Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Calculus Capcity Matrixssecondssememster113 14
Uploaded by
api-2436260140 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views8 pagesOriginal Title
calculus capcity matrixssecondssememster113 14
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views8 pagesCalculus Capcity Matrixssecondssememster113 14
Uploaded by
api-243626014Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 8
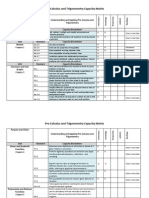
Calculus Capacity Matrix
Purpose and Vision
Understanding and Applying Calculus
I
n
f
o
r
m
a
t
i
o
n
K
n
o
w
l
e
d
g
e
K
n
o
w
-
h
o
w
w
i
s
d
o
m
P
o
r
t
f
o
l
i
o
Unit Standard Capacity Breakdown X
Review
Algebra
Exponential Rules X
Radicals X
Use interval notation
X X Approaching
Limits
Solve and use properties of inequalities X
Solve equations involving Absolute Value X
Solve Inequalities involving Absolute Value X
Complex numbers X
Factoring polynomials and Rational Expressions X
Solving quadratics equations-factoring, completing the
square and quadratic formula
X
Synthetic division X
Unit Standard Capacity Breakdown
Limits and their
Properties
Chapter 3
Sec 3.2
Estimate a limit using a numerical or graphical approach
X X Approaching
Limits
Sec. 3.2
Formal Definition of a limit (delta epsilon proof)
X
Sec. 3.2
Evaluate limits using properties of limits
X
Sec. 3.2
Develop and use a strategy for finding limits
X X Approaching
Limits
Sec. 3.3
Evaluate limits using dividing out and rationalizing
techniques
X
Sec. 3.3
Evaluate limits using the squeeze theorem
X
Calculus Capacity Matrix
Purpose and Vision
Understanding and Applying Calculus
I
n
f
o
r
m
a
t
i
o
n
K
n
o
w
l
e
d
g
e
K
n
o
w
-
h
o
w
w
i
s
d
o
m
P
o
r
t
f
o
l
i
o
Unit Section Capacity Matrix
Limits and their
Properties
Chapter 3
Sec. 3.4
Use properties of continuity
X
Sec. 3.4 Difference Quotient X
Sec. 3.4
Use the Intermediate Value Theorem
X
Sec 3.5
Determine infinite limits from the left and right
X
Sec 3.5
Find and sketch vertical asymptotes of the graphs of
functions
X
Sec 3.4
Recognizing continuity graphically
X
Sec 3.4
Mathematical definition of continuity
X
Sec 3.4 Types of discontinuity: jump, point, infinite
X
Unit Section Capacity Matrix
Differentiation
Chapter 4
Sec 4.1
Find the slope of the tangent line to a curve at a
point
X
Sec 4.1
Use the limit definition to find the derivative of a
function
X
Sec 4.1
Understand the relationship between
differentiability and continuity
X
Sec 4.2
Find the derivative of a function using the
constant rule
X
Calculus Capacity Matrix
Purpose and Vision
Standard
Understanding and Applying Calculus
I
n
f
o
r
m
a
t
i
o
n
K
n
o
w
l
e
d
g
e
K
n
o
w
-
h
o
w
w
i
s
d
o
m
P
o
r
t
f
o
l
i
o
Unit Section Capacity Matrix
Differentiation
Chapter 4
Sec 4.2
Find the derivative of a function using the sum
and difference rule
X
Sec 4.2 Use derivatives to find rates of change
X
Sec 4.3
Find the derivatives of a function using the
product rule
X
Sec 4.3
Find the derivative of a function using the
quotient rule
X
Sec 4.3 Find a higher-order derivative of a function X
Sec 4.4
Find the derivative of a composite function using the chain
rule. Find the derivative of a function using the general
power rule and simplify the derivatives of a function using
algebra
X X Related Rates
Sec. 4.5
Distinguish between functions written in implicit
