Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SQL Sublanguages Classified by Functionality
Uploaded by
VasuG0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
75 views5 pagesSQL statements are classified into 5 sublanguages based on their functionality: DDL for structure changes, DML for record changes, DRL for data retrieval, TCL for transaction control, and DCL for data authorization. The document provides examples of using DDL statements like CREATE, ALTER, and DROP to define and modify database tables, DML statements like INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE to manipulate the data within tables, and TCL statements like COMMIT and ROLLBACK to manage transactions.
Original Description:
Sql2 Ddl Dml Tcl
Original Title
Sql2 Ddl Dml Tcl
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentSQL statements are classified into 5 sublanguages based on their functionality: DDL for structure changes, DML for record changes, DRL for data retrieval, TCL for transaction control, and DCL for data authorization. The document provides examples of using DDL statements like CREATE, ALTER, and DROP to define and modify database tables, DML statements like INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE to manipulate the data within tables, and TCL statements like COMMIT and ROLLBACK to manage transactions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
75 views5 pagesSQL Sublanguages Classified by Functionality
Uploaded by
VasuGSQL statements are classified into 5 sublanguages based on their functionality: DDL for structure changes, DML for record changes, DRL for data retrieval, TCL for transaction control, and DCL for data authorization. The document provides examples of using DDL statements like CREATE, ALTER, and DROP to define and modify database tables, DML statements like INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE to manipulate the data within tables, and TCL statements like COMMIT and ROLLBACK to manage transactions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
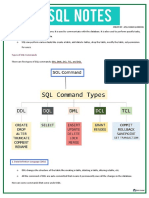
SQL STATEMENTS ARE CLASSIFIED INTO 5 SUBLANGUAGES BASED ON THEIR FUNCTIONALITY:
1. DDL(Data Definition language)
2. DML(Data Manipulation language)
3. DRL(Data Retrieval language)
4. TCL(Transaction Control Language)
5. DCL(Data Control Language USED BY DBA).
1. DDL: (DATA DEFINITION LANGUAGE)
----------
USED TO PERFORM STRUCTURE ORIENTED CHANGES.
STATEMENTS AVAILABLE ARE
1. CREATE 2.DROP 3. ALTER (keywords add , modify , drop , rename)
4. RENAME 5.TRUNCATE
1.create: This statement is used create new
----------- objects like table,view,synonym,etc.
Table is base object in rdbms.
Table is used to hold data.
syntax for creating tables:
----------------------------------
create table <tablename>(columnname1 datatype,...);
Maximum -> 1000 columns/table can be given.
open sqlplus tool:
-----------------------
select start/programs/oracle/application development/sql plus
username - scott
password - tiger
By default scott user is available in oracle used for testing purpose.
sql prompts open
Ex1:
sql>create table item_masters ( it_no number(3) ,
it_name varchar2(10) , qoh number(3) , rol number(3) ) ;
QOH -> QUANTITY ON HAND
ROL -> REORDER LEVEL
To check for table in database:
----------------------------------------
sql> desc item_masters;
(DESCRIBES THE STRUCTURE)
Ex2:
sql>create table item_trans(it_no number(3) ,
tran_type char(1) , qty number(3) , tran_date date) ;
sql>desc item_trans;
======================================================
2. drop: Used to remove existing objects.
----------
syn: drop table <tablename>;
ex:
sql>drop table item_trans;
sql>desc itemtrans;
======================================================
3. ALTER: STATEMENT USED TO CHANGE EXISTING
-------------- STRUCTURES USING KEYWORDS LIKE
ADD, MODIFY, DROP, RENAME.
ADD: USED TO ADD NEW COLUMNS IN EXISTING
------- STRUCTURES.
syntax: alter table <tablename> add(columnname1 datatype,..);
Ex1:
sql>alter table item_masters add uom varchar2(10);
sql>desc item_masters;
UOM -> UNIT OF MEASUREMENT
Ex2:
sql>alter table item_trans add updt char(1);
sql>desc item_trans;
updt -> update
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
---------------
MODIFY: USED TO INCREASE / DECREASE WIDTH (or)
------------- change EXISTING DATATYPEs if that column is empty.
syntax: alter table <tabname> modify (colname1 datatype,..);
Ex1:
sql>alter table item_masters modify it_name varchar2(20);
sql>desc item_masters;
Ex2:
sql>alter table item_masters modify it_no varchar2(10);
sql>desc item_masters;
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
---------------
DROP: USED TO REMOVE EXISTING COLUMNS along
--------- with data.
