Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Theory of Stress and Strain
Uploaded by
Md ReyazOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Theory of Stress and Strain
Uploaded by
Md ReyazCopyright:
Available Formats
EGM 5653
CHAPTER 2
TheoriesofStressandStrain
EGM 5653
Advanced Mechanics of Materials
Namas Chandra
Advanced Mechanics of Materials
Chapter 2-1
EGM 5653
Objectives
Definition of stress/strain as tensor
Stress/strain on arbitrary planes
Principal quantities, Mohrs circle in 2-D and 3-D
Small displacement theories
Strain rosettes
Sections
2.1,2.2 Stress Definition
2.3 Stress tranformation, 2.4 Principal quanities
2.5 Equilibrium equation, 2.6 strain in any direction
2.7 strain transformation, 2.8 strain theory
2.9 Strain measurment
Namas Chandra
Advanced Mechanics of Materials
Chapter 2-2
EGM 5653
2.1 Stress at a point
Namas Chandra
Advanced Mechanics of Materials
Lt
A 0
F
t
A
Lt
A 0
FN
tN
A
Lt
A 0
FS
tS
A
Chapter 2-3
P
A
EGM 5653
2.2 Stress Notation (Tensor)
xx
T xy
xz
xy xz
yy yz
yz zz
Namas Chandra
Advanced Mechanics of Materials
Body force vector is
Bx , By , Bz
Chapter 2-4
P
A
EGM 5653
2.2 Alternate Stress Notation
xx
T xy
xz
xy xz
yy yz
yz zz
11 12 13
T 12 22 23
23 23 33
Namas Chandra
Advanced Mechanics of Materials
xx
T xy
xz
xy xz
yy yz
yz zz
Diagonal Normal
Off-diagonal-Shear
Eng. Shear= 2*Tensor Shear
Chapter 2-5
P
A
EGM 5653
2.2 Stress on arbitrary planes
xx
T xy
xz
xy xz
yy yz
yz zz
N cos i cos j cos k
li mj nk
N x i NY j N Z k
Stress on arbitrary plane is t T N
Namas Chandra
Advanced Mechanics of Materials
Chapter 2-6
EGM 5653
2.4 Stress Transformation (3-D to another 3-D)
e2
Consider two systems
X e1 , e2 , e3 and X e1, e2 , e3
e2
ei
is obtained from
ei
using a rigid body rotation.
We are interested to relate the unit vectors
e3
e3
1
e
e1
ei
in
from that of
We can see that,
e1 Q11e1 Q21e2 Q31e3
e2 Q12e1 Q22e1 Q32e3
.
e3 Q13e1 Q23e1 Q33e3
Qij cos(ei , ej )
Transformation matrix component
cos(old , new)
Namas Chandra
Advanced Mechanics of Materials
Chapter 2-7
EGM 5653
2.4 Stress Transformation (Vector)
Vector from old to new system,
e2
ai' Qmi am
e2
e3
e3
[a]' [Q]T [a ]
1
e
e1
Q11Q21Q31
a1
a Q Q Q
12 22 32
2
Q13Q23Q33
a3
Given, a 2e1
a Q a
'
Namas Chandra
Advanced Mechanics of Materials
a1
a 2
a
3
Find in terms of
'
$
{ei }
0 1
Q 1 0
0 0
0 1 0 2
1 0 0 0
0 0 1 0
0
0
0
2
0
Chapter 2-8
EGM 5653
2.4 Stress Transformation (Tensor)
e2
Tensor from old to new system,
e2
e$n
Tij' Qmi e$m .TQ
nj
QmiQnj (e$m .T e$n )
e3
1
e
e3
e1
Thus
Tij' Qmi QnjTmn
T11' T12' T13'
Q11 Q12
'
Q Q
'
'
T
T
T
22
21 22 23
12
T31' T32' T33'
Q13 Q23
13 Q11 Q12
Q13 T11 T12 T
Q32 . T21 T22 T 23 . Q12 Q22
Q33 T31 T32 T 33 Q13 Q23
Q 13
Q 32
Q 33
T Q T Q
'
Namas Chandra
Advanced Mechanics of Materials
Chapter 2-9
EGM 5653
2.4 Stress Transformation (Tensor)
0 1 0
T 1 2 0
0 0 1
T Q T Q
'
2 1
1 0
0 0
Namas Chandra
Advanced Mechanics of Materials
0 1
1 0
Q
0 0
0
0
0
0
1
Chapter 2-10
EGM 5653
2.4 Stress Transformation (All tensors)
0 1
1 0
Q
0 0
0
0
'
ai' Qmi am
Tij' QmiQnjTmn
Scalar
Vector
Second Order Tensor
Tijk' QmiQnj QrkTmnr
Third Order Tensor
th
Tijk ... QmiQnj Qok .....QspTmno
...