form and explicit form. Use implicit
differentiation to find the derivatives of a function
X X Related Rates
Sec. 4.6
Find a related rate and use the related rates to
solve real-life problems
X X Related Rates
Unit Section Capacity Breakdown
Applications of
Differentiation
Chapter 5
Sec 5.1
Understand the definition of extrema of a
function on an interval
X
Sec 5.1
Understand the definition of local(relative)
extrema on an open interval
X
Sec 5.1 Find extrema on a closed interval X
Sec 5.2
Use Rolles Theorem
X
Calculus Capacity Matrix
Purpose and Vision
Understanding and Applying Calculus
I
n
f
o
r
m
a
t
i
o
n
K
n
o
w
l
e
d
g
e
K
n
o
w
-
h
o
w
w
i
s
d
o
m
P
o
r
t
f
o
l
i
o
Unit Section Capacity Matrix
Applications of
Differentiation
Chapter 5
Sec 5.2 Be able to use the Mean Value Theorem X
Sec 5.3
Determine intervals on which a function is
increasing or decreasing
X
Sec 5.3
Apply the first derivative test to find relative
extrema of a function
X
Sec 5.4
Determine intervals on which the function is
concave upward or concave downward
X
Sec. 5.4
Find any points of inflection of the graph of a
function
X
Sec. 5.4
Apply the second derivative test to find relative
extrema of a function
X
Sec 5.7 Use calculus to solve optimization problems X
Unit Section Capacity Matrix
Trigonometric Functions Sec 9.1 Convert between degrees and radians X
Sec 9.1 Use angles to model and solve real life problems
X X Robotics 101
Sec 9.2
Identify a unit circle and describe its relationship
to real numbers
X
Sec 9.2
Evaluate trigonometric functions using the unit
circle.
X
Sec 9.2
Use the domain and period to evaluate sine and
cosine functions
X
Sec 9.2
Use a calculator to evaluate trigonometric
function.
X X Robotics 101
Sec 9.3
Evaluate trigonometric functions of acute angles.
X
Calculus Capacity Matrix
Purpose and Vision
Understanding and Applying Calculus
I
n
f
o
r
m
a
t
i
o
n
K
n
o
w
l
e
d
g
e
K
n
o
w
-
h
o
w
w
i
s
d
o
m
P
o
r
t
f
o
l
i
o
Unit Section Capacity Matrix
Trigonometric Functions
Sec 9.3 Use fundamental trigonometric identities X X Robotics 101
Sec 9.3
Use trigonometric functions to model and solve
real -life problems.
X X Robotics 101
Sec 9.4 Evaluate trigonometric functions of any angle
X
Sec 9.4
Use reference angles to evaluate trigonometric
functions.
X
Sec. 9.5/9.6
Sketch the graphs of basic sine, cosine and
tangent functions
X
Sec. 9.5/9.6
Use amplitude and period to help sketch the
graphs of sine, cosine and tangent functions
X
Sec 9.5/9.6
Use sine, cosine and tangent to solve real life
data.
X X Robotics 101
Sec 9.8 Solve real life problems involving right triangle X
Sec 9.8
Solve real life problems involving directional
bearings
X
Sec 9.8
Solving real life problems involving harmonic
motion.
X
Unit Section Capacity Matrix
Analytic Trigonometry
Sec 10.1
Recognize and write the fundamental
Trigonometric Identities
X
Sec 10.1
Use the fundamental trigonometric identities to
evaluate, simplify and rewrite trigonometric
expressions.
X
Calculus Capacity Matrix
Purpose and Vision
Understanding and Applying Calculus
I
n
f
o
r
m
a
t
i
o
n
K
n
o
w
l
e
d
g
e
K
n
o
w
-
h
o
w
w
i
s
d
o
m
P
o
r
t
f
o
l
i
o
Unit Section Capacity Matrix
Analytical Trigonometry Sec 10.2 Establish trigonometric identities X
Sec 10.3
Use standard algebraic techniques to solve
trigonometric equations.
