Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Diazepam
Uploaded by
Ivanne HisolerOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Diazepam
Uploaded by
Ivanne HisolerCopyright:
Available Formats
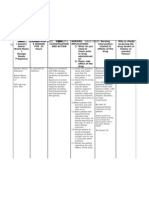
Drug Data Classification Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindications Adverse Reaction Nursing Responsibilities
Generic Name Pharmacologic It increases neuronal membrane General Indications Concentrations CNS: Transient, mild Before
Diazepam Class permeability to chloride ions by - Short-term - Hypersensitivity drowsiness initially; sedation, - Discuss risk of fetal abnormalities with
Benzodiazepine binding to stereospecific management of anxiety - Preexisting CNS depression, lethargy, apathy, patients desiring to become pregnant.
Trade Name benzodiazepine receptors on the - Insomnia associated depression or coma fatigue, disorientation, - Instruct about side effects of drug:
Valium Therapeutic Class postsynaptic GABA neuron within the with anxiety - Respiratory depression restlessness, confusion, Drowsiness, dizziness, GI upset,
Antiepileptic, CNS and enhancing the GABA - Sleepwalking - Acute pulmonary delirium, headache, slurred dreams, difficulty concentrating, fatigue,
Minimum Dose Anxiolytic, Skeletal inhibitory effects resulting in - Night terrors insufficiency or sleep speech, dysarthria, stupor, nervousness, crying.
2mg/day muscle relaxant hyperpolarisation and stabilization. - Premedication before apnea rigidity, tremor, mild - Assess for hypersensitivity.
anaesthesia - Severe hepatic paradoxical excitatory - Reduce dose of opioid analgesics with
Maximum Dose Pregnancy Risk Pharmacokinetics - Adjunct in the impairment reactions, extrapyramidal IV diazepam; dose should be reduced
60mg/day Factor management of - Acute narrow angle symptoms, visual and by at least one-third or eliminated.
D A: Readily and completely absorbed seizures glaucoma auditory disturbances - Instruct not to stop taking the drug
Contents from the GI tract, peak plasma - Muscle spasms - Children < 6 mth CV: Bradycardia, without consulting the health care
Diazepam concentrations after 30-90 min (oral). - Acute symptoms of - Pregnancy and lactation. tachycardia, CV collapse, provider.
Rapidly absorbed, peak plasma alcohol withdrawal hypertension and - Observe the 15 rights of drug
Precaution
Availability and concentrations after 10-30 min - Premedication before hypotension, edema administration.
- Impaired renal and
color (rectal). anaesthesia Dependence: Drug
hepatic function
- Tablets-2, 5, 10 D: Readily crosses the blood-brain dependence with withdrawal During
- Chronic pulmonary
mg barrier; redistributed into fat depots syndrome - Do not administer intrarterially; may
insufficiency
- Oral solution- and tissues. Protein-binding: 98-99%. Dermatologic: Urticaria, produce arteriospasm, gangrene.
- Organic cerebral
1mg/mL, 5mg/mL M: Extensively hepatic; converted to pruritus, skin rash, dermatitis - Carefully monitor P. BP, respiration
changes; elderly
- Rectal pediatric desmethyldiazepam, oxazepam and GI: Constipation, diarrhea, during IV administration.
- History of alcohol or drug
gel- 2.5, 5, 10mg temazepam. dry mouth, salivation, - Change from IV therapy to oral therapy
addiction.
- Injection- E: Urine (as free or conjugated nausea, anorexia, vomiting, as soon as possible.
5mg/mL metabolites) difficulty in swallowing, - Do not use small veins for IV injection.
Drug interaction
elevation in blood enzymes, - Instruct to take drug exactly as
Drug to drug
Routes of Drug Half Life hepatic impairment prescribed.
