Professional Documents
Culture Documents
6 4 Notes Gas Exchange
Uploaded by
api-2565112510 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
75 views13 pagesIdentify the respiratory components. Be able to draw something like this. State the difference between ventilation, gas exchange, and cell respiration. Award for each of the following structures clearly drawn and labelled.
Original Description:
Original Title
6 4 notes gas exchange
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentIdentify the respiratory components. Be able to draw something like this. State the difference between ventilation, gas exchange, and cell respiration. Award for each of the following structures clearly drawn and labelled.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
75 views13 pages6 4 Notes Gas Exchange
Uploaded by
api-256511251Identify the respiratory components. Be able to draw something like this. State the difference between ventilation, gas exchange, and cell respiration. Award for each of the following structures clearly drawn and labelled.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 13
6.
4 Gas Exchange
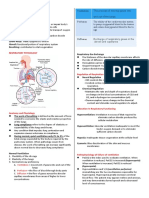
Respiratory System
Why do we need to breathe?
To intake oxygen
To exhale carbon dioxide
What is oxygen used for?
Aerobic respiration
And what is aerobic respiration used for?
Energy production (ATP!)
Definitions: Ventilation, Gas
Exchange, and Cell Respiration
Ventilation
The process of inhaling and exhaling, with oxygen
entering the alveoli (large surface area)
Gas Exchange
The process of exchanging one gas for the other
between alveoli and capillaries (carbon dioxide for
oxygen)
Cell Respiration
The chemical process occurring in mitochondria
where energy is released as ATP
What composes the human respiratory system?
Mouth
Nose
Trachea
Bronchi
Bronchioles
Lungs
Alveoli
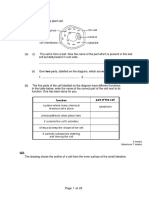
Identify the respiratory components.
6
1
2
3
4
5
Be able to draw something like this.
Why are alveoli shaped like they are?
Small alveoli increase surface area of tissue
exposed to open air
Gases only have to go through
one layer of cells (thin capillary
wall) to get into blood vessel
There are so many capillaries
blood easily diffuses
How is air drawn into the lungs?
Diaphragm muscle contracts
Intercostal muscles
between ribs contract
Lungs can open up more
More volume with same
amount of gas = decreased
air pressure
Air rushes into lungs to
balance pressure
How is air pushed out of the lungs?
Diaphragm muscle relaxes
Pushes on lungs to
deflate
Intercostal muscles relax
Chest cavity gets smaller
Pushes air out of lungs
Air is exhaled
IB Exam Question
1. State the difference between ventilation,
gas exchange, and cell respiration. (3 marks)
Ventilation
The process of inhaling and exhaling, with oxygen
entering the alveoli (large surface area)
Gas Exchange
The process of exchanging one gas for the other
between alveoli and capillaries (carbon dioxide for
oxygen)
Cell Respiration
The chemical process occurring in mitochondria
where energy is released as ATP
IB Exam Question
2. Draw a diagram of the human gas
exchange system.
(5 marks)
Award [1] for each of the following structures clearly
drawn and labelled.
mouth / nose;
trachea;
bronchi;
bronchioles;
lungs;
alveoli;
diaphragm;
ribs / rib eye / intercostal muscles;
IB Exam Question
3. List the features of the alveoli that
adapt them to gas exchange.
(3 marks)
Alveoli increase surface area between blood
and respiratory gases
Single layer of cells allows for short diffusion
distance of gas into blood
Dense network of capillaries near the surface
increases absorption
IB Exam Question
4. Explain the need for, and the mechanism
of, ventilation of the lungs in humans.
(8 marks)
draws fresh air / oxygen into the lungs;
removal / excretion of CO2;
maintains concentration gradient of O2 / CO2 /
respiratory gases;
diaphragm contracts;
intercostal muscles contract;
increased volume (of thorax / thoracic cavity);
decreasing air pressure in lungs;
air rushes in down air pressure gradient;
opposite of the above causes exhalation;
abdominal muscles contract during active exhalation;
elastic recoil of lungs helps exhalation;
You might also like
- IB Biology: Botany Lab TestDocument2 pagesIB Biology: Botany Lab Testapi-256511251No ratings yet
- ProkaryoteeDocument28 pagesProkaryoteeapi-256511251No ratings yet
- LabgradinginfoDocument2 pagesLabgradinginfoapi-256511251No ratings yet
- May Ib Biololgy CalendarDocument2 pagesMay Ib Biololgy Calendarapi-256511251No ratings yet
- VirusesDocument31 pagesVirusesapi-256511251No ratings yet
- Statistical Analysis Notes-1Document32 pagesStatistical Analysis Notes-1api-256511251No ratings yet
- March CalendarDocument2 pagesMarch Calendarapi-256511251No ratings yet
- April Ib Calendar 2016Document1 pageApril Ib Calendar 2016api-256511251No ratings yet
- Exam Schedule 2016-1Document1 pageExam Schedule 2016-1api-256511251No ratings yet