n
Order Tensor
{
{
n
Namas Chandra
Advanced Mechanics of Materials
Chapter 2-11
EGM 5653
2.4.2 Principal Stresses
% I% n 0
%
n n In
11
12
13
21
22
23 0
31
32
33
( 11 )1 12 2 13 3 0
211 ( 22 ) 2 23 3 0
311 32 2 ( 33 ) 3 0
1 , 2 , 3 are the direction cosines
Namas Chandra
Advanced Mechanics of Materials
is the one of the principal values
This is a cubic equation in
Solution to this equation gives the
three principal stress values.
1 2 3
For each of the values, find the
direction corresponding to that
principal value,
1 2 3 1
2
Chapter 2-12
EGM 5653
2.4.2 Principal Stresses-example
2 0 0
T 0 3 4
0 4 3
Given:
T I
For 1 5
Find principal values and directions.
1 5
2 2
3 5
0
4 (2 )( 2 25) 0
3
2 1 n1 0n2 0n3 0
0 (3 1 ) n2 4n3 0
0 4n2 (3 1 ) n3 0
3n1 0 n1 0
n 2 e1
Namas Chandra
Advanced Mechanics of Materials
2n2 4n3 0
4n2 8n3 0
1
2
2
2
2
n1 n2 n3 1 n3
and n2
5
5
1
n 1
2e2 e3
5
1
n 3
e2 2e3
5
Chapter 2-13
EGM 5653
2.4.2 Stress Invariants
I1 xx yy zz
xx xy yy yz xx zx
I2
xy yy yz zz zx zz
xx yy yy zz zz xx 2 xy 2 yz 2 zx
xx xy zx
I 3 xy yy yz
zx yz zz
In terms of principal
Stresses,
Namas Chandra
Advanced Mechanics of Materials
I1 1 2 3
I 2 1 2 2 3 3 1
I 3 1 2 3
Chapter 2-14
EGM 5653
2.4.4 Octohedral Stresses
cos 2 cos 2 cos 2 1
1
3
(i j k)
oct 13 I1 13 1 2 3
oct 13
1 2
1 2 1 2
2
oct 13 I1 13 xx yy zz
oct
1
3
yy zz xx yy xx 6( 2 xy yz2 zx2 )
2
xx
Namas Chandra
Advanced Mechanics of Materials
Chapter 2-15
EGM 5653
2.4.5 Mean and Deviatoric Stresses
I1 xx yy zz 1 2 3
m
3
3
3
% T% T
T% T%
T
m
d
m
Tij 13 Tkk ij Tij
0
m 0
Tm 0 m 0
0
0 m
Namas Chandra
Advanced Mechanics of Materials
xx m
xy
xz
Td xy
yy m
yz
xz
yz
zz
m
Chapter 2-16
P
A
EGM 5653
2.4.6 Coordinate Transformation in 2-D
T Q T Q
T
xx xx cos 2 yy sin 2 2 xy sin cos
yy xx sin 2 yy cos 2 2 xy sin cos
xy xx yy sin cos xy (cos 2 sin 2 )
xx 12 xx yy 12 xx yy cos 2 xy sin 2
yy 12 xx yy 12 xx yy cos 2 xy sin 2
xy 12 xx yy sin 2 xy cos 2
Namas Chandra
Advanced Mechanics of Materials
Chapter 2-17
EGM 5653
2.4.7 Mohrs Circle in 2-D
Center
Radius
1
2
xx
1
4
yy , 0
xx
yy
xy
2
1
2
1
2
max
Namas Chandra
Advanced Mechanics of Materials
xx yy
1
4
xx
yy
xy
xx yy
1
4
xx
yy
xy
1
4
xx
yy
xy
2
Chapter 2-18
EGM 5653
2.4.7 Mohrs Circle in 3-D
The best way to draw Mohrs
circle in 3-D is first to find
the principal stresses.
