Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Module 4: Short Questions
Uploaded by
captainhass0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
81 views2 pagesFor what kind of problems in multidimensional heat transfer are analytical solutions possible? what is meant by "shape factor" in two-dimensional heat transfer analysis? what are the advantages and disadvantages of numerical and analytical methods?
Original Description:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentFor what kind of problems in multidimensional heat transfer are analytical solutions possible? what is meant by "shape factor" in two-dimensional heat transfer analysis? what are the advantages and disadvantages of numerical and analytical methods?
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
81 views2 pagesModule 4: Short Questions
Uploaded by
captainhassFor what kind of problems in multidimensional heat transfer are analytical solutions possible? what is meant by "shape factor" in two-dimensional heat transfer analysis? what are the advantages and disadvantages of numerical and analytical methods?
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Module 4: Short questions
1. For what kind of problems in multidimensional heat transfer are analytical
solutions possible? Name some common analytical methods in steady state
multidimensional heat transfer?
2. What are the limitations of analytical methods? In spite of their limitations, why
are analytical solutions useful?
3. What is meant by “shape factor” in two-dimensional heat transfer analysis? What
is the advantage of using such a method? Is there a shape factor in 1D heat
transfer?
4. How do numerical solution methods differ from analytical methods? What are
the advantages and disadvantages of numerical and analytical methods?
5. What is the basis of energy balance method in numerical analysis? How does it
differ from the formal finite difference method using Taylor series
approximation? For a specified nodal network, will these two methods result in
the same or a different set of equations?
6. Consider a medium in which the finite difference formulation of a general interior
node is given in its simplest form as
Tm −1 − 2Tm + Tm +1 g& m
+ =0
Δx 2 k
(a) Is heat transfer in this medium steady or transient?
(b) Is heat transfer one-, two-, or three-dimensional?
(c) Is there heat generation in the medium?
(d) Is the nodal spacing constant or variable?
(e) Is thermal conductivity of the medium constant or variable?
7. Consider a medium in which the finite difference formulation of a general interior
node is given in its simplest form as
g& l 2
Tleft + Ttop + Tright + Tbottom − 4Tnode + m = 0
k
(a) Is heat transfer in this medium steady or transient?
(b) Is heat transfer one-, two-, or three-dimensional?
(c) Is there heat generation in the medium?
(d) Is the nodal spacing constant or variable?
(e) Is thermal conductivity of the medium constant or variable?
8. What is an irregular boundary? What is a practical way of handling irregular
boundary surfaces with the finite difference method?
9. When performing numerical calculations of heat diffusion on a structured
Cartesian grid in two dimensions, a simplified form of the equations states that the
temperature at a node is simply the average of its four adjacent neighbours. What
assumption is NOT required to allow this simplified form
a) must have no heat generation
b) must not be at a domain boundary
c) must have uniform cell dimensions in both directions
d) must be a solid medium
You might also like
- A Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsFrom EverandA Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Module 4: Short Questions: K G X T T TDocument2 pagesModule 4: Short Questions: K G X T T TRohan KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Module 4: Short Questions: K G X T T TDocument2 pagesModule 4: Short Questions: K G X T T TKarthiik88No ratings yet
