Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Levels of Organization 2
Uploaded by
api-2584000310 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
179 views11 pagesOriginal Title
levels of organization 2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
179 views11 pagesLevels of Organization 2
Uploaded by
api-258400031Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 11
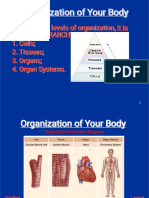
Levels Of Organization
Recognize the levels of
organization within the human
body (including cells, tissues,
organs, and systems).
The levels of organization from
smallest to largest size:
Cells
Tissues
Organs
Organ
System
Organism
Cells
The basic unit of structure and
function in the human body
Over 200 different cells in your body
with special jobs
Examples: nerve cells, blood cells,
and bone cells.
Tissues
A group of similar type of cells
that work together to perform
the same function.
There are four basic types of
tissue in the human body:
Tissues
1. Nerve tissue carries
impulses back and forth to
the brain from the body
Three types of muscle tissue
Muscle tissue (cardiac, smooth, skeletal)
contract and shorten, making body parts move
Skeletal
Cardiac
Smooth
3. Epithelial tissue covers the surfaces of
the body, inside (as lining and /or covering
of internal organs) and outside (as layer of
skin)
4. Connective tissue connects all parts of
the body and provides support (for
example tendons, ligaments, cartilage).
Organs
A group of two or
more different types
of tissue that work
together to perform
a specific function.
For example, the heart is made of muscle tissue
and connective tissues which functions to pump
blood throughout the body.
The task is generally more complex than that of
the tissue.
Organ
System
A group of two or more organs that work
together to perform a specific function.
Each organ system has its own function but
the systems work together and depend on
one another.
There are 11 different organ systems in the
human body.
Organism
Sum of all cells, tissues, organs
and organ systems makes an
organism
You might also like
- Levels of OrganizationDocument15 pagesLevels of Organizationmoazh1310No ratings yet
- From Cells To Tissue To Organs To Organ Systems: LS1.A: Structure and FunctionDocument3 pagesFrom Cells To Tissue To Organs To Organ Systems: LS1.A: Structure and FunctionSaleh AlsowayanNo ratings yet
- Body Systems OrganizationDocument12 pagesBody Systems Organizationmegha139No ratings yet
- Microsoft Word - TISSUES OF THE BODY - MEDICS 20102011Document5 pagesMicrosoft Word - TISSUES OF THE BODY - MEDICS 20102011AJAY KUMARNo ratings yet
- Why Human Beings Are Considered Complex Organisms Group 5Document37 pagesWhy Human Beings Are Considered Complex Organisms Group 5Nuraini Zul100% (3)
- Introduction To The Body As A Whole: Abdul Quddoos Lecturer SAHARA College of Pharmacy, NarowalDocument23 pagesIntroduction To The Body As A Whole: Abdul Quddoos Lecturer SAHARA College of Pharmacy, NarowalAyeshaNo ratings yet
- Unit-2, (Lecture-4th) Characterstics To Living OrganismDocument24 pagesUnit-2, (Lecture-4th) Characterstics To Living OrganismNavneet ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Basic AnatomyDocument2 pagesBasic Anatomyafriesen72No ratings yet
- Lesson 3 G6Document14 pagesLesson 3 G6Neven FathyNo ratings yet
- 2nd - Human Organ SystemsDocument26 pages2nd - Human Organ SystemsJaeshelle Florendo100% (1)
- 01 Animal TissueDocument8 pages01 Animal TissueRohit SharmaNo ratings yet