Using the three principal
stresses, the three circles can
then be drawn.
The horizontal direction then
indicates the principal
direction.
Namas Chandra
Advanced Mechanics of Materials
Chapter 2-19
EGM 5653
Problem 2.5 (page72)
Given: Stress components xx 80 Mpa; yy 60 Mpa; zz 20 Mpa
xy 20 Mpa; xz 40 Mpa; yz 10 Mpa
Find: Stress vector on a plane normal to
1
n
(1, 2,1)
6
Stress vector
i 2 j k
80 20 40
T% 20 60 10
40 10 20
%
65.32i 61.24 j 32.66k
Tn
Namas Chandra
Advanced Mechanics of Materials
Chapter 2-20
EGM 5653
Problem 2.5 (page72)
Given: Stress components xx 80 Mpa; yy 60 Mpa; zz 20 Mpa
xy 20 Mpa; xz 40 Mpa; yz 10 Mpa
Find: Invariants
I1 xx yy zz 160 Mpa
First Invariant
I2
Second Invariant
Third Invariant
2
2
2
xx yy
yy zz
zz xx
xy
yz
zx 5500
xx xy zx
I 3 xy yy yz 0
zx yz zz
Namas Chandra
Advanced Mechanics of Materials
Chapter 2-21
EGM 5653
Problem 2.5 (page72)
Given: Stress components xx 80 Mpa; yy 60 Mpa; zz 20 Mpa
xy 20 Mpa; xz 40 Mpa; yz 10 Mpa
Find: Principal Values, max. shear and oct. shear stress
Characteristic Equation
3 160 2 5500 0 0
max 12 1 3 55 Mpa
2
1
oct
1
2
2
3
3
1
9
( 2 160 5500) 0
44.97Mpa
1 110 Mpa
2
2 50 Mpa
1 0
Namas Chandra
Advanced Mechanics of Materials
Chapter 2-22
EGM 5653
2.5 Equation of Motion
xx yx zx
Bx 0
x
y
z
xy yy zy
By 0
x
y
z
xz yz zz
Bz 0
x
y
z
Namas Chandra
Advanced Mechanics of Materials
Chapter 2-23
EGM 5653
2.2 Equation of Motion (deformation)
x * x * (x, y, z)
y y (x, y, z)
*
z z (x, y, z)
*
x x(x , y , z )
*
y y(x * , y* , z* )
z z(x , y , z )
*
Namas Chandra
Advanced Mechanics of Materials
Chapter 2-24
EGM 5653
2.2 Strain of a Line Element
Engineering strain: Definition
ds* ds
E
ds
Finite or Green Strain
xx
u 1 u v
w
x 2 x x
x
yy
2
2
2
w
v 1 u v
y 2 y y
y
2
2
2
w 1 u
v
w
zz
z 2 z z
z
Namas Chandra
Advanced Mechanics of Materials
Chapter 2-25
EGM 5653
2.7.3 Shear Strain (Angle Change between elements)
PA : (l1 , m1 , n1 )
PB : (l 2 , m 2 , n 2 )
P*A* : (l1* , m1* , n1* ) P*B* : (l*2 , m*2 , n *2 )
cos
2
cos * l1*l*2 m1*m*2 n1*n *2
Let PA & PB be along x and y axes
12 xy 2 xy
23 yz 2 yz
31 zx 2 xz
12 (1 E1 )(1 E 2 ) cos *
;
Namas Chandra
Advanced Mechanics of Materials
*
2
Chapter 2-26
EGM 5653
2.7.4 Principal Strains
This theory is analogous to stress theory
xx M
xy
xy
xz
yy M
yz
xz
yz
zz M
where,
I 1 xx yy zz
or
M I 1M I 2 M I 3 0 I 2
3
1 2
M E E
2
xx xy
xy yy
xx xz
xz zz
yy yz
yz zz
xx yy xx zz yy zz 2xy 2xz 2yz
xx xy xz
I 3 xy yy yz
xz yz zz
Namas Chandra
Advanced Mechanics of Materials
Chapter 2-27
EGM 5653
2.8 Small Displacement Theory
Here the strains are infinitesimal and rigid body motion is negligible.