- Quiz 4Document3 pagesQuiz 4KoksNo ratings yet
- Crystallization Notes 1Document6 pagesCrystallization Notes 1chandrakiranNo ratings yet
- Heat TransferDocument10 pagesHeat TransferRAVEENA RAVINo ratings yet
- MidSem 2016Document2 pagesMidSem 2016avi0341No ratings yet
- Engineering Optimization Theory and Practice 4th EditionDocument22 pagesEngineering Optimization Theory and Practice 4th EditionPunit BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Mcq's Thermal and Statistical Physics-1Document6 pagesMcq's Thermal and Statistical Physics-1Ehtasham AhmadNo ratings yet
- Unit Iii Thermal Physics: Department of Science and Humanities MCQ For Regulations 2017Document19 pagesUnit Iii Thermal Physics: Department of Science and Humanities MCQ For Regulations 2017Thaya GanapathyNo ratings yet
- Modelling and Simulation of Heat ExchangDocument11 pagesModelling and Simulation of Heat Exchangnejmiddin boughattasNo ratings yet
- Module 2.1 H M T - HEAT EXCHANGERSDocument12 pagesModule 2.1 H M T - HEAT EXCHANGERSandreslloydralfNo ratings yet
- C1A - Part 1Document28 pagesC1A - Part 1HenriqueMassarddaFonsecaNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Correlations For Multilayer Insulation SystemsDocument5 pagesHeat Transfer Correlations For Multilayer Insulation SystemsPankil ShahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3-2Document19 pagesChapter 3-2Mãnęl GüzęllikNo ratings yet
- (Questions Only) ME 366, ONLINE REGULAR QUIZ 1 2022-2023Document12 pages(Questions Only) ME 366, ONLINE REGULAR QUIZ 1 2022-2023somenewguyonthewebNo ratings yet
- Week8 L19QuizV2 PDFDocument2 pagesWeek8 L19QuizV2 PDFAminaMouhoucheNo ratings yet
- CH61014 Advanced Heat Transfer MS 2018Document1 pageCH61014 Advanced Heat Transfer MS 2018Arif AliNo ratings yet
- (FS 2010) Introduction To Finite Element Modelling in Geosciences: Basic PrinciplesDocument10 pages(FS 2010) Introduction To Finite Element Modelling in Geosciences: Basic Principlessandip4884No ratings yet
- DX DF Using The: S DX DT K DX DDocument4 pagesDX DF Using The: S DX DT K DX DRajeshNo ratings yet
- Paper Eco SQ Abs Q 150502Document11 pagesPaper Eco SQ Abs Q 150502Laser AerospaceNo ratings yet
- Triangular FinsDocument20 pagesTriangular FinslokeshkalwarNo ratings yet
- Steady One-Dimensional Heat Flow in A Longitudinal Triangular and Parabolic FinDocument10 pagesSteady One-Dimensional Heat Flow in A Longitudinal Triangular and Parabolic FinJuan Fernando Cano LarrotaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document22 pagesChapter 4Nawaf Al-TamimiNo ratings yet
- ME302 Heat and Mass Transfer Tutorial Sheet #1: Introduction and Heat Conduction EquationDocument3 pagesME302 Heat and Mass Transfer Tutorial Sheet #1: Introduction and Heat Conduction EquationNik SainiNo ratings yet
- Engineering Thermodynamics Odd Sem Mid Term 2018-19 (DITUStudentApp)Document2 pagesEngineering Thermodynamics Odd Sem Mid Term 2018-19 (DITUStudentApp)Niban IlawurNo ratings yet
- Problem Set FD ExplicitDocument6 pagesProblem Set FD ExplicitUna Si NdésoNo ratings yet
- Question Bank Ty 04Document7 pagesQuestion Bank Ty 04Arshad PathanNo ratings yet
- Numerical Methods For Coupled Systems (CPLED) : February 9, 2016Document5 pagesNumerical Methods For Coupled Systems (CPLED) : February 9, 2016gauravbmcNo ratings yet
- HT MCQ (CO3) QuestionsDocument4 pagesHT MCQ (CO3) Questionseafz111No ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument3 pagesGujarat Technological UniversityPARMAR MAHENDRANo ratings yet
- Heat Kernels On Metric Spaces With Doubling Measure: Alexander Grigor'yan, Jiaxin Hu and Ka-Sing LauDocument43 pagesHeat Kernels On Metric Spaces With Doubling Measure: Alexander Grigor'yan, Jiaxin Hu and Ka-Sing LauFuzzylatexNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer MCQDocument167 pagesHeat Transfer MCQgaith.tw1997No ratings yet
- PhysicesDocument3 pagesPhysicesradwakosber297No ratings yet
