resource allocation on the basis of
performance, to delegate greater authority over the management to a lower level of management as practicable,
and to introduce a result oriented and cost effective management.
Government Malaysian was implemented MBS from year 1990 till now. But MBS still have some problem that can be
improve to be better. The problems of MBS are:
Over-emphasis on the technical aspects and neglect of human variables.
Little attention to develop understanding, receptivity and capability in using data.
Inadequate support from top level administrators.
Lack of trained staff.
Inadequate support from the Treasury itself.
Trained staff being promoted to unrelated jobs.
To solve the problem of MBS, Government Malaysian was planning to implement a new budgeting system.
Government Malaysian hope that the new budgeting system, Outcome Based Budgeting (OOB) can adopted within
the next three years in public sector.
Outcome Based Budgeting (OOB)
The Second Finance Minister, Datuk Seri Ahmad Husni Hanadzlah said that there have five (5) selected ministries
will be use Outcome Based Budgeting (OBB) as test-bedded in 2012 and OOB will be rolled out across all the
ministries start from 2013 onward. The first five selected ministries is finance, human resources and public works,
while the other two ministries will be identified later.
Some of the countries have been successfully implemented OOB, like New Zealand and Canada. Malaysian Prime
Minister, Datuk Seri Najib Tun Razak was still debatable the idea to implement OOB in the 2010 budget. The
purpose is to ensure the concept of value for money, which is efficient, effective and economic, for the budget
expenditure management can be achieve.
OBB is an integrated system that uses goals, mission and objectives to explain why the money is being spent to
achieve a specific outcome and it enables policymakers to determine which activities are cost-effective to achieve
national priorities. The purpose of implementation of OBB is use to overcome the weaknesses and problem that
have been faced when implement MBS.
Share This Essay
5/21/2014 Reformation Budgeting System In Malaysia Accounting Essay
http://www.ukessays.com/essays/accounting/reformation-budgeting-system-in-malaysia-accounting-essay.php 3/3
Order Now Instant Price
submit Tweet
To share this essay on Reddit, Facebook, Twitter, or Google+ just click on the buttons below:
Request Removal
If you are the original writer of this essay and no longer wish to have the essay published on the UK Essays website
then please click on the link below to request removal:
Request the removal of this essay.
More from UK Essays
Free Essays Index - Return to the FREE Essays Index
More Accounting Essays - More Free Accounting Essays (submitted by students)
Accounting Essay Writing Service -find out more about how we can help you
Example Accounting Essays - See examples of Accounting Essays (written by our in-house experts)
Copyright 2003 - 2014 - UK Essays is a trading name of All Answers Ltd. All Answers Ltd is a company registered in England and Wales Company Registration No: 4964706.
VAT Registration No: 842417633. Registered Data Controller No: Z1821391. Registered office: Venture House, Cross Street, Arnold, Nottingham, Nottinghamshire, NG5 7PJ.