Then,
u
v
w
xx , yy , zz
x
y
z
1 w v
1 v u
1 w u
xy
, xz
, yz
2 x y
2 x z
2 y z
and the Magnification factor is,
M E
Namas Chandra
Advanced Mechanics of Materials
Chapter 2-28
EGM 5653
2.9 Strain Measurements
The direction cosines or arms a,b,and c are
(la , ma , na ) (1,0,0), (lb , mb , nb ) (cos ,sin , 0), (lc , mc , nc ) (cos 2,sin 2, 0)
The extensional strains are
a xx
b xx (cos 2 ) yy (sin 2 ) 2 xy (cos )(sin )
c xx (cos 2 2) yy (sin 2 2) 2 xy (cos 2)(sin 2)
Namas Chandra
Advanced Mechanics of Materials
Chapter 2-29
EGM 5653
2.9 Strain Measurements contd.
Therefore,
xx a
( a 2b ) sin 4 2 c sin 2
4sin 2 sin 2
2 a (sin 2 cos 2 2 sin 2 2 cos 2 ) 2(b sin 2 2 c sin 2 )
xy
4sin 2 sin 2
When 60o
yy
2(b c ) a
b c
xx a , yy
, xy
3
3
When 45o
1
xx a , yy c , xy b ( a c )
2
Namas Chandra
Advanced Mechanics of Materials
Chapter 2-30
EGM 5653
Solved Problem 2.55
2.55 A Square panel in the side of a ship is loaded so that the panel is in a
zz ofzx plane
zy 0strain (
state
)
a. Determine the displacements for the panel given that the
deformations shown and the strain components for the (x,y)
coordinate axes.
b. Determine the strain components for the (X,Y) axes.
Namas Chandra
Advanced Mechanics of Materials
Chapter 2-31
EGM 5653
Problem 2.55 (contd)
Namas Chandra
Advanced Mechanics of Materials
Chapter 2-32
EGM 5653
Problem 2.74
2.74 Show that for Ex 2.12 when =600 the principal strains are given by
1
1
( a b c ) R; 2 ( a b c ) R
3
3
1/ 2
1
R (2 a b c )2 3( b c )2
3
and the maximum strain is located at angle ccw from x axis
tan 2
Namas Chandra
Advanced Mechanics of Materials
3( b c )
2( a b c )
Chapter 2-33
EGM 5653
Problem set in chapter 2 (HW2)
No
Homework
(due date)
Suggested Problems
In-class and others
2.2, 2.6, 2.7, 2.21,2.25, 2.45, 2.4, 2.10,2.13, 2.18, 2.26,
2.54, 2.57, 2.58, 2.67
2.42, 2.56, 2.59, 2.64, 2.71,
2,77, 2.73,2.76
(9 Feb 2006)
Namas Chandra
Advanced Mechanics of Materials
Chapter 2-34
You might also like
- Theory of Elasticity - Fatigue PDFDocument33 pagesTheory of Elasticity - Fatigue PDFLUIS ISAAC LEON PARONo ratings yet
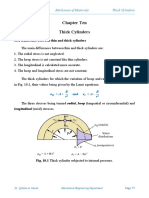
- Cylinders, Compound Cylinders, Press & Shrink FitsDocument9 pagesCylinders, Compound Cylinders, Press & Shrink Fitstvsaagar100% (1)
- 4.1 Thick Walled CylindersDocument27 pages4.1 Thick Walled CylindersDASitchNo ratings yet
- Thick Pressure Vessels - Engineering LibraryDocument5 pagesThick Pressure Vessels - Engineering LibraryAvishay TufikianNo ratings yet
- Stress in Pressure CylinderDocument3 pagesStress in Pressure CylinderbmyertekinNo ratings yet
- Thick CylinderDocument4 pagesThick CylinderJason Gibbs50% (2)
- Lames Equation & JustificationDocument14 pagesLames Equation & Justificationjamil vora100% (1)
- EGF316 Thin and Thick Cylinders - NotesDocument20 pagesEGF316 Thin and Thick Cylinders - NotesAlokWardhanSingh100% (1)
- 12.fatigue ShigleyDocument18 pages12.fatigue Shigleysong perezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Strength Calculation of JointsDocument76 pagesChapter 3 Strength Calculation of Jointsrobel metiku100% (1)
- Thick Wall CylinderDocument7 pagesThick Wall Cylinderchuckhsu1248No ratings yet
- Finite Element MethodDocument32 pagesFinite Element MethodParvind Lolldharry100% (1)
