Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Condensation Exam Q Ms - 3
Uploaded by
sureshthevanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Condensation Exam Q Ms - 3
Uploaded by
sureshthevanCopyright:
Available Formats
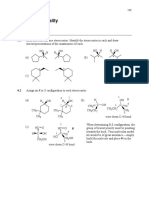
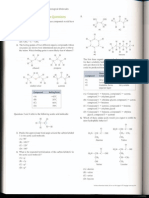
1.
(a) (i)
C C C C C C
H
H
H H
H
H H
H
H
C C O
O O
C C O
H
H
H
H
C
O
C O
O
C C O
H
H
H
H
1 mark for each repeat unit (1)(1) 2
(ii) 1 mark for each monomer (1)(1) 2
(b) C=O absorbs radiation/breaks (1)
ester linkage hydrolysed (1) 2
[6]
2. (a)
H O C ( C H ) C O H
O
H N ( C H ) N H
2
O
4
2 2 e 2
H
C
C N
C
H H
(1)
O
C ( C H ) C N ( C H ) N
H
2
H
O
4 2 6
monomers connected by NHCO (1)
correct repeat shon (1)
H C N
C C
H H
condensation addition (1) for
b
ot
h
!
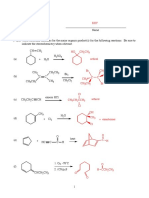
(b) (i) "Cl
#
/ $OCl
2
1
(ii) HCl 1
Christ The King Sixth Form College 1
(c)
H N ( C H ) N H O C ( C H ) C O
O
3 2 6 3 2 4
+ +
( 1 )
O
2
allow 1 mark for: both H
3
N
+
(CH
2
)
6
NH
3
+
and
H O C ( C H ) C O
O
2
O
4
(d) (i) 4 1
(ii)
H
R
O
N C
O H H
H
C
where R=H, CH
3
, CH
2
OH or CH
2
C
6
H
5
(1) 1
(iii) any three different cheica!!y or "io!o#ica!!y correct difference$
"etween aino acid$ and the ny!on onoer$ (1)(1)(1) % e#
% protein monomers are amino acids / nylon monomers are a
(di)amine/base and a (di)acid
% protein monomers ha&e different types/' groups / nylon
monomers are to types/no &ariation
% protein monomers ha&e stereo/optical isomers/are chiral
% protein monomers ha&e higher melting points/
form (itterions
other &o$$i"!e an$wer$ inc!'de(
% nylon monomers ha&e longer chain length/no other functional
groups / no aromatic content / are symmetrical etc )
dont allow comparisons solubility or M
r
[13]
Christ The King Sixth Form College 2
You might also like
- Critical Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants Involving 8-Hydroxyquinoline and Its Metal Chelates: Critical Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants in Solution: Part B: Equilibrium Constants of Liquid-Liquid Distribution SystemsFrom EverandCritical Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants Involving 8-Hydroxyquinoline and Its Metal Chelates: Critical Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants in Solution: Part B: Equilibrium Constants of Liquid-Liquid Distribution SystemsNo ratings yet
- Allow R CH NH and COOH in Any Order: C H N COO R HDocument1 pageAllow R CH NH and COOH in Any Order: C H N COO R HsureshthevanNo ratings yet
- Selected Constants Oxydo-Reduction Potentials: Tables of Constants and Numerical Data Affiliated to The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry, Vol. 8From EverandSelected Constants Oxydo-Reduction Potentials: Tables of Constants and Numerical Data Affiliated to The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry, Vol. 8No ratings yet
- 4.4, 4.5 Exam Questions MsDocument9 pages4.4, 4.5 Exam Questions MsswanderfeildNo ratings yet
- Schaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionFrom EverandSchaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- 4.4, 4.5 Organic Chemistry Reactions and Isomers TestDocument4 pages4.4, 4.5 Organic Chemistry Reactions and Isomers TestKaren JulaoNo ratings yet
- Compendium On Problems in Physical-Organic ChemistryDocument27 pagesCompendium On Problems in Physical-Organic ChemistryHaryokoe buzzNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Introduction To General Organic and Biochemistry 12th Edition Frederick A Bettelheim William H Brown Mary K Campbell Shawn o Farrell Omar Torres IsDocument7 pagesSolution Manual For Introduction To General Organic and Biochemistry 12th Edition Frederick A Bettelheim William H Brown Mary K Campbell Shawn o Farrell Omar Torres IsLuisMurraymrzye100% (85)
- Chapter 6: Chirality: ProblemsDocument35 pagesChapter 6: Chirality: ProblemsAlejandra BriceñoNo ratings yet
- Alcohol AnswersDocument6 pagesAlcohol Answerslucylovesbooks6770No ratings yet
- Isomerism Review 2Document10 pagesIsomerism Review 2ayesha sheikhNo ratings yet
- GOC DPPR -01 Single Answer Type QuestionsDocument16 pagesGOC DPPR -01 Single Answer Type QuestionsKalyan ReddtNo ratings yet
