Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Etp426 s252057 Jarrod Stockman Teaching Portfolio Sept 2014 Part 1a
Uploaded by
api-2358374700 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
64 views5 pagesOriginal Title
etp426 s252057 jarrod stockman teaching portfolio sept 2014 part 1a
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
64 views5 pagesEtp426 s252057 Jarrod Stockman Teaching Portfolio Sept 2014 Part 1a
Uploaded by
api-235837470Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
Standard 2
Know The Content And How To Teach It.
2.1 Demonstrate knowledge and understanding of the concepts,
substance and structure of the content and teaching strategies of
the teaching area.
2.2 Organise content into an effective learning and teaching
sequence.
2.3 Use curriculum, assessment and reporting knowledge to design
learning sequences and lesson plans.
2.4 Understand and respect Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander
people to promote reconciliation between Indigenous and non-
Indigenous Australians
2.5 Know and understand literacy and numeracy teaching strategies
and their application in teaching areas.
2.6 Implement teaching strategies for using ICT to expand curriculum
learning opportunities for students.
Back to Contents Page
2.1 Demonstrate knowledge and understanding of the concepts, substance
and structure of the content and teaching strategies of the teaching area
2.2 Organise content into an effective learning and teaching sequence.
2.3 Use curriculum, assessment and reporting knowledge to design learning
sequences and lesson plans.
Reflective Journal Entry: (Math Preparation) 21
st
Aug
2014
Direct Instruction is a structured and well planned
teaching system that requires the teacher to read the
lesson a head of the class and know the mastery test
content and when the test itself is coming up. The reason
for this is if a student or group are not firm on its content
then one can make teaching adjustments, differentiate,
emphasise or go over the lesson content again until firm
learning is accomplished.
I am reading nearly 2 lessons ahead of myself to
understand what is coming up during class sessions. It
takes about 30 minutes on average to read/prepare each
lesson being Language, Spelling, Paired Reading and
Math) however it is beneficial because when behaviours
arise and I need to call our behaviour management officer
I can do so while still teaching the lesson with more
confidence.
Math Lesson example
Math Assessment
example
Math Remedies example
Math Planning Page
example
Reflective Journal Entry:
Math Preparation)
21
st
Aug 2014
To increase my planning
skills and knowledge of
the lessons, mentor
suggested at the
beginning of the Prac that
I create a sequences of
lessons sheet and read
each lesson content.
Lesson 86 Lesson 87 Lesson 88 Lesson 89 Lesson 90
New Exercise
Introduction
New Exercise
Introduction
New Exercise
Introduction
New Exercise
Introduction
New Exercise
Introduction
Student Learning
Objective
1. Learn how to
solve 3 digit
addition
problems with
carrying.
2. Compose 2
dimensional
figures
1. Learn how to
carry to solve
money
problems
2. Solve 3 digit
addition
problems with
carrying.
1. Count the
value of coins
added to dollar
amounts
2. Write the
greater than,
less than, and
equals signs
(>,<).
1. Say additional
and
subtraction
facts with the
same small
number; find
missing
numbers in
number
families
2. Solve 3 digit
addition
problems with
carrying and
with 3 addends
1. Learn how to
solve 3 digit
addition
problems with
carrying
multiple digits
2. Count and
write the value
of coins added
to dollar
amounts
Teacher Material Presentation Book 3,
White Board, W/B pen,
Board Display CD,
Computer
Student Material Workbook, pencil
Additional Practice Student Practice
Software
Math Planning Page Preparation
2.4 Understand and respect Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people to promote
reconciliation between Indigenous and non-Indigenous Australians
Reflective Journal Entry: (Language and Culture) 24
th
J une 2014
Additional to my work as a Child Safety Officer in Weipa, Aurukun, Napranum and Mapoon,
completing my prac here in Hopevale confirms a sense of respect for the Aboriginal and
Torres Straight islander histories, cultures and languages. The other day I was allowed to
observe teacher Lil Bowen, a local, who teaches the local language here in Hopevale; the
local language being Guugu Yimidhir. What was simply amazing was listening to Lil singing a
local customary song in unison. So wonderful to hear 40,000 years of tradition and history in
one sitting. Lil taught me some body parts and a simple sentence like Ngalinhun maraarr
duna-manaadhi Man walking in the rain.
The culture has some parallel similarities to my New Zealand Maori indigenous history like
language, dance living off and respecting land.
I feel privileged to work with the children here.