Syntax: alter table <tablename> drop column columnname;
Ex1:
SQL>ALTER TABLE ITEM_MASTERS DROP COLUMN UOM;
SQL>DESC ITEM_MASTERS1
note:We cannot drop multiple columns at a time.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
--------------
RENAME: USED TO CHANGE EXISTING COLUMNNAMEs.
--------------
syntax: alter table <tablename> rename column <oldcolname> to <newcolname>;
Ex1:
SQL>ALTER TABLE ITEM_MASTERS RENAME COLUMN
IT_NAME TO ITEMNAME;
SQL> DESC ITEM_MASTERS;
NOTE: We cannot rename multiple columns at a time.
======================================================
4. RENAME : Statement USED TO CHANGE existing objectname.
syntax: rename <oldobjectname> to <newobjname>;
Ex1:
SQL> RENAME ITEM_MASTERS TO ITEMMAT;
SQL> DESC ITEM_MASTERS --does not exists
SQL> DESC ITEMMAT --object exists.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
--------------
5. TRUNCATE : USED TO EMPTY/remove existing table data
-------------------- ( i.e data will be removed permanently,
but empty structure remains).
syntax: Truncate table <tablename>;
note: emp , dept tables given by manufacturer along
------- with data used for testing purpose.
To check tables:
---------------------
sql>desc dept --3 columns
sql>desc emp --8 columns
To check for data:
----------------------
sql>select * from dept; --4 rows
sql>select * from emp; --14 rows
Ex1:
SQL>TRUNCATE TABLE emp;
sql>desc emp; --3 columns
sql>select * from emp; --no rows selected
======================================================
2. DML: (DATA MANUPILATION LANGUAGE)
----------
USED TO PERFORM RECORD ORIENTED CHANGES.
STATEMENTS AVAILABLE ARE INSERT,UPDATE,DELETE.
1.INSERT: STATEMENT USED TO PROVIDE NEW RECORDS TO EXISTING TABLES.
CHARACTERS AND DATES SHOULD BE GIVEN WITHIN SINGLE QUOTES.
characters are case sensitive.
oracle statements are case insensitive.
SYNTAX:
-------------
INSERT INTO <TABLENAME>[(COLUMNNAMES)]
VALUES(LIST OF VALUES);
Insert can be used in 3 ways:
1. Inserting data to all columns.
2. Inserting data to specific columns.
3. Inserting data dynamically.
1. Inserting data to all columns:
----------------------------------------
SQL>SELECT * FROM DEPT;
SQL>INSERT INTO DEPT VALUES(50,'HR','HYD');
SQL>SELECT * FROM DEPT;
2. Inserting data to specific columns:
-----------------------------------------------
SQL>SELECT * FROM EMP;
SQL>INSERT INTO EMP(EMPNO,ENAME,JOB,HIREDATE,DEPTNO)
VALUES(100,'NAVEEN','MANAGER','01-JAN-01',20);
SQL>SELECT * FROM EMP;
3. Inserting data dynamically:
---------------------------------------
IT CAN BE DONE USING INSERTION OPERATOR -> & PROMPT.
SQL>INSERT INTO EMP(EMPNO,ENAME,SAL,DEPTNO)
VALUES(&eno,'&ename',&SAL,&DEPTNO);
Enter value for eno: 1003
Enter value for ename: SAI
Enter value for sal: 70000
Enter value for deptno: 30
SQL> /
(REEXECUTES LATEST STATEMENT IN BUFFER)
Enter value for eno: 1004
Enter value for ename: RAM
Enter value for sal: 40000
Enter value for deptno: 10
SQL>SELECT * FROM EMP;
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
---------------
2.UPDATE: STATEMENT USED TO CHANGE EXISTING RECORDS.
SYNTAX:
-------------
UPDATE <TABLENAME> SET COLUMNNAME1 = VALUE , ... [WHERE <CONDITION>];
WHERE CLAUSE: USED TO PROVIDE CONDITIONS
-------------------------- ON REQUIRED RECORDS.
where clause will support for update,select,delete statements.
EXAMPLES:
-----------------
SQL>UPDATE EMP SET COMM = 5000 WHERE EMPNO=7902 or EMPNO = 7566 or empno = 7900;
SQL>SELECT * FROM EMP WHERE EMPNO=7902 or EMPNO = 7566 or empno = 7900;
sql>UPDATE EMP SET SAL=25000 , COMM = 5000;
SQL>SELECT * FROM EMP;
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
---------------
3.DELETE: STATEMENT USED TO REMOVE REQUIRED RECORDS.