- Increased CNS
administration 20-80 hr GU: Incontinence, urinary
depression with alcohol,
Oral retention, changes in libido, After
omeperazole
Intramuscular menstrual irregularities - Maintain patients receiving parenteral
- Increased pharmacologic
Intravenous Hematologic: Decreased benzodiazepines in bed for 3 hours.
effects of diazepam if
Rectal Hct, blood dyscrasias - Do not permit ambulatory patients to
combined with cimetidine,
Other: Phlebitis, thrombosis, operate a vehicle following an injection.
disulfiram, hormonal
hiccups, fever, diaphoresis, - Instruct patient to report adverse
contraceptives
paresthesias, muscular reactions.
- Decreased effects of
disturbances, gynecomastia, - Monitor EEG in patients treated for
diazepam with
pain, burning, redness after status epilepticus, seizures may recur
theophyllines, ranitidine
IM injection after initial control.
- Monitor liver and renal function, CBC
Drug to food
during long term therapy.
- none reported
- Taper dosage gradually after long-term
therapy.
- Document that drug has been given.
Source: Source: Source: Source: Source: Source: Source:
Karch, Amy: 2009 Karch, Amy: 2009 http://mims.com.ph/, Karch, Amy: 2009 http://mims.com.ph/ http://mims.com.ph/ Karch, Amy: 2009 Lippincott’s Karch, Amy: 2009 Lippincott’s Nursing Drug Guide,
Lippincott’s Nursing Lippincott’s Nursing Drug Lippincott’s Nursing Drug Guide, pp. 374-376 Nursing Drug Guide, pp. 374-376 pp. 374-376
Drug Guide, pp. 374 Guide, pp. 374-376
You might also like
- Promethazine HCLDocument2 pagesPromethazine HCLIvanne Hisoler100% (8)
- Diazepam (Valium) Drug StudyDocument1 pageDiazepam (Valium) Drug StudyEmika Dizon100% (7)
- Diazepam Drug StudyDocument1 pageDiazepam Drug StudyAndee Salegon100% (3)
- Naloxone and Benzylpenicillin DRUG STUDYDocument3 pagesNaloxone and Benzylpenicillin DRUG STUDYNasrah N. Musa100% (3)
- Drug Study CardinalDocument21 pagesDrug Study CardinalDrei LanuzoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - MidazolamDocument8 pagesDrug Study - MidazolamKian HerreraNo ratings yet
- Diazepam Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDiazepam Drug StudyCheezy BreadNo ratings yet
- Drug Study On DiazepamDocument1 pageDrug Study On DiazepamMaya Acosta BiruarNo ratings yet
- Drug-Study - DiphenhydramineDocument2 pagesDrug-Study - DiphenhydramineJoevence Gazo CuaresmaNo ratings yet
- MIDAZOLAM Drug StudyDocument3 pagesMIDAZOLAM Drug StudyEur Miole60% (5)
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyAbie Jewel Joy Roque100% (1)
- Drug Study - DiazepamDocument1 pageDrug Study - Diazepammarengbib100% (1)
- 10 DRUG-STUDY-Atropine-SulfateDocument2 pages10 DRUG-STUDY-Atropine-SulfateamitNo ratings yet
- MidazolamDocument2 pagesMidazolamDesireemae Riosa-Candaroma100% (6)
- Ritalin LA: Initial, 20 MG PO qAM May Adjust Dose in Weekly 10-mg Incremen TS, Not To Exceed 60 Mg/day (Patients Requiring A Lower InitialDocument2 pagesRitalin LA: Initial, 20 MG PO qAM May Adjust Dose in Weekly 10-mg Incremen TS, Not To Exceed 60 Mg/day (Patients Requiring A Lower InitialKwin SaludaresNo ratings yet
- Phenobarbital Drug StudyDocument3 pagesPhenobarbital Drug StudyCheezy Bread100% (1)
- Levetiracetam Drug StudyDocument2 pagesLevetiracetam Drug Studykaycelyn jimenez50% (2)
