Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CH 11 4 Guided Cornell Notes
Uploaded by
api-2383973690 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
295 views1 pageOriginal Title
ch 11 4 guided cornell notes
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
295 views1 pageCH 11 4 Guided Cornell Notes
Uploaded by
api-238397369Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Ch 11-4 Meiosis Guided Cornell Notes
Cue Column Student Notes
Mendels principles of genetics requires
what two things?
Define homologous. Give an example.
Define diploid. Give an example.
Define gamete. Give an example.
Define haploid. Give an example.
Define meiosis.
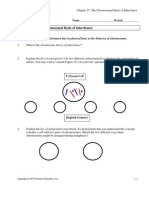
Draw and label the phases of meiosis.
List the major events in each phase. (see
Figure 11-15)
Define tetrad. Draw an example. (see
Figure 11-16)
Define crossing-over. Draw an example.
(see Figure 11-16)
How many gametes are formed in male
animals in meiosis? (see Figure 11-17)
How many gametes are formed in female
animals in meiosis? (see Figure 11-17)
Summary
If a diploid cell begins with 4n
chromosomes, how many chromosomes
would the haploid gamete cells have?
At the end of meiosis I, are the daughter
cells haploid or diploid? How do you know?
When does DNA replication occur in
meiosis?
Where in the body does meiosis occur?
Where does it NOT occur?
How does crossing-over affect the alleles
on a chromatid? (see Figure 11-16)
You might also like
- HW 2Document11 pagesHW 2John33% (30)
- Gizmo (Meiosis)Document8 pagesGizmo (Meiosis)Elijah50% (6)
- List of All Run Commands For WindowsDocument10 pagesList of All Run Commands For Windowsdixityog100% (1)
- BIOL 1408 Final Exam Review - Chapter 1 - 10 - Concepts and ConnectionsDocument8 pagesBIOL 1408 Final Exam Review - Chapter 1 - 10 - Concepts and ConnectionsTristan ScottNo ratings yet
- CH 3.4-3.6 Meiosis Gizmo - StudentDocument11 pagesCH 3.4-3.6 Meiosis Gizmo - StudentKaylia SimmondsNo ratings yet
- Human Heredity Principles and Issues 11th Edition Cummings Test Bank 1Document36 pagesHuman Heredity Principles and Issues 11th Edition Cummings Test Bank 1nicholasmooney16101989rzk100% (29)
- Human Heredity Principles and Issues 11th Edition Cummings Test Bank 1Document15 pagesHuman Heredity Principles and Issues 11th Edition Cummings Test Bank 1yvette100% (43)
- Mitosis Vs Meiosis PracticeDocument3 pagesMitosis Vs Meiosis Practiceapi-293001217No ratings yet
- 7 Science Workbook - HeredityDocument27 pages7 Science Workbook - HeredityJorge SanchezNo ratings yet
- How Dna Controls The Workings of The CellDocument2 pagesHow Dna Controls The Workings of The Cellapi-238397369No ratings yet
- RagragsakanDocument6 pagesRagragsakanRazel Hijastro86% (7)
- Engineering Discourse Communities RMDocument4 pagesEngineering Discourse Communities RMapi-336463296No ratings yet
- APBIO 8.7 WorksheetDocument5 pagesAPBIO 8.7 Worksheetcarolagianserra06No ratings yet
- Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles: Name - PeriodDocument9 pagesChapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles: Name - PeriodmynameNo ratings yet
- ch.13 Meiosis Guided ReadingDocument7 pagesch.13 Meiosis Guided ReadingGrace SalaNo ratings yet
- Meiosis Review Student SheetDocument2 pagesMeiosis Review Student SheetApichayaNo ratings yet
- Q. & A. Chap 05Document14 pagesQ. & A. Chap 05umamahfarooq75No ratings yet
- Principles of Inhe..Document2 pagesPrinciples of Inhe..anoopstudieNo ratings yet
