Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hairpin Exchangers: Delta T Heat Exchangers
Uploaded by
daniel oliveiraOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Hairpin Exchangers: Delta T Heat Exchangers
Uploaded by
daniel oliveiraCopyright:
Available Formats
Delta T Heat Exchangers
Hairpin Exchangers
Hairpin heat exchangers utilize true counter-current flow, which maximizes the temperature
differences between the shellside and the tubeside fluids, unlike the multi-pass Shell and
Tube designs where correction factors are used to account for the inefficiencies resulting
from co-current passes.
When your process calls for a temperature cross (when the hot fluid outlet temperature is
below the cold fluid outlet temperature), a hairpin heat exchanger is the most efficient
design and will result in fewer sections and less surface area.
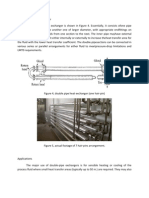
Double-pipe heat exchangers use a single pipe within a pipe design and are commonly
used for high fouling services such as slurries, where abrasive materials are present, and
for smaller duties. Standard shell diameters range from 2 to 6.
Multi-tube heat exchangers are used for larger duties with standard designs established for
shell diameters up to 30; with surface area in excess of 10,000 ft per section.
Koch Heat Transfer (formerly Brown Fintube) has avariety of unique enhancement devices
for different process conditions.
When to use Hairpin Heat Exchangers
A hairpin heat exchanger should be considered when one or more of the following
conditions exist:
The process results in a temperature cross
High pressure tubeside application
A low allowable pressure drop is required on one side
Cyclic service
High flow rate ratios between shellside and tubeside fluids
High terminal temperature differences (300F or greater)
When an augmentation device will enhance the heat transfer
coefficient
When the exchanger is subject to thermal shock
When flow induced vibration may be a problem
When heating or cooling vapours
When complete vaporization is required
When solids are present in the process stream
When the mechanical advantages of a hairpin are preferred
You might also like
- Calculation of Target Torque for Bolts (ASME PCC-1Document1 pageCalculation of Target Torque for Bolts (ASME PCC-1daniel oliveiraNo ratings yet
- Frigidaire Service Tech-Talk Manual PDFDocument60 pagesFrigidaire Service Tech-Talk Manual PDFjunkguru50% (2)
- 1-Classification of Heat Exchangers & Selection CriteriaDocument56 pages1-Classification of Heat Exchangers & Selection CriteriaShahid_Rao786100% (1)
- Heat Exchanger DesignDocument13 pagesHeat Exchanger DesignDaksh Parashar80% (5)
- Heat Exchanger PresentationDocument66 pagesHeat Exchanger PresentationMahmoud100% (1)
- Air Cooled Heat Exchanger Handbook: Fundamentals, Calculations, Design and Q&AFrom EverandAir Cooled Heat Exchanger Handbook: Fundamentals, Calculations, Design and Q&ANo ratings yet
- Nozzle ProDocument185 pagesNozzle Progoodspeed_ph83% (6)
- QC InspectionDocument18 pagesQC InspectionUNSTOPPAPAUL100% (1)
- Valves - Schlumberger FTCDocument25 pagesValves - Schlumberger FTCMarwenNo ratings yet
- Heat and Heat ExchangerDocument20 pagesHeat and Heat ExchangerDamisha DamishaNo ratings yet
- AP Government GATE Online Classes: Heat TransferDocument88 pagesAP Government GATE Online Classes: Heat TransferRohan lallNo ratings yet
- Commissioning Summary TemplateDocument5 pagesCommissioning Summary Templatedaniel oliveiraNo ratings yet
- Double Pipe Heat ExchangerDocument6 pagesDouble Pipe Heat ExchangerKhaqan Amin50% (8)