- PhylogenyDocument16 pagesPhylogenyapi-256511251No ratings yet
- ArchaeaDocument9 pagesArchaeaapi-256511251No ratings yet
- Mechanisms of EvolutionDocument14 pagesMechanisms of Evolutionapi-256511251No ratings yet
- Evolution of Living ThingsDocument19 pagesEvolution of Living Thingsapi-256511251No ratings yet
- Chapter 25 Origin of LifeDocument14 pagesChapter 25 Origin of Lifeapi-256511251No ratings yet
- SpeciesDocument10 pagesSpeciesapi-256511251No ratings yet
- Evolution of PopulationsDocument21 pagesEvolution of Populationsapi-256511251No ratings yet
- Chap22 Darwin and EvolutionDocument21 pagesChap22 Darwin and Evolutionapi-256511251No ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Bio Sem2 Chapter 1Document7 pagesBio Sem2 Chapter 1Neko Kuro100% (1)
- NCERT-QUESTIONS-BREATHINGDocument10 pagesNCERT-QUESTIONS-BREATHINGTanisha SubudhiNo ratings yet
- 9700 BIOLOGY: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2013 SeriesDocument9 pages9700 BIOLOGY: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2013 Seriesyeelin96No ratings yet
- G9 Science Q1 - Week 1-2 Respiratory-Circulatory-SystemDocument34 pagesG9 Science Q1 - Week 1-2 Respiratory-Circulatory-SystemSandra Lee LigsaNo ratings yet
- Physiology Revised Syllabus I MBBSDocument25 pagesPhysiology Revised Syllabus I MBBSArpitha SNo ratings yet
- Part 1 Respiratory AssessmentDocument67 pagesPart 1 Respiratory AssessmentAaron ConstantinoNo ratings yet
- Medical Physiology: Integration Using Clinical Cases: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument14 pagesMedical Physiology: Integration Using Clinical Cases: Multiple Choice QuestionswanderagroNo ratings yet
- 2021 Anatomy Respiratory Module BCQsDocument12 pages2021 Anatomy Respiratory Module BCQsAmsha MangiNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia in Children: Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, and Etiology - UpToDateDocument33 pagesPneumonia in Children: Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, and Etiology - UpToDateYeidhy Karin Cayo CoñezNo ratings yet
- 2019 May P1Document56 pages2019 May P1juanfogedaNo ratings yet
- Veterinary Sistemic PathologyDocument602 pagesVeterinary Sistemic PathologyEstefania Morales100% (1)
- Protections of the Upper Airway Shield the Lower AirwayDocument3 pagesProtections of the Upper Airway Shield the Lower AirwayPaul JacksonNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Biology from the Edexcel 2009 SyllabusDocument53 pagesIGCSE Biology from the Edexcel 2009 SyllabusBonnyNo ratings yet
- CAP Case StudyDocument127 pagesCAP Case StudyMenggay SanDiego100% (1)
- The Histological Effects of Covid-19 On The Lower Respiratory SystemDocument9 pagesThe Histological Effects of Covid-19 On The Lower Respiratory SystemIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Physiology Lab ReportDocument15 pagesRespiratory Physiology Lab ReportThalia PacamalanNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Physiology: Ventilation Perfusion DiffusionDocument6 pagesRespiratory Physiology: Ventilation Perfusion DiffusionShiara Ruth EdrosoloNo ratings yet
- Case Studies: Restrictive and Obstructive Respiratory Conditions Case Study # 1Document5 pagesCase Studies: Restrictive and Obstructive Respiratory Conditions Case Study # 1psyarjavierNo ratings yet
- ICRP 23 Reference ManDocument504 pagesICRP 23 Reference ManFlávio Augusto SoaresNo ratings yet
- Cardiogeneicpulmonaryedema December2019Document9 pagesCardiogeneicpulmonaryedema December2019Amaranto Santoso ongkoNo ratings yet
- Human Body HandbookDocument27 pagesHuman Body Handbookgksamy100% (1)
- Bacterial Pneumonia Case StudyDocument11 pagesBacterial Pneumonia Case StudySheila May LumhodNo ratings yet
- Ujian 1Document10 pagesUjian 1Tajul Azhar BaharudinNo ratings yet
- Pakistan International School Biology Exam ReviewDocument13 pagesPakistan International School Biology Exam Reviewmtayyab zahidNo ratings yet
- Case Study PneumoniaDocument13 pagesCase Study Pneumonialavparedes93% (44)
- Levin (1993) - Drowning and Near Drowning (Klasifikasi Tenggelam)Document16 pagesLevin (1993) - Drowning and Near Drowning (Klasifikasi Tenggelam)Filbert TandeanNo ratings yet
- Year 8 Science Progress 3 Practice Questions and AnswersDocument23 pagesYear 8 Science Progress 3 Practice Questions and AnswersMohammedNo ratings yet
- Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (Ards) : Muamar Aldalaeen, RN, Mba, HCRM, Cic, Ipm, MSN, Phd. Haneen Alnuaimi, MSNDocument59 pagesAcute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (Ards) : Muamar Aldalaeen, RN, Mba, HCRM, Cic, Ipm, MSN, Phd. Haneen Alnuaimi, MSNAboodsha ShNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument36 pagesRespiratory SystemPritha Bhuwapaksophon100% (1)
- Tuberculosis Associated Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseDocument12 pagesTuberculosis Associated Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseinetNo ratings yet