Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Transfer Processes: Checkpoint (p.111)
Uploaded by
LaplaceNerd0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
221 views6 pagesConduction is a process whereby heat flows through a body. Materials which conduct heat well are called conductors. Insulators can conduct heat between two bodies but the transfer rate is low.
Original Description:
Original Title
C1_Ch04_FS_e
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentConduction is a process whereby heat flows through a body. Materials which conduct heat well are called conductors. Insulators can conduct heat between two bodies but the transfer rate is low.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
221 views6 pagesTransfer Processes: Checkpoint (p.111)
Uploaded by
LaplaceNerdConduction is a process whereby heat flows through a body. Materials which conduct heat well are called conductors. Insulators can conduct heat between two bodies but the transfer rate is low.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
Pearson Education Asia Limited 2009
All rights reserved
NSS Physics in Life Full Solution of Textbooks
(Heat and Gases)
Chapter Transfer Processes
Checkpoint (p!""")
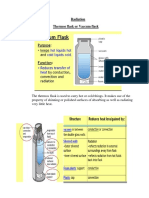
1. Conduction is a process whereby heat flows through a body from a region of
higher temperature to a region of lower temperature. Materials which conduct
heat well are called conductors , while those which do not conduct heat well are
called insulators .
2. A
3. (a) ncorrect. Conduction can ta!e place within a body or between two bodies.
(b) correct
(c) ncorrect. "eat can be transferred in air through conduction but the transfer
rate is #ery low.
(d) incorrect
(e) ncorrect. nsulators can conduct heat between two bodies but the transfer
rate is low.
#xercise (p!""")
1. $
2. %
3. &he en#elope is filled with inert gas which is a poor conductor of heat. "eat is
not readily transferred from the hot filament to the en#elope by conduction.
Moreo#er, heat is carried away from the glass en#elope to the surrounding air at
room temperature. &herefore, the glass en#elope will ha#e a lower temperature
than the filament.
'. (a) (lastic is a good insulator of heat. "eat is not readily transferred from the
hot metal plate to the plastic handle by conduction.
(b) Air is a good insulator of heat while metal is a good conductor of heat. )#en
they are at the same temperature of *+,C, heat is not conducted to the
human body through air as effecti#e as through metal in a sauna room.
-. Chinese clay pot is made of clay which is a good insulator of heat. t reduces the
rate of conduction of heat from the food to the surroundings and !eeps food hot
for a long time. Also, the lid reduces the heat lost by e#aporation of water.
.. &he air trapped in the /ac!ets is e0pelled when the /ac!ets are pressed. &his
decreases the insulating ability of the /ac!et.
1luffing up the /ac!ets help redistribute the cotton or the goose2down to trap air
inside the /ac!ets.
1
Pearson Education Asia Limited 2009
All rights reserved
NSS Physics in Life Full Solution of Textbooks
(Heat and Gases)
*. 1. &he waffle iron is made of metal which is a good conductor of heat.
2. &he waffle iron has an une#en surface. &his increases the surface area for
the conduction of heat.
3. (a) correct
(b) correct
Checkpoint (p!""$)
1. $
2. (a) correct
(b) correct
(c) incorrect
#xercise (p!""$)
1. C
2. A
3. (a) &he heating element is installed near the bottom of the !ettle to facilitate
heat transfer by con#ection.
(b) f the heating element is installed near the top of the !ettle, heat is mainly
transferred from the heating element to the water by conduction. 4ince
water is a poor conductor of heat, the rate of heat transfer is much lower
than that in (a).
'. (a) 4mo!e rises with the hot air. (eople should crawl across the floor to a#oid
suffocation caused by the smo!e.
(b) 4mo!e is carried upwards by the con#ection current of air. 5hen the air
abo#e the incense is heated, it becomes less dense and rises. &he air
gradually cools down as it rises and stops rising at a certain le#el abo#e the
stic!. &his leads to the spread out of smo!e.
(c) &he rear part of a light shade is usually slotted to facilitate heat lost to the
surroundings by con#ection. &his pre#ents the lamp from o#erheating.