- Fluid Mechanics - A. K. Choudhary and Om PrakashDocument98 pagesFluid Mechanics - A. K. Choudhary and Om PrakashRohit ThakurNo ratings yet
- O Q (Gate, Ies, Ias) : Bjective Uestions Previous 20-Years GATE Questions Lame's TheoryDocument13 pagesO Q (Gate, Ies, Ias) : Bjective Uestions Previous 20-Years GATE Questions Lame's TheoryharshdeepNo ratings yet
- ETBX Stress-Life Fatigue Analysis ModuleDocument11 pagesETBX Stress-Life Fatigue Analysis ModuleLeonardo Da Rosa Gonçalves100% (1)
- Hydraulic PipingDocument1 pageHydraulic Pipingpandunugraha04100% (1)
- Buckling Fatigue AnalysisDocument55 pagesBuckling Fatigue AnalysisHarshit Garg100% (2)
- The Analysis of Piping Under PressureDocument21 pagesThe Analysis of Piping Under PressureTrungSon NguyenNo ratings yet
- Bulk Modulus 1Document17 pagesBulk Modulus 1rocks100% (1)
- Stress For Thick Walled Cylinders Using LaméDocument3 pagesStress For Thick Walled Cylinders Using LaméSaudagar S. Jagdev100% (1)
- Note 1478591647Document65 pagesNote 1478591647B. RanjitNo ratings yet
- Design of Hyd. CylindersDocument10 pagesDesign of Hyd. CylindersVinod YbNo ratings yet
- Behaiviour of PE PipesDocument106 pagesBehaiviour of PE PipeskavoshyarpajouhanNo ratings yet
- In Elastic Buckling of Geometrically Imperfect TubesDocument16 pagesIn Elastic Buckling of Geometrically Imperfect TubesSiva RajNo ratings yet
- Solid Element Formulation OverviewDocument36 pagesSolid Element Formulation OverviewasdqwexNo ratings yet
- Lame Thick Cylinder EquationsDocument17 pagesLame Thick Cylinder Equationsbeegmac100% (2)
- Simple Stresses and Strains PDFDocument104 pagesSimple Stresses and Strains PDFyaminiNo ratings yet
- Aisi O1: Cold Work Tool SteelDocument7 pagesAisi O1: Cold Work Tool Steeltewiinaba777No ratings yet
- 6177-4 Hertz Contact StressesDocument10 pages6177-4 Hertz Contact StressesVictor GearNo ratings yet
- Thick Walled Cylinders (Corrected)Document17 pagesThick Walled Cylinders (Corrected)John Larry CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Fracture MechanicsDocument7 pagesFracture MechanicsDEEPAKNo ratings yet
- Differential Transformation Method for Mechanical Engineering ProblemsFrom EverandDifferential Transformation Method for Mechanical Engineering ProblemsNo ratings yet
- Numerical Solution of Partial Differential Equations—II, Synspade 1970: Proceedings of the Second Symposium on the Numerical Solution of Partial Differential Equations, SYNSPADE 1970, Held at the University of Maryland, College Park, Maryland, May 11-15, 1970From EverandNumerical Solution of Partial Differential Equations—II, Synspade 1970: Proceedings of the Second Symposium on the Numerical Solution of Partial Differential Equations, SYNSPADE 1970, Held at the University of Maryland, College Park, Maryland, May 11-15, 1970Bert HubbardNo ratings yet
- HPS Notes of Lecture PDFDocument63 pagesHPS Notes of Lecture PDFsbhalesh100% (2)
- High Precision Position Control of Electro-Hydraulic Servo SystemDocument10 pagesHigh Precision Position Control of Electro-Hydraulic Servo Systemamin342No ratings yet
- Nonlinear Finite Element Analysis and Adina: Proceedings of the 4th ADINA ConferenceFrom EverandNonlinear Finite Element Analysis and Adina: Proceedings of the 4th ADINA ConferenceNo ratings yet