Fair Use Policy Terms & Conditions Privacy Policy Cookies Complaints Fraud About us Free Resources Sitemap Language
Join us on Google+ Find us on Facebook Follow us on Twitter
You might also like
- Outcome Based BudgetingDocument23 pagesOutcome Based BudgetingAzliza Azrah Mohd Zakaria0% (1)
- Explain The Advantage of Non Financial PerfomanceDocument5 pagesExplain The Advantage of Non Financial PerfomanceIchiehara YukeidoNo ratings yet
- Ways of Curbing InflationDocument3 pagesWays of Curbing InflationPooja EkkaNo ratings yet
- Accounting Information System Individual AssignmentDocument3 pagesAccounting Information System Individual Assignmentmarlon_akay100% (1)
- Advanced Public Sector AccountingDocument408 pagesAdvanced Public Sector AccountingFatin Ferdinand100% (1)
- Performance Measurement. The ENAPS ApproachDocument33 pagesPerformance Measurement. The ENAPS ApproachPavel Yandyganov100% (1)
- Performance Based Budgeting: Some ViewsDocument4 pagesPerformance Based Budgeting: Some ViewsadityatnnlsNo ratings yet
- Agricultural Policy in NigeriaDocument6 pagesAgricultural Policy in NigeriaEmmanuel Umo Effiong100% (1)
- On Nara BPS Yun Jeong KimDocument17 pagesOn Nara BPS Yun Jeong Kimjulio prestanNo ratings yet
- Public Finance and Economic Management Reforms in MalawiDocument15 pagesPublic Finance and Economic Management Reforms in MalawiInternational Consortium on Governmental Financial ManagementNo ratings yet
- Assignment of Brac DocumentaryDocument24 pagesAssignment of Brac DocumentarySayed AlamNo ratings yet
- Public Sector AccountingDocument17 pagesPublic Sector AccountingAnthony ChaiNo ratings yet
- Financial Ratios in ContractsDocument2 pagesFinancial Ratios in ContractsDeyeck VergaNo ratings yet
- Sme CorpDocument13 pagesSme CorpFaridz RahimNo ratings yet
- Responsibility of Fiscal Policy UPDATEDDocument24 pagesResponsibility of Fiscal Policy UPDATEDFiona RamiNo ratings yet
- Benefits of Accounting StandardsDocument2 pagesBenefits of Accounting Standardsmanikkin bagasNo ratings yet
- Advance Man Acc AssigDocument28 pagesAdvance Man Acc AssigNURUL AMALINA BINTI ROSLI STUDENTNo ratings yet
- Tradeoff Theory and The Pecking Order Theory Are Theories of Capital StructureDocument4 pagesTradeoff Theory and The Pecking Order Theory Are Theories of Capital StructureFarhat NaweedNo ratings yet
- Financial Stability Review, 25 Nov 2010Document5 pagesFinancial Stability Review, 25 Nov 2010The PariahNo ratings yet
- GST Singapore - Policy RationaleDocument4 pagesGST Singapore - Policy Rationaleteju.rv100% (1)
- Concept Note For Good GovernanceDocument5 pagesConcept Note For Good Governanceaimthm100% (2)
- Approaches and Techniques in BudgetingDocument13 pagesApproaches and Techniques in BudgetingMary Grace Ocampo PaciaNo ratings yet
- SDMT - Final Assignment Case Study PDFDocument3 pagesSDMT - Final Assignment Case Study PDFCR7 الظاهرةNo ratings yet
- Financial Management Practices: An Indepth Study Among The Ceo of Small and Medium Enterprise (Smes)Document37 pagesFinancial Management Practices: An Indepth Study Among The Ceo of Small and Medium Enterprise (Smes)sgdfgfdfNo ratings yet
- Outcome Based Budgeting in MalaysiaDocument22 pagesOutcome Based Budgeting in Malaysiakeysp0% (3)
- Assignment 2: BME 2044 Malaysian Economy Prepared For: Madam Sherly GeorgeDocument41 pagesAssignment 2: BME 2044 Malaysian Economy Prepared For: Madam Sherly GeorgeSyaznee IdrisNo ratings yet
- Budgeting As A Mechanism For Management Planning and ControlDocument50 pagesBudgeting As A Mechanism For Management Planning and ControlMatthewOdaliNo ratings yet
- Prosedur PenyelidikanDocument38 pagesProsedur PenyelidikanNor ShahirahNo ratings yet
- Article Review AssignmentDocument2 pagesArticle Review AssignmentAndualem GetuNo ratings yet