- Metaphase I Encompasses The Alignment of Paired Chromosomes Along The CenterDocument4 pagesMetaphase I Encompasses The Alignment of Paired Chromosomes Along The CenterClaudine Cabanero CaballeroNo ratings yet
- CH 15 HomeworkDocument5 pagesCH 15 HomeworkChristineSkorupaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Worksheet OpenstaxDocument9 pagesChapter 7 Worksheet Openstaxapi-255334265No ratings yet
- Principles of InheritanceDocument2 pagesPrinciples of InheritanceDOOMSDAY PANTHERSNo ratings yet
- Tugas Menjawab Soal Di Buku Campbell (Rangkaian Tugas Mandiri 3)Document6 pagesTugas Menjawab Soal Di Buku Campbell (Rangkaian Tugas Mandiri 3)Afif AzizNo ratings yet
- Review Questions Observable Patterns Inheritance (KEY)Document2 pagesReview Questions Observable Patterns Inheritance (KEY)kylevNo ratings yet
- Mitosis and Meiosis Discussion QuestionsDocument5 pagesMitosis and Meiosis Discussion QuestionsRichard Rna NaabNo ratings yet
- Extensions and Modification of Mendelian InheritanceDocument11 pagesExtensions and Modification of Mendelian Inheritancelilibethduyac72No ratings yet
- Sci Sumative ReviewerDocument4 pagesSci Sumative ReviewerGianni Micha E. AnsaldoNo ratings yet
- Revision Que Class 10Document20 pagesRevision Que Class 10Naren KarthikNo ratings yet
- Remediation Packet - Spring Semester 2 by Michael AcostaDocument6 pagesRemediation Packet - Spring Semester 2 by Michael AcostaFlozieNo ratings yet
- Chromosome MutationsDocument14 pagesChromosome MutationsBrian MachachaNo ratings yet
- Important Questions For CBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 5Document17 pagesImportant Questions For CBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 5twilightNo ratings yet
- Ends With 2 Cells Original Homologous Pairs Separate Ending Human Cells Have 46 Starts With One Cell Sister Chromatids SeparateDocument18 pagesEnds With 2 Cells Original Homologous Pairs Separate Ending Human Cells Have 46 Starts With One Cell Sister Chromatids SeparateProThaThaKing ClashNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 Reading GuideDocument7 pagesChapter 14 Reading GuideGustav AveroNo ratings yet
- Student Exploration: MeiosisDocument8 pagesStudent Exploration: MeiosisAshtyn CurnowNo ratings yet
- Principles of Inheritance and VariationDocument7 pagesPrinciples of Inheritance and VariationNeeraj MisraNo ratings yet
- Meiosis Open-Ended QuestionsDocument1 pageMeiosis Open-Ended QuestionseNo ratings yet
- Revision OneDocument10 pagesRevision OneDaniel BerryNo ratings yet
- Yr10 Biology Revision GuideDocument9 pagesYr10 Biology Revision Guideanas.amr.abdullahNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Lecture NotesDocument13 pagesModule 2 Lecture NotesDanica FayeNo ratings yet
- Your Results For "Practice Test"Document10 pagesYour Results For "Practice Test"Yoona Carly ChaNo ratings yet
- Genetics Test Study GuideDocument4 pagesGenetics Test Study Guideapi-233736029No ratings yet
- Chapters 15Document7 pagesChapters 15bakelake101No ratings yet
- Human Heredity Principles and Issues 11Th Edition Cummings Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument24 pagesHuman Heredity Principles and Issues 11Th Edition Cummings Test Bank Full Chapter PDFAshleyMaciasowbj100% (8)
- 4 3 PT II Answers With PedigreeDocument3 pages4 3 PT II Answers With PedigreeprincessneoneoNo ratings yet
- Lamo JST - Copy of Copy of MeiosisSEDocument8 pagesLamo JST - Copy of Copy of MeiosisSECrackerzNo ratings yet