---------------
syntax:
-------
delete from <tablename> [where <condition>];
SQL>DELETE FROM EMP WHERE JOB = 'CLERK';
SQL>SELECT * FROM EMP;
1) ddl statements are permanent.
2) dml statements are temporary(transactions).
======================================================
3.TCL :(Transaction control language).
----------
Statements available are (commit & rollback).
commit : used to save the transacted data permanently in database.
rollback:used to cancel the transaction from memory.
sql>rollback;
sql>select * from emp;
SQL>DELETE FROM EMP WHERE JOB = 'CLERK';
sql>commit;
SQL>SELECT * FROM EMP;
note: when we exit,ddl,dcl then autocommit takes place.
savepoint : used to temporarily save the transaction.
======================================================
You might also like
- Difference Between SQL and SQL PlusDocument90 pagesDifference Between SQL and SQL PlusSudhakar UppalapatiNo ratings yet
- DBMS Record NewDocument93 pagesDBMS Record New5026 SHIBU MNo ratings yet
- SQLDocument19 pagesSQLramuNo ratings yet
- DBMS RecordDocument107 pagesDBMS Record5026 SHIBU MNo ratings yet
- Oracle SQL FAQ: What Is SQL and Where Does It Come From?Document8 pagesOracle SQL FAQ: What Is SQL and Where Does It Come From?jyotipc_mcaNo ratings yet
- CS2258 DBMS ManualDocument57 pagesCS2258 DBMS ManualRaj Bharath RajuNo ratings yet
- Cs2258 Dbms Record ITDocument76 pagesCs2258 Dbms Record ITHariss KumarNo ratings yet
- CS6312 DBMS Lab Syllabus and ProjectsDocument56 pagesCS6312 DBMS Lab Syllabus and ProjectsKavi AnanthNo ratings yet
- Learn SQL Basics with Experiments on DML and DDL StatementsDocument8 pagesLearn SQL Basics with Experiments on DML and DDL StatementsAshley_RulzzzzzzzNo ratings yet
- Government Polytechnic, Muzaffarpur: Name of The LabDocument23 pagesGovernment Polytechnic, Muzaffarpur: Name of The LabHrithik SharmaNo ratings yet
- DB2Document6 pagesDB2Vijay KumarNo ratings yet
- SqlinterviewDocument5 pagesSqlinterviewdawokel726No ratings yet
- Dbms Complete Lab ManualDocument172 pagesDbms Complete Lab ManualR Gandhimathi RajamaniNo ratings yet
- Script FirstDocument5 pagesScript FirstkashafNo ratings yet
- SQL Statements SyntaxDocument2 pagesSQL Statements SyntaxKUSHAL H BNo ratings yet
- Advance JavaDocument9 pagesAdvance JavasaiNo ratings yet
- DBMS Practical FileDocument26 pagesDBMS Practical FileOSCAR AHINAMPONGNo ratings yet
- Database PracticalDocument30 pagesDatabase PracticalHarshNo ratings yet
- SQL Lab AssignDocument22 pagesSQL Lab Assignnaveen sumanNo ratings yet
- Oracle 10g - SQL (Fast N Final)Document73 pagesOracle 10g - SQL (Fast N Final)manaenglishNo ratings yet
- DBMS Lab ManualDocument261 pagesDBMS Lab ManualMr.D.Daniel Assistant ProfessorNo ratings yet
- Dbms LabDocument9 pagesDbms Labvijaya naga praveenaNo ratings yet
- Dbms Complete Lab ManualDocument184 pagesDbms Complete Lab Manualrajat7169451734No ratings yet
- Data Manipulation Language Commands 1Document12 pagesData Manipulation Language Commands 1Vinoth RagunathanNo ratings yet
- Ani SQLDocument173 pagesAni SQLKarnasula BhuvaneswariNo ratings yet
- Experiment of DBMSDocument7 pagesExperiment of DBMSAlkesh KhareNo ratings yet
- Study of Basic SQL CommandsDocument73 pagesStudy of Basic SQL Commandsprsd912010No ratings yet
- DDLDocument7 pagesDDLpavan kumar PiratlaNo ratings yet
- SQL LessonDocument56 pagesSQL LessonMusammat Samina100% (1)
- DbmslabmanualDocument81 pagesDbmslabmanualCharitha IddumNo ratings yet
- Dbms Complete Lab ManualDocument86 pagesDbms Complete Lab ManualAsif AmeerNo ratings yet
- A Helpful Hand: Lab ManualDocument168 pagesA Helpful Hand: Lab Manuallalith48No ratings yet
- Dbms Complete Lab ManualDocument177 pagesDbms Complete Lab ManualMouniga Ve75% (4)
- SQL Study of CommandsDocument74 pagesSQL Study of CommandsArun Ravi100% (1)
- SQL Full CourseDocument19 pagesSQL Full CourseschiopuNo ratings yet
