Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Question Bank - Basic Electronics
Uploaded by
Divyang PatelOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Question Bank - Basic Electronics
Uploaded by
Divyang PatelCopyright:
Available Formats
!"#$% '()%*+,-$%# .
/0011023
45)#*$,- !"-6
CBAPTER-1
CIRC0IT C0NCEPTS
Questions:
1. Befine the following
Coulomb's Law
Electiic Foice
Conuuctois
Insulatois
Nagnetic Foice
Nagnetic Flux Bensity
2. Explain in biief
Ampeie's Law
Electiic Potential
voltage souice
Cuiient souice
Capacitoi
Inuuctance
S. Bow the equivalent iesistance is calculateu foi Resistois in Seiies anu
Paiallel.
4. Bow the equivalent iesistance is calculateu foi Capacitois in Seiies anu
Paiallel.
S. Bow the equivalent iesistance is calculateu foi Inuuctois in Seiies anu
Paiallel.
6. Explain Kiichhoff's Law foi Cuiient with one example.
7. Explain Kiichhoff's Law foi voltage with one example.
8. What aie the vaiious measuiing Instiuments available foi electiical
paiameteis.
9. What is analogy between electiical anu mechanical components. (Foice-
cuiient & Foice-voltage Analogy)
1u. Wiite shoit Note on Resistance Stiain uauge.
NCQ:
Q.1 Kiichhoff's laws aie valiu foi
A. lineai ciicuit only
B. passive time invaiiant ciicuits
C. non-lineai ciicuits only
B. both lineai anu non-lineai ciicuits
Q.2 All the iesistances in figuie shown below aie 1 u each. The value of cuiient
in Ampeie thiough the batteiy is
A. 11S
B. 21S
C. 41S
B. 81S
Q.S Two iesistois R1 anu R2 given combineu iesistance of 4.S u when in seiies
anu 1 u when in paiallel, the iesistance aie
A. 1.S u anu S u
B. 2 u anu 2.S u
C. 1 u anu S.S u
B. 4 u anu u.S u
Q.4 In given figuie, the value of iesistance R in u is
A. 1u
B. 2u
C. Su
B. 4u
Q.S The unit of inuuctance is Beniy. It can also be iepiesenteu as
A. vSec
B. v - Sec
C. vA
B. v - SecA
Q.6 The eneigy stoieu in an inuuctoi of inuuctance L Beniy is iepiesenteu as,
A. i2L
B. iL2
C. (12)L.i2
B. L2i
Q.7 The voltage inuuceu in an inuuctoi of L Beniy is iepiesenteu as,
A. Li
B. L uiut
C. Li
B. L2i
Q.8 A paiallel plate capacitoi has a capacitance of C faiau. It aiea of the plates is
uoubleu anu the uistance between them is half, the capacitance of the capacitoi
is
A. 1C faiau
B. 2C faiau
C. 4C faiau
B. 16C faiau
Q.9 Which of the followings is the expiession foi eneigy stoieu in a capacitoi
A. Cv
B. C uvut
C. Cv
B. (12)Cv2
Q.1u A bianch of a netwoik is saiu to be active when it consists of one
A. iesistoi
B. voltage souice
C. inuuctoi
B. capacitoi
CBAPTER-2
CIRC0IT ANALYSIS TECBNIQ0ES
Questions:
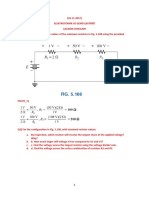
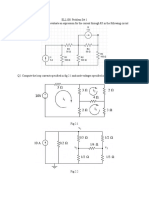
1. Consider the circuit shown in Figure 1. Reduce the portion of the
circuit to the left of terminals ab to (a) a Thvenin equivalent and (b)
a Norton equivalent. Find the current through R=16, and comment on
whether resistance matching is accomplished for maximum power
transfer.
2. Consider the circuit of Figure 2, including a dependent source.
Obtain the Thvenin equivalent at terminals ab.
3. By means of nodal analysis, find the current delivered by the 10-V
source and the voltage across the 10-resistance in the circuit shown
in Figure-3
4. For the network shown in Figure 4, find the current delivered by
the 10-V source and the voltage across the 3-resistor by means of
mesh-current analysis.
5. Determine the voltage across the 20-resistor in the following circuit
of Figure-5 with the application of superposition.
