Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unit 4 Project
Uploaded by
api-266092088Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Unit 4 Project
Uploaded by
api-266092088Copyright:
Available Formats
By: Kaylee Propst
Unit 4 Project
Government 1
11/23/14
~Legislative Branch~
Who: House of Representatives and the Senate. These put together create what we call
The United States Congress.
What: They make laws that the citizens will have to follow.
Extra: Approve presidential nominations, control the budget, may remove the president,
and they can pass laws over what the president says with a 2/3 vote of both houses.
Executive Branch
Who: This power is vested in the President of America.
What: He, along with his fellow helpers, are able to enforce and carry out laws that were
made by Congress.
Extra: The big man can also veto (turn down) laws enacted by Congress.
Judicial Branch
Who: Supreme Court
The members are chosen by the President and confirmed by Senate.
What: They are in charge of making sure the laws are constitutional. Which means they
are in charge of interpreting and explaining the Constitution.
Extra: Their decisions that they make are final and they can declare a presidents actions
unconstitutional.
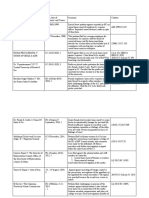
Legislative Branch: Powers Explained
Taxation: Congress may collect taxes
Borrowing Money: Can borrow money on the credit of the USA
Regulating Commerce: Can regulate commerce with foreign nations
Naturalization: Establish a uniform rule of Naturalization
Bankruptcy: Make a world known law on the subject of bankruptcy
Coining Money: Regulate values of money
Post Offices: To provide post offices
Declaring War: Can declare war and make certain calls on captures on land and water
Raising Army and Navy: They must support raising armies and provide a navy
Legislative Branch : REPORTS
Taxation: Congress is
Regulating Commerce: Congress may regulate the rights and liabilities
of employers and employees, as labor disputes adversely affect the free
flow of commerce. Otherwise, contracts that do not involve any
property or activities that move in interstate commerce are not
ordinarily part of interstate commerce. http://legaldictionary.thefreedictionary.com/Commerce+Clause
Borrowing Money: Allowed to
borrow money on the credit of USA.
Borrowing and the Federal Debt. ( <Link)
Naturalization: An example
of naturalization in our
nation, is how immigrants
have to take an oath or
meet certain requirements
legally to become a citizen.
Bankruptcy: On January 23, 2006, the Supreme Court, in Central Virginia
Coining:
Money:http://www.inve
stopedia.com/terms/g/
greshams-law.asp
An Example is
Gresham's law.
allowed to lay and collect
taxes. In Westerville, the
citizens pay taxes, that
come out of their checks,
and it helps goes to help
fund our public schools.
Community College v. Katz, declined to apply state sovereign immunity from
Seminole Tribe v. Florida,[52] to defeat a trustee's action under 11 U.S.C. 547 to
recover preferential transfers made by a debtor to a state agency. The Court ruled
that Article I, section 8, clause 4 of the U.S. Constitution (empowering Congress to
establish uniform laws on the subject of bankruptcy) abrogates the state's sovereign
immunity in suits to recover preferential payments.[53]
(http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bankruptcy_in_the_United_States#Bankruptcy_crimes)
Raising Army and Navy:
An example is if
somewhere in the future
Congress may have to
go to the last resort and
call for a draft if we as a
nation were ever in a
crisis.
Declaring War:
http://america.aljazeera.com/blogs/scrutineer/2014/9/
11/obama-sidesteps-congressindeclaringwar.html.
Obama is sidestepping congress on war issues, but
constitution states that congress has the right to declare
war if chosen.