X
Sec 10.3 Solve trigonometric equations of quadratic type
X
Sec 10.3
Solve trigonometric equations involving multiple
angles
X
Sec 10.3
Use inverse trigonometric functions to solve
trigonometric equations
X
Sec 10.4
Use sum and difference formulas to evaluate, and
solve trigonometric functions
X
Sec 10.5
Use double angle formulas to evaluate, and solve
trigonometric functions
X
Sec 10.5
Use Power reducing formulas to evaluate, and
solve trigonometric functions
X
Sec 10.5
Use half angle formulas to evaluate, and solve
trigonometric functions
X
Sec 10.5
Use Product to sum formulas to evaluate, and
solve trigonometric functions
X
Sec 10.5
Use trigonometric formulas to rewrite real life
models
X
Unit Section Capacity Matrix
Calculus Capacity Matrix
Purpose and Vision
Understanding and Applying Calculus
I
n
f
o
r
m
a
t
i
o
n
K
n
o
w
l
e
d
g
e
K
n
o
w
-
h
o
w
w
i
s
d
o
m
P
o
r
t
f
o
l
i
o
Unit Section Capacity Matrix
Trigonometric Functions
and Calculus
Chapter 11
Sec 11.1 Determine the limits of trigonometric functions X
Sec 11.2
Find and use the derivatives of sine and cosine
functions
X
Sec 11.2
Find and use the derivatives of other
trigonometric functions
X
Sec 11.2
Apply the first Derivative test to find the minima
and maxima of a function
X
Sec 11.2
Apply the First Derivative test to find the minima
and maxima of a function
X
Sec 11.3
Integrate trigonometric functions using
trigonometric identities and u substritution
X
Polar Coordinates
Chapter 10
P9.1
Convert between polar and rectangular coordinates.
Graph functions given in polar coordinates
X
P9.2
Write complex numbers in polar form. Know and use
De Moivres Theorem
X
P9.3
Evaluate parametric equations for given values of
parameter
X
P9.4
Convert between parametric and rectangular forms of
equations
X
P9.5
Graph curves described by parametric equation and find
parametric equations for a given graph
X
P9.6
Use parametric equations in applied contexts to model
situations and solve problems
X
CCSS
Represent complex numbers on the complex plane in
rectangular and polar form (including real and imaginary
numbers), and explain why the rectangular and polar forms
of a given complex number represent the same number.
X
Calculus Capacity Matrix
You might also like
- Calculus Capcity Matrix Second Sememster 13 14Document8 pagesCalculus Capcity Matrix Second Sememster 13 14api-245300570No ratings yet
- Capacity Matrix Total Year 13-14Document8 pagesCapacity Matrix Total Year 13-14api-243909487No ratings yet
- N4 MathematicsDocument38 pagesN4 MathematicsTheophilus Hlulani100% (1)
- Ap Calculus BC SyllabusDocument15 pagesAp Calculus BC Syllabusapi-306402864No ratings yet
- NAG C Library Chapter Introduction S - Approximations of Special FunctionsDocument9 pagesNAG C Library Chapter Introduction S - Approximations of Special FunctionsSamuel Pinto'oNo ratings yet
- 16th Sep - Pure MathematicsDocument133 pages16th Sep - Pure Mathematicssalem05alnuaimiNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Learning ResourcesDocument4 pagesUnit 3 Learning Resourcesapi-318119777No ratings yet
- Module 7Document18 pagesModule 7shaina sucgangNo ratings yet
- Principles of Mathematics, Grade 10, Academic (MPM2D) : A Quadratic FunctionsDocument9 pagesPrinciples of Mathematics, Grade 10, Academic (MPM2D) : A Quadratic FunctionsMagne AhoNo ratings yet
- 【书】nonlinear optimization (SC function)Document158 pages【书】nonlinear optimization (SC function)Xinyu MinNo ratings yet
- MFE 1 Week 4 SlidesDocument46 pagesMFE 1 Week 4 SlidesSangheon SongNo ratings yet
- Final Vocab 2014-2015Document3 pagesFinal Vocab 2014-2015api-283145266No ratings yet
- N4 MathematicsDocument33 pagesN4 MathematicsLogan JesseNo ratings yet
