Professional Documents
Culture Documents
06 Exam B Answer Test
Uploaded by
kangalbert860 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views6 pagesAnswers
Chemistry
Science
Test
Secondary School
Original Title
06 Exam b Answer Test
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAnswers
Chemistry
Science
Test
Secondary School
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views6 pages06 Exam B Answer Test
Uploaded by
kangalbert86Answers
Chemistry
Science
Test
Secondary School
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
59
SOLUTIONS
Examination Set B Paper 1
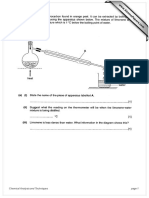
© At 10°C, the physical state of the substance
is a liquid, which implies that its melting point must
be below 10 °C. At 60 °C, its physical state is a
vapour, and thus, its boiling point must be below
60°C but above 10 °C.
‘A The distilled water molecules, manganate(VIl)
ions (which cause the solution to be purple) as
well as the colourless potassium ions will diffuse.
So, increasing the temperature of both liquids
will cause the average speed of the particles to
increase, and hence they diffuse faster. Increasing
the pressure of the pocket of air above the liquids
will have no effect on the rate of diffusion,
8 Burottes allow variable measurements of
volumes to one decimal place. Pipettes can only
measure fixed volumes like 20.0 or 25.0 om®.
Measuring cylinders do not allow measurement to
one decimal piace if the capacity is above 10 ml,
and beakers should never be used to measure
volumes of liquids as the uncertainty in the
measurements will be very high. Beakers are used
to hold liquids and the graduations at the sides
provide an estimation of the volume of liquids in the
beakers.
‘A The best way to determine the purity of
water is to measure its boiling point. Placing the
thermometer bulb above the water is akin to 10
measuring the temperature of the vapour in simple
or fractional dstilation. The temperature of the
vapour that is measured does not indicate the
purity of the water in the flask as there could be
solutes that are not as easily vaporised as water
‘As some solutes are also colourless and could also
be volatile, such as alcohols, chromatography and
checking for residue after evaporation are not good
methods to determine the purity of water.
B__ The prefix, ‘iso’, means ‘the same’. So, i
‘isoelectronic’ means ‘having the same electronic
configuration’, The number of electrons in Cris 18,
which is the same as that in an atom of the inert
gas Ar.
© Isotopes are atoms of the same element, so
they must have the same number of protons but a
diferent number of neutrons (or nucleons) in the
nucleus.
‘A _XandY are metals from the same group in
the Periodic Table as their atoms have the same
number of valence electrons in their outermost
shells, ie. 1 electron each. Atoms of X have one
more electron shell than atoms of Y. Hence atoms
of X can lose their valence electrons more easily
‘Sc utions to Examination Set B
than atoms of Y due tothe larger atomic radi and
4reater inner electron shielding effect. Hence X
is more reactive as it can form positive ions more
easily than Y. Z is a halogen (7 valence electrons)
and hence is more likely to form negative ions. Itis
not possible to compare the reactivity of a metal
(or ¥) against a non-metal (Z in this case) as
both have very different properties. As X and Y
are alkali metals, they will form basic oxides and
not acidic oxides, which are generally oxides of
nnon-metals.
B Caisavery reactive metal. The fact that
Ca forms a white solid with X indicates that the
‘compound is ionic and that X is a non-metal. X also
has to be a Group V element based on the formula
of the white solid, tis stated in the question that X
is a gas, and referring to the Periodic Table, X has
to be nitrogen as phosphorus is a solid at room
temperature.
D There are three covalent bonds between the
two nitrogen atoms and as each covalent bond.
has a pair of electrons, so a total of 6 electrons
are involved in bonding. Each nitrogen atom has
a total of 7 electrons each, and only 3 of them are
involved in forming the 3 covalent bonds. Hence
there are 4 electrons that are not bonded and the
total number of unbonded electrons in the nitrogen
molecule should be 4 x 2 = 8
D Calcium bromide has a ratio of 1 Ca2*ion
to 2 Br ions and that differs from the 1:1 ratio in
NaCI. Carbon monoxide is a covalent compound
aand does not form a lattice structure unless itis
Cooled into a solid. Copper is a metal and hence
the structure should consist of copper(II) ions in a
sea of electrons. The ratio of Mg fons to O* ions
is the same as that between Na* and CI-, and as
magnesium oxide is also ionic like sodium chloride,
their lattice structures should be very similar.