- Project Standards and Specifications Inspection of Pumps Rev01Document7 pagesProject Standards and Specifications Inspection of Pumps Rev01hiyeonNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchangers V1 16-10-2019Document72 pagesHeat Exchangers V1 16-10-2019Bal krishna srivastava100% (1)
- Double Pipe Heat ExchangerDocument6 pagesDouble Pipe Heat ExchangerharisNo ratings yet
- Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger: Research TitleDocument10 pagesShell and Tube Heat Exchanger: Research TitleDimas SatriaNo ratings yet
- External Pressure CalculationsDocument40 pagesExternal Pressure Calculationsmisterdavi50% (2)
- Wet H2S Cracking Problem in Oil Refinery ProcessesDocument12 pagesWet H2S Cracking Problem in Oil Refinery Processeschellahari2922No ratings yet
- Heat Exchanger Equipment Field Manual: Common Operating Problems and Practical SolutionsFrom EverandHeat Exchanger Equipment Field Manual: Common Operating Problems and Practical SolutionsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- Double Pipe Heat ExchangerDocument5 pagesDouble Pipe Heat ExchangerSheb LorenoNo ratings yet
- Double Pipe by Sannan & HarisDocument72 pagesDouble Pipe by Sannan & HarisQuân Nguyễn ĐìnhNo ratings yet
- Heat ExchangerDocument44 pagesHeat Exchangerweldy puteraNo ratings yet
- All Wiring Diagrams For Honda Civic Si 2008 ModelDocument163 pagesAll Wiring Diagrams For Honda Civic Si 2008 ModelBaba Ile FurnNo ratings yet
- Leak Test PDFDocument48 pagesLeak Test PDFdaniel oliveira100% (1)
- Heat ExchangersDocument56 pagesHeat ExchangersGeeva Prasanth ANo ratings yet
- Handles 26” Vacuum Filtrate PumpsDocument6 pagesHandles 26” Vacuum Filtrate Pumpsdaniel oliveiraNo ratings yet
- HEAT TRANSFER: TYPES OF HEAT EXCHANGERSDocument36 pagesHEAT TRANSFER: TYPES OF HEAT EXCHANGERSCarol Mae CelisNo ratings yet
- Compactheat ExchangersDocument124 pagesCompactheat Exchangersarun aryaNo ratings yet
- Ahmad PHTDocument12 pagesAhmad PHTEngineer TalhaNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchanger Types and SelectionDocument4 pagesHeat Exchanger Types and Selection12mchc07No ratings yet
- Plate Heat Ex ChangersDocument5 pagesPlate Heat Ex Changersmuftah faragNo ratings yet
- HX PresentationDocument14 pagesHX PresentationPriyankaNo ratings yet
- Intercambiador de CalorDocument55 pagesIntercambiador de Calorandy pandaNo ratings yet
- Intercambiador de CalorDocument54 pagesIntercambiador de CalorCristian NipasNo ratings yet
- Heat ExchangerDocument5 pagesHeat ExchangerMurtaza NaeemNo ratings yet
- Test of A Tubular CondenserDocument9 pagesTest of A Tubular CondenserDevin Bea0% (1)
- Second Law Analysis of Plate Heat Exchange: Submitted By: Waleed Zaki Al-Jumaydi Sami Farag Al - RefaiDocument52 pagesSecond Law Analysis of Plate Heat Exchange: Submitted By: Waleed Zaki Al-Jumaydi Sami Farag Al - Refaiوليد عاتقNo ratings yet
- of HXEDocument31 pagesof HXEetayhailuNo ratings yet
- PHT Lec 1Document32 pagesPHT Lec 1M.Attique Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Drop Through The Exchanger, Which Can Result in HigherDocument6 pagesDrop Through The Exchanger, Which Can Result in Higherjoana_vibar100% (1)
- Conceptual Diagram of A Plate and Frame Heat Exchanger02Document9 pagesConceptual Diagram of A Plate and Frame Heat Exchanger02sai thesisNo ratings yet
- Act 3 ConclusionDocument13 pagesAct 3 ConclusionVon A. DamirezNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Research Background: Heat Exchanger FCB40302Document68 pages1.1 Research Background: Heat Exchanger FCB40302ImranMustaffaNo ratings yet