6. Use deltawye transformation for network reduction and determine
the current through the 12-ohm resistor in the circuit of Figure-6
7. Determine the Thvenin and Norton equivalent circuits as viewed
by the load resistance Rin the network of Figure-7
(i) Find the value of R if the power dissipated by Ris to be a maximum.
(ii) Obtain the value of the power in part (b).
8. Reduce the circuit of Figure-8 to a Thvenin and a Norton
equivalent circuit.
9. Find the Thvenin and Norton equivalent circuitsfor the
configuration of Figure-9 as viewed from terminals ab.
10. Obtain the Thvenin and Norton equivalent circuits for the portion
of the circuit to the left of terminals ab in Figure 10, and find the
current in the 200-ohm resistance.
11. In the circuit given in Figure 11, determine the currentIthrough
the 2-ohm resistor by (a) the nodalvoltage method, and (b) mesh-
current analysis.
12. Find the voltage across the 8-A current source in the circuit of
Figure 12 with the use of nodal analysis & Determine the current in
the 0.5-resistor of the circuit by mesh analysis.
Figure.1 Figure.2
Figure.3 Figure.4
Figure.5 Figure.6
Figure.7 Figure.8
Figure.9 Figure.10
Figure.11 Figure.12
NCQ:
1. In an electrical network to neglect a current source the current
source is:
a) Open Circuited.
b) Short Circuited.
c) Replaced by a capacitor.
d) Replaced by an Inductor.
2. Which of the following theorem is applicable for both linear and
nonlinear circuits?
a) Superposition theorem.
b) Thevenin's theorem.
c) Norton's theorem.
d) none of these.
3. In an electrical network to neglect a voltage source the voltage
source is:
a) Open Circuited.
b) Short Circuited.
c) Replaced by a capacitor.
d) Replaced by an Inductor.
4. In figure, the total power consumed is
a) 10 W
b) 12 W
c) 16 W
d) 20 W
5. What is maximum power transfer condition?
a) Rs = RL
b) Rs < RL
c) Rs > RL
d) None of the above.
6. In Thevenins Theorem which term to be determined?
a) Vth, Isc
b) Vth,Rth
c) Rth, Isc
d) None of the above
7. In Nortons Theorem which term to be determined?
a) Vth, Isc
b) Vth,Rth
c) Rth, Isc
d) None of the above
8. In Thevenins equivalent circuit Rth is Parallel connection with Vth?
a) True
b) False
c) May be
d) None of the above
9. In Nortons equivalent circuit Rth is Parallel connection with Isc ?
a) True
b) False
c) May be
d) None of the above
10. Star network is also known as
a) T-network
b) X- network
c) Y-network
d) Z-network
CBAPTER-S
ANAL0u B0ILBINu BL0CKS ANB 0PERATI0NAL ANPLIFIERS
Questions:
NCQ:
1. 789:8 $# ";"-<
9 Biffeiential amplifiei ! 0scillatoi
= Rectifiei > None of the above
2. ?,(*"@) @"$- ,A "- $B)"( ,CD"EC $#<
9 Infinite ! veiy high
= Low > veiy low
S. !"-BF$B*G ,A "- $B)"( ,CD"EC $#<
9 Infinite ! veiy high
= Low > veiy low
4. 75*C5* $EC)B"-%) ,A "- $B)"( ,CD"EC $#<
9 Infinite ! veiy high
= Low > Zeio
S. =:HH ,A "- $B)"( ,CD"EC $#<
9 Infinite ! veiy high
= Low > veiy low
1. Explain Iueal opeiational amplifiei anu its chaiacteiistics.
2. Explain Piopeities of piactical op-amps.
S. Explain inveiting & non-inveiting amplifiei.
4. Explain summing amplifiei.
S. Explain Cuiient-to-voltage Amplifiei, Cuiient-to-cuiient amplifiei &
Chaige-to-chaige amplifiei.
6. Expalin integiatoi & uiffeientiatoi.
7. Explain Inuuctoiless (Active) Filteis.
8. Befine:
i) 0PEN-L00P v0LTAuE uAIN A
ii) INP0T RESISTANCE R
i
iii) 00TP0T RESISTANCE R
o
iv) Common-Noue Rejection Ratio (CNRR)
v) INP0T 0FFSET v0LTAuE v
0S
vi) INP0T BIAS C0RRENT I
B
vii) INP0T 0FFSET C0RRENT I
0S
viii) Powei-Supply Rejection Ratio (PSRR)
ix) Slew Rate
9. Explain opeiation of analog computeis.
1u. Explain piactical application of op-amp: An automotive
powei-assisteu steeiing system.