- Che 135 Process Engineering LaboratoryDocument9 pagesChe 135 Process Engineering LaboratoryMichael Jemziel GulayNo ratings yet
- ME415: CFD Theory - Quiz 2: Section A: MCQDocument3 pagesME415: CFD Theory - Quiz 2: Section A: MCQJohan LiebertNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2: Thermal Engineering Mec551: Q R T RK R RDocument2 pagesTutorial 2: Thermal Engineering Mec551: Q R T RK R RSya JemiNo ratings yet
- Heat Conduction Term ProjectDocument7 pagesHeat Conduction Term ProjectRashed KaiserNo ratings yet
- HW#7Document3 pagesHW#7muhammed mohsinNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0735193309002863 MainDocument8 pages1 s2.0 S0735193309002863 MainEthan SunNo ratings yet
- Edexcel Module Heat Transfer and Combustion - H2 Outcome 2 - Tutorial 1Document10 pagesEdexcel Module Heat Transfer and Combustion - H2 Outcome 2 - Tutorial 1konticvNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer: Roll No. Total No. of Pages: 02 Total No. of Questions: 09 B.Tech. (ME) (2011 Onwards) (Sem. - 6)Document2 pagesHeat Transfer: Roll No. Total No. of Pages: 02 Total No. of Questions: 09 B.Tech. (ME) (2011 Onwards) (Sem. - 6)PiyushNo ratings yet
- 1st SEM CHEM 1001 - 2016Document6 pages1st SEM CHEM 1001 - 2016Swastik KashyapNo ratings yet
- Test 1 Report: MechanicalDocument6 pagesTest 1 Report: MechanicalanmolNo ratings yet
- Effective Thermal Conductivity of Composite: Numerical and Experimental StudyDocument7 pagesEffective Thermal Conductivity of Composite: Numerical and Experimental StudyAkinbode Sunday OluwagbengaNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer CH5Document27 pagesHeat Transfer CH5Khojah AbdulrahmanNo ratings yet
- Numerical Methods in Heat ConductionDocument35 pagesNumerical Methods in Heat Conductionsantiago alonso perilla lozanoNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Solutions To First ChaterDocument29 pagesHeat Transfer Solutions To First ChaterDiana Kaplan CCNY100% (1)
- Transient Heat Transfer Across A Multi-Layer WallDocument10 pagesTransient Heat Transfer Across A Multi-Layer WallJuan Pablo MorenoNo ratings yet
- Jimma Notes and Questions For Exit ExamDocument752 pagesJimma Notes and Questions For Exit ExambereketNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Roll #13...Document10 pagesHeat Transfer Roll #13...hammad00No ratings yet
- Me (3) - 2Document16 pagesMe (3) - 2aviralNo ratings yet
- Triangular Fine XPDocument12 pagesTriangular Fine XPPrem Kumar YadavNo ratings yet
- Grupo 10Document7 pagesGrupo 10YuneskyNo ratings yet
- Bioheat Transfer Equation With Transient Heat Flux Conditions To Skin Tissue An Analytical ApproachDocument10 pagesBioheat Transfer Equation With Transient Heat Flux Conditions To Skin Tissue An Analytical ApproachDr. Indira RNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper Physcis Class 11thDocument5 pagesSample Paper Physcis Class 11thVasudha DubeyNo ratings yet
- Artigo para A PublicacaoDocument10 pagesArtigo para A PublicacaoLucas Santos de OliveiraNo ratings yet
- The Numerical Method of Lines For Partial Differential EquationsDocument3 pagesThe Numerical Method of Lines For Partial Differential Equations19-070 Rejina Paulina MarbunNo ratings yet
- Genmix: A General Computer Program for Two-Dimensional Parabolic PhenomenaFrom EverandGenmix: A General Computer Program for Two-Dimensional Parabolic PhenomenaNo ratings yet
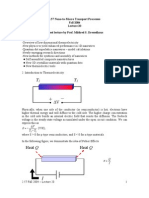
- d dT J Lq L dx dx: q=J (Π - Π) q=J (Π - Π)Document6 pagesd dT J Lq L dx dx: q=J (Π - Π) q=J (Π - Π)captainhassNo ratings yet
- Q FV V: 2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004Document7 pagesQ FV V: 2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004captainhassNo ratings yet
- Taking Birth Control Pills To Fight AcneDocument2 pagesTaking Birth Control Pills To Fight AcnecaptainhassNo ratings yet
- Q FV V: 2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004Document5 pagesQ FV V: 2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004captainhassNo ratings yet