- Analytical Chemistry AQA AnswersDocument30 pagesAnalytical Chemistry AQA AnswersAhmad BustamiNo ratings yet
- PRACTICE SHEET - 02 (Chemistry) : Basic Concept of Organic (IUPAC, Isomerism)Document5 pagesPRACTICE SHEET - 02 (Chemistry) : Basic Concept of Organic (IUPAC, Isomerism)ABD 17No ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Enol Forms and Geometric IsomerismDocument9 pagesOrganic Chemistry Enol Forms and Geometric Isomerismsarvesh goyalNo ratings yet
- Test Ranjeet ShahiDocument9 pagesTest Ranjeet Shahisabhari_ramNo ratings yet
- Problems in IsomerismDocument5 pagesProblems in IsomerismAt Tanwi100% (1)
- 4.10 - 4.11 Organic Synthesis and Structure Determination MSDocument30 pages4.10 - 4.11 Organic Synthesis and Structure Determination MSAdnan ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- CHEM 135 Exam 2 F15 KeyDocument7 pagesCHEM 135 Exam 2 F15 KeyMikeNo ratings yet
- ViewpdfDocument12 pagesViewpdfBhargav SinghaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry (15-21) Previous Year QDocument16 pagesChemistry (15-21) Previous Year QMuhammad Nure FerdousNo ratings yet
- Problem Set # 5, February 2017 71.: H + I 2HIDocument4 pagesProblem Set # 5, February 2017 71.: H + I 2HIArdiansyah YayanNo ratings yet
- CHM 1321 Assignment 1 Answers: CN H H H H HDocument10 pagesCHM 1321 Assignment 1 Answers: CN H H H H HSara YuenNo ratings yet
- MCQs pdf-1 PDFDocument5 pagesMCQs pdf-1 PDFEmman Ann100% (3)
- Chapter 1 ReviewDocument2 pagesChapter 1 ReviewGmat PrepNo ratings yet
- Chem Unit 5 Organic AnswersDocument47 pagesChem Unit 5 Organic Answersareyouthere92No ratings yet
- G.O.C & Isomerism _ DPP 04 (of Lec 07) __ (Arjuna JEE 2023)Document3 pagesG.O.C & Isomerism _ DPP 04 (of Lec 07) __ (Arjuna JEE 2023)jeemainsmaterial97No ratings yet
- Nomenclature 2 PKBDocument4 pagesNomenclature 2 PKBPawan BabelNo ratings yet
- 4.4, 4.5 TEST MS REVIEWDocument4 pages4.4, 4.5 TEST MS REVIEW3estherNo ratings yet
- organic chemDocument3 pagesorganic chemlinda.wairepoNo ratings yet
- Alcohol MarkschemeDocument23 pagesAlcohol MarkschemeqwedsaNo ratings yet
- Most Important PaperDocument11 pagesMost Important PaperVILLAIN EX.No ratings yet
- CH203 Fall 2014 Exam 1 Grading Key PDFDocument8 pagesCH203 Fall 2014 Exam 1 Grading Key PDFBUCH203No ratings yet
- IsomerismDocument16 pagesIsomerismAnusmita MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Organic Chemistry 7Th Edition Brown Iverson Anslyn Foote 1133952844 9781133952848 Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesSolution Manual For Organic Chemistry 7Th Edition Brown Iverson Anslyn Foote 1133952844 9781133952848 Full Chapter PDFrichard.parga191100% (14)
- Mock Test 6 P 2 Bks DDocument22 pagesMock Test 6 P 2 Bks DRare RootNo ratings yet
- Aieee 2006 PaperDocument21 pagesAieee 2006 PaperjanmanchiNo ratings yet
- CHM 1321 Assignment 3 - : AnswersDocument5 pagesCHM 1321 Assignment 3 - : AnswersSara YuenNo ratings yet
- StereochemistryDocument53 pagesStereochemistryalyssa_marie_ke100% (17)
- Alcohol, Phenol & Ether: A O CH C HDocument6 pagesAlcohol, Phenol & Ether: A O CH C HJitendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Objectives: UNIT 3. HydrocarbonsDocument52 pagesObjectives: UNIT 3. HydrocarbonsMarcelaNo ratings yet
- Goc Stereo PDFDocument32 pagesGoc Stereo PDFDeepak GargNo ratings yet
- Zumdahl Biology Tie inDocument2 pagesZumdahl Biology Tie injimmy615615No ratings yet
- ISOMERISM types questionsDocument16 pagesISOMERISM types questionssurendra chowdary Makineni100% (1)
- Organic Chem Mcqs PDFDocument18 pagesOrganic Chem Mcqs PDFDIPA NAGNo ratings yet
- Dhisha Jee Mains and Neet-185-206Document22 pagesDhisha Jee Mains and Neet-185-206jeevavelayyaNo ratings yet
- Isomerism DPP - With Solution PDFDocument20 pagesIsomerism DPP - With Solution PDFPiyush Agarwal50% (2)
- Apch11 EstersDocument2 pagesApch11 Estersloly62006No ratings yet
- Chemistry Mock Test 1 PDFDocument9 pagesChemistry Mock Test 1 PDFVikas SinghNo ratings yet