6. I()F +"*) ,A "- $B)"( ,CD"EC $#<
9 Infinite ! veiy high
= Low > veiy low
7. 7CD"EC $# "<
9 voltage-contiolleu voltage souice
(vCvS)
! voltage-contiolleu cuiient
souice (vCCS)
= Cuiient-contiolleu voltage souice
(CCvS)
> Cuiient-contiolleu cuiient
souice (CCCS)
8. 7CD9EC 5#)#<
9 0nly +ve voltage ! 0nly -ve voltage
= Bual supply, i.e., vcc > None of the above
9. JG) @"$- "-B =:HH %"- "(#, K) )LC+)##)B $- MMMMMN
9 Newton's ! Becibels
= voltampeies > None of the above
1u. JG) *OC$%"( ,C)- (,,C @"$- ,A "- P=QR0 789:8 $# MMN
9 2 x 1u
S
! 2 x 1u
6
= Infinite > Zeio
11. I()F *"+) ,A P= QR0 789:8 $# MMMMMMMN
9 u.S vv ! u.S vs
= u.S mvv > u.S kvv
CBAPTER-4
BIuITAL B0ILBINu BL0CKS ANB C0NP0TER SYSTENS
Questions:
1. Obtain the truth table for the logic block
shown in Figure
2. For the NOR and inverter realizations
shown in Figure, find the truth table, the
type of gate realized, and the expression for
the logic output,in each case.
3. Draw the logic diagram for the
following Boolean
expressions (without any simplification).
4.
5.
6. Draw the logic diagram of an SR latch using only NAND gates, and
obtain the truth
table for that implementation.
7. J and K are the external
inputs to the JKFF shown in
Figure.
Note that gates 1 and 2 are
enabled only when the clock
pulse is high.
Consider the four cases of
operation and explain what
happens.
8. Draw a block diagram for a 2-to-4 decoder. Obtain the truth table,
and develop a logic diagram.
9. Show a block diagram of a 4-bit, parallel-input shift-right register
and briefly explain its operation.
10. What is the basic difference between the weighted resistor and the
R2R ladder D/A converters?
NCQ:
1. Convert hexadecimal value 16 to decimal.
A. 2210 B. 1610
C. 1010 D. 2010
2. Convert the following decimal number to 8-bit binary.
187
A. 101110112 B. 110111012
C. 101111012 D. 101111002
3.The output of an AND gate with three inputs, A, B, and C, is HIGH
when ________.
A. A = 1, B = 1, C = 0
B. A = 0, B = 0, C = 0
C. A = 1, B = 1, C = 1
D. A = 1, B = 0, C = 1
4. The output of an exclusive-NOR gate is HIGH if ________.
A. the inputs are equal
B. one input is HIGH, and the other input is LOW
C. the inputs are unequal
D. none of the above
5.Determine the values of A, B, C, and D that make the sum
term equal to zero.
A. A = 1, B = 0, C = 0, D = 0
B. A = 1, B = 0, C = 1, D = 0
C. A = 0, B = 1, C = 0, D = 0
D. A = 1, B = 0, C = 1, D = 1
6.Which of the following expressions is in the sum-of-products (SOP) form?
A. (A + B)(C + D)
B. (A)B(CD)
C. AB(CD)
D. AB + CD
7. How is a J-K flip-flop made to toggle?
A. J = 0, K = 0
B. J = 1, K = 0
C. J = 0, K = 1
D. J = 1, K = 1
8.A positive edge-triggered D flip-flop will store a 1 when ________.
A.
the D input is HIGH and the clock transitions from HIGH to
LOW
B.
the D input is HIGH and the clock transitions from LOW to
HIGH
C. the D input is HIGH and the clock is LOW
D. the D input is HIGH and the clock is HIGH
9.If both inputs of an S-R flip-flop are LOW, what will happen when the clock
goes high?