Post Offices:
http://www.washingtonpost.com/n
ews/volokhconspiracy/wp/2014/10/02/bonidyv-united-states-the-secondamendment-at-the-post-office/
Bonidy v. United States: The Second
Amendment at the post office
Executive Branch: Powers Explained
Commander in Chief: President shall be in charge of the army and navy
Pardons: President has power to grant Reprieves and Pardons for Offences
Treaties: He can make treaties
Ambassadors: Appoint ambassadors with the advice and approval of Senate
Judges: The president can nominate/appoint judges
State of the Union: Must inform Congress about State of the Union from time to time
Executive Branch: REPORTS
Commander in
Chief:
http://www.politico.
com/news/stories/0
110/31896.html
President Obama's
evolution as
commander-inchief
Pardons:
http://www.propublica
.org/article/obamahas-grantedclemency-morerarely-than-anymodern-president
Obama Has Granted
Clemency More
Rarely Than Any
Modern President
Treaties:
http://www.cnn.co
m/2010/POLITICS/04
/08/obama.russia.tr
eaty/
Obama, Russian
president sign arms
treaty
Ambassadors:http://www.was
hingtonpost.com/opinions/ob
amas-ambassador-nomineesare-a-disservice-todiplomacy/2014/02/06/2273ef
9e-8e86-11e3-b22712a45d109e03_story.html
Obamas ambassador
nominees are a disservice to
diplomacy
Supreme Court
Judges:
http://en.wikipedia.
org/wiki/Barack_Ob
ama_Supreme_Cou
rt_candidates
Barack Obama
Supreme Court
candidates
State of the Union:
http://www.whiteho
use.gov/the-pressoffice/2014/01/28/p
resident-barackobamas-stateunion-address
President Barack
Obama's State of
the Union Address
Judicial Branch: Powers Explained
Judicial Review: The Judicial power must extend to all powers
Issues Between States: Part of the power the judicial must extend toooooooo
Treason: Treason must have two witnesses or someone who admits to it, before someone is
convicted of it. Treason against the US will only consist of levying war against them, or
giving the enemies aid and comfort.
Judicial Branch: REPORT
Judicial Review:
http://www.fbm.com/US_Supr
eme_Court_Expands_Judicial
_Review_of_Clean_Water_Act
_Enforcement_Orders_03-222012/
U.S. Supreme Court Expands
Judicial Review of Clean
Water Act Enforcement
Orders
Issues Between States: Current
Issues and Programs in Social
Welfare.
http://www.socialwelfarehisto
ry.com/recollections/currentissues-and-programs-insocial-welfare/
Treason:
http://www.outsidethebeltwa
y.com/treason-and-thewikileaks-case/
Treason And The Wikileaks
Case
Checks & Balances
Legislative checks Executive: The Legislative Branch approves presidential nominations and controls the
budget. They can remove the president and can pass laws over what the president says with a 2/3 vote
from both houses. An example is when Congress passed a farm bill over Bush veto in 2008.
Legislative checks Judicial: Congress can impeach judges and make them the office. An example is when
Judge G. Thomas Porteous Faces Impeachment Trial In Congress in 2010.
Executive checks Legislative: The president can veto congressional legislation. An example is how, Obama
threatens veto of House border-spending bill.
Executive check Judicial: Can forgive a class of crime and they nominate the judges to the Federal Court
System and to the Supreme Court. An example is when Obama nominated Jill Parrish for federal court judge
in 2014
Judicial checks Executive: They can declare presidential acts unconstitutional. An example is when
Legislation Declared Unconstitutional in 2005.
Judicial checks Legislative: Supreme Court can also declare presidential act unconstitutional and can also
declare treaties unconstitutional. An example is during the Riley v. California case in 2014.