- Application and Interpretations Standard Level SyllabusDocument6 pagesApplication and Interpretations Standard Level SyllabusTheTrolLordNo ratings yet
- University of SahiwalDocument6 pagesUniversity of SahiwalRana ShahzaibNo ratings yet
- 954 Math T (PPU) Semester 2 Topics-SyllabusDocument4 pages954 Math T (PPU) Semester 2 Topics-SyllabusJosh, LRTNo ratings yet
- Matlab ExerciseDocument1 pageMatlab ExerciseRaviyank PatelNo ratings yet
- Calculus and Vectors - Chapter 1Document6 pagesCalculus and Vectors - Chapter 1myobNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument10 pagesUntitledapi-171616606No ratings yet
- Maths AA SL and HL Calculator ChecklistDocument1 pageMaths AA SL and HL Calculator ChecklistFatito CevallosNo ratings yet
- Scheme of Examination: Engineering Mathematics - IIDocument34 pagesScheme of Examination: Engineering Mathematics - IIvamsiNo ratings yet
- Calculus Video BookDocument35 pagesCalculus Video BookHarpreet BediNo ratings yet
- Algebric Modeling Scope and Sequence 4th Quarter 2012-2013Document3 pagesAlgebric Modeling Scope and Sequence 4th Quarter 2012-2013api-70433300No ratings yet
- Precalculus Functions and Graphs 13th Edition Swokowski Test BankDocument6 pagesPrecalculus Functions and Graphs 13th Edition Swokowski Test Bankjohnboonepieqngfrdx100% (14)
- MATH 150 Course OutlineDocument5 pagesMATH 150 Course OutlinePerter K MNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Identities and EquationDocument80 pagesTrigonometric Identities and EquationCoolman Poon100% (2)
- MWN 780 Assignment1 Block 1Document5 pagesMWN 780 Assignment1 Block 1DenielNo ratings yet
- Y8 TBAT by UnitDocument5 pagesY8 TBAT by UnitHana JuiceNo ratings yet
- Syllabus CM1015 CMDocument8 pagesSyllabus CM1015 CMinhytrv6vt7byuin32No ratings yet
- Cs6402-Design and Analysis of Algorithm Question Bank Unit-IDocument12 pagesCs6402-Design and Analysis of Algorithm Question Bank Unit-IKpsmurugesan KpsmNo ratings yet
- Applications of DerivativeDocument5 pagesApplications of DerivativeMohamed EmadNo ratings yet
- Year 1 MT Vacation Work, Vectors and MatricesDocument5 pagesYear 1 MT Vacation Work, Vectors and MatricesRoy VeseyNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Plan Due Jan 24Document7 pagesCurriculum Plan Due Jan 24api-253074922No ratings yet
- 03PC11 Chapter03 8th DDocument67 pages03PC11 Chapter03 8th DYi-Ying Lu0% (1)
- Gen Math Mod 2Document8 pagesGen Math Mod 2Joselito UbaldoNo ratings yet
- M.sc. (IT) - Part I Practical ListDocument16 pagesM.sc. (IT) - Part I Practical ListNitu MukundanNo ratings yet
- ECL 222-A Numerical Methods-Day 1: Department of Physics, University of Colombo Electronics & Computing Laboratary IiDocument23 pagesECL 222-A Numerical Methods-Day 1: Department of Physics, University of Colombo Electronics & Computing Laboratary IiyasintharaNo ratings yet
- Honors Final ReviewDocument7 pagesHonors Final ReviewVivian HoNo ratings yet
- SL Year Plans DP 2024Document6 pagesSL Year Plans DP 2024Elias GranditsNo ratings yet
- Ran Peng MT 6aDocument15 pagesRan Peng MT 6aTan Chin HuatNo ratings yet
- CPE A4 - Pelin DemirciDocument18 pagesCPE A4 - Pelin DemirciPelin DemirciNo ratings yet
- To CalculusDocument4 pagesTo CalculusAryan KumarNo ratings yet
- AlgodetensoresDocument90 pagesAlgodetensorescuentaparadescargarNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Syllabus For 1st & 2nd Year / A - LevelDocument10 pagesMathematics Syllabus For 1st & 2nd Year / A - LevelJavaria IdreesNo ratings yet
- Downloads 132Document46 pagesDownloads 132chenamoni.sharath ChandraNo ratings yet
- MathematicsDocument15 pagesMathematicsLuis VasquezNo ratings yet
- SEM 1 MCA 11 MathematicsDocument379 pagesSEM 1 MCA 11 MathematicsMalatesh HavanagiNo ratings yet