A. No change will occur in the output.
B. An invalid state will exist.
C. The output will toggle.
D. The output will reset.
10. Implementation of the Boolean expression results in
________.
A. three AND gates, one OR gate
B. three AND gates, one NOT gate, one OR gate
C. three AND gates, one NOT gate, three OR gates
D. three AND gates, three OR gates
CBAPTER-S
SIuNAL PR0CESSINu
Questions:
1. Biaw anu explain the block uiagiam of anti-noise system to suppiess the
noise in an aiiciaft.
2. Biffeientiate between continuous anu uisciete signals.
S. Explain how a basic signal piocessing system woiks.
4. What aie the Common signal piocessing opeiations.
S. Explain the Basic elements of uigital communication systems.
6. Finu expiessions foi the Fouiiei coefficients foi the following waves:
(a) Rectangulai pulse tiain
(b) Tiiangulai wave
(c) Sawtooth wave
(u) Squaie wave
(e) Balf-iectifieu sine wave
7. Explain the fiequency tianslation piocess with help of piouuct
mouulatoi.
8. Explain sampling with help of switching samplei.
9. Explain the noise in the channel in any communication system.
1u. Explain the following piopeities of signals with example of each:
(a) Peiiouicity anu Causality
(b) Evenness anu 0uuness
(c) Eneigy-type anu powei type.
NCQ:
Q.1 Channel is
a) meuium
b) signal
c) caiiiei
u) none of these
Q.2 Analog signal vaiies with
a) sampling time
b) time continuously
c) sampling fiequency
u) none of these
Q.S Bisciete signal is iepiesenteu by
a) couing
b) mouulation
c) uemouulation
u) sequence of samples
Q.4 Caiiiei signal has
a) constant magnituue
b) constant fiequency
c) vaiiable fiequency
u) vaiiable time
Q.S Nouulating signal has
a) low fiequency
b) low mouulation
c) high fiequency
u) none of these
Q.6 In oiuei to ieuuce inteifeience, the signal shoulu be
a) amplifieu
b) multiplieu
c) uemouulateu
u) mouulateu
Q.7 Nessages tiavel fiom tiansmittei to ieceivei with help of
a) Tiansmittei
b) Receivei
c) channel
u) antennas
Q.8 An example foi an analog signal
a) Sine wave
b) impulse signal
c) sample signal
u) None of these
Q.9 Non electiic signal is conveiteu into electiical signal by
a) tiansmittei
b) ieceivei
c) line
u) none of these
Q.1u In amplituue mouulation, amplituue is
a) constant
b) zeio
c) vaiiable
u) none of these
CBAPTER-6
C0NN0NICATI0N SYSTENS
Questions:
Q.1 Explain the moue of piopagation of electiomagnetic wave in fiee space
anu atmospheie. Also uefine Signal multipath, Signal fauing anu Line of
Sight.
Q.2 Befine the teim Antenna, uive the functions of an Antenna.
Also Befine (a) Rauiation Intensity (b) Rauiation iesistance (c)Rauiation
pattein (u)Powei uain (e)Beam wiuth (f)Polaiization (g) Yagi 0ua
Antenna
Q.S What is mouulation. What is the neeu of mouulation. Explain Amplituue
mouulation with suitable wavefoim, also uefine mouulation Inuex.
Q.4 Explain the geneiation of BSB SC AN. What is envelop uetectoi.
Also uive the significance of vSB AN.
Q.S Befine Caison's Rule. uive five uiffeience between AN anu FN.
Q.6 Biaw anu Explain the block uiagiam of supeihetiouyne ieceivei.
Q.7 State Sampling Theoiem. Befine Companuing.
Q.8 What is multiplexing. Explain TBN.
Q.9 Explain PCN couing Scheme.
Q.1u Explain moue of piopagation of tiansmission line.
NCQ:
Q.1 Coaxial tiansmission line commonly opeiates in ...
(a) TE moue (b) TN moue (C) TEN moue (u)none
Q.2 vC0 is ......