B Hydrogen chloride has a simple covalent
molecular structure and hence, is expected to
have very low melting and boiling points. itis
a gas under room conditions. However, not al
covalent compounds stay covalent when dissolved
in water. In this case, hydrogen chloride ionises
in water to form H* (or HO") and CI- ions. Hence
hydrochloric acid is @ good conductor of electricity
in the aqueous state as its ions function as charge
carriers
D The M, of Cl is 71, and hence the molar
mass of Cz is 71 g/mol. So, 36.5 g of Ci. contains
only 0.5 mol of molecules, and this value is x.
36 g of water is equivalent to 2 mol of water
(M, of HzO = 18) and hence it contains 4x water
molecules.
13 A The number of moles of manganate(Vil) ions
is concentration x volume, which is
73.0. am x 0.050 molidm? . The mole ratio
between MnO. and Fe®*is 1 :§, and it means that
for every 1 mol of MnO, ions in the reaction, there
should be 5 mol of Fe ions for complete reaction.
As there are (22.09. 0,050) moles of MaO,-ions,
that means that there should be (5 x 289°. x 0,050)
mol of Fe?* ions. So, the concentration,
which is number of moles divided by the volume,
23.00 0,050 ] mol
250 gra
ooo ¢™
which simplifies to the answer A.
[5x
should be
14 A Based on the equation, the mole ratio of
H2S : 0, : SO» should be 2 :3 : 2. As equal number
cof moles of any two gases occupy the same
volume at the same temperature and pressure,
their volume ratio is also 2 : 3 : 2. Hence if 5 dm?
of HSis present, then the volume of ©, should be
7.5 dm?, and O; is in excess (as 9 dm? is provided).
Thus, the volume of SO, obtained is the same as,
the volume of H,S that reacted, which is 5 dm®,
15 DM, of NaOH is 40. So, the number of moles
in 18g NeOHte 18 = O.4mel Aa tho concntraton
is 0.2 mol/dm®, the volume that can be prepared is
0.4 a
ge72am
16 B_ A,ofNais 23. So, 230 g of Nais equivalent to
10 moles of Na.
NaCl > Nat + Cr
Hence the number of moles of Cr" ions discharged
is also 10 moles, and that is equivalent to 5 moles
of chlorine molecules or chlorine gas.
2Cr > Cp +26
As the molar volume is 24 dm? at r.t.p., 5 moles of
chlorine gas will occupy a volume of 120 dm? at rp.
17 A Cations are attracted to the cathode while
anions are attracted to the anode. Both SO,* and
OH ions should migrate to the anode but only
OH is discharged as oxygen gas, while Cu®> and
H+ ions migrate to the cathode. As copper is below
hydrogen in the reactivity series, copper will be
discharged at the cathode, forming a plating on the
electrode.
48 © Allreactions involving oxidation with oxygen
are exothermic, like combustion and rusting.
Likewise, the direct combination of a metal and
a halogen to form a halide is exothermic as the
halogen behaves very much like oxygen with a
metal in this case. Photosynthesis involves the
absorption of sunlight to form sugar and thus it is
endothermic,
19 A 2H,O,{aq) > 2H,0()) + O29)
‘The above equation can be rewritten as follows to
show all the bonds.
°.
O— 0 > 2 4 N\ +0=
™~ wou
Solutions to Examination Set 8
60
20
21
22
23
24
26
In the decomposition of two moles of hydrogen
peroxide, 2 moles of O—O bond break while one
mole of O=0 bond forms, and the enthalpy change,
AH, Is ~496 + 2(148) = ~204 kJ. So, for one mole
of hydrogen peroxide, the value should be
102 ki.
© _Aniincrease in temperature causes the
particles to gain energy and thus, move faster and
Collide more frequently. Also, as the particles gain
more energy due to the increase in temperature,
the proportion of particles with an energy level
greater than the activation energy (minimum
energy required for a reaction to occur) also
increases. Activation energy can only be changed
by the use of a catalyst while the change in
enthalpy, AH, remains a constant.