- Dbms FileDocument25 pagesDbms FileKanika JawlaNo ratings yet
- Table FragmentationDocument14 pagesTable FragmentationSraVanKuMarThadakamallaNo ratings yet
- SQL Fruit CommandsDocument6 pagesSQL Fruit Commandsreadingisfun1933No ratings yet
- Co-Related Subqueries and Schema ObjectsDocument26 pagesCo-Related Subqueries and Schema ObjectsalphaNo ratings yet
- DBMS Lab Manual GuideDocument43 pagesDBMS Lab Manual Guidedeepa45No ratings yet
- DBMS Unit 3 - Part 1 FinalDocument31 pagesDBMS Unit 3 - Part 1 Finalnehatabassum4237No ratings yet
- SQL NotesDocument74 pagesSQL NotesMaheshNo ratings yet
- Types of SQL CommandsDocument56 pagesTypes of SQL CommandsAnant MoreNo ratings yet
- DBMS EXP LAB Manual (1)Document81 pagesDBMS EXP LAB Manual (1)cc5405No ratings yet
- DBMS Lab ManualDocument22 pagesDBMS Lab ManualSenthil PrakashNo ratings yet
- DDL DML DCL CommandsDocument66 pagesDDL DML DCL CommandsPRADEEP PRADEEPNo ratings yet
- Mca II Dbms LabmannualDocument29 pagesMca II Dbms LabmannualGhanshyam KumarNo ratings yet
- Programs Exp 1-15Document85 pagesPrograms Exp 1-15surendhar surendhar (RA1911003020346)No ratings yet
- TaskDocument24 pagesTaskvasundharaNo ratings yet
- Lab ActivityDocument5 pagesLab ActivityUpasana YNo ratings yet
- SQL CommandDocument4 pagesSQL CommandRicha PandeyNo ratings yet
- SQL - PLSQL DocumentDocument49 pagesSQL - PLSQL DocumentNishanthNo ratings yet
- Day 2 SQLDocument1 pageDay 2 SQLElisha MuppallaNo ratings yet
- Day3 SQLDocument12 pagesDay3 SQLRama Raju IndukuriNo ratings yet
- DBMSDocument14 pagesDBMSdevsutaria2006No ratings yet
- Notes On Structural Query LanguageDocument3 pagesNotes On Structural Query LanguageGunjanNo ratings yet
- DBMS ManualDocument64 pagesDBMS ManualAravind KumarNo ratings yet
- Oracle NotesDocument49 pagesOracle NotesAbiramiNo ratings yet
- DB Queries AnswersDocument8 pagesDB Queries AnswersVasuGNo ratings yet
- DWH Testing ResumeDocument4 pagesDWH Testing ResumeVasuGNo ratings yet
- Basic Unix TutorialDocument27 pagesBasic Unix Tutorialprabir175No ratings yet
- Sql5 Sub QueriesDocument1 pageSql5 Sub QueriesVasuGNo ratings yet
- Etl TestingDocument28 pagesEtl TestingVasuG100% (2)
- sql1 DatatypesDocument2 pagessql1 DatatypesVasuGNo ratings yet
- SQL TopicsDocument45 pagesSQL TopicsVasuGNo ratings yet
- HDFS TestingDocument15 pagesHDFS TestingVasuGNo ratings yet
- Sql4 Where Groupby Having Orderby JoinsDocument2 pagesSql4 Where Groupby Having Orderby JoinsVasuGNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Excel 2013 - Quick Reference GuideDocument2 pagesMicrosoft Excel 2013 - Quick Reference GuideTrevorLincecumNo ratings yet
- A Test Methodology For An Effective Regression TestingDocument6 pagesA Test Methodology For An Effective Regression TestingVasuGNo ratings yet
- Audit Your Etl With ChecksumDocument1 pageAudit Your Etl With ChecksumVasuGNo ratings yet
- TestingDocument52 pagesTestingVasuGNo ratings yet
- A Test Methodology For An Effective Regression TestingDocument6 pagesA Test Methodology For An Effective Regression TestingVasuGNo ratings yet
- ISTQB Sample Paper 1Document8 pagesISTQB Sample Paper 1wilfred2005No ratings yet
- Testing FactsDocument5 pagesTesting FactsVasuGNo ratings yet
- Istqb Foundation Level Syllabus - 2014Document78 pagesIstqb Foundation Level Syllabus - 2014Joshua HolderNo ratings yet
- Documentum Architecture White PaperDocument47 pagesDocumentum Architecture White PaperwongwswNo ratings yet
- CIS250 Final Exam QuestionsDocument5 pagesCIS250 Final Exam Questionsbanrez16100% (1)
- What is MapReduceDocument19 pagesWhat is MapReducePraveen KumarNo ratings yet
- DBMS Lab QuestionsDocument56 pagesDBMS Lab QuestionsMadhul LambaNo ratings yet
- Database Testing Techniques and Best PracticesDocument21 pagesDatabase Testing Techniques and Best Practicesavumaa22No ratings yet