(a) voltage contiol oscillatoi (b)viueo contiol oscillatoi
(C) voltage common oscillatoi (u) viueo Common oscillatoi
Q.S What is the Range of mouulation Inuex in AN
(a) u to 1 (b) -1to u (C) 1 to (u)-1 to 1
Q.4 What is the Range of mouulation Inuex in FN
(a) u to 1 (b) -1to u (C) 1 to (u)-1 to 1
Q.S What is Nyquist Ciiteiia foi sampling
(a) Fs < Fm (b) Fs < 2 Fm (C) Fs > Fm (u Fs >2 Fm
Q.6 What is SNR
(a) Signal to noise iatio (b) Signal to noise ieceivei
(C) Signal to noise ieception (u)Signal to noise iepeatei
Q.7 PCN is
(a) Bigital couing scheme (b) Analog couing scheme (C) Both
(u)none
Q.8 PAN is
(a) Pulse Amplituue Nouulation (b) Pulse Analog Nouulation
(C) Pulse Angulai Nouulation (u) Pulse Anu Nouulation
Q.9 TBN is
(a) Time Bivision Nultiplexing (b) Time Buiation Nultiplexing
(C) Time Bepenuent Nultiplexing (u) Time Bouble Nultiplexing
Q.1u RF Stanus foi
(a) Rauio Fiequency (b) Receivei Fiequency
(C) Rejection Fiequency (u) Repeatei fiequency
CBAPTER-7
BASIC C0NTR0L SYSTENS
Questions:
1. Wiite notes on open loop contiol systems anu closeu loop contiol systems
with the help of neat block uiagiams. uive some suitable ieal life examples
of both types of systems.
2. Compaie 0pen Loop veisus Closeu Loop contiol systems.
S. Classify the feeuback contiol systems by puipose.
4. Befine & explain the tiansfei function using Block uiagiam of an
elementaiy feeuback contiol system.
S. Wiite at least six block uiagiam ieuuction techniques with block uiagiams.
6. Explain the effect of feeuback on Sensitivity, Stability, Bynamic iesponse
anu Banuwiuth.
7. Explain uynamic iesponse of contiol system with the help of neat block
uiagiam.
8. Befine & Explain steauy state eiioi.
9. uive the classification of Feeuback Contiol Systems by Contiol Action.
1u. Explain Bigital Contiol System with the help of example.
NCQ:
0N P- "- ,C)- (,,C %,-*+,( #O#*)E
9 0utput is inuepenuent of contiol
input
! 0utput is uepenuent on contiol
input
= 0nly system paiameteis have effect
on the contiol output
> None of the above
/N 9 %,-*+,( #O#*)E $- FG$%G *G) %,-*+,( "%*$,- $# #,E)G,F B)C)-B)-*
,- *G) ,5*C5* $# 6-,F-
9 Closeu loop system ! Semi-closeu loop system
= 0pen system > None of the above
SN 9- "5*,E"*$% *,"#*)+ $# " MMMMMM (,,C %,-*+,( #O#*)EN
9 open ! closeu
= paitially closeu > any of the above
RN JG) $-$*$"( +)#C,-#) FG)- *G) ,5*C5* $# -,* )T5"( *, $-C5* $# %"(()B
9 Tiansient iesponse ! Eiioi iesponse
= Bynamic iesponse > Eithei of the above
UN MMMMMMM $# " %(,#)B (,,C #O#*)EN
9 Auto-pilot foi an aiiciaft ! Biiect cuiient geneiatoi
= Cai staitei > Electiic switch
2N JG) *+"-#A)+ A5-%*$,- $# "CC($%"K() *, FG$%G ,A *G) A,((,F$-@V
9 Lineai anu time-in vaiiant systems ! Lineai anu time-vaiiant
systems
= Lineai systems > Non-lineai systems
QN W$*G A))BK"%6 MMMMM $-%+)"#)#N
9 system stability ! sensitivity
= gain > effects of uistuibing signals
XN I*)"BO I*"*) '++,+ A,+ JOC)D1 #O#*)E A,+ 5-$*) #*)C $-C5* $# MMMMMMMMMMN
9 Finite ! Infinite
= Zeio > All of above
YN I*)"BO I*"*) '++,+ A,+ JOC)D/ #O#*)E A,+ 5-$*) +"EC $-C5* $# MMMMMMMMMMN
9 Finite ! Infinite
= Zeio > All of above
01N I*)"BO I*"*) '++,+ A,+ JOC)D0 #O#*)E A,+ 5-$*) "%%)()+"*$,- $-C5* $#
MMMMMMMMMMN
9 Finite ! Infinite
= Zeio > All of above
You might also like
- Electric Circuits and Electron Devices Unit I Circuit Analysis Techniques Part-ADocument8 pagesElectric Circuits and Electron Devices Unit I Circuit Analysis Techniques Part-ASalai Kishwar JahanNo ratings yet
- Circuit Theory Practice ProblemsDocument0 pagesCircuit Theory Practice Problemsaishuvc1822No ratings yet
- Question Paper Code:: Reg. No.Document0 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: Reg. No.aishuvc1822No ratings yet