A Inexperiment 1, as the amount of
hydrochloric acd is just sufficient to react with al
the calcium carbonate, there is no excess. Hence
to obtain the second graph for experiment 2,
both the hydrochloric acid and calcium carbonate
‘must increase in quantity. The volume of the
acid in experiment 2 is higher while its starting
concentration remains the same. Hence, the rate of
change in concentration ofthe acid will be slower.
[Note that the starting concentrations of the acids
in experiment 1 and experiment 2 are the same.
However, as more acid is used in experiment 2, the
decrease in concentration will take a longer time.}
D__ Mis the symbol of an element, hence its
‘oxidation state is zero. The oxidation state of
‘oxygen is -2. If we let the oxidation state of Mn in
MnO,-to be x, then x+ 4(-2) =—1, and this gives
X= #7, In MnO and MnOs, the oxidation states of
Mn are +2 and +4 respectively, based on the same
‘method of determination.
A Cris the reducing agent as it causes the
oxidation state of Fe to reduce from +3 (in Fe*) to
0 (in Fe), and its oxidation state is increased from 0
(in Cr) t0 43 (in Cr?
© Silicon dioxide is the oxide of a non-metal and
is an example of an acidic oxide. Hence it can be
neutralised by a base, such as aqueous sodium
hydroxide. Sodium hydroxide neutralises silicon
dioxide to form sodium silicate, thus fusing the
Glass bottle and the glass stopper together.
D__Amphotetic oxides are metal oxides (but the
converse is not true). Amphoteric oxides react with
both acids and bases to form salts.
© Ethanoic acid is a weak acid and partially
ionises into ions. It still consists of mainly ethanoic
acid molecules, which are neutral. There are few
hydrogen ions and thus the pH is about 4. The
other three options are either strong acids or strong
bases, which ionise completely when dissolved
in water. Thus their pHs are either close to 1 (for
acids) or 14 (for bases) but not close to 7.
D__ Firstly, the unknown substance forms a
colourless solution and hence it must be soluble
in water. That rules out calcium sulfate, which is
insoluble in water. Secondly, al nitrates are soluble
in water and hence will not form precipitates with
barium ions. Lastly, it forms a white precipitate
with barium nitrate solution, Hence, the unknown
substance must be a sulfate as the white
precipitate is the insoluble barium sulfate.
B_ The gas that turns limewater milky is carbon
dioxide. Calcium carbonate precipitate is formed,
thus causing the miky appearance. Next, the gas
that changes the colour of acidified potassium
dichromate(V\) from orange to green is sulfur
dioxide. Sulfur dioxide reduces the chromium in the
dichromate(V1) from +6 oxidation state (orange) to
+3 oxidation state (green).
D__Allthe alkali metals have very low melting and
boiling points. In fact, caesium can melt in your hands
(ifit does not react with the sweat from your hands).
B__ Indium has a valency of 3 while sulfur has a
valency of 2. The formula of the compound formed
is thus IngS3
B Across a period, as the atomic number
increases, the nuclear charge increases and
hence the atomic radius will decrease. Also, the
last element, a noble gas, is the only element in
a period with atoms that have completely filed
‘outermost shells. The valence electrons increase
by one with each successive element across the
Period for Periods 1 to 3.
B Between caesium and sodium, the former is
the more reactive alkali metal. Between chlorine
and iodine, the former is the more reactive halogen
Hence the reaction between caesium and chlorine
will be the most vigorous.
B As can displace X from its salt, Y is more
reactive than X. Also, the sulfate of Z easily
decomposes. This means that Z is a more stable
‘element than both X or Y
© The best test for metals isthe electrical
conductivity test. Some metals, such as the Group
| and II metals, have lower melting points and
boiling points than the other metals. Also, some
metals such as gold and platinum are unreactive
and do not form oxides or salts easily.