- C1102 Introduction To Organic Chemistry: Lebanese University Faculty of SciencesDocument84 pagesC1102 Introduction To Organic Chemistry: Lebanese University Faculty of SciencesBlack InsomniaNo ratings yet
- Work Book (Phase - IV) : SubjectiveDocument21 pagesWork Book (Phase - IV) : SubjectiveAshwani Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- inorganic dpp pdfDocument3 pagesinorganic dpp pdfashutosh99878No ratings yet
- Chemistry Entrance Test 3Document7 pagesChemistry Entrance Test 3Eljesa LjusajNo ratings yet
- Carbs: Nature's Most Abundant MoleculesDocument24 pagesCarbs: Nature's Most Abundant MoleculesGulus CfNo ratings yet
- OrganicDocument6 pagesOrganicTrent SwordsNo ratings yet
- IIT-JAM 2011 Chemistry Paper: Key ConceptsDocument8 pagesIIT-JAM 2011 Chemistry Paper: Key Conceptsprakhar vishwakarma100% (1)
- Organic Chem p2 QuestionsDocument64 pagesOrganic Chem p2 QuestionsBilawalSadiqNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1: Catenation'Document4 pagesTutorial 1: Catenation'AdellNo ratings yet
- Halogenolalkanes and Alcohols HWDocument7 pagesHalogenolalkanes and Alcohols HWKizzy-Anne BoatswainNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 SHT-601 Sec II PDFDocument7 pagesAssignment 1 SHT-601 Sec II PDFNehaNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Fundamental (Base) Quantities and Their Units: 13/03/2019, 22?42 Page 1 of 6Document6 pages1.1 Fundamental (Base) Quantities and Their Units: 13/03/2019, 22?42 Page 1 of 6sureshthevanNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme June 2002 GCE: Physics A Unit PA10Document7 pagesMark Scheme June 2002 GCE: Physics A Unit PA10sureshthevanNo ratings yet
- 5090 Nos SW 7Document6 pages5090 Nos SW 7sureshthevanNo ratings yet
- 5090 Nos SW 0Document3 pages5090 Nos SW 0sureshthevanNo ratings yet
- 5090 Nos SW 8Document8 pages5090 Nos SW 8sureshthevanNo ratings yet
- 5090 Nos SW 2Document7 pages5090 Nos SW 2sureshthevanNo ratings yet
- 5090 Nos SW 9Document6 pages5090 Nos SW 9sureshthevanNo ratings yet
- January Series: Physics Specification ADocument8 pagesJanuary Series: Physics Specification AsureshthevanNo ratings yet
- AQA PA10 W MS Jan04Document7 pagesAQA PA10 W MS Jan04sureshthevanNo ratings yet
- 5090 Nos SW 6Document5 pages5090 Nos SW 6sureshthevanNo ratings yet
- 5090 Nos SW 1Document5 pages5090 Nos SW 1sureshthevanNo ratings yet
- 5090 Nos SW 3Document6 pages5090 Nos SW 3sureshthevanNo ratings yet
- 5090 Nos SW 4Document7 pages5090 Nos SW 4sureshthevanNo ratings yet
- 5090 Nos SW 5Document8 pages5090 Nos SW 5sureshthevanNo ratings yet
- OCR GCSE Science Revision ResourcesDocument3 pagesOCR GCSE Science Revision ResourcessureshthevanNo ratings yet
- June 2015 QP - Unit 1 WJEC Physics A-LevelDocument23 pagesJune 2015 QP - Unit 1 WJEC Physics A-LevelsureshthevanNo ratings yet
- AQA AS Physics A Chapter 1 Textbook AnswersDocument4 pagesAQA AS Physics A Chapter 1 Textbook Answerscathylister80% (5)
- O Level Biology (5090) : Unit 5: Coordination, Response, Movement and HomeostasisDocument8 pagesO Level Biology (5090) : Unit 5: Coordination, Response, Movement and HomeostasissureshthevanNo ratings yet
- Es8 Asp G QQ 3Document2 pagesEs8 Asp G QQ 3sureshthevanNo ratings yet
- Es8 Asp F QQ 3Document2 pagesEs8 Asp F QQ 3sureshthevanNo ratings yet
- Year 8 Science Exam Revision GuideDocument51 pagesYear 8 Science Exam Revision GuidesureshthevanNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument12 pagesAtomic StructuresureshthevanNo ratings yet
- Year 7 Cells and Reproduction-2Document10 pagesYear 7 Cells and Reproduction-2sureshthevan100% (1)
- Module 1 Electricity ConceptsDocument26 pagesModule 1 Electricity Conceptssureshthevan0% (1)
- Condensation Exam Q - 4Document4 pagesCondensation Exam Q - 4sureshthevanNo ratings yet
- Aqa Phy3h W QP Jun10 2Document16 pagesAqa Phy3h W QP Jun10 2sureshthevanNo ratings yet
- F324 HW 1 - 3Document9 pagesF324 HW 1 - 3sureshthevanNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces and Properties of H2ODocument4 pagesIntermolecular Forces and Properties of H2OsureshthevanNo ratings yet
- Consolidation of 1.2 Ms - 3Document3 pagesConsolidation of 1.2 Ms - 3sureshthevanNo ratings yet