Checkpoint (p!"%&)
1. C
2. can A
3. C
2
Pearson Education Asia Limited 2009
All rights reserved
NSS Physics in Life Full Solution of Textbooks
(Heat and Gases)
#xercise (p!"%&)
1. %
2. %
3. (a) &he balloon has a light2coloured surface to reduce the heat lost from the hot
balloon to the surroundings by radiation. &his helps maintain the
temperature of the hot air in the balloon and hence reduce the consumption
of fuel.
(b) &he "ubble 4pace &elescope is wrapped in shiny metal foil to reduce the
absorption or emission of heat by radiation. &his helps maintain the
temperature of the telescope within a suitable range.
(c) &he radiator is painted blac! to enhance heat transfer to the surroundings by
radiation.
'. (a) &his reduces the absorption or emission of heat by radiation.
(b) f the spacesuits were blac!, they will absorb or emit a large amount of heat
by radiation. A large amount of energy will be re6uired to maintain a steady
temperature inside the spacesuits.
-. (a) &he pot is painted blac! to enhance the absorption of radiation in heating up
the water.
(b) &he plate is shiny to minimi7e the absorption of radiation by the plate and
ma0imi7e the reflection of the sunlight to the pot. &he plate is conca#e in
shape to con#erge light to the pot.
Chapter #xercise (p!"'")
1. C
2. %
3. $
'. A
-. A
.. A
*. $
3. A
8. %
1+. $
11. %
12. A
3
Pearson Education Asia Limited 2009
All rights reserved
NSS Physics in Life Full Solution of Textbooks
(Heat and Gases)
13. As the temperature of the body is higher than the surroundings, heat is lost from
the body to the surroundings by conduction through the air, e#aporation of sweat
and radiation.
5hen the wind is blowing, the warm and humid air around the body is blown
away
(1A)
. &his enhances the heat lost by conduction
(1A)
and e#aporation
(1A)
.
&herefore, people feel colder in the wind2chill.
1'. "eat can be transferred from the flame to the finger by conduction and radiation
(1A)
. "owe#er, air and wood are poor conductors of heat
(1A)
. 9nly a small
amount of energy is transferred from the flame to the finger by conduction. n
addition, the energy transferred by radiation from the flame to the finger is also
#ery small and it is not enough to burn the finger
(1A)
.
1-. 1irst, heat is transferred from the heating element at the bottom to the air around
by conduction
(1A)
. &hen, heat is distributed 6uic!ly throughout the air inside the
o#en by natural con#ection
(1A)
. 1inally, heat is transferred from the air to the
food uniformly through conduction
(1A)
.
1.. 4ince the pastry is a good insulator of heat, the rate of conduction of heat from
the hot oil to the ice2cream inside is low
(1A)
. Moreo#er, the frying time is short
so that only a small amount of heat is transferred to the ice2cream
(1A)
. &hus, e#en
the fried pastry is at a high temperature, the ice2cream inside does not melt.
1*. An oil2filled heater warms up the surrounding air
(1A)
and heat is e#enly
distributed throughout the air in the room by natural con#ection
(1A)
. 9n the other
hand, a radiant heater consists of a heating element that produces infrared
radiation
(1A)
, which will be emitted or reflected to the surroundings. &he ob/ects
in the room absorb the radiation and become hotter
(1A)
.
13. (a) &he rac! is placed at the top of the container to enhance con#ection in the
air inside the free7er. &he colder and denser air around the rac! sin!s and at
the same time, the warmer and less dense air around the food rises to ta!e
its place. A con#ection current is formed in the air inside the free7er
(1A)
.
"eat is readily carried away from the food to the surrounding air by
con#ection
(1A)
.
(b) (i) (lastic is a better insulator of heat than metal
(1A)
. &he rate of heat lost
to the surroundings is lower if the wall is made of plastic instead of
metal
(1A)
.
(ii) As air is a good insulator of heat
(1A)
, the air between the double layers
reduces the heat lost by conduction
(1A)
.