‘A The members of the homologous series share
the same general formula. Their empirical formula
is usually diferent, and each successive member
differs from the previous member by one carbon
atom and two hydrogen atoms. As the molecules
of successive members get bigger and heavier,
the intermolecular forces of attraction increase and
hence their boiling points will also increase.
B Concentrated sulfuric acid is a powerful
dehydrating agent. It will remove a water molecule
from an alcohol molecule, forming an alkene in the
process,
tions to Examination Set B
37 B__ Atemperature that is too high, such as above
32°C (depending on the yeast species), will cause
the enzymes involved in fermentation to denature
and the process of fermentation will be slowed
down significantly.
38 A This is due to the formation of colourless
dibromoalkane from the unsaturated alkene.
Incidentally, this is also a common test for
unsaturation in Organic Chemistry.
38 D_— Asystematic manner to determine the
polymer is shown below.
Step 1: Draw the structure of at least 3 monomers.
in the following manner.
aq occa ca oa ce
oc cc oo
f | | | |
CH, Ci CH; Cl CH; Cr
Step 2: Remove the double covalent bonds.
ci cr ci cr ci ci
c c ¢ ¢ ¢c ¢
CH, Cl CH, Cl CHp Ci
Step 3: Insert single bonds between all carbon
atoms in the chain.
ca ococaiai ica ca
—c—¢—c—c —c—c—
CHy Cl CH, Ci CH, Cl
40 © The monomers can be determined as
follows:
Step 1: Draw the polymer as shown below.
9° oi ° °
i i |
— Nom CANCE C—N-me ONO —
|
H H H H
Step 2: Cleave the bond between the carbonyl
(C=O) and (N-H) as shown below.
° ° ° 9
I t I
YEOH OF NO FNC
H H H 4
Stop 3: Separate the cleaved fragments as shown
below. Omit repeated fragments
Step 4: Complete the monomers by adding a water
molecule to each monomer;
-OH to the C=O part of the monomer and an H to
N-H part of the monomer.
°
I
H-N-m-C—O-—H
H
Examination Set B Paper 2
Section A
At (a) They are atoms of the same element with
different numbers of neutrons. t1
(o)
Number of
protons
Number of
neutrons
Number of
electrons
= | Formula
£
1 10
oe | 4 2
L
[1 mark for every 2 correct answers)
‘AZ (a) It lowers the pH of water and soil, and thus kills
plants and fish. (1)
Itoorrodes buildings and metal structures. ft]
(©) (i) From lightning activty/intemal combustion
engines ti
(i) From volcanoes/combustion of fossil
fuels 0]
A3_ (a) Itis the average mass of one atom of an
1
element compared to 75 of the mass of one atom
of carbon-12 ('2C). a)
(b) Chlorine has two main isotopes; “C/ and 37Cy,
m
CI has an abundance of 75% while °7C/ has a
relative abundance of 25%, i
(6) (9) Colourtess solution turns brown. tt)
Cix(q) + 2Ki(aq) > 2KCi(aq) + Io2q) (2)
[1,(s) is also acceptable as iodine is not very
soluble in water. Thus the solution not only
turns brown due to dissolved fodine, black
solid deposits may also be seen due to iodine
cexystals formed)
[1 mark for correct state symbols and 1 mark
for balanced equation with correct chemical
formulae]
(i) Colourless liquid begins to appear. [1]
CHa) + Ce{a) > CHACK!) + HCG) 2)
[1 mark for correct state symbols and 1 mark for
balanced equation with correct chemical formulae}
Solutions to Examination Set B
aa
(d) Ci, — oxidation state is 0 (zero). t
[Ci is an element, and the oxidation state of an
element is always zero]
NaCt- oxidation state of Clis 1 tt]
[Cl exists as Cr ions in NaCi, and the oxidation
state follows the charge of the ion.
NaOC! - oxidation state of Clis +1 tt]
[The oxidation state of oxygen in a compound is
~2, and that for Na is +1. Since the overall oxidation
state of NaOCl is 0 (zero), the oxidation state of CI
has to be +1.]
(@) Covalent bonding tH
(b) C-O bond a
One mole of C-O bond requires the least amount
of energy to break. tt]
(c) Bond energy of C-O bond
twice the bond energy = 360 x 2
Bond energy of C=O bond = 743 ku/mol
‘The bond energy of C=O bond is more than twice
the bond energy of C-O bond.