- Fatigue Design Procedures: Proceedings of the 4th Symposium of the International Committee on Aeronautical Fatigue held in Munich, 16–18 June 1965From EverandFatigue Design Procedures: Proceedings of the 4th Symposium of the International Committee on Aeronautical Fatigue held in Munich, 16–18 June 1965E. GassnerNo ratings yet
- Piping DesignDocument4 pagesPiping DesignTerry YongNo ratings yet
- Shaft Stress CalculationsDocument2 pagesShaft Stress CalculationsVivek PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- ThickWalledCylinder and PressShrinkFit ShigDocument17 pagesThickWalledCylinder and PressShrinkFit ShigArooj WaniNo ratings yet
- CH-10 Thick CylindersDocument19 pagesCH-10 Thick Cylindersمحمد خريبطNo ratings yet
- Effect Method Young's Modulus Estimation Fatigue LifeDocument15 pagesEffect Method Young's Modulus Estimation Fatigue LifeTeoTyJayNo ratings yet
- Experiments To Study The Gaseous Discharge and Filling of VesselsDocument12 pagesExperiments To Study The Gaseous Discharge and Filling of VesselsArun BabuNo ratings yet
- Dowling Material PropertiesDocument17 pagesDowling Material PropertiesCarlos A CuencaNo ratings yet
- Drag ForceDocument9 pagesDrag ForceImran BahaNo ratings yet
- Hoop StressDocument35 pagesHoop StressRezaSohrabiNo ratings yet
- Hobbacher-2015-Recommendations For Fatigue Design of Welded Joints and ComponentsDocument26 pagesHobbacher-2015-Recommendations For Fatigue Design of Welded Joints and Componentsbalaji817150No ratings yet
- Stresses in Thin, Thick, Spherical PVsDocument22 pagesStresses in Thin, Thick, Spherical PVsSuresh SjNo ratings yet
- CH-2 Basics of ControllersDocument14 pagesCH-2 Basics of ControllersSatya Sai Babu Yeleti100% (1)
- KLA AppNote StrainRateDocument6 pagesKLA AppNote StrainRatep dNo ratings yet
- Uniaxial Tension Compression Tests and Cyclic BendingDocument10 pagesUniaxial Tension Compression Tests and Cyclic Bendingmodestboy110No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Frictional Losses in Hydraulic PipelinesDocument56 pagesChapter 4 Frictional Losses in Hydraulic PipelinesTu Dang TrongNo ratings yet
- Stress Strain Laws - Lect05Document16 pagesStress Strain Laws - Lect05Manoj VermaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document34 pagesChapter 4Nanang NaberNo ratings yet
- Numerical ExamplesDocument20 pagesNumerical ExampleslitrakhanNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Solids Week 8 LecturesDocument17 pagesMechanics of Solids Week 8 LecturesFlynn GouldNo ratings yet
- CE207 Final Exam Formula BookletDocument7 pagesCE207 Final Exam Formula BookletangrytemperNo ratings yet
- Unit V Partial Differential Equations: SolutionDocument19 pagesUnit V Partial Differential Equations: SolutionCurious ManNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Functions (Paper 2) : (KEDAH 2013)Document2 pagesTrigonometric Functions (Paper 2) : (KEDAH 2013)Thiyaku MaruthaNo ratings yet
- Signal Flow DiagramsDocument20 pagesSignal Flow DiagramsSingappuliNo ratings yet
- 8.8 Linearity Rules of IntegrationDocument2 pages8.8 Linearity Rules of IntegrationNaUfal PaiNo ratings yet
- CS10-8L: Computer Programming Laboratory Exercise #2: Variables, Scripts and VisualizationsDocument7 pagesCS10-8L: Computer Programming Laboratory Exercise #2: Variables, Scripts and VisualizationsBING BONGNo ratings yet