You might also like
- Constitutional Law-Harvard OutlineDocument82 pagesConstitutional Law-Harvard OutlineJosh Critselous100% (8)
- 9 Markers On The US ConstitutionDocument3 pages9 Markers On The US ConstitutionLiam HargadonNo ratings yet
- Child Protective ServicesDocument40 pagesChild Protective ServicesKathleen Dearinger80% (5)
- Bar Bri Con Law OutlineDocument24 pagesBar Bri Con Law Outlinelulubelle329No ratings yet
- New York Course Constitutional Law: Professor Erwin ChemerinskyDocument58 pagesNew York Course Constitutional Law: Professor Erwin ChemerinskyJae Yong Lee100% (5)
- Gratuity Written ArgumentsDocument9 pagesGratuity Written Argumentsiona_hegdeNo ratings yet
- Get A Knife Get A Dog, But Get Rid of Gun'sDocument2 pagesGet A Knife Get A Dog, But Get Rid of Gun'sACADEMICVENUE100% (1)
- Plenary Power - WikipediaDocument5 pagesPlenary Power - WikipediaBashir AbdulleNo ratings yet
- Mag CHP 03 OutlineDocument6 pagesMag CHP 03 Outlineapi-267189291No ratings yet
- Matthew Shea - Resist DCDocument5 pagesMatthew Shea - Resist DCJohn SutherlandNo ratings yet
- ConLaw Amar 2004Document88 pagesConLaw Amar 2004Liam MurphyNo ratings yet
- Powers of Congress: I. Expressed Powers: Definition & ExamplesDocument2 pagesPowers of Congress: I. Expressed Powers: Definition & ExamplesJakeNo ratings yet
- Con Law Bible 1Document176 pagesCon Law Bible 1Liam MurphyNo ratings yet
- Dorothy Moon Article Against COS With Deceptive COS RebuttalDocument6 pagesDorothy Moon Article Against COS With Deceptive COS Rebuttalairlifter2No ratings yet
- Best - Con Law I Outline Vandevelde - NBDocument22 pagesBest - Con Law I Outline Vandevelde - NBHaifa NeshNo ratings yet
- Resist DC Part 1 and 2 Agenda21Document6 pagesResist DC Part 1 and 2 Agenda21Hal ShurtleffNo ratings yet
- State Sovereignty CRS Report 2008Document29 pagesState Sovereignty CRS Report 2008Jim Neubacher100% (1)
- 2 (Constitution)Document21 pages2 (Constitution)parisha dhebarNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 GovernmentDocument5 pagesUnit 4 Governmentapi-266082464No ratings yet
- Constitution Law OUTLINEDocument28 pagesConstitution Law OUTLINEchazNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Key Terms: The Imperial PresidencyDocument4 pagesChapter 13 Key Terms: The Imperial PresidencyJenny YangNo ratings yet
- Key Terms: National and State PowersDocument25 pagesKey Terms: National and State PowersRecio JaneNo ratings yet
- McCulloch Vs Maryland Case BriefDocument5 pagesMcCulloch Vs Maryland Case BriefIkra MalikNo ratings yet
- American Government and Politics - 1/3 Term Exam: Sebastian BermudezDocument3 pagesAmerican Government and Politics - 1/3 Term Exam: Sebastian Bermudezsebastian bermudezNo ratings yet
- US Government Political System, Constitution, PartiesDocument13 pagesUS Government Political System, Constitution, PartiesSavannah Kate GrilloNo ratings yet
- Con Law Outline-29Document41 pagesCon Law Outline-29Scott HymanNo ratings yet
- Constitutional Law OutlineDocument18 pagesConstitutional Law OutlineBoyk1182No ratings yet
- Con Law 1L OutlineDocument23 pagesCon Law 1L Outlinebethora100% (1)
- Powers of CongressDocument25 pagesPowers of CongressCarol Heid100% (1)
- Constitutional Law OutlineDocument25 pagesConstitutional Law OutlineAdam SteinbaughNo ratings yet
- Con Law OutlineDocument72 pagesCon Law OutlineAdam DippelNo ratings yet
- BIANCA ORDONEZ - Constitution Articles and Amendments OverviewDocument4 pagesBIANCA ORDONEZ - Constitution Articles and Amendments OverviewbiancaNo ratings yet
- AP Government CramDocument31 pagesAP Government CramcuamiNo ratings yet