- 2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004: F M F F FDocument5 pages2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004: F M F F FcaptainhassNo ratings yet
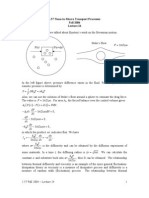
- Lecture 18Document6 pagesLecture 18captainhassNo ratings yet
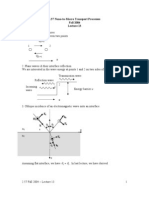
- 2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004 Guest Lecture by Prof. Mildred S. DresselhausDocument10 pages2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004 Guest Lecture by Prof. Mildred S. DresselhauscaptainhassNo ratings yet
- N F T e U F T F TD D: 2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004Document6 pagesN F T e U F T F TD D: 2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004captainhassNo ratings yet
- 2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004Document7 pages2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004captainhassNo ratings yet
- 2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004: I T KXDocument8 pages2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004: I T KXcaptainhassNo ratings yet
- Lecture 14Document8 pagesLecture 14captainhassNo ratings yet
- 2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004 - Lecture 15 Guest Lecture by Prof. DresselhausDocument10 pages2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004 - Lecture 15 Guest Lecture by Prof. DresselhauscaptainhassNo ratings yet
- 2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004:) N N N N (NDocument8 pages2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004:) N N N N (NcaptainhassNo ratings yet
- 2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004: Ae Be CeDocument7 pages2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004: Ae Be CecaptainhassNo ratings yet
- 2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004Document9 pages2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004captainhassNo ratings yet
- 2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004: Nlms 2Document7 pages2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004: Nlms 2captainhassNo ratings yet
- 2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004: V L KK VKK N VDocument7 pages2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004: V L KK VKK N VcaptainhassNo ratings yet
- 2.57 Nano-To-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004: Ikn A IkxDocument7 pages2.57 Nano-To-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004: Ikn A IkxcaptainhassNo ratings yet
- 2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004: A Wigner-Seitz Primitive Unit CellDocument6 pages2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004: A Wigner-Seitz Primitive Unit CellcaptainhassNo ratings yet
- 2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004Document6 pages2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004captainhassNo ratings yet
- 2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004: E HN MDocument10 pages2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004: E HN McaptainhassNo ratings yet
- 2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004: Ja (j-1) A (j+1) ADocument9 pages2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004: Ja (j-1) A (j+1) AcaptainhassNo ratings yet
- 2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004Document7 pages2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004captainhassNo ratings yet
- 5 - AC Motor Starter PDFDocument10 pages5 - AC Motor Starter PDFPrem KumarNo ratings yet
- Three-Phase Induction Motor: Version 2 EE IIT, KharagpurDocument8 pagesThree-Phase Induction Motor: Version 2 EE IIT, KharagpurHarsh PatelNo ratings yet
- 2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004Document8 pages2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004captainhassNo ratings yet