Photo: Presents Awards
Photo: Working with
students
Hope Vale Language
Chart
2.5 Know and understand literacy and numeracy teaching strategies and their application
in teaching areas.
Numeracy in an Indigenous Cultural Context
Indigenous are seen to be a minority class of disadvantaged Australians. We need to be (re) considering in our 'quality' teaching
and learning practices, and in our assessment and reporting practices that Indigenous students learn better with visual and verbal
instruction. Reinforced learning can be better achieved when there are practical hands on experiences (DEST, What Works,
2013).
Successful learning is deemed to be achieved when families and community are involved, children know what is expected of
them by teachers, parents understand high expectations of teachers and where teachers shape the lesson according to the needs
of the students for the Indigenous (DEST, What Works, 2013).
To be numerate is to use mathematics effectively to meet the general demands of life, at home, in paid work, and for
participation in community and civic life. (AAMT, 1997 pg 10)
Reflective Journal Entry: (Math and Literacy) 15
th
Aug 2014
Teaching literacy and numeracy affect how that student learns and views the world in life and teachers should strive to make
literacy and numeracy an enjoyable and informative part of all learning experiences. Anderson and Freebody (DEEWR, 2005,
p. 8) noted that There are strong connections between a young childs early language experience and later literacy
development.
As stated above a teacher needs to be prepared to adapt to the ever changing class environment to keep the students
engaged in their learning. The above lessons today covered literacy (language) and math and the strategies included keeping
the momentum of instruction and engagement of students while managing other variables that can slow the pace of the lesson
such as giving student team points, disruptive behaviour, students getting out of seats to go toilet or requesting a drink, a
student feeling lethargic due to lack of sleep at home to name a few. Once the strategy of managing class behaviours and
teaching is more confidently delivered in a math and literacy context the same can be adopted in other teaching areas. For
example a paired reading lesson. Before the lesson commences expectations are set by teacher and rules about the task
including following teachers instructions. Upon commencement of the lesson teacher can adapt to the learning style of each
individual for example a less confident reader is paired with a stronger reader. Effective literacy teaching is a much debated
topic, but the literature generally agrees that the teachers knowledge of various forms of literacy, including good pedagogical
strategies and tasks, is essential (Ryan, 2008).
Reference:
Department of Education, Science and Training. (2013) What Works. The Work Program Core Issues 4. Commonwealth of Australian Government
The Australian Association of Mathematics Teachers, inc (1998), Teachers of Mathematic or Numeracy? Adelaide,
Ryan, M. (2008). Engaging middle years students: literacy projects that matter. Journal of Adolescent and Adult Literacy, 52(3), 190-201
DEEWR. (2005). Literacy and Numeracy: A Review of the Literature. Retrieved May, 2014
2.6 Implement teaching strategies for using ICT to expand curriculum learning opportunities
for students.
Reflective Journal Entry: (Language
and Culture) 15
th
Aug 2014
Today I taught math and found that
another way in keeping the
students engaged in this context is
by teaching with enthusiasm and
knowing you lesson or in this case
script. To expand on the students
learning I included an ICT math
program that links with the lesson.
For example the new math topic
today was greater than, less than
symbols (<,>) and how to use them.
Children were asked a series of
question that related to the symbols
and the greater than or less than
numbers and how to apply the
symbols. The class were given four
example questions to answer to
consolidate their learning.