- Con Law Quiz #1 Study GuideDocument8 pagesCon Law Quiz #1 Study GuideJonathan NaleNo ratings yet
- Con Law OutlineDocument14 pagesCon Law Outlinetm05101No ratings yet
- American PresidentsDocument13 pagesAmerican PresidentsRadu RoșianuNo ratings yet
- The 7 Articles of The Us ConstitutionDocument1 pageThe 7 Articles of The Us ConstitutionAlexander Font RamosNo ratings yet
- United States District Court For The District of Columbia U.S. House of RepresentativesDocument24 pagesUnited States District Court For The District of Columbia U.S. House of RepresentativesJacqueline ThomsenNo ratings yet
- Mcculloch V. Maryland:: Theories of Constitutional InterpretationDocument14 pagesMcculloch V. Maryland:: Theories of Constitutional Interpretationfbarber13No ratings yet
- AP US Government and Politics Midterm ReviewDocument17 pagesAP US Government and Politics Midterm ReviewWarpaintItNo ratings yet
- Constitutional LawDocument29 pagesConstitutional Lawmark nagraniNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Page 5Document4 pagesLecture 3 - Page 5magdalinechelangat50No ratings yet
- Constitutional Law: The ConstitutionDocument8 pagesConstitutional Law: The ConstitutioncryziaNo ratings yet
- Citizenship in The Nation: Merit Badge Counselor WorkbookDocument9 pagesCitizenship in The Nation: Merit Badge Counselor Workbookygarcia3535No ratings yet
- NSL Notes - Chapter 3Document9 pagesNSL Notes - Chapter 3APNSL100% (1)
- Government Honors - Chapter 3 2015Document22 pagesGovernment Honors - Chapter 3 2015cyndalea100% (1)
- Con Law Oultine-PersonalDocument5 pagesCon Law Oultine-PersonalAshley DanielleNo ratings yet
- The Powers of The President of The United StatesDocument3 pagesThe Powers of The President of The United StatesArian's LifestyleNo ratings yet
- U S Inc Defines All Crime As Commercial As A Result of The Fall of The RepublicDocument3 pagesU S Inc Defines All Crime As Commercial As A Result of The Fall of The Republicg100% (1)
- Powers of The President of The United StatesDocument5 pagesPowers of The President of The United StatesViệt DũngNo ratings yet
- Remarks of Mr. Calhoun of South Carolina on the bill to prevent the interference of certain federal officers in elections: delivered in the Senate of the United States February 22, 1839From EverandRemarks of Mr. Calhoun of South Carolina on the bill to prevent the interference of certain federal officers in elections: delivered in the Senate of the United States February 22, 1839No ratings yet
- Constitutional Convertion-1 3Document3 pagesConstitutional Convertion-1 3api-269178075No ratings yet
- What Is The Legislative Branch OverviewDocument3 pagesWhat Is The Legislative Branch Overviewapi-241101238No ratings yet
- Chapter 11Document31 pagesChapter 11api-259245937No ratings yet
- Us History Regents Review Sheet 2Document16 pagesUs History Regents Review Sheet 2api-242847854No ratings yet
- Chapter-1 Civics and Government 25 To 50Document10 pagesChapter-1 Civics and Government 25 To 50inzali naylaNo ratings yet
- APUSH Constitution Test Study GuideDocument9 pagesAPUSH Constitution Test Study Guidemartialartsgrl21No ratings yet
- Separation of PowersDocument24 pagesSeparation of Powersnkata560% (1)
- Constitutional Law - Hassel - Fall 2011Document31 pagesConstitutional Law - Hassel - Fall 2011James E. WoulfeNo ratings yet
- Blog - The American System of Government - Separation of Powers - LawShelf Educational MediaDocument4 pagesBlog - The American System of Government - Separation of Powers - LawShelf Educational MediaAbhimanyu SinghNo ratings yet