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyKate Chavez100% (3)
- Mycophenolate MofetilDocument1 pageMycophenolate MofetilAndyPua100% (1)
- Inhalation Anesthetic Drug StudyDocument4 pagesInhalation Anesthetic Drug StudyElisse RodulfoNo ratings yet
- MorphineDocument3 pagesMorphineCen Janber Cabrillos100% (1)
- Ativan (Lorazepam) Drug StudyDocument3 pagesAtivan (Lorazepam) Drug StudyCHERISE CORDOVA100% (2)
- DiphenhydramineDocument1 pageDiphenhydramineYanejoulce SacanleNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY EpinephrineDocument2 pagesDRUG STUDY EpinephrineCarlo Francisco D. Canto78% (9)
- Alprazolam Drug StudyDocument3 pagesAlprazolam Drug StudyFrancis Corpuz100% (5)
- Drug Study SertralineDocument5 pagesDrug Study SertralineJose Luis Hernandez50% (2)
- Drug Study HaloperidolDocument2 pagesDrug Study HaloperidolRobert Martin Rivera PuertaNo ratings yet
- Aripiprazole AbilifyDocument2 pagesAripiprazole AbilifyKristi Wray100% (2)
- OfloxacinDocument2 pagesOfloxacinCarla Arciaga100% (1)
- Clorazepate Dipotassium (Drug Study)Document2 pagesClorazepate Dipotassium (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse6888No ratings yet
- Heparin InjectionDocument2 pagesHeparin InjectiongagandipkSNo ratings yet
- Haloperidol Drug StudyDocument2 pagesHaloperidol Drug StudyNajmah Saaban100% (5)
- DiazepamDocument1 pageDiazepamStephanie PeNo ratings yet
- Phenytoin Drug StudyDocument1 pagePhenytoin Drug StudyRoland Yuste100% (3)
- Ethosuximide - (Zarontin)Document2 pagesEthosuximide - (Zarontin)Roshleen Ann De Pedro0% (1)
- NaloxoneDocument3 pagesNaloxoneTracyNo ratings yet
- Benztrop, Congentin: Drug StudyDocument4 pagesBenztrop, Congentin: Drug StudyHamimah Bint AliNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Midazolam: RecommendedDocument5 pagesDrug Study: Midazolam: RecommendedShara Lailanie A. AzisNo ratings yet
- PhenobarbitalDocument1 pagePhenobarbitalSherwin LauronNo ratings yet
- Ranitidine Tramadol Ketorolac Ampicillin Paracetamol Drug StudyDocument10 pagesRanitidine Tramadol Ketorolac Ampicillin Paracetamol Drug Studyshiramu91% (11)
- PhenobarbitalDocument2 pagesPhenobarbitalJeremy_Fabio_5332100% (2)
- Drug Stidy TramadolDocument2 pagesDrug Stidy TramadolRez ApegoNo ratings yet
- FentanylDocument3 pagesFentanylDavid Villanueva67% (3)
- DIazepamDocument1 pageDIazepamJonalin Magbanua100% (1)
- Drug Classification Action of Drug Indication and Contraindication Side Effect Nursing ConsiderationDocument2 pagesDrug Classification Action of Drug Indication and Contraindication Side Effect Nursing ConsiderationDanica Kate GalleonNo ratings yet
- diphenhydrAMINE (BENADRYL)Document1 pagediphenhydrAMINE (BENADRYL)Amanda CoadNo ratings yet
- Chlorpromazine Drug StudyDocument7 pagesChlorpromazine Drug Studyjennachristy03100% (3)
- Drug Study AminophyllineDocument1 pageDrug Study Aminophyllinejunie100% (3)
- Lui Sh-Colored Lips and Finger Nails Blur Red VisionDocument1 pageLui Sh-Colored Lips and Finger Nails Blur Red VisionMagdayao Romamea100% (1)
- Vhince Pisco BSN III NCM 117 - Drug StudyDocument3 pagesVhince Pisco BSN III NCM 117 - Drug StudyVhince Norben PiscoNo ratings yet