'
Pearson Education Asia Limited 2009
All rights reserved
NSS Physics in Life Full Solution of Textbooks
(Heat and Gases)
18. (a) 5hen one end of the glass rod is heated, the molecules at that end gain
energy and #ibrate #igorously
(1A)
. As molecules are bound together by
intermolecular forces, molecules of higher !inetic energy set their
neighbouring molecules to #ibrate more #igorously
(1A)
. As a result, energy
is transferred along the glass rod from the heated end to another end.
n the copper rod, energy is also transferred by free electrons
(1A)
. 5hen the
free electrons at the heated end gain energy from the heat source, their
!inetic energy increase and 6uic!ly transfer the energy to the other electrons
and the copper ions by collisions
(1A)
. &hus, energy is transferred rapidly
along the copper rod.
(b) &he student is incorrect
(1A)
. f thinner rods are used, the rates of conduction
of heat in the rods are reduced. As a result, it ta!es more time for the wa0es
to melt and hence a longer time for the pins to drop
(1A)
.
2+. (a) &he temperature of the hotplate is still higher than that of the heat sin!s
after the hotplate is switched off. "eat is transferred from the hotplate to the
heat sin!s by conduction. &his leads to the rise of temperatures of the heat
sin!s
(1A)
.
(b) thermistor thermometer :thermocouple thermometer (Any reasonable
answers)
(1A)
(c) "eat sin! A has a lower heat capacity
(1A)
. t is assumed that the hotplate
transfers heat to the two heat sin!s at the same rate. 1or the time inter#al
between t ; + and t
1
, heat sin! A has a higher temperature rise than heat sin!
B. According to
T C Q =
, heat sin! A should ha#e a lower heat capacity
(1A)
.
(d) f a graph is steeper after t ; t
2
(a more negati#e slope), this means the
temperature drops at a higher rate per unit time and the corresponding heat
sin! loses heat at a higher rate
(1A)
.
(e) (i) 5hen the two heat sin!s are at the same temperature, heat sin! A loses
heat to the surroundings at a higher rate.
(1A)
(ii) (1) (aint the heat sin! blac!.
(1A)
(2) Ma!e more fins on the heat sin! to increase the area in contact
with the air.
(1A)
21.
(HKCEE 2007 P1 Q3)
22. (a) &he outer #acuum pot has two2layer walls with a #acuum in between
(1A)
.
<acuum can pre#ent heat lost from the food to the surroundings by
conduction or con#ection
(1A)
.
(b) (1) &he heat loss from the food to the surroundings is minimi7ed. t means
most of the supplied energy is used to coo! the food and few energy is
-
Pearson Education Asia Limited 2009
All rights reserved
NSS Physics in Life Full Solution of Textbooks
(Heat and Gases)
wasted.
(2) %uring the coo!ing process, the !itchen and the li#ing room do not get
hot. &his can sa#e energy in air2conditioning.
(Any reasonable answers)
(c) t is relati#ely safer to use a thermal coo!er than flame coo!ing
(1A)
. &he
chance of ha#ing a fire is lower. (Any reasonable answers)
.
You might also like
- ANSWERS Heat Transfer BookletDocument5 pagesANSWERS Heat Transfer BookletNovenda Ermina FatraNo ratings yet
- All MCQ HVDC PDFDocument158 pagesAll MCQ HVDC PDFshaikh wajed khalil43% (7)
- Siepan 8PU - LV SwitchboardsDocument8 pagesSiepan 8PU - LV SwitchboardsSatnam MahleyNo ratings yet
- Transformer FundamentalsDocument198 pagesTransformer Fundamentalsvipinraj100% (1)
- Critical Radius: When Adding Insulation Increases Heat TransferDocument11 pagesCritical Radius: When Adding Insulation Increases Heat Transferدنيا قيس كاظمNo ratings yet
- Transfer of Thermal Energy: Test Yourself 10.1 (Page 168)Document5 pagesTransfer of Thermal Energy: Test Yourself 10.1 (Page 168)Jack Kowman100% (8)