No, the energy needed to break a mole of double
bond is more than twice the energy needed to
break a mole of single bond between two identical
elements. 1)
(@) (i) Reactants:
Type of bond and | Bondbreaking |
quantity energy (ks)
6C-H 4126
20-0 360 x2
20-H 43x2 |
| 30. | 496x3
|
a
Total eneray needed for bond breaking
412 6 + 360 x 2 + 463 2 + 496 x 3
5056 kd a
Products
| Type of bond and | Bond forming
| quantity energy (kd)
[4c | 143 x4
80-H 468 x8 |
i
Total energy given out in bond forming
= 743 x 4 +463 x8
6676 kJ i
{i AH =05 x (-6676 + 5056)
=-810KJ ia)
INote that the chemical equation and all the
Previous workings are for 2 moles of methanol,
So, in the final calculation for one mole of
‘methanol, the difference in bond energies has
to be divided by 2 (or multiplied by 0.5). Also,
combustion is exothermic, hence AH is negative.)
63
(e)
energy
reactants
\ jaH
products
13]
[Deduct 1 mark for each of the following that is
incorrect, up to a maximum of 3 marks:
+ correct shape of graph;
+ energy level of products is lower than energy
level of reactants;
+ labeling of activation energy, E, (arrow must
point up as it gains heat);
+ labelting of enthalpy change AH (direction of
arrow must be downwards as itis exothermic
i.e, heat is lost)]
AS (a) (i) Molar mass of H,Op = 1x24 16x2
=34
Concentration of HO; = me
= 0.500 molidm? [1]
(ii) No. of moles of HzO.
100
= Im? x ~
= 0.800 mold? x 5
= 0.0500 mot tt)
am?
From the equatio
‘no. of moles of HzO,
2x no. of moles of Oz
0.0500
2
= 0.0260 mol io}
So, no. of moles of O2
Volume of O, = 0.0250 x 24
(0.600 dm? "1
(b) Use a glowing splint. oT
if oxygen is produced, the glowing splint will be
relighted (1
{c) Store hydrogen peroxide in opaque bottles. [1]
Store hydrogen peroxide in dark and cool or cold
places t
AB (a) Cs—Cy 10]
(b) Petroleum gas )
Itis used as fuel for cooking. tf
(6) Cs- Cy n
Solutions to Examination Set B
(d) High temperature (1)
Use of a catalyst ny
(e) CopHsa(s) > C2He(9) + 13C2H.(9) 12
[1 mark for equation, mark for balancing the
equation]
(f) Bubble the products into reddish-brown bromine
Section B
water. tt]
Ethene will decolourise bromine. tt]
(a) acidified
water reservoir
hydrogen
gas
platinum platinum
electrode electrode
positive negative
electrode electrode
(anode) (cathode) gy
{1 mark for diagram above to measure volume of
gases]
{1 mark for labelling cathode, anode, oxygen gas
and hydrogen gas}
(0) (i) Cathode: 2H"(aq) + 22° > H,(9) (1)
‘Anode: 40H-(aq) > O,{g) + 2H-0() +4e- [1]
Ratio of volume of hydrogen to
volume of oxygen = 2:7 t
(il) Oxygen gas is more soluble than hydrogen
{gas and some of it dissolves in water. AS a
result, the volume of oxygen gas collected is
less than half of the hydrogen gas collected. [1]
(©) () Over time, the chloride ion in the electrolyte
becomes more concentrated as hydroxide ions
are oxidised to oxygen. Hence chlorine is
discharged. it)
(i) 15% i)
[Based on the trend, the increase is 5% for
every 10 minutes.)
(il) Chlorine is a very reactive element, Some
of it reacted with the platinum anode to form
platinum chloride. i
‘The platinum chioride formed is insoluble in
water. I formed a layer on the anode and acted
as an insulator, thus preventing the transfer of
electrons between the chloride ions and the
anode. 0
BB (a) As temperature gets higher, the kinetic energy
of the particles increases. [1]
Hence the particles move with greater average
speed [1] and collide more frequent, [1] leading to
a faster rate of reaction.