- Chicken Run Case StudyDocument5 pagesChicken Run Case StudyMrapizz Azhar0% (1)
- Bottlenecks and Budget Execution Paper 2015Document26 pagesBottlenecks and Budget Execution Paper 2015Macro Fiscal PerformanceNo ratings yet
- Debt To Equity RatioDocument9 pagesDebt To Equity RatioSHRI0588No ratings yet
- Buena Terra Corporation Is Reviewing Its Capital Budget For The UpcomingDocument2 pagesBuena Terra Corporation Is Reviewing Its Capital Budget For The UpcomingAmit PandeyNo ratings yet
- Management Accounting EssayDocument5 pagesManagement Accounting EssayvardaNo ratings yet
- MFRS 108Document22 pagesMFRS 108Yeo Chioujin0% (1)
- Pretest L1 FloristDocument5 pagesPretest L1 FloristnisasuriantoNo ratings yet
- Project Allowance BriefDocument3 pagesProject Allowance BriefSection Officer SR-INo ratings yet
- Budget and BudgetryDocument6 pagesBudget and Budgetryram sagar100% (1)
- What Is A Projectvs ProgramDocument2 pagesWhat Is A Projectvs ProgramRCC NPCC100% (1)
- St. Mary'S Universty Business Faculty Department of AccountingDocument58 pagesSt. Mary'S Universty Business Faculty Department of AccountingHeni Girma100% (2)
- Martha Olwenyi 0772574677: Result Based Monitoring & EvaluationDocument38 pagesMartha Olwenyi 0772574677: Result Based Monitoring & EvaluationRonald Matsiko100% (1)
- Corporate Governance & Its Impact On Firm PerformanceDocument12 pagesCorporate Governance & Its Impact On Firm PerformanceMubashar HussainNo ratings yet
- Financial Investintitu Man Ass 02Document9 pagesFinancial Investintitu Man Ass 02semahegn amareNo ratings yet
- 6 Dimensions of Organizational CultureDocument2 pages6 Dimensions of Organizational CultureEstella Balubar BawalanNo ratings yet
- "Performance-Based Budgeting: A Review of Experience and Lessons", Indian Journal of Social Work, 72 (4), October 2011, Pp. 483-504.Document21 pages"Performance-Based Budgeting: A Review of Experience and Lessons", Indian Journal of Social Work, 72 (4), October 2011, Pp. 483-504.ramakumarrNo ratings yet
- The Various Objectives of Government Budget Are: 1. Reallocation of ResourcesDocument23 pagesThe Various Objectives of Government Budget Are: 1. Reallocation of ResourcesSantosh ChhetriNo ratings yet
- Assignment Case Study SGHE5013Document27 pagesAssignment Case Study SGHE5013ctkhadeejaNo ratings yet
- Poverty in Malaysia - eDocument7 pagesPoverty in Malaysia - eMuni IrahNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Budgetary Control On Organisational PerformanceDocument24 pagesThe Impact of Budgetary Control On Organisational Performancekenedy nuwaherezaNo ratings yet
- Assignment QuestionDocument4 pagesAssignment QuestionkammilaNo ratings yet
- Environmental AccountingDocument52 pagesEnvironmental AccountingFalah Ud Din SheryarNo ratings yet
- Tpc.4.Budgetng For Bsa.3Document21 pagesTpc.4.Budgetng For Bsa.3Khainza DianaNo ratings yet
- Governmental and Not Profit AccountingDocument4 pagesGovernmental and Not Profit AccountingPahladsingh100% (1)
- Accounting CodeDocument5 pagesAccounting CodeMohd MirulNo ratings yet
- Effect of Work Environment On Employee PerformanceDocument13 pagesEffect of Work Environment On Employee PerformanceashleyNo ratings yet
- Is Fiscal Policy the Answer?: A Developing Country PerspectiveFrom EverandIs Fiscal Policy the Answer?: A Developing Country PerspectiveNo ratings yet
- SPECIMEN LTR - Selcare Clinic To SME (Waiver On DOS)Document1 pageSPECIMEN LTR - Selcare Clinic To SME (Waiver On DOS)Fa IzNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument9 pagesReportFa IzNo ratings yet
- Employment Application FormDocument5 pagesEmployment Application FormFa IzNo ratings yet