- Pole Mounted Substation Construction - Ausgrid NS122 - NSADocument181 pagesPole Mounted Substation Construction - Ausgrid NS122 - NSAmanxman_1100% (1)
- 6.11 Electrical Cables and Connectors (Konspekts)Document10 pages6.11 Electrical Cables and Connectors (Konspekts)Rūdis SavickisNo ratings yet
- Electric Motor ToshibaDocument3 pagesElectric Motor ToshibaMaulana Rifaldi100% (1)
- Maintenance and Troubleshooting of Induction MotorDocument20 pagesMaintenance and Troubleshooting of Induction MotorMiraj100% (1)
- 1.2 Data Schedule LTB245E1Document2 pages1.2 Data Schedule LTB245E1Jose Alberto Jorge JiménezNo ratings yet
- MPPTCL Technical Specification for 132/33 kV, 40 MVA Power TransformersDocument112 pagesMPPTCL Technical Specification for 132/33 kV, 40 MVA Power TransformersRamphani NunnaNo ratings yet
- Shaffer® 11 - 5,000 Psi USER MANUALDocument77 pagesShaffer® 11 - 5,000 Psi USER MANUALBodega 3001No ratings yet
- 132KV Siemens Breaker DrawingDocument13 pages132KV Siemens Breaker DrawingAnil100% (1)
- Bansal Classes Physics Target IIT JEE Thermal Expansion and Calorimetry GuideDocument15 pagesBansal Classes Physics Target IIT JEE Thermal Expansion and Calorimetry Guidesanits591No ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Long AnswerDocument32 pagesHeat Transfer Long Answerdipzbarma5No ratings yet
- F3 Physics Sample Assignment QuestionsDocument5 pagesF3 Physics Sample Assignment QuestionsAngus AnizNo ratings yet
- Heat and Mass Transfer Module 1 Lesson 2Document13 pagesHeat and Mass Transfer Module 1 Lesson 2cool kidNo ratings yet
- ES311 Assignment & Tutorial 6Document7 pagesES311 Assignment & Tutorial 6HemanthSurya0% (1)
- HT Tutorial 1-3Document3 pagesHT Tutorial 1-3pawanNo ratings yet
- ThermalDocument2 pagesThermalAlyssa ColeNo ratings yet
- MIDTERMSDocument3 pagesMIDTERMSMiya GomezNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 (Question)Document4 pagesTutorial 1 (Question)Muhd IlyasNo ratings yet
- 3 1 Last Year QueDocument24 pages3 1 Last Year QueSAnNo ratings yet
- CLASS VII Physics HeatQADocument6 pagesCLASS VII Physics HeatQAtojendra laltenNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document2 pagesTutorial 1David Ng Qing KaiNo ratings yet
- Physics 7B Thermal Equilibrium and Ideal Gas DiscussionDocument5 pagesPhysics 7B Thermal Equilibrium and Ideal Gas DiscussionNorphinNo ratings yet
- Part2 ch02Document5 pagesPart2 ch02api-3705610No ratings yet
- Phet Lab Black BodyDocument3 pagesPhet Lab Black BodyAaliyah GarciaNo ratings yet
- 7 Heat SolutionsDocument2 pages7 Heat Solutionssmi_santhoshNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Solutions To First ChaterDocument29 pagesHeat Transfer Solutions To First ChaterDiana Kaplan CCNY100% (1)
- Heat Transfer Question BankDocument7 pagesHeat Transfer Question Bankprakhar dubeyNo ratings yet
- Back Questions On Thermal ExpansionDocument4 pagesBack Questions On Thermal ExpansionBenFranksNo ratings yet
- Physics MechanicsDocument207 pagesPhysics MechanicsAamerNo ratings yet
- Blackbody Spectrum SIM WorksheetDocument3 pagesBlackbody Spectrum SIM Worksheet1UpValeNo ratings yet
- Ch02 SolutionDocument7 pagesCh02 Solutionapi-3700944No ratings yet
- Chapter-4 QA Section-E&FDocument4 pagesChapter-4 QA Section-E&FronikNo ratings yet
- Answers To End-Of-Chapter Questions For Chapter 9, Conduction, Convection and RadiationDocument3 pagesAnswers To End-Of-Chapter Questions For Chapter 9, Conduction, Convection and RadiationMencam AsongNo ratings yet
- Thermal Energy Calculations and ConceptsDocument8 pagesThermal Energy Calculations and ConceptsPraphul MalolNo ratings yet