Photo: Math Concepts Program using computer & projector
You might also like
- Teaching Mathematics in the Middle School Classroom: Strategies That WorkFrom EverandTeaching Mathematics in the Middle School Classroom: Strategies That WorkNo ratings yet
- CURR.-DEVT-ACTIVITIES Lopez Rose Ann UDocument9 pagesCURR.-DEVT-ACTIVITIES Lopez Rose Ann URose ann Il100% (2)
- MATH ResearchDocument6 pagesMATH ResearchJhoana LazatinNo ratings yet
- Article Review Sir FurkanDocument3 pagesArticle Review Sir Furkanapi-289755581No ratings yet
- All Out Line ReportsDocument72 pagesAll Out Line ReportsEinsidleNolalisanNo ratings yet
- Challenges and Issues of MTB: Stories of Primary Mathematics TeachersDocument11 pagesChallenges and Issues of MTB: Stories of Primary Mathematics TeachersKrung KrungNo ratings yet
- Teachers As Curriculum Leaders: A. PedagogyDocument14 pagesTeachers As Curriculum Leaders: A. PedagogySmp ParadoNo ratings yet
- Section Three Part 2Document79 pagesSection Three Part 2api-546995290No ratings yet
- Psa 2Document4 pagesPsa 2tafuma ndavambiNo ratings yet
- Vso MathsDocument107 pagesVso Mathsapi-231761810No ratings yet
- Learning Sheet No. 1 - PROED 5Document3 pagesLearning Sheet No. 1 - PROED 5Enriquez BernadetteNo ratings yet
- Critical Reflection: Siti Liyana Binti Omar Tesl Sem 4 Pismp Ambilan Jun 2014Document3 pagesCritical Reflection: Siti Liyana Binti Omar Tesl Sem 4 Pismp Ambilan Jun 2014LIYANA OMARNo ratings yet
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in MathematicsDocument16 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in MathematicsAngel Mickee TurquezaNo ratings yet
- ITL 520 Learning Map Assignment - Timothy GeyerDocument12 pagesITL 520 Learning Map Assignment - Timothy GeyerTimothy GeyerNo ratings yet
- Learning Plans in The Context of The 21 CenturyDocument62 pagesLearning Plans in The Context of The 21 CenturyAnna Rica SicangNo ratings yet
- Jurnals and BooksDocument7 pagesJurnals and BooksTESL10620 Aida Nur Athilah Binti Mat SohNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 Lesson 1 BDocument6 pagesMODULE 1 Lesson 1 BPortes, Hannah GraceNo ratings yet
- ITL 520 Assignment 4 SampleDocument15 pagesITL 520 Assignment 4 SampleTimothy GeyerNo ratings yet
- Z Integrative ActivitiesDocument17 pagesZ Integrative Activitiesapi-251033000100% (1)
- Almie Tuto - Final ExaminationDocument6 pagesAlmie Tuto - Final ExaminationAlmie TutoNo ratings yet
- Pino's ResearchDocument37 pagesPino's ResearchGovernor RichyNo ratings yet
- Selfreflectionpgppt Ivey 2013-14Document17 pagesSelfreflectionpgppt Ivey 2013-14api-232354143No ratings yet
- Resume English Material DevelopmentDocument22 pagesResume English Material DevelopmentfakhiraanisamaharaniNo ratings yet
- HBMT 3203 Teaching of Elementary Mathematics Part IvDocument18 pagesHBMT 3203 Teaching of Elementary Mathematics Part IvSeo WenbingNo ratings yet
- Webinar Material PDFDocument148 pagesWebinar Material PDFb chakradhar reddyNo ratings yet
- K To 12 CurriculumDocument95 pagesK To 12 CurriculumshivauneamarioNo ratings yet
- The Teaching Tool BoxDocument8 pagesThe Teaching Tool Boxma1973No ratings yet
- 9.chapter IiDocument9 pages9.chapter IiLee GorgonioNo ratings yet
- MATHEMATICS Textbook For Class VIIIDocument10 pagesMATHEMATICS Textbook For Class VIIIJacob Moore33% (9)
- Introduction To Teaching AidsDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Teaching AidsPATRICK NICKSONNo ratings yet
- What Is IMsDocument4 pagesWhat Is IMsrose cruzNo ratings yet
- Teaching Strategies 2 PPT Presentation 2 Edited-1Document96 pagesTeaching Strategies 2 PPT Presentation 2 Edited-1Jessy Grace Costo - TizonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Modules 1 2Document9 pagesChapter 1 Modules 1 2Dan Dan SoyNo ratings yet
- Leandri Visagie Educ4001 Assessment3Document9 pagesLeandri Visagie Educ4001 Assessment3api-298893238No ratings yet