- 2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004: DT Q K T Q DX Q (W/M K (W/M-K) Is Thermal ConductivityDocument5 pages2.57 Nano-to-Macro Transport Processes Fall 2004: DT Q K T Q DX Q (W/M K (W/M-K) Is Thermal ConductivitycaptainhassNo ratings yet
- L-44 (GDR) (Et) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document15 pagesL-44 (GDR) (Et) ( (Ee) Nptel)yashaswiyellapragadaNo ratings yet
- Problem Solving On D C Machines PDFDocument16 pagesProblem Solving On D C Machines PDFSelvaraj ParamasivanNo ratings yet
- Equ. Circuit & Power Flow DiagramDocument7 pagesEqu. Circuit & Power Flow DiagramShareef KhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document30 pagesChapter 3Angel PaguayNo ratings yet
- Course DescriptionsDocument28 pagesCourse DescriptionsRoberto HoffmanNo ratings yet
- Civil NDTDocument63 pagesCivil NDTArjuna De Silva100% (1)
- CFD Class M.techDocument52 pagesCFD Class M.techdankshavali shaikNo ratings yet
- Uk Komputer Statistik - Putri AmelliaDocument7 pagesUk Komputer Statistik - Putri AmelliaHendra BudiantoroNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Pub Numerical and Statistical Methods For Computer Engineering Gujarat Technological University 2017 2nbsped 9789352604852 9352604857Document598 pagesDokumen - Pub Numerical and Statistical Methods For Computer Engineering Gujarat Technological University 2017 2nbsped 9789352604852 9352604857Sasmita NayakNo ratings yet
- I. TOPIC: Solving Quadratic Equations by FactoringDocument2 pagesI. TOPIC: Solving Quadratic Equations by FactoringJo-Amver Valera ManzanoNo ratings yet
- Or-Week 2 - Introduction To LP - Simplex MethodDocument31 pagesOr-Week 2 - Introduction To LP - Simplex MethodMadina MukhamejanNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan 8 BezierDocument16 pagesPertemuan 8 Bezierali_chaemNo ratings yet
- Civil EngineeringDocument3 pagesCivil EngineeringDhaked Shahab67% (3)
- Roots of Polynomial EquationsDocument59 pagesRoots of Polynomial EquationsAdeyemi DorcasNo ratings yet
- System of Linear Equations MatlabDocument3 pagesSystem of Linear Equations MatlabJohn RoaNo ratings yet
- Chapter TwoDocument14 pagesChapter TwoHanan ShayiboNo ratings yet
- Numerical Analysis - ErrorsDocument9 pagesNumerical Analysis - ErrorsMiguel YorroNo ratings yet
- Lec3 Gradient Based Method Part IDocument30 pagesLec3 Gradient Based Method Part IAbhay JindalNo ratings yet
- Ma 214 HW4Document3 pagesMa 214 HW4arvind muraliNo ratings yet
- Polynomial FunctionDocument6 pagesPolynomial FunctionSaifodin AlangNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Learning CompetenciesDocument2 pagesIntermediate Learning CompetenciesEDITHA PAGUYONo ratings yet
- Crank Nicholson MethodDocument7 pagesCrank Nicholson MethodHassan Tajdar HamidNo ratings yet
- Teaching Plan For MSG456Document4 pagesTeaching Plan For MSG456dikkanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Reservoir SimulationDocument25 pagesIntroduction To Reservoir SimulationWenKhai LimNo ratings yet
- Predictor Corrector MethodsDocument5 pagesPredictor Corrector MethodsM2C7r6No ratings yet
- Submitted By: Submitted To: Dr. Arindam DasDocument11 pagesSubmitted By: Submitted To: Dr. Arindam DaskitamuNo ratings yet
- Complex Numbers 1Document10 pagesComplex Numbers 1limkewchongNo ratings yet
- MA1203 Matematika Bisnis II Silabus 2018-2019Document2 pagesMA1203 Matematika Bisnis II Silabus 2018-2019Aldi AnugrahNo ratings yet
- Algebraic Expressions FactorizationDocument39 pagesAlgebraic Expressions Factorizationthinkiit100% (3)
- STEEL DESIGN - Column Procedure CheckDocument7 pagesSTEEL DESIGN - Column Procedure CheckOsama MamdouhNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The CFD ProcessDocument4 pagesIntroduction To The CFD ProcessYashwanth SrinivasaNo ratings yet
- Process Synthesis and DesignDocument21 pagesProcess Synthesis and Designkishore dasmunshiNo ratings yet
- Simplex Algorithm - WikipediaDocument20 pagesSimplex Algorithm - WikipediaGalata BaneNo ratings yet