- 2nd Quarter Exam Math 10Document4 pages2nd Quarter Exam Math 10Michelle Jaranilla84% (25)
- Rancangan Pengajaran Harian ContohDocument6 pagesRancangan Pengajaran Harian ContohCt KursiahNo ratings yet
- College Mathematics 9th Edition Cleaves Solutions ManualDocument20 pagesCollege Mathematics 9th Edition Cleaves Solutions ManualSteveJacobsafjg100% (44)
- Preparation For Calculus and Functions: Pamantasan NG CabuyaoDocument7 pagesPreparation For Calculus and Functions: Pamantasan NG CabuyaoJhon Mark SantoniaNo ratings yet
- Ma8151 Engg - Ineering Mathematics I MCQDocument120 pagesMa8151 Engg - Ineering Mathematics I MCQpriya dharshini80% (5)
- Divisibility Rules: Divisible (Whole Numbers Only) - Able To Be Divided Without RemainderDocument1 pageDivisibility Rules: Divisible (Whole Numbers Only) - Able To Be Divided Without RemainderOctagon EduCentreNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Higher-Order Linear ODEDocument18 pages2.2 Higher-Order Linear ODEBenya Srisoogcharoen100% (1)
- Methods of DifferentiationDocument13 pagesMethods of DifferentiationVishruth Reddy BuruguNo ratings yet
- Test of Mathematics For University Admission: Paper 1 2018 Worked AnswersDocument25 pagesTest of Mathematics For University Admission: Paper 1 2018 Worked AnswersNguyễn Hoàng AnNo ratings yet
- Linear Equations Worksheet 1Document9 pagesLinear Equations Worksheet 1LubnaLatifNo ratings yet
- Fourier Transform PairsDocument5 pagesFourier Transform Pairsrendy AnggaraNo ratings yet
- M 111 RevDocument13 pagesM 111 RevDexter BordajeNo ratings yet
- Inequalities, Algebra Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorDocument4 pagesInequalities, Algebra Revision Notes From A-Level Maths TutorA-level Maths TutorNo ratings yet
- Biography of AlDocument3 pagesBiography of AlAmmar AddinNo ratings yet
- CG Chapter 5Document61 pagesCG Chapter 5kiramelaku1No ratings yet
- Hanoi Open Mathematical Competition 2015: Junior Section ImportantDocument6 pagesHanoi Open Mathematical Competition 2015: Junior Section ImportantHung Son NguyenNo ratings yet
- Emory Poster TemplateDocument1 pageEmory Poster TemplateDp PdNo ratings yet
- Newton - Gregory Formula For Forward InterpolationDocument1 pageNewton - Gregory Formula For Forward Interpolationsharad94210No ratings yet
- Math 10 Problem SetDocument2 pagesMath 10 Problem SetMonka GigaNo ratings yet
- Intro To ScilabDocument7 pagesIntro To Scilabchristine_straubNo ratings yet
- (Catherine Twomey Fosnot, Bill Jacob) Constructing AlgebraDocument220 pages(Catherine Twomey Fosnot, Bill Jacob) Constructing AlgebraFe-humildad Amor-paz EsperanzaNo ratings yet
- A Report On Face Recognition Using Principal Component AnalysisDocument13 pagesA Report On Face Recognition Using Principal Component AnalysissharibNo ratings yet
- Literal EquationsDocument4 pagesLiteral Equationsapi-348347219No ratings yet
- Variables and Mathematical StatementsDocument5 pagesVariables and Mathematical StatementsJenica Mariel GabaisenNo ratings yet
- Section 1.1 Matrix Multiplication, Flop Counts and Block (Partitioned) MatricesDocument4 pagesSection 1.1 Matrix Multiplication, Flop Counts and Block (Partitioned) MatricesMococo CatNo ratings yet