- AmloDocument1 pageAmloamy navajaNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Ordered: Indications: Contraindications BeforeDocument3 pagesGeneric Name: Ordered: Indications: Contraindications BeforeChenime Añana0% (1)
- MethadoneDocument2 pagesMethadoneIvanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- Drug Study MCL or TechDocument7 pagesDrug Study MCL or TechKyra Lalaine Angub CervantesNo ratings yet
- Schizophrenia DSDocument2 pagesSchizophrenia DSCatungal RophineNo ratings yet
- DroperidolDocument1 pageDroperidolIvanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- AcetazolamideDocument3 pagesAcetazolamideGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Activity 2 Drug Study LinaoDocument21 pagesActivity 2 Drug Study LinaoNursing ClassNo ratings yet
- Metocloprramide HydrochlorideDocument2 pagesMetocloprramide HydrochlorideBeatrizz P GellaNo ratings yet
- Limos Drug-StudyDocument2 pagesLimos Drug-StudyClaire LimosNo ratings yet
- Lumantas MD v. CalapizDocument2 pagesLumantas MD v. CalapizIvanne Hisoler100% (1)
- Persons - Midterms NotesDocument23 pagesPersons - Midterms NotesEvina Michaela LupangoNo ratings yet
- Daily Assignment PlanDocument2 pagesDaily Assignment PlanIvanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- Case Digest (QC v. Ericta)Document1 pageCase Digest (QC v. Ericta)Ivanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- Land Titles Cases (6.21.14)Document31 pagesLand Titles Cases (6.21.14)Ivanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- Contract of Lease (Motor Vehicle)Document3 pagesContract of Lease (Motor Vehicle)Ivanne Hisoler71% (7)
- Republic vs. Castellvi DigestDocument1 pageRepublic vs. Castellvi DigestIvanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- Eminent Domain Case DigestsDocument18 pagesEminent Domain Case DigestsIvanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- Terbutaline SulfateDocument1 pageTerbutaline SulfateIvanne Hisoler100% (2)
- FurosemideDocument2 pagesFurosemideIvanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- Magnesium SulfateDocument1 pageMagnesium SulfateIvanne Hisoler67% (3)
- Penicillin G BenzathineDocument1 pagePenicillin G BenzathineIvanne Hisoler100% (7)
- OxytocinDocument1 pageOxytocinIvanne Hisoler100% (7)
- MethadoneDocument2 pagesMethadoneIvanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- MethotrexateDocument2 pagesMethotrexateIvanne Hisoler83% (6)
- MetoclopramideDocument1 pageMetoclopramideIvanne Hisoler89% (27)
- HydrocortisoneDocument2 pagesHydrocortisoneIvanne Hisoler100% (15)
- DroperidolDocument1 pageDroperidolIvanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- HydralazineDocument1 pageHydralazineIvanne Hisoler75% (8)
- Dopamine HCLDocument1 pageDopamine HCLIvanne Hisoler100% (3)
- DisulfiramDocument1 pageDisulfiramIvanne Hisoler100% (1)
- DactinomycinDocument1 pageDactinomycinIvanne Hisoler0% (2)
- DigoxinDocument1 pageDigoxinIvanne Hisoler100% (3)
- AmpicillinDocument1 pageAmpicillinIvanne Hisoler100% (1)
- Housing StandardsDocument19 pagesHousing StandardsRashika Kala100% (1)
- Business Studies 05Document22 pagesBusiness Studies 05Nepomuk Balthasar HaindlNo ratings yet
- New Trends in Mechanical VentilationDocument4 pagesNew Trends in Mechanical Ventilationashley_castro_4No ratings yet