- Quarter 4 Module 5Document10 pagesQuarter 4 Module 5jiyuskie09No ratings yet
- Grade 9 Module 3Document20 pagesGrade 9 Module 3Paul AniceteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 NotesDocument11 pagesChapter 8 NotesGonzalo Jose SequeiraNo ratings yet
- Human Heredity Principles and Issues 11Th Edition Cummings Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesHuman Heredity Principles and Issues 11Th Edition Cummings Test Bank Full Chapter PDFevelyn.trudnowski238100% (17)
- Does Stress Induce (Para) Sex? Implications For Candida Albicans EvolutionDocument7 pagesDoes Stress Induce (Para) Sex? Implications For Candida Albicans EvolutionPresty Dwi FitrianiNo ratings yet
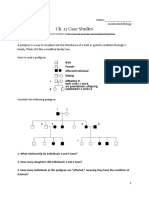
- Inquiry Into Genetic Disorders Case StudiesDocument10 pagesInquiry Into Genetic Disorders Case Studiesapi-394564312No ratings yet
- Mendel Experiments: Did He Predicted Chromosomes?Document9 pagesMendel Experiments: Did He Predicted Chromosomes?Niranjan S ReddyNo ratings yet
- Study Guide AnswersDocument3 pagesStudy Guide AnswersmisterbrownerNo ratings yet
- Fruit Fly ExperimentDocument24 pagesFruit Fly ExperimentHarry BerryNo ratings yet
- GeneticDocument8 pagesGeneticemilylim85No ratings yet
- Biology 10th Edition Solomon Solutions Manual 1Document6 pagesBiology 10th Edition Solomon Solutions Manual 1donald100% (31)
- Biology 10Th Edition Solomon Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument27 pagesBiology 10Th Edition Solomon Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFlewis.barnes1000100% (17)
- Patterns of Inheritance NOTESDocument25 pagesPatterns of Inheritance NOTESRadhika RaniNo ratings yet
- BIO and CHEMDocument13 pagesBIO and CHEMKingfrancis Buga-asNo ratings yet
- General Biology Chapter 9 AssignmentDocument2 pagesGeneral Biology Chapter 9 AssignmentMia mooreNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Essentials of Biology 5th EditionDocument8 pagesSolution Manual For Essentials of Biology 5th EditionDeanBucktdjx100% (33)
- Chapter 14 Mendel and The Gene IdeaDocument9 pagesChapter 14 Mendel and The Gene IdeaJUNG LEENo ratings yet
- And Variation Genetics: Heredity: ScienceDocument15 pagesAnd Variation Genetics: Heredity: ScienceMichelle Casayuran - Regala100% (2)
- Crumbling Genome: The Impact of Deleterious Mutations on HumansFrom EverandCrumbling Genome: The Impact of Deleterious Mutations on HumansRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Dna ReviewDocument2 pagesDna Reviewapi-238397369No ratings yet
- Decoding The Genetic Code 2014Document2 pagesDecoding The Genetic Code 2014api-238397369No ratings yet
- Atoms and The Periodic Table CrosswordDocument1 pageAtoms and The Periodic Table Crosswordapi-238397369No ratings yet
- Periodic TableDocument1 pagePeriodic Tableapi-238397369No ratings yet
- Atom Reading GuideDocument1 pageAtom Reading Guideapi-238397369No ratings yet
- The Lesson of The KaibabDocument2 pagesThe Lesson of The Kaibabapi-238397369No ratings yet
- Meiosis WebquestDocument3 pagesMeiosis Webquestapi-238397369No ratings yet
- Mitosis Vs MeiosisDocument2 pagesMitosis Vs Meiosisapi-238397369No ratings yet
- Examining The Stages in Ecological Succession Full PageDocument2 pagesExamining The Stages in Ecological Succession Full Pageapi-238397369No ratings yet
- Cornell Notes - The Cell CycleDocument1 pageCornell Notes - The Cell Cycleapi-238397369No ratings yet
- Properties and Changes ReviewDocument2 pagesProperties and Changes Reviewapi-238397369No ratings yet
