Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Solar Irradiance
Uploaded by
Totztutz Togodunz Tonztunz0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
39 views1 pagesolar
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentsolar
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
39 views1 pageSolar Irradiance
Uploaded by
Totztutz Togodunz Tonztunzsolar
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
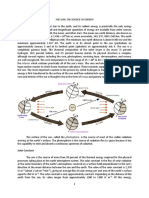
Solar irradiance
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Solar irradiance is a measure of the irradiance (power per unit area on the Earth's surface)
produced by the Sun in the form of electromagnetic radiation, which is perceived by humans as
sunlight. Solar irradiance in a specific area may be measured as insolation, the solar radiation
energy per unit area during a given time, or as direct insolation, insolation which reaches a
location on Earth after absorption and scattering in the atmosphere. Total solar irradiance (TSI),
is a measure of the amount of solar radiative energy incident on the entirety of the Earth's upper
atmosphere. This represents a fraction of the Solar constant, the total amount of electromagnetic
radiation emanating from the Sun in all directions.
Although the energy output of the Sun is fairly constant, solar irradiance "varies significantly
from one place to another and changes throughout the year".
[1]
Sunlight only reaches the parts of
the Earth that are facing the Sun at any given time, and the most intense irradiance is experienced
by those parts that are not at an angle to the Sun as it passes over. The calculation of solar
irradiance for a given area is useful for planning to obtain solar power.
[1]
Solar activity and
irradiance measurement is a concern of space agencies. For example, the American space
agency, NASA, has launched a Solar Irradiance Monitors on its Solar Radiation and Climate
Experiment (SORCE) satellite.
You might also like
- Week 2Document58 pagesWeek 2Abdalrahman YahyaNo ratings yet
- Solar Radiation: Direct Radiation and Diffuse Radiation and Reflected RadiationDocument2 pagesSolar Radiation: Direct Radiation and Diffuse Radiation and Reflected RadiationnehaNo ratings yet
- Group 3 - Solar Radiation and Earth's Energy BalanceDocument49 pagesGroup 3 - Solar Radiation and Earth's Energy BalanceJohn Carlo AbalaNo ratings yet
- Solar Constant, Beam and Diffuse Radiation, Attenuation of Solar RadiationDocument15 pagesSolar Constant, Beam and Diffuse Radiation, Attenuation of Solar RadiationBalajagannath NadarNo ratings yet
- Class Note 1 B - 2B - Radiation and Temperature-1Document23 pagesClass Note 1 B - 2B - Radiation and Temperature-1Mangal MurmuNo ratings yet
- The Sun: Earth's Primary Energy SourceDocument23 pagesThe Sun: Earth's Primary Energy SourceMangal MurmuNo ratings yet
- Measuring Sunlight Intensity With Recorders And CalculationsDocument6 pagesMeasuring Sunlight Intensity With Recorders And CalculationsVed NarsekarNo ratings yet
- ME444 Solar Energy Document TitleDocument15 pagesME444 Solar Energy Document TitleGuhan Sidharth MNo ratings yet
- M2. SOLAR RadiationDocument56 pagesM2. SOLAR Radiationaskanth31No ratings yet
- Solar RadiationDocument17 pagesSolar RadiationPardha Saradhi JNo ratings yet
- Solar Energy BasicsDocument25 pagesSolar Energy BasicsSujit Kumar100% (1)
- Solar Radiation Hand Book (2008) : Typical Climatic Data For Selected Radiation StationsDocument80 pagesSolar Radiation Hand Book (2008) : Typical Climatic Data For Selected Radiation StationsGirish PatilNo ratings yet
- Unit-2 SolarDocument28 pagesUnit-2 Solar2k21cse093No ratings yet
- Solar Radiation: Solar Radiation - Sun-Earth Relationships - Array Orientation - Solar Radiation Data SetsDocument32 pagesSolar Radiation: Solar Radiation - Sun-Earth Relationships - Array Orientation - Solar Radiation Data Setsrajyalakshmi_me6622No ratings yet
- Radiation and Energy BalanceDocument23 pagesRadiation and Energy BalanceglaydelleNo ratings yet
- Radiation and Energy BalanceDocument23 pagesRadiation and Energy BalanceglaydelleNo ratings yet
- Interview Questions - TechnicalDocument37 pagesInterview Questions - TechnicalVikas PanchalNo ratings yet
- Introduction to the Fundamentals of Solar EnergyDocument82 pagesIntroduction to the Fundamentals of Solar EnergySumit RoyNo ratings yet
- Passive Solar HeatingDocument40 pagesPassive Solar HeatingVer Bautista100% (1)
- 1.solar EnergyDocument70 pages1.solar EnergyRohan JindalNo ratings yet