- ANAPHY REV Chapt 1Document8 pagesANAPHY REV Chapt 1crptzxraffNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Human BodyDocument2 pagesIntroduction To The Human BodyjonelbambaNo ratings yet
- Speech SciebnceDocument2 pagesSpeech SciebnceluisNo ratings yet
- Body OrganizationDocument4 pagesBody OrganizationGlaizel PanalNo ratings yet
- Cell: Vertebrate Body OrganizationDocument11 pagesCell: Vertebrate Body OrganizationSyuri MustikaNo ratings yet
- Información de TissueDocument2 pagesInformación de TissueEduardo Boixo MartínezNo ratings yet
- Cells To Organisms Year 8Document16 pagesCells To Organisms Year 8FarmanNo ratings yet
- Human Body: How Is The Human Body Similar To A Well-Tuned Machine?Document9 pagesHuman Body: How Is The Human Body Similar To A Well-Tuned Machine?Montse GilNo ratings yet
- Animal TissueDocument28 pagesAnimal TissueArjunNo ratings yet
- Human Organ Systems. 2021 22Document4 pagesHuman Organ Systems. 2021 22BABU ANo ratings yet
- Pines City Colleges Medical Laboratory Science Anatomy and Physiology Laboratory ManualDocument9 pagesPines City Colleges Medical Laboratory Science Anatomy and Physiology Laboratory ManualLynch Devin Kirtug-SalengNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument33 pagesTissuesAnonymous imF0MCd9UNo ratings yet
- TX Bio Ch30Document48 pagesTX Bio Ch30Mario Alberto Mora OrtizNo ratings yet
- Is Cell Important For HumansDocument2 pagesIs Cell Important For HumansniallevetriscaNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument4 pagesTissuesJaveria ZaidiNo ratings yet
- Group 7Document9 pagesGroup 7Prinz ToshNo ratings yet
- Human TissuesDocument7 pagesHuman Tissuesapi-269312030No ratings yet
- Anaphy ReviewerDocument12 pagesAnaphy ReviewerRuby Jane LaquihonNo ratings yet
- OrgansDocument2 pagesOrgansAbiramee RamalingamNo ratings yet
- 7 Animal Tissues Human Organ Systems IntroDocument18 pages7 Animal Tissues Human Organ Systems IntroHunzala Rasheed AlamNo ratings yet
- Cell and Tissues ResubDocument9 pagesCell and Tissues Resubsilly GooseNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissues: Epithelial Tissue Is Made Up of Layers of Tightly Packed Cells That Line The SurfacesDocument3 pagesAnimal Tissues: Epithelial Tissue Is Made Up of Layers of Tightly Packed Cells That Line The SurfacesJamesNo ratings yet
- Science 4 Lesson 2.1 FinalDocument34 pagesScience 4 Lesson 2.1 FinalAlicia PerezNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument4 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyAnonymous 2k0o6az6lNo ratings yet
- Basic Body TissueDocument7 pagesBasic Body Tissueapi-278577147No ratings yet
- P.E Anatomical TermsDocument26 pagesP.E Anatomical TermsGerald Mapalo FactorNo ratings yet
- Co2 Lesson 1.1 Human Anatomy Week 4Document10 pagesCo2 Lesson 1.1 Human Anatomy Week 4accfor everythingNo ratings yet
- Á Léqééã Péaéuéiéã Uééxéñsãuééré Kéluéliéuréã Aqé×Iémüsévé Wûxiééré Xéuééïqéré Ìuéléévélééré Éæsééãyrélééjééré Éï Qéwûéìuéwhéuéã LéqéèDocument51 pagesÁ Léqééã Péaéuéiéã Uééxéñsãuééré Kéluéliéuréã Aqé×Iémüsévé Wûxiééré Xéuééïqéré Ìuéléévélééré Éæsééãyrélééjééré Éï Qéwûéìuéwhéuéã LéqéèAlapati Vinod KumarNo ratings yet
- Body Organization 1Document4 pagesBody Organization 1Mohab GarawanyNo ratings yet
- Mapeh 3 - ModuleDocument19 pagesMapeh 3 - ModulePatricia Jean San SebastianNo ratings yet
- Define and Explain The Organization of Cell-Tissue-Organ-Organism! Define and Explain The Organization of Cell-Tissue - Organ-Organism!Document7 pagesDefine and Explain The Organization of Cell-Tissue-Organ-Organism! Define and Explain The Organization of Cell-Tissue - Organ-Organism!Ahmad SolihinNo ratings yet