Also, with a higher energy level, more particles
will possess an energy that is greater than the
activation energy. [1] Hence the frequency of
successful collisions, leading to formation of
products, will increase. (1]
(b) There is less ultraviolet radiation reaching the
Earth's surface due to the blocking by clouds and
atmospheric gases. [1]
(c) Light from the photocopying machine provides
the energy to spit O, molecules to O atoms [1] and
the O atoms combine with O» molecules to form
ozone, O3 [1]
(d) Ozone is used for kiling microorganisms in the
purification of water. m
(e) When the ozone layer is thinned or depleted,
harmful ultraviolet rays will not be fully absorbed by
the ozone layer but can penetrate the atmosphere.
These ultraviolet rays can damage skin tissue and
even cause skin cancer. 1]
EITHER
B9 (a) (i)
ce | ou °
semass | 62.1 103 276
| Mole ratio | 62.1. 10.3 276
12 1 16
5.175 |=103 | = 1.725
simplest [6.175 | 103 4.725
ratio 1725 «| 4.725 | 1.725
=3 =6 1
i)
Empirical formula is C3H,0. ni
(i) No. of motes of NaOH
= 0.10 mold x P55. am?
= 0.00259 mol t)
No. of moles of carboxylic acid
= no. of moles of NaOH, 80,
M, of carboxylic acid
= __mass of carboxylic acid
NO. of moles of carboxylic acid
0.30
0.00258,
=116 ty
‘Solutions to Examination Set B
Lot the molecular formula be CarHarOrp 80
M,=12x3m+1x6m+16xm
16
36m-+ m+ 16m
58m
Hence the molecular formula is CeH;20,
1
(0) () Add acidified potassium dichromate(VI) to
the alcohol and warm the mixture. tt]
‘The colour ofthe dichromate( VI) will turn from
‘range to green. (1)
{i Aweak acid is one that ionises partially into
ions when dissolved in water. t)
(ii) Method 1 : Comparing rate of reaction
Measure the rate of reaction with a metal,
such as magnesium, or a metal carbonate,
such as calcium carbonate, with each of
the acids. All other reaction conditions, such as
concentration and temperature, should remain
the same for both tests to ensure a fair test. [1]
Hydrochloric acid will react faster than ethanoic
acid. ty
OR
Method 2: Finding pH
Measure the pH of hydrochlorio acid and
ethancic acid, with both acids at the same
concentration and temperature. fay
The pH of the hydrochloric acid will be lower.
ful
oR
9 (a) Calcium reacts very fast with hydrochloric acid
while zinc reacts moderately fast with hydrochloric
acid. (i)
Calcium reacts more vigorously than zine. Oi)
Effervescence is observed in both reactions. [1]
Ca+ 2HCI > CaCl, + Hy
OR Zn + 2HCI> ZnCl, + He 0
Copper does not react with hydrochloric acid. [1]
The rate of reaction of these metals with acid
indicates the reactivity of these metals. Thus the
trend in reactivity of these metals, in decreasing
‘order, is calcium, zine and copper. "1
(b) The metals used should have the same number
‘of moles instead of the same mass. {i}
This is because the metals have different relative
‘atomic masses and hence the same mass of these
‘metals have different molar quantities. As a result
the number of atoms for each of the metals would
be different: Since the initial number of reacting
articles is different, itis not a fair experiment. [1]
() Sulfuric acid reacts with calcium to form
insoluble calcium sulfate. 1
‘The calcium sulfate forms a layer on the surface
of the calcium metal and prevents the metal from
coming into contact with the acid, thus stopping the
reaction. ti]
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Self-Worth Theory of Achievement MotivationDocument18 pagesThe Self-Worth Theory of Achievement Motivationkangalbert86No ratings yet
