Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Oi Handout
Uploaded by
api-264647583Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Oi Handout
Uploaded by
api-264647583Copyright:
Available Formats
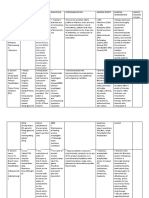
Orthopedic Impairments
By Dinah Williams
IDEA Description
Orthopedic Impairment: Severe orthopedic impairment that adversely affects a childs
educational performance. The term includes impairments caused by a congenital anomaly,
impairments caused by disease (e.g., poliomyelitis, bone tuberculosis), and impairments from
other causes (e.g. Cerebral palsy, amputations, and fractures or burns that cause contractures).
Characteristics
The IDEA category of orthopedic impairments contains a wide variety of disorders. These can be
divided into three main areas: neuromotor impairments, degenerative diseases, and
musculoskeletal disorders. The specific characteristics of an individual who has an orthopedic
impairment will depend on the specific disease and its severity, as well as additional individual
factors.
Neuromotor impairment is caused by neurological (brain/spinal cord) damage that also
affects a persons ability to move one, or more, body parts. The following are all examples
of Neuromotor Impairments: Epilepsy; Spina Bifida; Cerebral Palsy
Degenerative Diseases refer to medical problems that worsen over time and may affect
the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord), bones, blood vessels, or heart, such as the
following: Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis or Lou Gehrigs disease; Heart disease; Multiple
system atrophy; Cancer; Diabetes; and Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis
Musculoskeletal Disorders describe a variety of conditions that affect the muscles, bones,
and joints. Severity varies from person to person. Pain and discomfort interferes with everyday
activities. MSDs can affect all major areas of the body such as Low back pain, Fibromyalgia,
Gout, Rheumatoid arthritis, and Tendinitis.
Teaching Strategies
Most children with orthopedic impairments do not need any special modifications to
lessons as they are mentally capable of doing regular class work, unless you get into the multiple
impairment categories.
Accommodations
Furniture may need to be rearranged to accommodate wheelchairs, canes, and walkers.
Special desks may also be needed for these students. Some may need special writing implements
and computers for speech. Some may need a special helper for personal care skills. Some may
need extra breaks to rest, or for medication.
Sources for help in addition to the ones on the Prezi presentation
http://specialneedshandbook.wikispaces.com/Orthopedic+Impairment
Project IDEAL: Informing & Designing Education for all Learners
http://www.projectidealonline.org/orthopedicImpairments.php
National Association of Parents with Children in Special Education
http://www.napcse.org/exceptionalchildren/orthopedicimpairments.php
National Dissemination Center for Children with Disabilities
http://www.nichcy.org
Algozzine, B., & Ysseldyke, J. (2006). Assisting students with medical, physical, and multiple
disabilities: A practical guide for every teacher. Thousand Oaks, CA: Corwin Press.
American Academy of Special Education Professionals. (2006). Orthopedic impairments.
Retrieved April 16, 2008, fromhttp://aasep.org/professional-
resources/exceptionalstudents/orthopedicimpairment/index.html#c2738.
Baumberger, J. P., & Harper R. E. (2007). Assisting students with disabilities: A handbook for
school counselors (2nd ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: Corwin Press.
Dutton, M. (2005). Orthopaedic examination, evaluation, and intervention: A pocket
handbook. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Duchenne muscular dystrophy. (2007). Muscular Dystrophy Association. Retrieved April 16,
2008, fromhttp://www.mda.org/publications/tchrdmd/.
National Association of Parents with Children in Special Education. (2007). Exceptional children
and disability information. Orthopedic impairments. Retrieved April 16, 2008, from
http://www.napcse.org/exceptionalchildren/orthopedicimpairments.php.
National Dissemination Center for Children with Disabilities. (2004). Disability fact sheet no. 2:
Cerebral Palsy. Retrieved April 16, 2008, from http://www.nichcy.org/pubs/factshe/fs2.pdf.
National Dissemination Center for Children with Disabilities. (2004). Disability fact sheet no. 12:
Spina Bifida. Retrieved April 16, 2008, from http://www.nichcy.org/pubs/factshe/fs12.pdf.