- Final StudyDocument3 pagesFinal StudyK.Himaja ReddyNo ratings yet
- Signal & Sytem Lab-Manval PDFDocument26 pagesSignal & Sytem Lab-Manval PDFAnonymous FEjtNQnNo ratings yet
- Lesson Outline Grade 9 and 10 SY 2022-23Document12 pagesLesson Outline Grade 9 and 10 SY 2022-23Hassan AliNo ratings yet
- CPNA Course SyllabusDocument5 pagesCPNA Course SyllabusTorNo ratings yet
- SC Sem 2 Jac Maths Quest 9 Success CriteriaDocument6 pagesSC Sem 2 Jac Maths Quest 9 Success CriteriaJennifer McNeilNo ratings yet
- Global Convergence of Trust-Region Algorithms For Convex Constrained Minimization Without DerivativesDocument7 pagesGlobal Convergence of Trust-Region Algorithms For Convex Constrained Minimization Without DerivativesEmerson ButynNo ratings yet
- Linear ModellingDocument8 pagesLinear Modellingcracking khalifNo ratings yet
- ADA - Question - BankDocument6 pagesADA - Question - Bankananyanalawade2004No ratings yet
- Calculus StandardsDocument3 pagesCalculus StandardsMahmud Alam NauNo ratings yet
- Computational Mathematics: Module DescriptionDocument8 pagesComputational Mathematics: Module DescriptionmelvinNo ratings yet
- College Visits s1 14 15Document1 pageCollege Visits s1 14 15api-243626014No ratings yet
- End Interview ResumeDocument3 pagesEnd Interview Resumeapi-243626014No ratings yet
- Seminars s1 14 15 SeniorsDocument1 pageSeminars s1 14 15 Seniorsapi-243626014No ratings yet
- Internship SummaryDocument1 pageInternship Summaryapi-243626014No ratings yet
- Tours s1 14 15 SeniorsDocument1 pageTours s1 14 15 Seniorsapi-243626014No ratings yet
- Internship PresentationDocument8 pagesInternship Presentationapi-243626014No ratings yet
- Mentor Page 1 13 14Document2 pagesMentor Page 1 13 14api-243626014No ratings yet
- Employability Skills Matrix 09 10Document1 pageEmployability Skills Matrix 09 10api-243626014No ratings yet
- Mentor Senior PGDocument1 pageMentor Senior PGapi-243626014No ratings yet
- Physics Cap Matrix Marked For Final Exam 2014Document5 pagesPhysics Cap Matrix Marked For Final Exam 2014api-243626014No ratings yet
- Seminars s1 13 14Document1 pageSeminars s1 13 14api-243626014No ratings yet
- The Mechanical Advantage of Common Tools CalculationsDocument1 pageThe Mechanical Advantage of Common Tools Calculationsapi-243626014No ratings yet
- Projects s1 14 15 SeniorsDocument1 pageProjects s1 14 15 Seniorsapi-243626014No ratings yet
- Mentor April Entry 14Document1 pageMentor April Entry 14api-243626014No ratings yet
- Related SummaryDocument2 pagesRelated Summaryapi-243626014No ratings yet
- ToursDocument2 pagesToursapi-245442073No ratings yet
- Projects s1 13 14Document1 pageProjects s1 13 14api-243626014No ratings yet
- Works Cited - AllllloyDocument2 pagesWorks Cited - Allllloyapi-243626014No ratings yet
- Alloy Project OutlineDocument3 pagesAlloy Project Outlineapi-243626014No ratings yet
- Alloy Project PresenationDocument16 pagesAlloy Project Presenationapi-243626014No ratings yet
- Robot SchedDocument1 pageRobot Schedapi-243626014No ratings yet
- Connect The Company BoxDocument2 pagesConnect The Company Boxapi-243626014No ratings yet
- List of Terms For Ethic CodeDocument1 pageList of Terms For Ethic Codeapi-243626014No ratings yet
- English MatrixDocument18 pagesEnglish Matrixapi-243626014No ratings yet
- The Goal Is LeanDocument1 pageThe Goal Is Leanapi-243626014No ratings yet
- Project Planning StandardsDocument19 pagesProject Planning Standardsapi-245213984No ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering StandardsDocument1 pageMechanical Engineering Standardsapi-245297609No ratings yet
- Engineering Ethics StandardsDocument4 pagesEngineering Ethics Standardsapi-245297609No ratings yet