- UGRD-ITE6100B Fundamentals of Database System-Preliminary ExaminationDocument13 pagesUGRD-ITE6100B Fundamentals of Database System-Preliminary Examinationpatricia geminaNo ratings yet
- Oracle Gen QueriesDocument15 pagesOracle Gen QueriesJaveed ShaikNo ratings yet
- Dbms Lab Manual23-24Document47 pagesDbms Lab Manual23-24qz5jq94yh2No ratings yet
- Pivotier Product BriefDocument2 pagesPivotier Product BriefDevaang BhattNo ratings yet
- MetaDigger Manual 2016Document15 pagesMetaDigger Manual 2016BillLawrenceNo ratings yet
- Approval Framework AWE Configuring To Be Site Specific PDFDocument22 pagesApproval Framework AWE Configuring To Be Site Specific PDFNEKRONo ratings yet
- Manual Standby Database Under Oracle Standard EditionDocument3 pagesManual Standby Database Under Oracle Standard EditionchralesNo ratings yet
- Activity Exercise Assignment Week 10 CC105Document19 pagesActivity Exercise Assignment Week 10 CC105Embionada, Larz OmeirNo ratings yet
- PenjualanDocument3 pagesPenjualanSuhaimiNo ratings yet
- Oracle Dbas Deploying Highly Available SQL Server Systems: Joe YongDocument45 pagesOracle Dbas Deploying Highly Available SQL Server Systems: Joe YongKhairul AdamsNo ratings yet
- Hypercharge Oracle Truncate Table PerformanceDocument3 pagesHypercharge Oracle Truncate Table Performancecsalas71No ratings yet
- Movers and Packers Management SystemDocument29 pagesMovers and Packers Management SystemNeha GowdaNo ratings yet
- K L University Department of Computer Science & Engineering II/IV B.Tech Semester II Database Management Systems (13CS204) TEST-2 KeyDocument8 pagesK L University Department of Computer Science & Engineering II/IV B.Tech Semester II Database Management Systems (13CS204) TEST-2 KeyRami ReddyNo ratings yet
- D50079GC20 sg1Document16 pagesD50079GC20 sg1StevenandresElfoNo ratings yet
- DW Architecture & DataFlowDocument24 pagesDW Architecture & DataFlowGeetkiran KaurNo ratings yet
- HDFS file metadataDocument4 pagesHDFS file metadatageoinsysNo ratings yet
- Resetlogs and NoresetlogsDocument1 pageResetlogs and NoresetlogsdbareddyNo ratings yet
- (English) NoSQL Database Tutorial - Full Course For Beginners (DownSub - Com)Document72 pages(English) NoSQL Database Tutorial - Full Course For Beginners (DownSub - Com)brmonteiroNo ratings yet
- Business Object: Talent ProfilesDocument18 pagesBusiness Object: Talent Profilesknani9090No ratings yet
- 02 - Designing Applications and DatabasesDocument30 pages02 - Designing Applications and DatabasesMahesh PrasadNo ratings yet
- Introduction To R-Trees: Multidimensional DataDocument11 pagesIntroduction To R-Trees: Multidimensional DataRostomPiraCastuerasNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Database Processing: Fundamentals, Design, and Implementation, 13/E 13th Edition David M. Kroenke, David J. AuerDocument36 pagesTest Bank For Database Processing: Fundamentals, Design, and Implementation, 13/E 13th Edition David M. Kroenke, David J. Aueramyharveyqznmbipkyr100% (13)
- Fundamentals of Data ScienceDocument62 pagesFundamentals of Data ScienceDr. C. Deepa HoD AI&DS100% (1)
- IDENTIFIKASI PAD KABUPATEN KEPU LA UAN SANGIHEDocument8 pagesIDENTIFIKASI PAD KABUPATEN KEPU LA UAN SANGIHESentahanakeng Malahasa perkasaNo ratings yet
- RMS Pre-Bid PresentationDocument64 pagesRMS Pre-Bid PresentationShahid MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Learn Python Programming for Beginners: Best Step-by-Step Guide for Coding with Python, Great for Kids and Adults. Includes Practical Exercises on Data Analysis, Machine Learning and More.From EverandLearn Python Programming for Beginners: Best Step-by-Step Guide for Coding with Python, Great for Kids and Adults. Includes Practical Exercises on Data Analysis, Machine Learning and More.Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (34)