- Tisssues&organs - Bio PresentationDocument7 pagesTisssues&organs - Bio PresentationHania ZiembaNo ratings yet
- From Cells To Organ SystemsDocument19 pagesFrom Cells To Organ SystemsLori LorenzNo ratings yet
- From Cells To Organ SystemsDocument19 pagesFrom Cells To Organ SystemsLori LorenzNo ratings yet
- Body Organization: Chapter 22 Section 1Document12 pagesBody Organization: Chapter 22 Section 1thegedusNo ratings yet
- Anatomical, Physiological and Mechanical Bases of Movements: Body Really Made Of? "Document10 pagesAnatomical, Physiological and Mechanical Bases of Movements: Body Really Made Of? "Jay Carlo BagayasNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Fisiologi & Biomekanika: Dasar Perancangan Teknik Biomedis Kode: 1103 Rudi Setiawan, S.T, M.TDocument35 pagesAnatomi Fisiologi & Biomekanika: Dasar Perancangan Teknik Biomedis Kode: 1103 Rudi Setiawan, S.T, M.TAdeputra WijayaNo ratings yet
- Reagan Body Systems Booklet 3-13Document76 pagesReagan Body Systems Booklet 3-13api-26963416No ratings yet
- Refresher Course: Names. (Biomechanics, 1990)Document21 pagesRefresher Course: Names. (Biomechanics, 1990)Kirby AnaretaNo ratings yet
- Cells, Tissues, and Organs: For Use With The Unit: The Inside Story Reading in The Content Area. (LA.A.2.2.1.4.1)Document4 pagesCells, Tissues, and Organs: For Use With The Unit: The Inside Story Reading in The Content Area. (LA.A.2.2.1.4.1)Nichole TurkNo ratings yet
- Exercises 1 Tissues: 1. Define What Tissues AreDocument9 pagesExercises 1 Tissues: 1. Define What Tissues AreMaria MarmitaNo ratings yet
- The Human Body Is Organised in The Following WayDocument22 pagesThe Human Body Is Organised in The Following WayFarah AsnidaNo ratings yet
- Tissues, Organs and SystemsDocument6 pagesTissues, Organs and SystemsRehan AsifNo ratings yet
- With Your Partner Measure The Width of Your Wrist in Millimeters (MM)Document9 pagesWith Your Partner Measure The Width of Your Wrist in Millimeters (MM)Mary RosaNo ratings yet
- Human Body Study Guide AnswersDocument2 pagesHuman Body Study Guide Answersapi-325864985No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 (Anatomy)Document63 pagesChapter 1 (Anatomy)Phan Sokkheang100% (1)
- ANATOMYDocument2 pagesANATOMYJecie CodillaNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Organ SystemsDocument11 pages2.3 Organ SystemsUdesh RajNo ratings yet
- 7wa 10 26 15Document4 pages7wa 10 26 15api-258400031No ratings yet
- Spring 2015 Semester Exam ReviewDocument5 pagesSpring 2015 Semester Exam Reviewapi-258400031No ratings yet
- Succession NotesDocument2 pagesSuccession Notesapi-258400031No ratings yet
- District Assessment Review 2015Document4 pagesDistrict Assessment Review 2015api-258400031No ratings yet
- Human Reproductive System WebsiteDocument46 pagesHuman Reproductive System Websiteapi-258400031No ratings yet
- Respiratory2 0Document26 pagesRespiratory2 0api-258400031No ratings yet
- Natural Selection Vs Selective Breeding PPDocument16 pagesNatural Selection Vs Selective Breeding PPapi-258400031No ratings yet
- Humans in Space PPDocument14 pagesHumans in Space PPapi-258400031No ratings yet
- Stimulus and Response PP 2013Document28 pagesStimulus and Response PP 2013api-258400031No ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Function RDDocument18 pagesCell Structure and Function RDapi-258400031No ratings yet
- Safety Contract EngDocument1 pageSafety Contract Engapi-258400031No ratings yet