Pierangelo, R., & Giuliani, G. (2007). The educator's manual of disabilities and disorders. San
Francisco, CA: Wiley & Sons.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Increase Font Size On Web BrowsersDocument2 pagesIncrease Font Size On Web Browsersapi-264486418No ratings yet
- Developmental Delay Presentation HandoutDocument3 pagesDevelopmental Delay Presentation Handoutapi-264552550No ratings yet
- Multiple Disabilites HandoutDocument2 pagesMultiple Disabilites Handoutapi-264486418No ratings yet
- ch9 OrganizationDocument39 pagesch9 Organizationapi-264486418No ratings yet
- Speech or Language Impairment HandoutDocument3 pagesSpeech or Language Impairment Handoutapi-264486418No ratings yet
- Law Comparison ChartDocument2 pagesLaw Comparison Chartapi-264552550No ratings yet
- Speech or Language Impairment HandoutDocument3 pagesSpeech or Language Impairment Handoutapi-264552550100% (1)
- Procedural SafeguardsDocument21 pagesProcedural Safeguardsapi-236207623No ratings yet
- Language MattersDocument1 pageLanguage Mattersapi-264486418No ratings yet
- Intellectual Disability HandoutDocument2 pagesIntellectual Disability Handoutapi-264486418No ratings yet
- Disability Presentation Emotional DisturbancesDocument2 pagesDisability Presentation Emotional Disturbancesapi-264486418No ratings yet
- List of Common AcronymsDocument1 pageList of Common Acronymsapi-264486418No ratings yet
- F A T City NotesDocument2 pagesF A T City Notesapi-264486418No ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- EU Harmonized Standards May 2014Document30 pagesEU Harmonized Standards May 2014ajitbasrur445No ratings yet
- Dr. Hossam Eldin Sayed Ali: Lecturer of Medical Biophysics The Research Institute of OphthalmologyDocument32 pagesDr. Hossam Eldin Sayed Ali: Lecturer of Medical Biophysics The Research Institute of OphthalmologyRiya MathurNo ratings yet
- PainoxiaDocument66 pagesPainoxiaOmar WahbiNo ratings yet
- Package - Insert - 08586 - H - en - 30427 - CA 19-9 PDFDocument8 pagesPackage - Insert - 08586 - H - en - 30427 - CA 19-9 PDFadybaila4680No ratings yet
- Poster PresentationDocument1 pagePoster PresentationVency KatiraNo ratings yet
- Front Matter 2021Document18 pagesFront Matter 2021Евгений ПанковецNo ratings yet
- Name of DrugDocument6 pagesName of DrugKathleen ColinioNo ratings yet
- Anti-Allergy Drug GuidelinesDocument8 pagesAnti-Allergy Drug GuidelinesYojna PatilNo ratings yet
- Onnetsutherapys 130128035904 Phpapp01 PDFDocument70 pagesOnnetsutherapys 130128035904 Phpapp01 PDFjavi_reyes_17No ratings yet
- Fora 6 Brochure PDFDocument8 pagesFora 6 Brochure PDFFatma IsmawatiNo ratings yet
- Cleft Lip and Cleft PalateDocument27 pagesCleft Lip and Cleft Palatenamah odatNo ratings yet
- The Journal of Rheumatology Volume 42, No. 7Document7 pagesThe Journal of Rheumatology Volume 42, No. 7salclNo ratings yet
- Ayurved TerminologiesDocument30 pagesAyurved TerminologiesVipul RaichuraNo ratings yet
- What Are Early Indicators of Mesothelioma. Realizing The Early Signs ofDocument2 pagesWhat Are Early Indicators of Mesothelioma. Realizing The Early Signs ofthasyaNo ratings yet
- Dentists in LimassolDocument26 pagesDentists in LimassolANDREASBOULNo ratings yet
- Human Sexuality and Sexual DisordersDocument42 pagesHuman Sexuality and Sexual DisordersAbdul Gafoor FahmyNo ratings yet
- Free Journal List For PublicationDocument11 pagesFree Journal List For PublicationSyed Saad AliNo ratings yet
- Sports Injuries ManagementDocument94 pagesSports Injuries ManagementSaha DirllahNo ratings yet
- Sonuplus 492 Operator ManualDocument72 pagesSonuplus 492 Operator ManualShoaib KhanNo ratings yet
- 113 - JCI Mock Survey QuestionDocument4 pages113 - JCI Mock Survey QuestionMohamad Attia100% (1)
- Addiction CaseDocument4 pagesAddiction CasePooja VarmaNo ratings yet
- 1303miha OnePager01neutralDocument2 pages1303miha OnePager01neutralAlex YamilNo ratings yet
- The Rubik's Cube Approach To Clinical MedicineDocument2 pagesThe Rubik's Cube Approach To Clinical Medicinehenrygoldstein100% (1)
- HealthDocument6 pagesHealthAngel Bernal PinedaNo ratings yet
- Erectile DysfunctionDocument31 pagesErectile Dysfunctionrahuldtc100% (1)
- Quiz Hospital DocumentationDocument5 pagesQuiz Hospital DocumentationJessica EdiosNo ratings yet
- Gen EpidemiologyDocument88 pagesGen EpidemiologyShibu Sebastian100% (1)
- AHA Elearning - ACLS Precourse Self-Assessment and Precourse WorkDocument3 pagesAHA Elearning - ACLS Precourse Self-Assessment and Precourse WorkAmmar bushraNo ratings yet
- Power Point Dr. ShintaDocument11 pagesPower Point Dr. ShintaAnonymous fOz6ToNo ratings yet
- Post Op InstructionsDocument5 pagesPost Op InstructionsAmar Bhochhibhoya0% (1)