- Endorsement Letter For OJT SampleDocument5 pagesEndorsement Letter For OJT SampleKhorchnoi Abaja Calimlim100% (1)
- ST Special Edition 150323Document13 pagesST Special Edition 150323H.S.No ratings yet
- MCQ (Pure) (Sp1)Document8 pagesMCQ (Pure) (Sp1)Huiming OngNo ratings yet
- 02 Exam APaper 2Document12 pages02 Exam APaper 2geoboom12No ratings yet
- 04 Exam BPaper 1Document13 pages04 Exam BPaper 1kangalbert86No ratings yet
- O Revision E&M IDocument11 pagesO Revision E&M Ikangalbert86No ratings yet
- 0608 w10 QP 1Document16 pages0608 w10 QP 1kangalbert86No ratings yet
- 03 Exam A AnswerDocument6 pages03 Exam A Answergeoboom12No ratings yet
- 01 Exam APaper 1Document13 pages01 Exam APaper 1kangalbert86No ratings yet
- Questions On Organic ChemistryDocument15 pagesQuestions On Organic Chemistrykangalbert86No ratings yet
- Measurements in ChemistryDocument16 pagesMeasurements in Chemistrykangalbert86No ratings yet
- O Level Chemistry Prelim QuestionsDocument7 pagesO Level Chemistry Prelim Questionschong56No ratings yet
- Whats The DifferenceDocument5 pagesWhats The DifferenceMas Bagaz NoviantoNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis of Molten CompoundsDocument12 pagesElectrolysis of Molten Compoundskangalbert86No ratings yet
- 0620 Unit1 QuestionsDocument12 pages0620 Unit1 QuestionsfarsxdchgNo ratings yet
- Prevalence and Correlates of Excessive Internet Use Among Youth in SingaporeDocument6 pagesPrevalence and Correlates of Excessive Internet Use Among Youth in Singaporekangalbert86No ratings yet
- Worksheet 1 - Measurements in Chemistry (Questions)Document5 pagesWorksheet 1 - Measurements in Chemistry (Questions)kangalbert86No ratings yet
- 5070 s13 QP 32Document8 pages5070 s13 QP 32kangalbert86No ratings yet
- 5070 s13 QP 22Document20 pages5070 s13 QP 22kangalbert86No ratings yet
- Using Computer Simulations To Enhance Science Teaching and LearningDocument10 pagesUsing Computer Simulations To Enhance Science Teaching and Learningkangalbert86100% (1)
- 5070 s13 QP 32Document8 pages5070 s13 QP 32kangalbert86No ratings yet
- 5070 s13 QP 21Document20 pages5070 s13 QP 21kangalbert86No ratings yet
- The Many Forms of ConstructivismDocument28 pagesThe Many Forms of Constructivismkangalbert86No ratings yet
- The Case of A Disruptive Preservice TeacherDocument12 pagesThe Case of A Disruptive Preservice Teacherkangalbert86No ratings yet
- Leslie Tay Hawker FoodDocument8 pagesLeslie Tay Hawker Foodkangalbert86No ratings yet
- Ionic Bonding Tcm18-189311Document5 pagesIonic Bonding Tcm18-189311kangalbert86100% (1)
- Bronfenbrenner Ecological TheoryDocument9 pagesBronfenbrenner Ecological Theorykangalbert86100% (1)
- The Development of Dynamic Inquiry Performances Within An Open Inquiry Setting - A Comparison To Guided Inquiry SettingDocument24 pagesThe Development of Dynamic Inquiry Performances Within An Open Inquiry Setting - A Comparison To Guided Inquiry Settingkangalbert86No ratings yet
- 0580 s11 QP 41Document16 pages0580 s11 QP 41Amina Koi DowuiNo ratings yet
- Fam CaseDocument9 pagesFam Casefam111222No ratings yet
- History, Politics & Economics of EducationDocument30 pagesHistory, Politics & Economics of Educationcreativelearnersulwe2018No ratings yet
- BtechCS 501 To 528 27 07 2017Document6 pagesBtechCS 501 To 528 27 07 2017Minal SharmaNo ratings yet
- Eduction Policy 1972 1980Document10 pagesEduction Policy 1972 1980Afsheen khanNo ratings yet