- The Journal of the Debates in the Convention which framed the Constitution of the United States, Volume II (of 2)From EverandThe Journal of the Debates in the Convention which framed the Constitution of the United States, Volume II (of 2)No ratings yet
- Legpro CaseDocument6 pagesLegpro CaseMi LagroNo ratings yet
- Foreign Law Firms in ChennaiDocument20 pagesForeign Law Firms in ChennaiUnimarks Legal SolutionsNo ratings yet
- Development of Criminal LawDocument8 pagesDevelopment of Criminal Lawyukta kapadiaNo ratings yet
- De Roy Vs CADocument2 pagesDe Roy Vs CABernadine Abad RacadioNo ratings yet
- Boy Scouts V COADocument3 pagesBoy Scouts V COAattyalanNo ratings yet
- Cases Relating To HarassmentDocument7 pagesCases Relating To HarassmentalbertNo ratings yet
- Unlawful Practice of Law Receiver Kevin Singer San Francisco Superior Court - Receivership Specialists - Jayne Kim State Bar of California Chief Trial Counsel - Kamala Harris California Attorney General - California State BarDocument44 pagesUnlawful Practice of Law Receiver Kevin Singer San Francisco Superior Court - Receivership Specialists - Jayne Kim State Bar of California Chief Trial Counsel - Kamala Harris California Attorney General - California State BarCalifornia Judicial Branch News Service - Investigative Reporting Source Material & Story IdeasNo ratings yet
- Persons (Nery) - Cases 1 (Civil Code Provisions) PDFDocument135 pagesPersons (Nery) - Cases 1 (Civil Code Provisions) PDFBingkat MacarimbangNo ratings yet
- R. v. ReddickDocument24 pagesR. v. ReddickDiana DavisonNo ratings yet
- Bank of The Philippine Islands v. J.R. Herridge Case DigestDocument4 pagesBank of The Philippine Islands v. J.R. Herridge Case DigestRyzer RowanNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For AdvocacyDocument4 pagesGuidelines For AdvocacySriram SankarapandianNo ratings yet
- Ong Vs People G.R. NO. 190475 April 10, 2013Document1 pageOng Vs People G.R. NO. 190475 April 10, 2013Emrico CabahugNo ratings yet
- Chaves Vs GonzalesDocument2 pagesChaves Vs Gonzalescmv mendozaNo ratings yet
- Can We Really Limit Liability - Al Tamimi & CompanyDocument3 pagesCan We Really Limit Liability - Al Tamimi & CompanysagaicaNo ratings yet
- "Sui Generis" SocietyDocument10 pages"Sui Generis" SocietyJoshua De Leon TuasonNo ratings yet
- Forman 1960 AmendmentDocument31 pagesForman 1960 AmendmentLia TarachanskyNo ratings yet
- Calde V CADocument2 pagesCalde V CABetson Cajayon100% (2)
- Chef Bee Vs 50 EggsDocument20 pagesChef Bee Vs 50 EggsheraldscribdNo ratings yet
- BOE OrderDocument4 pagesBOE OrderBrigid BerginNo ratings yet
- Motion To QuashDocument4 pagesMotion To QuashAlit Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- The European Union Lecture PDFDocument9 pagesThe European Union Lecture PDFVinod JuariaNo ratings yet
- A Comparative Study On The Difference Between Fraud and Undue InfluenceDocument21 pagesA Comparative Study On The Difference Between Fraud and Undue InfluenceAishani ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Patent Assignment ModelDocument5 pagesPatent Assignment ModelMarco BalestriniNo ratings yet
- Proclamation No 414 S 1957Document4 pagesProclamation No 414 S 1957John Ray LibiranNo ratings yet
- Module 4. Session 1. Activity 4. Flowchart On The Management of Cases of Child Abuse, Neglect, and ExploitationDocument1 pageModule 4. Session 1. Activity 4. Flowchart On The Management of Cases of Child Abuse, Neglect, and ExploitationSamKris Guerrero Malasaga88% (8)
- Gambrell v. United States Government Et Al - Document No. 3Document7 pagesGambrell v. United States Government Et Al - Document No. 3Justia.comNo ratings yet
- Police Patrol ReviewerDocument5 pagesPolice Patrol ReviewerGlen Iosa ComilangNo ratings yet