- Review of Journal: STEM The Boredom: Engage Students in The Australian Curriculum Using ICT With Problem-Based Learning and Assessment by Christopher Paul NewhouseDocument4 pagesReview of Journal: STEM The Boredom: Engage Students in The Australian Curriculum Using ICT With Problem-Based Learning and Assessment by Christopher Paul NewhouseFirda Annidaul KhusnaNo ratings yet
- Module 13 - Week 13: Cit Colleges of Paniqui FoundationDocument6 pagesModule 13 - Week 13: Cit Colleges of Paniqui FoundationKeith CatbaganNo ratings yet
- Assignmnet 1 - Bip3014 DR KhazailaDocument13 pagesAssignmnet 1 - Bip3014 DR KhazailaOliveMikaelsonNo ratings yet
- Peer Reflection SamplesDocument7 pagesPeer Reflection SamplesbonniNo ratings yet
- Ed 401 DETAILED LESSON PLANDocument7 pagesEd 401 DETAILED LESSON PLANNemuel DoroNo ratings yet
- San Esteban High School SBM Best PracticeDocument13 pagesSan Esteban High School SBM Best PracticeJoshua RamirezNo ratings yet
- Inquiry PowerpointDocument10 pagesInquiry Powerpointapi-270737189No ratings yet
- Pedagogy Teaching SkillsDocument5 pagesPedagogy Teaching Skillstimothydavid874No ratings yet
- Tools in Community Literacy ServiceDocument11 pagesTools in Community Literacy ServiceMichaela ParalejasNo ratings yet
- Assignment On DifferentiationDocument9 pagesAssignment On DifferentiationRuby Grewal Sharma0% (1)
- Language Orientation Virtual EnvironmentDocument16 pagesLanguage Orientation Virtual EnvironmentZulhitjarin NasutionNo ratings yet
- FS 4 Learning ActivitiesDocument23 pagesFS 4 Learning Activitiessiena jimenez84% (19)
- Sed SS 316 Chapter 2Document55 pagesSed SS 316 Chapter 2OLIGO CHERRY GAYNo ratings yet
- Muskingum University Lesson Plan 366Document10 pagesMuskingum University Lesson Plan 366api-387802907No ratings yet
- Lesson PlanningDocument25 pagesLesson Planningcalvin mateNo ratings yet
- M4R4 GTFDocument3 pagesM4R4 GTFGlenn CuevaNo ratings yet
- Acei PortfolioDocument18 pagesAcei Portfolioapi-264661011No ratings yet
- The Problem Background of The ProblemDocument73 pagesThe Problem Background of The ProblemNoel LacambraNo ratings yet
- Lts ActivityDocument67 pagesLts ActivityKristian Kenneth Angelo Reandino100% (1)
- Second Part - Mam Maria - Complete - Ar - Reading - 10012023Document26 pagesSecond Part - Mam Maria - Complete - Ar - Reading - 10012023Zejkeara ImperialNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document19 pagesChapter 1Abegail Tamises PiralNo ratings yet
- Inclusive Assessment Task 2 - Case StudyDocument8 pagesInclusive Assessment Task 2 - Case Studyapi-357549157No ratings yet
- Curriculum Compacting: An Easy Start to Differentiating for High Potential StudentsFrom EverandCurriculum Compacting: An Easy Start to Differentiating for High Potential StudentsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Hayley Mexted Dete Internship 020914Document1 pageHayley Mexted Dete Internship 020914api-235837470No ratings yet
- Hayley Mexted Referee Statement 020914Document1 pageHayley Mexted Referee Statement 020914api-235837470No ratings yet
- Finn Buckley Referee Statement 020914Document1 pageFinn Buckley Referee Statement 020914api-235837470No ratings yet
- Etp426 s252057 Jarrod Stockman Teaching Portfolio Sept 2014 Part 3Document7 pagesEtp426 s252057 Jarrod Stockman Teaching Portfolio Sept 2014 Part 3api-235837470No ratings yet
- Etp426 s252057 Jarrod Stockman Teaching Portfolio Sept 2014 Part 3aDocument6 pagesEtp426 s252057 Jarrod Stockman Teaching Portfolio Sept 2014 Part 3aapi-235837470No ratings yet
- Etp426 s252057 Jarrod Stockman Teaching Portfolio Sept 2014 Part 2Document9 pagesEtp426 s252057 Jarrod Stockman Teaching Portfolio Sept 2014 Part 2api-235837470No ratings yet