- JBT To TGT Arts Promotion July 2018 Orders by Vijay Kumar HeerDocument13 pagesJBT To TGT Arts Promotion July 2018 Orders by Vijay Kumar HeerVIJAY KUMAR HEERNo ratings yet
- De Luyen Tap WritingDocument23 pagesDe Luyen Tap WritingXuyen PhanNo ratings yet
- 2022 Postgraduate Information Brochure Deptchemeng Final Final Latest - zp214196Document20 pages2022 Postgraduate Information Brochure Deptchemeng Final Final Latest - zp214196Ronald ManyamaNo ratings yet
- Apprentices Act 1961Document68 pagesApprentices Act 1961Nidhi ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Approval SheetDocument1 pageApproval SheetClint M. MaratasNo ratings yet
- DME PG MD MS First Round Merit List 2023Document29 pagesDME PG MD MS First Round Merit List 2023Yash DhurveyNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Institutes Applied For Running Vocational CoursesDocument7 pagesGuidelines For Institutes Applied For Running Vocational CoursesSANJAY TIWARINo ratings yet
- Tuguegarao City, Cagayan 3500: St. Paul University PhilippinesDocument58 pagesTuguegarao City, Cagayan 3500: St. Paul University Philippinesmarchelly simon0% (1)
- Women'S University in Africa: Call For Applications - 2 Intake WuaDocument9 pagesWomen'S University in Africa: Call For Applications - 2 Intake WuaTanaka MachanaNo ratings yet
- CBET Framework and The Functions of TVET CDACCDocument21 pagesCBET Framework and The Functions of TVET CDACCCharles OndiekiNo ratings yet
- Summer Internship ReportDocument3 pagesSummer Internship ReportAyush TiwariNo ratings yet
- Government College of Engineering, KeonjharDocument5 pagesGovernment College of Engineering, Keonjharsriknta sahuNo ratings yet
- MoU RedefineDocument7 pagesMoU RedefineWelstand InternationalNo ratings yet
- Training For Success: A Policy To Expand Apprenticeships in The United StatesDocument66 pagesTraining For Success: A Policy To Expand Apprenticeships in The United StatesCenter for American ProgressNo ratings yet
- 05.12.22 STEM Letter FinalDocument3 pages05.12.22 STEM Letter FinalSinclair Broadcast Group - EugeneNo ratings yet
- PSTKB 6 7Document2 pagesPSTKB 6 7Shakil KhanNo ratings yet
- Animal Production (Ruminants) NC IIDocument78 pagesAnimal Production (Ruminants) NC IIMargerie FrueldaNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence in EducationDocument8 pagesArtificial Intelligence in EducationIshfaq MajidNo ratings yet
- Chnical Education and Skills Development Authority: Face-to-FaceDocument2 pagesChnical Education and Skills Development Authority: Face-to-FaceRowena Babagonio SarsuaNo ratings yet
- A Study On Working Capital Management and Inventory Management at Tata SteelDocument4 pagesA Study On Working Capital Management and Inventory Management at Tata SteelSujal KambleNo ratings yet
- Shortlisted Institutes For WebsiteDocument141 pagesShortlisted Institutes For WebsiteDrSenthil KumarNo ratings yet
- 034 Civil 2 SemDocument41 pages034 Civil 2 Semanshu rajNo ratings yet
- CV Template Bixter TrainingDocument2 pagesCV Template Bixter TrainingMartha ChristopherNo ratings yet
- ACFrOgBzlKNOas8Av0oIrxLk6LPsmUyfPV71fuO-olSCrlk-aaRzMJgBtQZYDaVjPHYiFoVHBE8hGosN0QGDEIWUvLuoMgQobUwqTVpR95rLt8O 2Qo7nGvwVxdjlmEqEVtW312kX 9sta7fqYIADocument74 pagesACFrOgBzlKNOas8Av0oIrxLk6LPsmUyfPV71fuO-olSCrlk-aaRzMJgBtQZYDaVjPHYiFoVHBE8hGosN0QGDEIWUvLuoMgQobUwqTVpR95rLt8O 2Qo7nGvwVxdjlmEqEVtW312kX 9sta7fqYIAblack webNo ratings yet
- Wzór Raportu PCEZ 2021Document16 pagesWzór Raportu PCEZ 2021DamianNo ratings yet