- Report on Plate Heat Exchanger Design and OperationDocument5 pagesReport on Plate Heat Exchanger Design and OperationLaxmi PrasannaNo ratings yet
- Fin Type Heat Exchanger: Presented by Shiv Kamal Upadhaya (21) Sonu Das (22) Nirmalya RoyDocument8 pagesFin Type Heat Exchanger: Presented by Shiv Kamal Upadhaya (21) Sonu Das (22) Nirmalya RoySonu DasNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Plate Type Heat Exchanger: M. E. Thermal Engineering Subject: Seminar (2730001)Document10 pagesPresentation On Plate Type Heat Exchanger: M. E. Thermal Engineering Subject: Seminar (2730001)jigs4568No ratings yet
- Heat and Mass Transfer Lab Research Paper Topic: Detailed Description of Compact Heat Exchanger With Practical ApplicationDocument9 pagesHeat and Mass Transfer Lab Research Paper Topic: Detailed Description of Compact Heat Exchanger With Practical ApplicationJaskirat SinghNo ratings yet
- Double Pipe Heat Exchanger: Open Ended Lab Lab Report NoDocument10 pagesDouble Pipe Heat Exchanger: Open Ended Lab Lab Report NoAsad UllahNo ratings yet
- Heat ExchangerDocument20 pagesHeat ExchangerankitNo ratings yet
- Bringing Efficiency To Heat Transfer: Product LiteratureDocument28 pagesBringing Efficiency To Heat Transfer: Product Literaturescreamingeagle22No ratings yet
- Types of Heat Exchangers - Classification of Heat ExchangersDocument3 pagesTypes of Heat Exchangers - Classification of Heat ExchangersMuhammet Ahmet SarıkayaNo ratings yet
- Na Gea Biofuels Mag Ad UsaDocument2 pagesNa Gea Biofuels Mag Ad UsaTharakeshNo ratings yet
- Plate Heat Exchanger: A Seminar Report OnDocument22 pagesPlate Heat Exchanger: A Seminar Report Onphb1986No ratings yet
- Part.a.classification of Heat ExchangersDocument11 pagesPart.a.classification of Heat ExchangersAhmed GadNo ratings yet
- Heat ExchangerDocument9 pagesHeat ExchangerChrissa Villaflores GanitNo ratings yet
- HE 04 Oct 21Document11 pagesHE 04 Oct 21Abir RahmanNo ratings yet
- Heat ExchangerDocument5 pagesHeat ExchangerAtta ur Rehman BhattiNo ratings yet
- Seminar On Heat PipeDocument27 pagesSeminar On Heat PipeRahul Mishra0% (1)
- Common Questions Heat Pipes PDFDocument2 pagesCommon Questions Heat Pipes PDFTeo Pei SanNo ratings yet
- ProjectDocument24 pagesProjectSantosh Kumar HottaNo ratings yet
- Shell and Tube Heat ExchangerDocument10 pagesShell and Tube Heat ExchangerahmadazaizehNo ratings yet
- What Are The Types of Heat ExchangersDocument9 pagesWhat Are The Types of Heat Exchangersjr gajelesNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchanger TypesDocument15 pagesHeat Exchanger TypesDanish BaigNo ratings yet
- A Piece of Equipment Built For Efficient Heat Transfer From One Medium To AnotherDocument19 pagesA Piece of Equipment Built For Efficient Heat Transfer From One Medium To AnotherKirti SuryawanshiNo ratings yet
- TOCE - Module IIIDocument75 pagesTOCE - Module IIIAnnwin Moolamkuzhi shibuNo ratings yet
- Simple Double-Pipe Heat Exchanger GuideDocument2 pagesSimple Double-Pipe Heat Exchanger GuideharisNo ratings yet
- Document 1Document4 pagesDocument 1SAMARTHNo ratings yet
- What Are Double Pipe Heat Exchangers and Their Working PrinciplesDocument8 pagesWhat Are Double Pipe Heat Exchangers and Their Working PrinciplesAngel RatuNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesFrom EverandMechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesNo ratings yet
- Praxair RandyDocument33 pagesPraxair Randydaniel oliveiraNo ratings yet
- Pre-Commissioning Checklist: Project Name: Job NoDocument1 pagePre-Commissioning Checklist: Project Name: Job Nomohamed hamedNo ratings yet