- h2p2 A States of MatterDocument1 pageh2p2 A States of Matterapi-238397369No ratings yet
- Mitosis Computer LabDocument2 pagesMitosis Computer Labapi-238397369No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 ContDocument12 pagesChapter 3 ContVenus Frias-AntonioNo ratings yet
- How To Write Effective Sex ScenesDocument4 pagesHow To Write Effective Sex ScenesAria DiemNo ratings yet
- Theological Differences Between Christianity and IslamDocument18 pagesTheological Differences Between Christianity and IslamMencari KhadijahNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4.2 - Operations On Modular ArithmeticDocument12 pagesLesson 4.2 - Operations On Modular ArithmeticMYLS SHRYNN ELEDANo ratings yet
- Acd 1Document3 pagesAcd 1Kath LeynesNo ratings yet
- J2 P IntroductionDocument9 pagesJ2 P IntroductionnitinvnjNo ratings yet
- Settlement Geography: Unit No-1&2Document11 pagesSettlement Geography: Unit No-1&2Arindam RoulNo ratings yet
- PRP RationaleDocument12 pagesPRP Rationalemarquezjayson548No ratings yet
- Q&A FractureDocument13 pagesQ&A FractureRed JimenoNo ratings yet
- Different Strategies in TeachingDocument12 pagesDifferent Strategies in TeachingCris MolinaNo ratings yet
- Report End of Chapter 1Document4 pagesReport End of Chapter 1Amellia MaizanNo ratings yet
- Urban Square Design: Landscape Design Studio III LAR 803Document44 pagesUrban Square Design: Landscape Design Studio III LAR 803Peter DokpesiNo ratings yet
- Price and Output Determination Under OligopolyDocument26 pagesPrice and Output Determination Under OligopolySangitha Nadar100% (1)
- Ef3 Englisch 04 14 08052014Document20 pagesEf3 Englisch 04 14 08052014PiPradoNo ratings yet
- ACO S Range BrochureDocument20 pagesACO S Range BrochureSyed RaziuddinNo ratings yet
- SSP 861603 - EN - Tire Pressure Monitoring SystemsDocument42 pagesSSP 861603 - EN - Tire Pressure Monitoring Systemsa.diedrichsNo ratings yet
- Tamang GrammarDocument12 pagesTamang Grammarsoftdina100% (1)
- LEASE CONTRACT Taytay Residentialhouse Kei Inagaki Nena TrusaDocument6 pagesLEASE CONTRACT Taytay Residentialhouse Kei Inagaki Nena TrusaJaime GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Implementasi Fault Management (Manajemen Kesalahan) Pada Network Management System (NMS) Berbasis SNMPDocument11 pagesImplementasi Fault Management (Manajemen Kesalahan) Pada Network Management System (NMS) Berbasis SNMPIwoncl AsranNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Introduction To PHP - PHP KeywordsDocument12 pages1.2 Introduction To PHP - PHP KeywordsOvie Nur FaizahNo ratings yet
- Types of Media and Media ConvergenceDocument70 pagesTypes of Media and Media ConvergenceYsmile De LaraNo ratings yet
- CCSI - HDPE - Subduct 50-4240-33 32-27 32-28 - Rev.0 - TelkomDocument1 pageCCSI - HDPE - Subduct 50-4240-33 32-27 32-28 - Rev.0 - TelkomAlvan umaraNo ratings yet
- Install NotesDocument6 pagesInstall NotesSchweinsteiger NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Priya - Rachna Kumari PrasadDocument17 pagesPriya - Rachna Kumari PrasadSumant priyadarshiNo ratings yet
- The Spokesman Weekly Vol. 32 No. 39 May 30, 1983Document12 pagesThe Spokesman Weekly Vol. 32 No. 39 May 30, 1983SikhDigitalLibraryNo ratings yet
- Case of Joneja Bright Steels: The Cash Discount DecisionDocument10 pagesCase of Joneja Bright Steels: The Cash Discount DecisionRHEANo ratings yet
- Catalogue Mega EnglishDocument40 pagesCatalogue Mega EnglishInotech Outillage Nouvelle CalédonieNo ratings yet