- NCERT Exemplar For Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 - Thermal Properties of Matter (Book Solutions)Document22 pagesNCERT Exemplar For Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 - Thermal Properties of Matter (Book Solutions)Sanjana MehtaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1-13 PDFDocument27 pagesTutorial 1-13 PDFPavanNo ratings yet
- 7 Heat SolutionsDocument7 pages7 Heat Solutionssmi_santhoshNo ratings yet
- Department of Chemical Engineering, NITK CH250: Heat Transfer Assignment - IIIDocument4 pagesDepartment of Chemical Engineering, NITK CH250: Heat Transfer Assignment - IIIUdayNo ratings yet
- Chap 13 SAM Transfer of Heat FinalDocument25 pagesChap 13 SAM Transfer of Heat FinalSNo ratings yet
- Ch16 HW08 SIM KeyDocument9 pagesCh16 HW08 SIM KeyJ100% (2)
- Active Physics Full Solutions Chapter 1 Temperature and Heat Transfer ExercisesDocument2 pagesActive Physics Full Solutions Chapter 1 Temperature and Heat Transfer ExercisesTSE WING HEI謝穎晞No ratings yet
- Prob. Sheet Basic ConceptsDocument3 pagesProb. Sheet Basic ConceptsAnonymous mXicTi8hBNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document2 pagesTutorial 1moven gastonNo ratings yet
- Additional Tutorial 3 Heat TransfeDocument6 pagesAdditional Tutorial 3 Heat TransfeTeeWenSengNo ratings yet
- Write Your Answers On The Exercise Sheet: Class 3. Understanding Conductive Cooling: A Thought ExperimentDocument6 pagesWrite Your Answers On The Exercise Sheet: Class 3. Understanding Conductive Cooling: A Thought Experimentmokhamad rizkiNo ratings yet
- Penabur International School - 8 - Gasses Law, Thermal Transfer - 1 - (Test) - Soal Siswa - RegaDocument7 pagesPenabur International School - 8 - Gasses Law, Thermal Transfer - 1 - (Test) - Soal Siswa - RegaFaber O.MNo ratings yet
- Temperature: Objective: - Desired Learning OutcomesDocument12 pagesTemperature: Objective: - Desired Learning OutcomesSyeda FarvaNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Integrated Science 2nd Edition Hewitt Solutions Manual 1Document6 pagesConceptual Integrated Science 2nd Edition Hewitt Solutions Manual 1james100% (31)
- Conceptual Integrated Science 2Nd Edition Hewitt Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument27 pagesConceptual Integrated Science 2Nd Edition Hewitt Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFsuzanne.guillory241100% (12)
- Questions On Chapter 10Document3 pagesQuestions On Chapter 10Tony AtefNo ratings yet
- Heat Mass Transfer and Thermophysical Analysis For Pyramid Type Solar StillDocument4 pagesHeat Mass Transfer and Thermophysical Analysis For Pyramid Type Solar StillIjsrnet EditorialNo ratings yet
- Perpan1 PR14 2016Document3 pagesPerpan1 PR14 2016Arnold GiovanniNo ratings yet
- 28th January 2019: ME 642 Convective Heat and Mass Transfer Home Assignment 5Document1 page28th January 2019: ME 642 Convective Heat and Mass Transfer Home Assignment 5Prikshit HoodaNo ratings yet
- HKCEE PHYSICS REVISION NOTES ON HEAT TRANSFER PROCESSESDocument40 pagesHKCEE PHYSICS REVISION NOTES ON HEAT TRANSFER PROCESSESLibertyTong100% (1)
- Chapterwise Super Thirty FinalDocument158 pagesChapterwise Super Thirty FinalAnil KumarNo ratings yet
- 14 Transmission of HeatDocument27 pages14 Transmission of HeatSesha Sai KumarNo ratings yet
- Heat and TemperatureDocument66 pagesHeat and TemperatureMark Francis HernandezNo ratings yet
- Suggested Problems-Ch 18Document1 pageSuggested Problems-Ch 18AlexElvirNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Mechanisms ExplainedDocument4 pagesHeat Transfer Mechanisms ExplainedSydney LezamaNo ratings yet