- Electric Circuit AnalysisDocument12 pagesElectric Circuit AnalysisMATHANKUMAR.SNo ratings yet
- WWW - Studyhaunters.blogspot - In: Question Paper Code: 22115Document5 pagesWWW - Studyhaunters.blogspot - In: Question Paper Code: 22115Sriram JNo ratings yet
- II B. Tech I Semester, Regular Examinations, Nov - 2012 Electrical Circuit Analysis - IDocument12 pagesII B. Tech I Semester, Regular Examinations, Nov - 2012 Electrical Circuit Analysis - IViswa ChaitanyaNo ratings yet
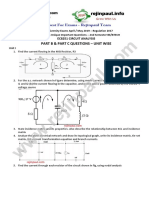
- Part B & Part C Questions - Unit Wise: Ec8251 Circuit AnalysisDocument4 pagesPart B & Part C Questions - Unit Wise: Ec8251 Circuit AnalysisAnonymous Ndsvh2soNo ratings yet
- Experiment 8Document3 pagesExperiment 8Nathaniel MendozaNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Code:: Reg. No.Document6 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: Reg. No.sunil1237No ratings yet
- Question Paper Code: 22115: B.E./B.Tech - Degree Examinations, April/May 2011 Regulations 2008Document5 pagesQuestion Paper Code: 22115: B.E./B.Tech - Degree Examinations, April/May 2011 Regulations 2008Vinodh GanesanNo ratings yet
- EE 1151 Circuit Theory Question BankDocument19 pagesEE 1151 Circuit Theory Question BankVIVEK AHLAWATNo ratings yet
- Kirchoff's Laws, Thevenin's Theorem, Superposition TheoremDocument3 pagesKirchoff's Laws, Thevenin's Theorem, Superposition TheoremarunajithNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios AnalogicaDocument22 pagesEjercicios AnalogicaManel GarciaNo ratings yet
- Ee6201 CT U1 5 QBDocument10 pagesEe6201 CT U1 5 QBsakilakumaresanNo ratings yet
- Bee Lab ManualDocument62 pagesBee Lab ManualSwetha VanamNo ratings yet
- Electronic Instrumentation July 2013Document0 pagesElectronic Instrumentation July 2013Prasad C MNo ratings yet
- PHM604 QB 2019 PDFDocument5 pagesPHM604 QB 2019 PDFAbhishek Yadav100% (1)
- Ies 11980 Only BJTDocument7 pagesIes 11980 Only BJTGaurav ShrimaliNo ratings yet
- JNTU Electrical Circuit Analysis Exam QuestionsDocument8 pagesJNTU Electrical Circuit Analysis Exam Questionssatya_vanapalli3422No ratings yet
- Electro-Elektrik ve Gemi Elektriği Soru ve CevaplarıDocument21 pagesElectro-Elektrik ve Gemi Elektriği Soru ve Cevaplarıserkan1234No ratings yet
- L2001a Lab ManualDocument13 pagesL2001a Lab ManualMuhammad Rais FawwaziNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Code:: Reg. No.Document0 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: Reg. No.Bala SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: InstructionsDocument2 pagesGujarat Technological University: InstructionsHet PatelNo ratings yet
- EE1205 - Circuit AnalysisDocument14 pagesEE1205 - Circuit AnalysisRameez FaroukNo ratings yet
- 3rd SemDocument13 pages3rd SemKiran KumarNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuits Exam Questions and AnswersDocument12 pagesElectrical Circuits Exam Questions and AnswersRohan MalthumkarNo ratings yet
- Bee Lab ManualDocument60 pagesBee Lab Manualravi828No ratings yet
- f5c4 ExerDocument3 pagesf5c4 Exerjalrizal7No ratings yet
- EDC Question-Papers Complete SetDocument13 pagesEDC Question-Papers Complete Setselvi04120% (1)
- Ecx3210 Tma2 2010 PDFDocument2 pagesEcx3210 Tma2 2010 PDFThamara Dananjaya GunarathnaNo ratings yet
- ME2143 Part I TutorialProbemSet 1Document3 pagesME2143 Part I TutorialProbemSet 1Zheng YongjiaNo ratings yet
- Electronics I 306a OkDocument3 pagesElectronics I 306a Okparupalli1997No ratings yet