- The Three Types of Addresses Used On The Internet IsDocument3 pagesThe Three Types of Addresses Used On The Internet IsFa IzNo ratings yet
- HRM Chap. 2Document36 pagesHRM Chap. 2Fa IzNo ratings yet
- HRM Chap. 2Document36 pagesHRM Chap. 2Fa IzNo ratings yet
- Sandra Lippert Law Definitions and CodificationDocument14 pagesSandra Lippert Law Definitions and CodificationЛукас МаноянNo ratings yet
- A Study On Mistakes and Errors in Consecutive Interpretation From Vietnamese To English. Dang Huu Chinh. Qhf.1Document38 pagesA Study On Mistakes and Errors in Consecutive Interpretation From Vietnamese To English. Dang Huu Chinh. Qhf.1Kavic100% (2)
- EmanDocument3 pagesEmanCh NawazNo ratings yet
- Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesCheat SheetFrancis TanNo ratings yet
- Lee Gwan Cheung Resume WeeblyDocument1 pageLee Gwan Cheung Resume Weeblyapi-445443446No ratings yet
- Timing Light Schematic or DiagramDocument2 pagesTiming Light Schematic or Diagramprihharmanto antokNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class11 Maths Notes 13 Limits and DerivativesDocument7 pagesCBSE Class11 Maths Notes 13 Limits and DerivativesRoy0% (1)
- 11 Chemistry NcertSolutions Chapter 2 ExercisesDocument54 pages11 Chemistry NcertSolutions Chapter 2 ExercisesGeeteshGuptaNo ratings yet
- Voucher-Zona Wifi-@@2000 - 3jam-Up-764-04.24.24Document10 pagesVoucher-Zona Wifi-@@2000 - 3jam-Up-764-04.24.24AminudinNo ratings yet
- Sonnet WorksheetDocument3 pagesSonnet WorksheetMary Cris EspirituNo ratings yet
- Questionnaire HRISDocument4 pagesQuestionnaire HRISAnonymous POUAc3zNo ratings yet
- The EagleDocument4 pagesThe EagleJunkoNo ratings yet
- 1574 PDFDocument1 page1574 PDFAnonymous APW3d6gfd100% (1)
- Cleric Spell List D&D 5th EditionDocument9 pagesCleric Spell List D&D 5th EditionLeandros Mavrokefalos100% (2)
- Modern Prometheus Editing The HumanDocument399 pagesModern Prometheus Editing The HumanHARTK 70No ratings yet
- Course-Outline EL 102 GenderAndSocietyDocument4 pagesCourse-Outline EL 102 GenderAndSocietyDaneilo Dela Cruz Jr.No ratings yet
- 7 Critical Reading StrategiesDocument1 page7 Critical Reading StrategiesWilliam Holt100% (2)
- English Preparation Guide DAF 202306Document12 pagesEnglish Preparation Guide DAF 202306TIexamesNo ratings yet
- Classroom Management PaperDocument7 pagesClassroom Management PaperdessyutamiNo ratings yet
- TLG 82201Document7 pagesTLG 82201beatmymeat100% (2)
- Business Enterprise Simulation Quarter 3 - Module 2 - Lesson 1: Analyzing The MarketDocument13 pagesBusiness Enterprise Simulation Quarter 3 - Module 2 - Lesson 1: Analyzing The MarketJtm GarciaNo ratings yet
- Use of ICT in School AdministartionDocument32 pagesUse of ICT in School AdministartionSyed Ali Haider100% (1)
- Story of Their Lives: Lived Experiences of Parents of Children With Special Needs Amidst The PandemicDocument15 pagesStory of Their Lives: Lived Experiences of Parents of Children With Special Needs Amidst The PandemicPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Basic Trigonometric FunctionDocument34 pagesBasic Trigonometric FunctionLony PatalNo ratings yet
- Paleontology 1Document6 pagesPaleontology 1Avinash UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- 9 - Digest - Mari Vs BonillaDocument2 pages9 - Digest - Mari Vs BonillaMarivic Escueta100% (1)
- You Are Loved PDFDocument4 pagesYou Are Loved PDFAbrielle Angeli DeticioNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios VocalesDocument10 pagesEjercicios Vocalesjavier_adan826303No ratings yet
- Bragg Waveguide and Its DescriptionDocument22 pagesBragg Waveguide and Its DescriptionPratibha Karki RawatNo ratings yet
- 2009-Journal of Pharmacy and PharmacologyDocument37 pages2009-Journal of Pharmacy and PharmacologyLeticia Bonancio CerqueiraNo ratings yet