- 06-11-23 Thermal Properties of Matter Physics DPPDocument4 pages06-11-23 Thermal Properties of Matter Physics DPPZomatoswiggyNo ratings yet
- Temperature 20022018Document66 pagesTemperature 20022018tibowehoxNo ratings yet
- Physics: Class 9th (KPK)Document13 pagesPhysics: Class 9th (KPK)Jawad AhmadNo ratings yet
- How it Works: Dealing in simple language with steam, electricity, light, heat, sound, hydraulics, optics, etc., and with their applications to apparatus in common useFrom EverandHow it Works: Dealing in simple language with steam, electricity, light, heat, sound, hydraulics, optics, etc., and with their applications to apparatus in common useNo ratings yet
- Full Solution of CH 25Document20 pagesFull Solution of CH 25LaplaceNerd0% (1)
- Position and Movement: Checkpoint (p.8)Document38 pagesPosition and Movement: Checkpoint (p.8)LaplaceNerdNo ratings yet
- Wave Motion: Checkpoint (p.10)Document13 pagesWave Motion: Checkpoint (p.10)LaplaceNerdNo ratings yet
- Force and Newton's Laws of Motion: Checkpoint (p.84)Document22 pagesForce and Newton's Laws of Motion: Checkpoint (p.84)LaplaceNerdNo ratings yet
- Forces in A Plane and Moment: Checkpoint (p.133)Document23 pagesForces in A Plane and Moment: Checkpoint (p.133)LaplaceNerdNo ratings yet
- Refraction of Light: Checkpoint (p.132)Document15 pagesRefraction of Light: Checkpoint (p.132)LaplaceNerdNo ratings yet
- Full Solution Ch1Document7 pagesFull Solution Ch1Tf ChowNo ratings yet
- P.7 Sci Lesson NotesDocument61 pagesP.7 Sci Lesson NotesAlex SsembalirwaNo ratings yet
- Denon PMA-720AE Ver.14 PDFDocument50 pagesDenon PMA-720AE Ver.14 PDFboroda241090% (10)
- Hoja de Datos Cable Xtu 1C (Xlpe)Document2 pagesHoja de Datos Cable Xtu 1C (Xlpe)Daniel CordovaNo ratings yet
- كتاب مشروع تخرج لمستشفىDocument153 pagesكتاب مشروع تخرج لمستشفىOlfa NablyNo ratings yet
- PCB ConnectorsDocument83 pagesPCB ConnectorsMuhammad ZakaNo ratings yet
- SPEC..600 Volt USE-2Document4 pagesSPEC..600 Volt USE-2quatudogonNo ratings yet
- Dielectric Properties Analysis of Gas Turbine Synchronous Generator by Polarization and Depolarization Current MeasuremenDocument4 pagesDielectric Properties Analysis of Gas Turbine Synchronous Generator by Polarization and Depolarization Current MeasuremenAriNo ratings yet
- Astm10 1001Document6 pagesAstm10 1001Jean CarlosNo ratings yet
- Defstan 61-12PT5Document24 pagesDefstan 61-12PT5Hattar MNo ratings yet
- Is 2551Document44 pagesIs 2551sankaractecheeeNo ratings yet
- Omron G8P 114P FD US DC12 DatasheetDocument6 pagesOmron G8P 114P FD US DC12 DatasheetCorretaje ResidencialNo ratings yet
- VD 300 InverterDocument162 pagesVD 300 Invertercarlos briceñoNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering ObjectivesDocument21 pagesElectrical Engineering Objectivesvan eric lardizabalNo ratings yet
- VD4 ABB - Disj A Vácuo PDFDocument120 pagesVD4 ABB - Disj A Vácuo PDFPaulo RebeloNo ratings yet
- KM 6310in ManualDocument27 pagesKM 6310in ManualCommunications ShipyardNo ratings yet
- 38smss4 Specification For Coupling Capacitor Voltage Transformer and or Carrier Coupler CapacitorDocument20 pages38smss4 Specification For Coupling Capacitor Voltage Transformer and or Carrier Coupler CapacitorengrandyNo ratings yet
- Mts9510a HX2011Document257 pagesMts9510a HX2011LayAnNo ratings yet
- Relay - Schneider Electric - Micom Serie20 - P115Document259 pagesRelay - Schneider Electric - Micom Serie20 - P115Jeffrey ChavezNo ratings yet
- Denon AVR-X5200W PDFDocument219 pagesDenon AVR-X5200W PDFboroda241086% (22)