- Manufacturing Assembly and Fabrication StandardsDocument1 pageManufacturing Assembly and Fabrication Standardsapi-244954731No ratings yet
- Mind MapDocument2 pagesMind MapJohn Emerald GoloNo ratings yet
- National University: Syllabus Subject: MathematicsDocument3 pagesNational University: Syllabus Subject: MathematicsFathmaakter JuiNo ratings yet
- E0005e Lecture05 Hough Transform - Dvi PDFDocument26 pagesE0005e Lecture05 Hough Transform - Dvi PDFtweenturboNo ratings yet
- Application of Derivatives - JEE (Main) - 2024Document77 pagesApplication of Derivatives - JEE (Main) - 2024Ritheesh NagarajanNo ratings yet
- More About Turing Machines: "Programming Tricks" Restrictions Extensions Closure PropertiesDocument54 pagesMore About Turing Machines: "Programming Tricks" Restrictions Extensions Closure PropertiesLalalalalalaNo ratings yet
- Vector Bundles and Homogeneous SpacesDocument27 pagesVector Bundles and Homogeneous SpacesCaleb JiNo ratings yet
- Rubrica Q4 P1 Par2 2021 1-1-1Document6 pagesRubrica Q4 P1 Par2 2021 1-1-1Carla RamirezNo ratings yet
- Laplace TransformDocument17 pagesLaplace TransformMr AliNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes 331 1Document103 pagesLecture Notes 331 1Shivani SharmaNo ratings yet
- 4th - Math 1Document4 pages4th - Math 1Mharbie GarciaNo ratings yet
- WS TerminologyDocument4 pagesWS Terminologyangel shopNo ratings yet
- Sin y X Where y 2 2 Sin y X: Derivatives of Inverse Trigonometric FunctionsDocument3 pagesSin y X Where y 2 2 Sin y X: Derivatives of Inverse Trigonometric FunctionsRaymar MacarayanNo ratings yet
- Point, Line, PlaneDocument12 pagesPoint, Line, Planeparadoja_hiperbolicaNo ratings yet
- Maths Class 9TH Science 2023 1Document8 pagesMaths Class 9TH Science 2023 1SYED salman saeedNo ratings yet
- M SC IV PDFDocument11 pagesM SC IV PDFabhitoshNo ratings yet
- HMMDocument25 pagesHMMSally JarkasNo ratings yet
- CPT - Part B - CalculusDocument4 pagesCPT - Part B - Calculuswon0503No ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 10-Circles: Exercise: 10.4 (Page No: 179)Document6 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 10-Circles: Exercise: 10.4 (Page No: 179)D . M . GamingNo ratings yet
- ICSE Mathematics Question BankDocument4 pagesICSE Mathematics Question BankAdina FatimaNo ratings yet
- Special Train Algebras Arising in Genetics: by H. GonshorDocument13 pagesSpecial Train Algebras Arising in Genetics: by H. GonshorGABRIEL GUMARAESNo ratings yet
- 1-2 Segments - WSDocument2 pages1-2 Segments - WSangel shopNo ratings yet
- Class 12th - Relations and FunctionsDocument33 pagesClass 12th - Relations and FunctionsessenzzoNo ratings yet
- Abstract Algebra - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument5 pagesAbstract Algebra - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediastaldNo ratings yet
- IMO Class 10Document2 pagesIMO Class 10Yash Swk100% (1)
- dg1-6 The Gauss Curvature (Detail)Document12 pagesdg1-6 The Gauss Curvature (Detail)publicacc71No ratings yet
- Math11 GenMath Q1Wk4-A-finalDocument2 pagesMath11 GenMath Q1Wk4-A-finalCynthia LiaresNo ratings yet
- ECON1003 UNIT 2 Version 1 - Part 1 REV 2Document29 pagesECON1003 UNIT 2 Version 1 - Part 1 REV 2Kyle MerrittNo ratings yet
- 05 Convolution of CT and DTDocument63 pages05 Convolution of CT and DTBhaskarNo ratings yet
- Dr. Siti Mariam Binti Abdul Rahman Faculty of Mechanical Engineering Office: T1-A14-12C E-Mail: Mariam4528@salam - Uitm.edu - MyDocument8 pagesDr. Siti Mariam Binti Abdul Rahman Faculty of Mechanical Engineering Office: T1-A14-12C E-Mail: Mariam4528@salam - Uitm.edu - MyahmadNo ratings yet
- 1 Lactus RectumDocument11 pages1 Lactus RectumAkpa KenechukwuNo ratings yet