Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Name of Polysacchari de Amylose
Uploaded by
3uvpCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Name of Polysacchari de Amylose
Uploaded by
3uvpCopyright:
Available Formats
Name of Specific
Number of Types of
Polysacchari Linkage Function of Enzyme Importance Source
Sugar Units Linked Sugar
de Sugar
Energy
Beta- Green
Amylose 50-5,000 α(1,4) D-Glucose storage in
amylase plants
plants
Energy
6 α(1,4) with Beta- Green
Amylopectin Up to 10 D-Glucose storage in
α(1,6) amylase plants
plants
Energy
α and β
Up to α(1,4) with storage in Animals,
Glycogen D-Glucose amylase,
50,000 α(1,6) bacteria and Bacteria
maltase
animal cells
Gives Green
Up to rigidity and plants,
Cellulose β(1,4) D-Glucose cellulase
15,000 structure to some
plants bacteria
Forms thin,
transparent,
α(1,6) +
Pullulan 80 to 480 D-Glucose pullulanase oil resistant, Yeast
α(1,4)
impermeabl
e to O2 films
Callose Up to 104 β(1,3) D-Glucose β(1,3) Produced by Green
glucanases plants in plants
response to
wounding
and
pathogen
infections
Gives
rigidity and
N-acetyl-D- strength to Fungi,
Chitin Very large β(1,4) chitinase
Glucosamine exoskeleton arthropods
s of
arthropods
Stores
20 to Endoinulinas
energy in Some plant
Inulin several β(2,6) D-Fructose e and
roots and tubers
thousands exoinulinase
rhizomes
Structural
Importance
in
vertebrates,
extracellular
Glucuronic
matrix of Animal
Up to acid + N- hyalunorida
Hyaluronan β(1,4) skin and connective
100,000 acetylglucosa se
connective tissue
mine
tissue,
viscosity
and
lubrication
in joints
In algae, cell
β(1,4) and Red
Agar-agar 1,000 Galactose agarase wall
α(1,3) seaweed
material
Murein Very large β(1,4) N-acetyl-D- Murein In bacteria, Bacterial
(Peptidoglyc Glucosamine hydrolase, gives
rigidity and
+ N-acetyl-D- strength to
an) cellosyl cell wall
Muramic Acid cell
envelope
Main -
In bacteria,
α(1,6), Some
Dextran Very large D-Glucose dextranase cellular
branch – bacteria
adhesive
α(1,3)
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Beatles - Allan Kozinn Cap 8Document24 pagesThe Beatles - Allan Kozinn Cap 8Keka LopesNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Intro - LatinDocument11 pagesLesson 1 Intro - LatinJohnny NguyenNo ratings yet
- Data Report Northside19Document3 pagesData Report Northside19api-456796301No ratings yet
- Concept of Intestate SuccessionDocument9 pagesConcept of Intestate SuccessionBodhiratan BartheNo ratings yet
- The Revival Strategies of Vespa Scooter in IndiaDocument4 pagesThe Revival Strategies of Vespa Scooter in IndiaJagatheeswari SelviNo ratings yet
- Course Title: Cost Accounting Course Code:441 BBA Program Lecture-3Document20 pagesCourse Title: Cost Accounting Course Code:441 BBA Program Lecture-3Tanvir Ahmed ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Effects of Violence On Transgender PeopleDocument8 pagesEffects of Violence On Transgender PeopleAdel Farouk Vargas Espinosa-EfferettNo ratings yet
- 6 Holly Fashion Case StudyDocument3 pages6 Holly Fashion Case StudyCaramalau Mirela-Georgiana0% (1)
- Flotect Vane Operated Flow Switch: Magnetic Linkage, UL ApprovedDocument1 pageFlotect Vane Operated Flow Switch: Magnetic Linkage, UL ApprovedLuis GonzálezNo ratings yet
- English 2Document53 pagesEnglish 2momonunu momonunuNo ratings yet
- Clique Pen's Marketing StrategyDocument10 pagesClique Pen's Marketing StrategySAMBIT HALDER PGP 2018-20 BatchNo ratings yet
- Doña PerfectaDocument317 pagesDoña PerfectadracbullNo ratings yet
- Siege by Roxane Orgill Chapter SamplerDocument28 pagesSiege by Roxane Orgill Chapter SamplerCandlewick PressNo ratings yet
- 150 Most Common Regular VerbsDocument4 pages150 Most Common Regular VerbsyairherreraNo ratings yet
- Heritageoil Corporategovernance AwDocument68 pagesHeritageoil Corporategovernance AwbeqsNo ratings yet
- PAPC - Internal Notes PDFDocument4 pagesPAPC - Internal Notes PDFHrushi Km GowdaNo ratings yet
- FeistGorman - 1998-Psychology of Science-Integration of A Nascent Discipline - 2Document45 pagesFeistGorman - 1998-Psychology of Science-Integration of A Nascent Discipline - 2Josué SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Earth & Life Science Q1 Module 2 - DESIREE VICTORINODocument22 pagesEarth & Life Science Q1 Module 2 - DESIREE VICTORINOJoshua A. Arabejo50% (4)
- StructDocument2 pagesStructandriessebastianNo ratings yet
- Importance of Time Management To Senior High School Honor StudentsDocument7 pagesImportance of Time Management To Senior High School Honor StudentsBien LausaNo ratings yet
- Dance Manual W. Learning Outcomes PDFDocument8 pagesDance Manual W. Learning Outcomes PDFJoshua Quijano LamzonNo ratings yet
- Creating Early Learning Environments PDFDocument25 pagesCreating Early Learning Environments PDFkrisnahNo ratings yet
- Trends Interiors Architecture Fashion Lifestyle: 6 Spring 2013 Collector's EditionDocument116 pagesTrends Interiors Architecture Fashion Lifestyle: 6 Spring 2013 Collector's EditionFernanda RaquelNo ratings yet
- Relation of Sociology with other social sciencesDocument4 pagesRelation of Sociology with other social sciencesBheeya BhatiNo ratings yet
- Madagascar's Unique Wildlife in DangerDocument2 pagesMadagascar's Unique Wildlife in DangerfranciscogarridoNo ratings yet
- Enneagram Type-2Document18 pagesEnneagram Type-2pundirNo ratings yet
- Alvin - Goldman - and - Dennis - Whitcomb (Eds) - Social - Epistemology - Essential - Readings - 2011 PDFDocument368 pagesAlvin - Goldman - and - Dennis - Whitcomb (Eds) - Social - Epistemology - Essential - Readings - 2011 PDFOvejaNegra100% (2)
- 20 Reasons Composers Fail 2019 Reprint PDFDocument30 pages20 Reasons Composers Fail 2019 Reprint PDFAlejandroNo ratings yet
- Boston Consulting Group Portfolio Analysis MatrixDocument16 pagesBoston Consulting Group Portfolio Analysis MatrixNimish SharmaNo ratings yet
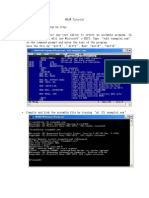
- MASM Tutorial PDFDocument10 pagesMASM Tutorial PDFShashankDwivediNo ratings yet