- Nine Algorithms That Changed the Future: The Ingenious Ideas That Drive Today's ComputersFrom EverandNine Algorithms That Changed the Future: The Ingenious Ideas That Drive Today's ComputersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (7)
- Linux: The Ultimate Beginner's Guide to Learn Linux Operating System, Command Line and Linux Programming Step by StepFrom EverandLinux: The Ultimate Beginner's Guide to Learn Linux Operating System, Command Line and Linux Programming Step by StepRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (9)
- Excel Essentials: A Step-by-Step Guide with Pictures for Absolute Beginners to Master the Basics and Start Using Excel with ConfidenceFrom EverandExcel Essentials: A Step-by-Step Guide with Pictures for Absolute Beginners to Master the Basics and Start Using Excel with ConfidenceNo ratings yet
- Dark Data: Why What You Don’t Know MattersFrom EverandDark Data: Why What You Don’t Know MattersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Blockchain Basics: A Non-Technical Introduction in 25 StepsFrom EverandBlockchain Basics: A Non-Technical Introduction in 25 StepsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (24)
- Clean Code: A Handbook of Agile Software CraftsmanshipFrom EverandClean Code: A Handbook of Agile Software CraftsmanshipRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (13)
- Software Engineering at Google: Lessons Learned from Programming Over TimeFrom EverandSoftware Engineering at Google: Lessons Learned from Programming Over TimeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- Monitored: Business and Surveillance in a Time of Big DataFrom EverandMonitored: Business and Surveillance in a Time of Big DataRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- The Advanced Roblox Coding Book: An Unofficial Guide, Updated Edition: Learn How to Script Games, Code Objects and Settings, and Create Your Own World!From EverandThe Advanced Roblox Coding Book: An Unofficial Guide, Updated Edition: Learn How to Script Games, Code Objects and Settings, and Create Your Own World!Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Generative Art: A practical guide using ProcessingFrom EverandGenerative Art: A practical guide using ProcessingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Introducing Python: Modern Computing in Simple Packages, 2nd EditionFrom EverandIntroducing Python: Modern Computing in Simple Packages, 2nd EditionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (7)
- What Algorithms Want: Imagination in the Age of ComputingFrom EverandWhat Algorithms Want: Imagination in the Age of ComputingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (41)
- Python Programming : How to Code Python Fast In Just 24 Hours With 7 Simple StepsFrom EverandPython Programming : How to Code Python Fast In Just 24 Hours With 7 Simple StepsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (54)
- Agile Metrics in Action: How to measure and improve team performanceFrom EverandAgile Metrics in Action: How to measure and improve team performanceNo ratings yet
- GROKKING ALGORITHMS: Simple and Effective Methods to Grokking Deep Learning and Machine LearningFrom EverandGROKKING ALGORITHMS: Simple and Effective Methods to Grokking Deep Learning and Machine LearningNo ratings yet
- CODING FOR ABSOLUTE BEGINNERS: How to Keep Your Data Safe from Hackers by Mastering the Basic Functions of Python, Java, and C++ (2022 Guide for Newbies)From EverandCODING FOR ABSOLUTE BEGINNERS: How to Keep Your Data Safe from Hackers by Mastering the Basic Functions of Python, Java, and C++ (2022 Guide for Newbies)No ratings yet
- Tiny Python Projects: Learn coding and testing with puzzles and gamesFrom EverandTiny Python Projects: Learn coding and testing with puzzles and gamesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)