- II B.Tech II Semester, Regular Examinations, April - 2012 Electrical Circuit Analysis - IiDocument8 pagesII B.Tech II Semester, Regular Examinations, April - 2012 Electrical Circuit Analysis - IiViswa ChaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Indian Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering Any FiveDocument4 pagesIndian Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering Any FiveNikhil V. JoshiNo ratings yet
- IAS Mains Electrical Engineering 1994Document10 pagesIAS Mains Electrical Engineering 1994rameshaarya99No ratings yet
- ALL The EIGHT Questions: Indian Ins-R:Itl:Jte of Technology, KharagpurDocument2 pagesALL The EIGHT Questions: Indian Ins-R:Itl:Jte of Technology, KharagpurIndranilNo ratings yet
- EEE 2202 ANALOGUE ELECTRONICS I - July17 - ExamDocument5 pagesEEE 2202 ANALOGUE ELECTRONICS I - July17 - Exameric wahomeNo ratings yet
- Experiment - 1: TheoryDocument6 pagesExperiment - 1: TheoryKiran Kumar KandregulaNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Code:: Reg. No.Document0 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: Reg. No.Manoj DNo ratings yet
- IES CONV Electronic Comm. 1998Document9 pagesIES CONV Electronic Comm. 1998gateandiesNo ratings yet
- Series-Parallel RLC Circuit AnalysisDocument3 pagesSeries-Parallel RLC Circuit AnalysisJhustine CañeteNo ratings yet
- Transistor ProblemsDocument9 pagesTransistor ProblemsAli AdnanNo ratings yet
- EEE Exclusive: Question Paper Code: 22115Document5 pagesEEE Exclusive: Question Paper Code: 22115aishuvc1822No ratings yet
- Electronic Devices & Circuits SyllabusDocument4 pagesElectronic Devices & Circuits SyllabusShareef KhanNo ratings yet
- Pulse and Digital CircuitsDocument8 pagesPulse and Digital CircuitsLalith KumarNo ratings yet
- Module-Wise Eln QBDocument5 pagesModule-Wise Eln QBRashmi SamantNo ratings yet
- Network Analysis ECE Question Bank 4,5,6Document5 pagesNetwork Analysis ECE Question Bank 4,5,6RajeshKanchanaNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Code:: (10 2 20 Marks)Document5 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: (10 2 20 Marks)Samraj JebasinghNo ratings yet
- Unsolved Problem SheetDocument20 pagesUnsolved Problem SheetDeveshNo ratings yet
- Question Bank For BTETC401 Network TheoryDocument23 pagesQuestion Bank For BTETC401 Network TheoryShiva DubeyNo ratings yet
- 16 131101 Basic ElectronicsDocument2 pages16 131101 Basic Electronicsdhvani5988No ratings yet
- Electrical Circuits and Electronics Exam QuestionsDocument3 pagesElectrical Circuits and Electronics Exam QuestionsSourav RoyNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Experiment No. 1Document9 pagesLaboratory Experiment No. 1JAMIR ARIOLANo ratings yet
- 21ELE13set1 PDFDocument3 pages21ELE13set1 PDFAishwaryanayakNo ratings yet
- ElectricalDocument18 pagesElectricalSanjay ChyNo ratings yet
- Solution:: Fig. 2 Shows The Required Common Base ConnectionDocument9 pagesSolution:: Fig. 2 Shows The Required Common Base ConnectionSwathi Gudivada100% (1)
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesFrom EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesNo ratings yet
- Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book (Linear IC): Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 1From EverandNewnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book (Linear IC): Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 1Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Philips EM3E Service ManualDocument63 pagesPhilips EM3E Service ManualSpun_GNo ratings yet
- CATALOG - Anti-Vandalism (En)Document16 pagesCATALOG - Anti-Vandalism (En)deceneu2005No ratings yet
- Open Source Real-Time Temperature MonitoringDocument39 pagesOpen Source Real-Time Temperature MonitoringdhaNo ratings yet