- AB-519 Alternative Test Methods Procedure Requirements PDFDocument13 pagesAB-519 Alternative Test Methods Procedure Requirements PDFedzky69No ratings yet
- Flash Vessels Flash Vessels Systems: ApplicationDocument1 pageFlash Vessels Flash Vessels Systems: Applicationhappale2002No ratings yet
- Journal of Solid MechanicsDocument10 pagesJournal of Solid Mechanicsdaniel oliveiraNo ratings yet
- Catalogo Pecas CARRIER 2012 PDFDocument260 pagesCatalogo Pecas CARRIER 2012 PDFtrutleptNo ratings yet
- Test and drain valve sizesDocument3 pagesTest and drain valve sizesfabian cardenasNo ratings yet
- Sathya - StoreDocument2 pagesSathya - StoreBala KulandaiNo ratings yet
- Lennox - High Wall Mini Split INVERTER 18 SEERDocument4 pagesLennox - High Wall Mini Split INVERTER 18 SEERWalter BernalNo ratings yet
- Master EMC Price ListDocument423 pagesMaster EMC Price ListSamir KadiyaNo ratings yet
- Pressure Drop (Fittings Etc) Elbows, Tees Elbows, Tees Elbows, TeesDocument4 pagesPressure Drop (Fittings Etc) Elbows, Tees Elbows, Tees Elbows, TeesSaidNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Cooling of Commercial BuildingDocument39 pagesCalculation of Cooling of Commercial BuildingFareed AlamNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Solar Water HeaterDocument5 pagesProject Report On Solar Water HeaterEIRI Board of Consultants and Publishers75% (4)
- HHP Compressed Air DrawingDocument1 pageHHP Compressed Air Drawingdhaneesh22No ratings yet
- Industrial Refrigeration: Components and ControlsDocument1,094 pagesIndustrial Refrigeration: Components and ControlsSudharshan ReddyNo ratings yet
- Science 3 - Week 7Document12 pagesScience 3 - Week 7MAE HERNANDEZNo ratings yet
- Rac Lab ManualDocument69 pagesRac Lab ManualHrshita SinghNo ratings yet
- Servis Manual Galactic Hisense Polupromyshlennye PDFDocument134 pagesServis Manual Galactic Hisense Polupromyshlennye PDFmikeNo ratings yet
- YLAA InstallationDocument62 pagesYLAA InstallationJoe YoungNo ratings yet
- PPR Pipes Donsen EnglishDocument8 pagesPPR Pipes Donsen EnglishJason RojasNo ratings yet
- HVAC PrinciplesDocument60 pagesHVAC PrinciplesshreyashNo ratings yet
- Checklist en 2014.10Document2 pagesChecklist en 2014.10ChandraSekaranBmNo ratings yet
- Mechanical VentilationDocument22 pagesMechanical VentilationesagcojrNo ratings yet
- Load Calculation NewDocument13 pagesLoad Calculation NewNaqqash SajidNo ratings yet
- CLASS 13620: DEP 31.38.01.14-Gen Class 13620, Rev. K Page 1 of 12Document12 pagesCLASS 13620: DEP 31.38.01.14-Gen Class 13620, Rev. K Page 1 of 12Bharuk MechNo ratings yet
- Raccordi A Inserto Forgiato PDFDocument3 pagesRaccordi A Inserto Forgiato PDFpeppino di capriNo ratings yet
- Appendix - X Mechanical Design Criteria, Equipment/Material and Technical SpecificationsDocument35 pagesAppendix - X Mechanical Design Criteria, Equipment/Material and Technical SpecificationsAijaz MalikNo ratings yet
- Lesson 12 English For Technicians 12 PDFDocument7 pagesLesson 12 English For Technicians 12 PDFАндрій ДячинськийNo ratings yet
- Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual: General InformationDocument12 pagesInstallation, Operation and Maintenance Manual: General InformationEduardo PedrazaNo ratings yet
- Vicinity Map: Ar. Venecio P. CodiaDocument1 pageVicinity Map: Ar. Venecio P. CodiaNefritiri BlanceNo ratings yet
- Instrument tag nos. from Scope of Work compression trainsDocument39 pagesInstrument tag nos. from Scope of Work compression trainsPrathamesh OmtechNo ratings yet