- ERU-Lect. Solar 1Document37 pagesERU-Lect. Solar 1Amroz AfzalNo ratings yet
- Radiation SolarDocument5 pagesRadiation SolarMuluken Temesgen100% (1)
- Unit IDocument40 pagesUnit IPragadees PalaniNo ratings yet
- Classics: Handbook of Solar Radiation Data For IndiaDocument6 pagesClassics: Handbook of Solar Radiation Data For IndiaSiddharth KandimallaNo ratings yet
- Renewable Energy Sources and Solar Radiation PhysicsDocument48 pagesRenewable Energy Sources and Solar Radiation PhysicsJaya RajNo ratings yet
- Solar Radiation Guide: Sun Structure, Characteristics & Earth RelationshipsDocument46 pagesSolar Radiation Guide: Sun Structure, Characteristics & Earth Relationshipsaman_88_vermaNo ratings yet
- Solar Energy Engineering Module on Radiation MeasurementDocument4 pagesSolar Energy Engineering Module on Radiation MeasurementChirayu JanamattiNo ratings yet
- Solar Energy BasicsDocument14 pagesSolar Energy BasicsSuprava GhoshPaulNo ratings yet
- The Sun's Untapped Potential: An Introduction to Solar EnergyDocument26 pagesThe Sun's Untapped Potential: An Introduction to Solar EnergyZohaib Hasan KhanNo ratings yet
- GWCC1Document2 pagesGWCC1Aastha SinghNo ratings yet
- Solar Radiation BasicsDocument15 pagesSolar Radiation BasicsYoussef KamounNo ratings yet
- Unit - 1 Solar Energy TechnologiesDocument69 pagesUnit - 1 Solar Energy TechnologiesVinoth MalaikaniNo ratings yet
- Sunlight - The Total Spectrum of EM Radiation from the SunDocument2 pagesSunlight - The Total Spectrum of EM Radiation from the SunprashanpriyaNo ratings yet
- Solar Energy Reaching The Earth's Surface The Solar ConstantDocument11 pagesSolar Energy Reaching The Earth's Surface The Solar ConstantRichard Simon KisituNo ratings yet
- Climatogy Power PointDocument197 pagesClimatogy Power PointBushasha buchuroNo ratings yet
- Sunlight Is A Portion of The: Vitamin DDocument1 pageSunlight Is A Portion of The: Vitamin DMaricon B. LabaoNo ratings yet
- Solar EnergyDocument43 pagesSolar Energyahmad.n.yassine99No ratings yet
- Unesco - Eolss Sample Chapters: Solar Radiation Energy (Fundamentals)Document10 pagesUnesco - Eolss Sample Chapters: Solar Radiation Energy (Fundamentals)Petrescu VasileNo ratings yet
- Solar PowerDocument32 pagesSolar PowerraihanNo ratings yet
- Unit-III Solar EnergyDocument27 pagesUnit-III Solar Energyabhishekbachchan626No ratings yet
- Lec20 WEATHER ELEMENTS AND THEIR INFLUENCE ON DIFFERENT CROPSDocument31 pagesLec20 WEATHER ELEMENTS AND THEIR INFLUENCE ON DIFFERENT CROPSYashasvi ThakurNo ratings yet
- Solar Radiation (Nazrul)Document8 pagesSolar Radiation (Nazrul)Ojana Pother PothikNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Physical Processes On EarthDocument65 pagesChapter 2 - Physical Processes On EarthClydeNo ratings yet
- Renewable Energy Basics OneDocument46 pagesRenewable Energy Basics OneqiTNo ratings yet
- Sunlight: Sunlight Is A Portion of TheDocument2 pagesSunlight: Sunlight Is A Portion of ThePatr IckNo ratings yet
- All Document Reader 1702874093129Document6 pagesAll Document Reader 170287409312961 SURAJ KUMAR TIRKINo ratings yet
- Solar Energy 11-01-2011Document108 pagesSolar Energy 11-01-2011DebarunSahaNo ratings yet
- Measure Solar Radiation Intensity Using PyranometersTITLEDocument13 pagesMeasure Solar Radiation Intensity Using PyranometersTITLEVISHAL VNo ratings yet
- Ocean Atmosphere Circulation Cells Weather ClimateDocument47 pagesOcean Atmosphere Circulation Cells Weather ClimateNaga LakshmiNo ratings yet
- Solar Energy Course OverviewDocument37 pagesSolar Energy Course OverviewMarshet MulatNo ratings yet
- Solar RadiationDocument15 pagesSolar RadiationShreya SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Solar NotesDocument35 pagesSolar NotesakirammugoyaNo ratings yet
- Titolo Presentazione Sottotitolo: Introduction To Photovoltaic GenerationDocument46 pagesTitolo Presentazione Sottotitolo: Introduction To Photovoltaic GenerationEliot KhNo ratings yet
- Operation and Maintenance of Solar ELECTRICSYSTEMS (Professional Elective)Document68 pagesOperation and Maintenance of Solar ELECTRICSYSTEMS (Professional Elective)santoshNo ratings yet
- Extraterrestrial and Terrestrial Solar RadiationDocument6 pagesExtraterrestrial and Terrestrial Solar RadiationAnmol sharmaNo ratings yet
- Solar RadiationDocument6 pagesSolar RadiationMaizan IsmailNo ratings yet
- The Sun: Its Spots and Flares - Astronomy Book for Beginners | Children's Astronomy BooksFrom EverandThe Sun: Its Spots and Flares - Astronomy Book for Beginners | Children's Astronomy BooksNo ratings yet