Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ecology Notes 13-14with Examples
Uploaded by
api-239451622Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ecology Notes 13-14with Examples
Uploaded by
api-239451622Copyright:
Available Formats
Ecology
Ecology - The study of how living things and their environment interact.
Ecosystem All the living and non-living things in an area and their
interactions with each other.
Biomes: An ecosystem that cover large areas of land, and has certain
types of plants, animals, soil and climate. For example, the rainforest or
the desert.
Photosynthesis The process by which green plants make their own
food by using energy from the sun.
Producers: Plants or tiny organisms that use photosynthesis to make
their own food.
Examples: flowers, trees, algae, plankton, basically any green plant
Consumers: An organism that eats plants or other animals for energy
Examples:
Herbivores: An animal that eats only plants
o Examples: cows, elephants, zebras, giraffe, koala, deer
Carnivores: An organism that eats only other animals
o Examples: lions, lady bugs, moray eel, crab spider, chameleon,
lion fish, tigers, praying mantis, owls, puffins, pitcher plant
Omnivores: an animal that eats both plants and animals
o Examples: humans, raccoons, catfish, mice, bears, ducks, pigs,
sea gulls,
Scavengers: A meat-eating animal that feeds on the remains of
dead animals
o Examples: hyenas, vultures, crayfish,
Parasites: An organism that takes food, and sometimes shelter,
from other living things
o Examples: tape worms, mosquitoes, hook worm, fleas, ticks
Decomposers: Organisms that break down the bodies of dead plants and
animals into useful substances like minerals in rich soil.
Examples: mushrooms, fungus, beetles, pill bugs, slugs, earthworms,
snails, molds, millipedes, bacteria
ALL ENERGY STARTS WITH THE SUN!!!!
Food Chain: The path of the energy in food from one organism to
another. The arrow points to the flow of energy. It starts with the sun
and travels to the producers, then the consumers, then the
decomposers.
Food Web: The overlapping food chains in an ecosystem.
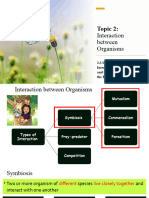
Predator: A living organism that hunts other living organisms for food.
Prey: A living organism that is hunted for food.
Symbiosis: a relationship between two kinds of organisms over time.
Parasitism: a relationship in which one kind of organism (a parasite) lives
on and may harm another organism (host). For example, a dog and a flea
or tick. The flea or tick lives and feeds on the dog and the dog is
irritated and may be harmed.
Mutualism: a relationship between two kinds of organisms that benefits
both. For example, bees drink nectar from flowers and carry away
pollen which pollinates other flowers.
Commensalism: a relationship between two kinds of organisms that
benefits one without harming the other. For example, a crab spider
resembles flower petals to hide from prey. When insects land on the
flower, they are quickly eaten by the spider and the flower is left
unharmed.
Niche: the role of a species in a community.
Invasive species: is a non-native or alien to the ecosystem in which its found.
Can be plants, animals, and other organisms (e.g., microbes).
Human actions are the primary means of invasive species introductions.
Have few natural predators and competitors
Can destroy the habitat of native plants and animals
Satellite imaging:
Invasive Species Forecasting System (ISFS) - observations from NASA
satellites and NASA engineering
Predicts quickly and inexpensively the location and spread of invasive plants
over regional areas.
Can look at remote, hard to reach areas
Look at how the land has changed over time
You might also like
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- What Is SymbiosisDocument13 pagesWhat Is SymbiosisRenae BillingsNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Overview of Normal Flora, Pathogenic - PPTX, First SessionDocument29 pagesOverview of Normal Flora, Pathogenic - PPTX, First SessionGeorge C. KasondaNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Normal Microbial Flora in Human Body-1st DiscussionDocument39 pagesNormal Microbial Flora in Human Body-1st DiscussionLexi LoreNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- First Periodical ExaminationDocument27 pagesFirst Periodical ExaminationLecyrc TapadNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- DLL 3rd ObservationDocument5 pagesDLL 3rd ObservationDanilo Alburo100% (1)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Communities WorksheetDocument2 pagesCommunities WorksheetJamie MakrisNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Quarter Test Science Chapter 1: Major Organs of Humans: C. BrainDocument21 pagesQuarter Test Science Chapter 1: Major Organs of Humans: C. Brain私は 花100% (1)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Second Quarter Assessment in Science 6Document7 pagesSecond Quarter Assessment in Science 6Marites Lilan OlanioNo ratings yet
- Unit A - Biological DiversityDocument82 pagesUnit A - Biological Diversityapi-524920626No ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- G7 Science Q2 - Week 6 - Ecological RelationshipDocument46 pagesG7 Science Q2 - Week 6 - Ecological RelationshipJessa-Bhel AlmueteNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- RPT 2020 DLP Science Year 6 KSSRDocument16 pagesRPT 2020 DLP Science Year 6 KSSRலோகாம்பிகை சிவானந்தன்No ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- COMMENSALISMDocument28 pagesCOMMENSALISMMaryjul Ramos RanayNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Chapter 1 EcologyDocument38 pagesChapter 1 EcologyRamil NacarioNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Relationships Between Populations in The BiocoenosisDocument13 pagesRelationships Between Populations in The BiocoenosisSeptim SalvarusNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- DLP 1ST CO 2021 2022tailorDocument5 pagesDLP 1ST CO 2021 2022tailorChlera Meiah Talondata100% (1)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Science-2nd Periodical TestDocument6 pagesScience-2nd Periodical TestLiza LoromeaNo ratings yet
- 2.3 (B) Interaction Between OrganismsDocument17 pages2.3 (B) Interaction Between OrganismsJoanne OngNo ratings yet
- Symbiosis Practice PDFDocument10 pagesSymbiosis Practice PDFMark ArceNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- S7LT IIh 10 - ECOLOGICAL RELATIONSHIPS CAYMEDocument17 pagesS7LT IIh 10 - ECOLOGICAL RELATIONSHIPS CAYMEMonica P. Ramos100% (1)
- EcosystemDocument6 pagesEcosystem26 Lee Janne 李晴 JR2D1No ratings yet
- Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 7Document7 pagesSemi-Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 7Bon Daniel Fajilan100% (2)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Energy Flow NotesDocument34 pagesEnergy Flow Notesapi-263638354No ratings yet
- Ecological InteractionsDocument4 pagesEcological Interactionsweng sumampongNo ratings yet
- Community EcologyDocument23 pagesCommunity EcologyCjoy MañiboNo ratings yet
- Parasite 1Document22 pagesParasite 1OnSolomonNo ratings yet
- Symbiotic RelationshipDocument4 pagesSymbiotic RelationshipEdsel BelbarNo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Detailed LESSON PLAN IN SCIENCE 7Document6 pagesDetailed LESSON PLAN IN SCIENCE 7Tasnimah100% (3)
- Microbial EcologyDocument23 pagesMicrobial EcologyUsman SurajNo ratings yet
- Comprehension - SymbiosisDocument4 pagesComprehension - Symbiosisapi-352881693No ratings yet
- 17 Ecological Relationships-S-Pogil-23nataliaDocument13 pages17 Ecological Relationships-S-Pogil-23nataliaapi-32508966478% (9)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)