- MOBILE TRACKING SYSDocument5 pagesMOBILE TRACKING SYStansen123467% (3)
- 5102024-00A Relay Kit Workboat 11 1 MEDocument2 pages5102024-00A Relay Kit Workboat 11 1 MEPatrickNo ratings yet
- Crop Yield Prediction Using Random Forest AlgorithmDocument11 pagesCrop Yield Prediction Using Random Forest AlgorithmVj KumarNo ratings yet
- Ece4009 - Wireless and Mobile Communication Review 2 Group Members Slot 1. 2. 3. TitleDocument10 pagesEce4009 - Wireless and Mobile Communication Review 2 Group Members Slot 1. 2. 3. TitledwijaNo ratings yet
- GSM ActixDocument64 pagesGSM ActixNenad100% (1)
- Str-X67xxseries An en PDFDocument19 pagesStr-X67xxseries An en PDFRenn PaculanangNo ratings yet
- Audiocodes Mediant Sbcs For Service ProvidersDocument9 pagesAudiocodes Mediant Sbcs For Service ProvidersrAVINo ratings yet
- Detailed Project Report: Depot Online SystemDocument168 pagesDetailed Project Report: Depot Online SystemNikhil JangirNo ratings yet
- Mediatek Confidential: MT7601U 802.11 B/G/N Single Chip Preliminary DatasheetDocument14 pagesMediatek Confidential: MT7601U 802.11 B/G/N Single Chip Preliminary DatasheetMd Kamruzzaman KhanNo ratings yet
- MSM MBA DMT Individual Assignment September 2021Document49 pagesMSM MBA DMT Individual Assignment September 2021online storeNo ratings yet
- 2.BP Travel - Create Quotes - Process Definition Document (PDD)Document15 pages2.BP Travel - Create Quotes - Process Definition Document (PDD)jeevaNo ratings yet
- Karmic WarriorsDocument354 pagesKarmic WarriorsdudleyclarkNo ratings yet
- ASTM STP1385 Durability 2000 Accelerated and Outdoor Weathering TestingDocument186 pagesASTM STP1385 Durability 2000 Accelerated and Outdoor Weathering TestingKYAW SOENo ratings yet
- CMOS Processing Technology Chapter Explains FEOL and BEOL StepsDocument1 pageCMOS Processing Technology Chapter Explains FEOL and BEOL StepsCarlos SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Oracle DBA Interview Q&ADocument8 pagesOracle DBA Interview Q&Amanideep thatikondaNo ratings yet
- How To Complete USPS Form 1583 in Five Minutes PDFDocument2 pagesHow To Complete USPS Form 1583 in Five Minutes PDFBang HNo ratings yet
- SN 75114Document11 pagesSN 75114Hector LopezNo ratings yet
- Graphing Polynomial FunctionsDocument30 pagesGraphing Polynomial FunctionsJean Aristonet Woods LeysonNo ratings yet
- Tutorial T1 PresentationDocument96 pagesTutorial T1 Presentationsykimk8921No ratings yet
- Scherer Evolution ASNE 2011 PDFDocument25 pagesScherer Evolution ASNE 2011 PDFio75No ratings yet
- Sylvia Langfield, Dave Duddell - Cambridge International As and A Level Computer Science Coursebook (2019, Cambridge University Press) - Libgen - LiDocument554 pagesSylvia Langfield, Dave Duddell - Cambridge International As and A Level Computer Science Coursebook (2019, Cambridge University Press) - Libgen - LiSahil KaundunNo ratings yet
- Jaguar XJS Help by Kirby PalmDocument201 pagesJaguar XJS Help by Kirby Palmrexgary100% (5)
- Set Up & Instruction Manual REV. 0.2 Set Up & Instruction Manual REV. 0.8Document39 pagesSet Up & Instruction Manual REV. 0.2 Set Up & Instruction Manual REV. 0.8LuisNo ratings yet
- DB2 Command Line Processor Tips and TricksDocument8 pagesDB2 Command Line Processor Tips and Tricksapi-3701299100% (1)
- TLE - Davao Room Assignments For September 2013 LETDocument53 pagesTLE - Davao Room Assignments For September 2013 LETScoopBoyNo ratings yet
- GEM Premier 3500 - Interface ProtocolDocument136 pagesGEM Premier 3500 - Interface ProtocolJoão VictorNo ratings yet
- How To Use KeygenDocument1 pageHow To Use KeygenearltonNo ratings yet