- CertificateDocument3 pagesCertificateRathnayaka NewilNo ratings yet
- Surgeons in Rangpur, Bangladesh - SOSBDocument11 pagesSurgeons in Rangpur, Bangladesh - SOSBWadood Md ZahedNo ratings yet
- Povidone-Iodine Solution MSDSDocument3 pagesPovidone-Iodine Solution MSDSBoksaRikoBondarNo ratings yet
- MINITACDocument2 pagesMINITACapi-19808945100% (1)
- Physical Assessment For Stroke PatientDocument4 pagesPhysical Assessment For Stroke Patientdana75% (4)
- 12 Compulsive Activities ChecklistDocument8 pages12 Compulsive Activities ChecklistShrey BadrukaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology 1 Exam 1 Study GuideDocument5 pagesPharmacology 1 Exam 1 Study GuideHeroNo ratings yet
- CertificateDocument1 pageCertificateriteshNo ratings yet
- Otto Gross A Case of Exclusion and Oblivion in TheDocument13 pagesOtto Gross A Case of Exclusion and Oblivion in TheVissente TapiaNo ratings yet
- Mental and Emotional Health PowerpointDocument36 pagesMental and Emotional Health PowerpointYen Aduana86% (7)
- Stress Management Stress Management: NptelDocument99 pagesStress Management Stress Management: NptelDKNo ratings yet
- Cosmetic Surgery EssayDocument7 pagesCosmetic Surgery Essayalisharenee0550% (2)
- A Guide To Safety Committee Meeting Tech3Document5 pagesA Guide To Safety Committee Meeting Tech3vsrslm100% (1)
- Dr. Hordinsky's ObituatiaryDocument1 pageDr. Hordinsky's ObituatiaryDiane HaugenNo ratings yet
- WHO Guidelines Hand Hygiene in Health CareDocument270 pagesWHO Guidelines Hand Hygiene in Health CareÐr Salma100% (1)
- Safety Data Sheet Idfilm 220 X: 1. Identification of The Substance/Preparation and The CompanyDocument4 pagesSafety Data Sheet Idfilm 220 X: 1. Identification of The Substance/Preparation and The CompanyHunterNo ratings yet
- BCG - The Future of Jobs in The Era of AI - 2021 - NeiDocument40 pagesBCG - The Future of Jobs in The Era of AI - 2021 - NeiHevertom FischerNo ratings yet
- Psychological Well Being - 18 ItemsDocument5 pagesPsychological Well Being - 18 ItemsIqra LatifNo ratings yet
- GNM Orderno2269 ListDocument32 pagesGNM Orderno2269 ListPriya singhNo ratings yet
- Vitalsigns PDFDocument36 pagesVitalsigns PDFSuneel Kumar PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Manual Steamvection ThermasolDocument6 pagesManual Steamvection ThermasolJosse RuizNo ratings yet
- Health & Safety Topic: HairDocument15 pagesHealth & Safety Topic: HairdyanNo ratings yet
- 1.causes For Neonatal Sepsis, Newborn Sepsis, Neonatal Infection, Sepsis TreatmentDocument12 pages1.causes For Neonatal Sepsis, Newborn Sepsis, Neonatal Infection, Sepsis TreatmentlardiyahNo ratings yet
- Tdiagnostics - Telangana.gov - in ViewFiles - Aspx ReportId p1s0K7qAzHwmL8S2z98THgDocument3 pagesTdiagnostics - Telangana.gov - in ViewFiles - Aspx ReportId p1s0K7qAzHwmL8S2z98THgyesawovNo ratings yet
- Practise-Book Reading Set1Document4 pagesPractise-Book Reading Set1Ketheesaran Lingam100% (1)
- Concepts Underlying The Design of Health ProgramsDocument31 pagesConcepts Underlying The Design of Health ProgramsMUTHUKUMARAN100% (1)
- Town Planning: Q. Identify The Problems in India Regarding Town PlanningDocument8 pagesTown Planning: Q. Identify The Problems in India Regarding Town PlanningYogesh BhardwajNo ratings yet