- Etp426 s252057 Jarrod Stockman Teaching Portfolio Sept 2014 Part 1Document11 pagesEtp426 s252057 Jarrod Stockman Teaching Portfolio Sept 2014 Part 1api-235837470No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Antarctic Explorer 020813Document3 pagesLesson Plan Antarctic Explorer 020813api-235837470No ratings yet
- Etp 410 Lesson Plan 1 Light Fantastic 6 Nov 2013Document4 pagesEtp 410 Lesson Plan 1 Light Fantastic 6 Nov 2013api-235837470No ratings yet
- CT SizingDocument62 pagesCT SizingMohamed TalebNo ratings yet
- Farmer Producer Companies in OdishaDocument34 pagesFarmer Producer Companies in OdishaSuraj GantayatNo ratings yet
- Opc PPT FinalDocument22 pagesOpc PPT FinalnischalaNo ratings yet
- 3 Carbohydrates' StructureDocument33 pages3 Carbohydrates' StructureDilan TeodoroNo ratings yet
- .Urp 203 Note 2022 - 1642405559000Document6 pages.Urp 203 Note 2022 - 1642405559000Farouk SalehNo ratings yet
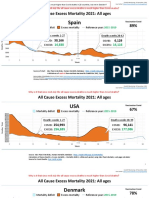
- Countries EXCESS DEATHS All Ages - 15nov2021Document21 pagesCountries EXCESS DEATHS All Ages - 15nov2021robaksNo ratings yet
- Time-Sensitive Networking - An IntroductionDocument5 pagesTime-Sensitive Networking - An Introductionsmyethdrath24No ratings yet
- Existential ThreatsDocument6 pagesExistential Threatslolab_4No ratings yet
- BNF Pos - StockmockDocument14 pagesBNF Pos - StockmockSatish KumarNo ratings yet
- Checklist & Guideline ISO 22000Document14 pagesChecklist & Guideline ISO 22000Documentos Tecnicos75% (4)
- C C C C: "P P P P PDocument25 pagesC C C C: "P P P P PShalu Dua KatyalNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 4 Daily Lesson Plan - CompressDocument3 pagesChemistry Form 4 Daily Lesson Plan - Compressadila ramlonNo ratings yet
- Service Manual: SV01-NHX40AX03-01E NHX4000 MSX-853 Axis Adjustment Procedure of Z-Axis Zero Return PositionDocument5 pagesService Manual: SV01-NHX40AX03-01E NHX4000 MSX-853 Axis Adjustment Procedure of Z-Axis Zero Return Positionmahdi elmay100% (3)
- Tplink Eap110 Qig EngDocument20 pagesTplink Eap110 Qig EngMaciejNo ratings yet
- Methods of Recording Retruded Contact Position in Dentate PatientsDocument15 pagesMethods of Recording Retruded Contact Position in Dentate PatientsYossr MokhtarNo ratings yet
- Mcdonald 2016Document10 pagesMcdonald 2016Andrika SaputraNo ratings yet
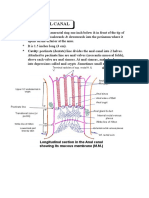
- Anatomy Anal CanalDocument14 pagesAnatomy Anal CanalBela Ronaldoe100% (1)
- Lecturenotes Data MiningDocument23 pagesLecturenotes Data Miningtanyah LloydNo ratings yet
- CX Programmer Operation ManualDocument536 pagesCX Programmer Operation ManualVefik KaraegeNo ratings yet
- Traveling Salesman ProblemDocument11 pagesTraveling Salesman ProblemdeardestinyNo ratings yet
- Washing Machine: Service ManualDocument66 pagesWashing Machine: Service ManualFernando AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- Aptitude Number System PDFDocument5 pagesAptitude Number System PDFharieswaranNo ratings yet
- LM74680 Fasson® Fastrans NG Synthetic PE (ST) / S-2050/ CK40Document2 pagesLM74680 Fasson® Fastrans NG Synthetic PE (ST) / S-2050/ CK40Nishant JhaNo ratings yet
- Pe 03 - Course ModuleDocument42 pagesPe 03 - Course ModuleMARIEL ASINo ratings yet
- Stress-Strain Modelfor Grade275 Reinforcingsteel With Cyclic LoadingDocument9 pagesStress-Strain Modelfor Grade275 Reinforcingsteel With Cyclic LoadingRory Cristian Cordero RojoNo ratings yet
- Dtu Placement BrouchureDocument25 pagesDtu Placement BrouchureAbhishek KumarNo ratings yet
- B.SC BOTANY Semester 5-6 Syllabus June 2013Document33 pagesB.SC BOTANY Semester 5-6 Syllabus June 2013Barnali DuttaNo ratings yet
- Space Hulk - WDDocument262 pagesSpace Hulk - WDIgor Baranenko100% (1)
- Online Extra: "Economists Suffer From Physics Envy"Document2 pagesOnline Extra: "Economists Suffer From Physics Envy"Bisto MasiloNo ratings yet
- Digital MetersDocument47 pagesDigital MetersherovhungNo ratings yet